Are meteor showers simply a spectacular celestial event, or could they hold deeper mysteries? While these cosmic displays of shooting stars have captivated humans for millennia, they are also associated with a range of unexplained phenomena that continue to baffle scientists and enthusiasts alike. From persistent meteor trails and sudden flares to mysterious sounds and electromagnetic anomalies, these enigmatic occurrences have sparked curiosity and intrigue. In this article, we will delve into the unexplained phenomena associated with meteor showers, explore the scientific studies and hypotheses attempting to unravel these mysteries, examine witness accounts, astrophotography evidence, and professional astronomer observations, and discuss some of the most intriguing and unresolved cases in meteor shower history. Join us on this journey through the unknown as we explore the fascinating world of unexplained phenomena intertwined with meteor showers.
Contents
- Meteor Showers: A Celestial Spectacle
- The Unexplained Phenomena
- Scientific Studies and Hypotheses
- Experiences and Testimonies
- Unresolved Mysteries
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. Can meteor showers be seen from anywhere on Earth?
- 2. How often do meteor showers occur?
- 3. What causes meteor showers?
- 4. Are meteor showers dangerous?
- 5. Can meteor showers be predicted?
- 6. Why do meteor showers have different names?
- 7. How long do meteor showers last?
- 8. Do all meteor showers produce the same number of shooting stars?
- 9. Can meteor showers be photographed?
- 10. Can meteor showers be heard?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. Can meteor showers cause damage to the Earth’s surface?
- 2. How do scientists study meteor showers?
- 3. Are persistent meteor trails a common occurrence?
- 4. What causes sudden meteor flares?
- 5. Can meteor showers produce mysterious sounds and vibrations?
- 6. Are there electromagnetic anomalies associated with meteor showers?
- 7. What causes unusual colors in meteors?
- 8. How do sonic booms relate to meteor showers?
- 9. Can meteorites provide insights into the composition of the solar system?
- 10. Are there any unsolved mysteries associated with meteor showers?
- References
- Read More
Meteor Showers: A Celestial Spectacle
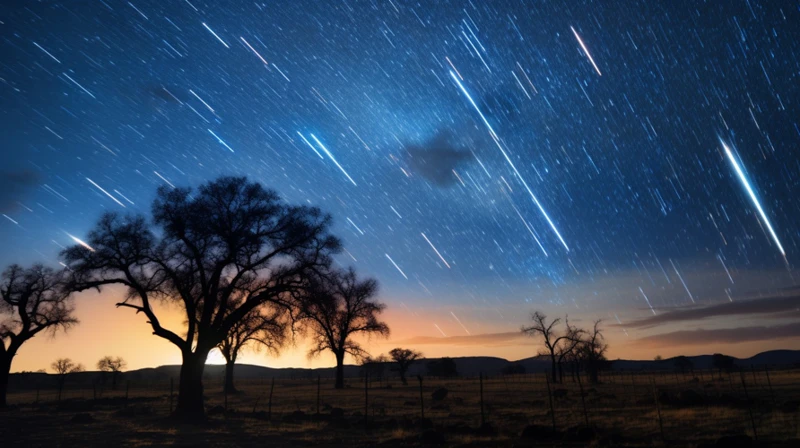

Meteor showers are a mesmerizing celestial spectacle that has fascinated humans for centuries. These displays occur when Earth passes through debris left behind by comets or asteroids, resulting in a breathtaking shower of shooting stars. The most well-known meteor showers, such as the Perseids and the Leonids, occur annually and provide sky-gazers with a remarkable show. While meteor showers can be witnessed from various locations around the world, they are best observed in areas with minimal light pollution, allowing for optimal stargazing experiences. These celestial events captivate both amateur and professional astronomers, who eagerly anticipate the peak times for each shower. During these peak periods, viewers can witness dozens or even hundreds of meteors streaking across the sky (source). It is truly a spectacle that ignites a sense of wonder and awe, reminding us of the vastness and beauty of the cosmos. Whether you are a seasoned astronomer or a casual sky-watcher, witnessing a meteor shower is an experience that leaves a lasting impression. So grab a blanket, find a comfortable spot, and prepare to be enchanted by the celestial magic unfolding above.
1. The Nature of Meteor Showers
The nature of meteor showers is a captivating phenomenon that continues to intrigue astronomers and sky-gazers alike. These spectacular displays occur when the Earth passes through streams of cosmic debris left behind by comets or asteroids. As our planet moves through these debris fields, the fragments collide with Earth’s atmosphere, creating a dazzling show of shooting stars. Meteor showers are named after the constellation from which the meteors appear to radiate, such as the Perseids from the Perseus constellation. The particles burn up in the atmosphere due to friction, resulting in the bright streaks of light that we see as meteors. The mesmerizing display is enhanced by the Earth’s rotation, which causes the meteors to appear to streak across the sky. While the majority of these meteors are small, some larger ones can create fireballs or bolides that are particularly striking. Understanding the nature of meteor showers allows us to appreciate the beauty and wonder of these cosmic events and reminds us of the dynamic relationship between Earth and space.
2. Historical Significance
The historical significance of meteor showers stretches back through the annals of time. Across cultures and civilizations, these celestial events have been imbued with profound meaning and symbolism. Ancient civilizations, such as the Greeks and the Romans, believed that meteor showers were a sign from the gods, foretelling important events or messages from above. In Chinese culture, meteor showers were often seen as omens, with each meteor representing a significant event or person in the future. Even in more recent history, meteor showers have played a role in shaping our understanding of the cosmos. The famous Leonid meteor shower of 1833, for example, sparked widespread scientific interest and study. It was during this event that astronomers first realized the true nature of meteor showers as Earth intersecting with debris trails left by comets. Throughout history, meteor showers have captured our imagination, inspired awe and wonder, and provided a glimpse into the mysteries of the universe. They serve as a reminder of our connection to the cosmos and our place within the grand tapestry of time and space. (source)
The Unexplained Phenomena

The unexplained phenomena associated with meteor showers add an extra layer of intrigue to these already captivating events. One such phenomenon is the presence of persistent meteor trails in the sky. These trails, also known as persistent trains, occur when a meteor burns up in Earth’s atmosphere but leaves behind a glowing trail that can last for several seconds or even minutes after the meteor itself has disappeared (source). Another puzzling phenomenon is sudden meteor flares, where a meteor suddenly increases in brightness for a brief moment before returning to its original intensity. These flares can be unpredictable and add an element of surprise to meteor watching (source).
In addition to visual phenomena, meteor showers have also been associated with mysterious sounds and vibrations. Some witnesses have reported hearing low rumbling sounds or even hissing noises during meteor showers. These auditory experiences are not yet fully understood and continue to puzzle astronomers (source).
Electromagnetic anomalies have been observed during meteor showers. These anomalies include disruptions in radio signals and interference with electronic equipment. While the exact cause of these disruptions is still unclear, some theories suggest that the ionization of the atmosphere by meteors may play a role (source).
Lastly, one cannot overlook the unusual colors exhibited by meteors during showers. While most meteors appear as white streaks across the sky, some display vibrant colors such as green, blue, or even red. These colors are believed to be the result of the ionization and excitation of gases in the atmosphere caused by the meteor’s passage (source). The unexplained phenomena associated with meteor showers add an element of mystery and wonder to these cosmic events, leaving scientists and skywatchers eager to unravel their secrets and understand the forces at play.
1. Persistent Meteor Trails
Persistent meteor trails are a fascinating phenomenon associated with meteor showers. After a meteor streaks through the Earth’s atmosphere, it leaves behind a glowing trail that can linger for several seconds or even minutes. These trails, also known as meteor smoke or persistent trains, can be seen as glowing streaks of light that gradually fade away. The persistence of these trails raises questions about the composition and behavior of meteoric particles. Scientists believe that the trails are formed by the ionization of gases in the atmosphere as the meteor passes through. This ionization creates a temporary path of glowing particles that continue to emit light even after the meteor has passed. Some reports suggest that these persistent trails can exhibit different colors and shapes, adding to their mystique. While the exact mechanisms behind the formation and behavior of persistent meteor trails are still being studied, they contribute to the enchanting and mysterious nature of meteor showers.
2. Sudden Meteor Flares
Sudden meteor flares are an intriguing phenomenon that adds an element of unpredictability to meteor showers. While most meteors follow a predictable trajectory, occasionally, there are instances where a meteor suddenly brightens significantly, creating a momentary burst of intense light. These flares can be so bright that they momentarily outshine even the brightest stars in the night sky, leaving spectators in awe. The cause of these sudden flares has puzzled scientists and astronomers for years. One hypothesis suggests that the change in brightness may be due to the angle at which the meteor enters Earth’s atmosphere, causing the sunlight to reflect off the surface of the meteor in a way that amplifies its luminosity. Another theory proposes that the composition of the meteor itself plays a role, with certain elements or minerals causing the flare when heated to a specific temperature. However, the exact mechanism behind these sudden bursts of brightness remains a subject of ongoing research and speculation. Capturing these flares on camera is a challenge, as they typically occur in a matter of seconds or less. Professional astrophotographers and amateur sky-watchers often try to anticipate these moments, hoping to document and study these elusive events further (source). These sudden meteor flares not only add a sense of excitement to meteor showers but also serve as a reminder of the countless mysteries that continue to unfold in the vastness of the night sky.
3. Mysterious Sounds and Vibrations
The phenomenon of mysterious sounds and vibrations associated with meteor showers adds an element of intrigue to these cosmic events. Many witnesses have reported hearing peculiar noises and feeling vibrations during meteor showers, leaving them bewildered and wondering about the source of these sensations. Some describe the sounds as resembling hissing, crackling, or even booming noises. These auditory experiences often occur concurrently with the sighting of a meteor, creating an eerie and otherworldly atmosphere (source). While the exact cause of these sounds and vibrations remains uncertain, several theories have been proposed to explain this phenomenon. One hypothesis suggests that the sounds are produced by low-frequency electromagnetic waves generated by the interaction between the meteor and Earth’s atmosphere. These waves may then be converted into audible sounds through a process called electrophonic transduction. Another possibility is that the sounds are a result of atmospheric disturbances caused by the meteor’s passage, such as the heating and compression of air molecules. Additionally, it has been suggested that the vibrations could be caused by shock waves produced by the meteor’s entry into the atmosphere. Despite ongoing research and investigation, the origins of these mysterious sounds and vibrations during meteor showers continue to elude scientists. The phenomenon remains as captivating and perplexing as ever, leaving us to marvel at the unexplained wonders of the universe.
4. Electromagnetic Anomalies
Electromagnetic anomalies associated with meteor showers have long puzzled scientists and sky-watchers alike. During these celestial events, some observers have reported experiencing disruptions in electronic devices, malfunctioning of compasses, or even unusual fluctuations in local power grids. These anomalies have been documented in various meteor shower events around the world, adding another layer of intrigue to these already awe-inspiring displays. While the exact cause of these electromagnetic disturbances remains unclear, some researchers propose that they may be linked to the highly charged particles generated by meteors as they enter Earth’s atmosphere. These charged particles could potentially interfere with electromagnetic fields, leading to the observed anomalies. Additionally, it is worth noting that these anomalies have also been reported in connection with other unexplained phenomena, such as UFO sightings and crop circle formations, leading to further conjecture and speculation among enthusiasts. Although no definitive explanation has been established, the study of these electromagnetic anomalies continues to be a subject of interest and investigation within the scientific community (source). The mystery surrounding these phenomena adds an element of intrigue to the already captivating world of meteor showers.
5. Unusual Meteor Colors
Unusual meteor colors add an extra level of intrigue and mystery to the already mesmerizing display of shooting stars. While most meteors appear as streaks of white or yellowish light, there have been numerous reports of meteors displaying vibrant and unexpected hues. These unusual colors can range from greens and blues to reds and purples, creating a stunning visual spectacle in the night sky. The phenomenon of colorful meteors has been observed and documented by astronomers and sky-watchers alike. The exact causes behind these unique hues are still not fully understood, but they are believed to be a result of the composition and structure of the meteor itself. Different elements and compounds present in a meteor can produce specific colors when they interact with Earth’s atmosphere and undergo thermal excitation. For example, the presence of copper or magnesium in a meteor can create blue or greenish colors, while nitrogen compounds can produce reds and purples. Additionally, the angle at which the meteor enters the atmosphere and its speed can also contribute to the variation in colors observed. Despite ongoing research and scientific explanations, the true nature of these unusual meteor colors continues to captivate the imagination of sky enthusiasts, further enhancing the celestial spectacle that meteor showers provide. So, the next time you find yourself gazing at the night sky during a meteor shower, keep an eye out for the possibility of witnessing these awe-inspiring bursts of colorful cosmic beauty.
Scientific Studies and Hypotheses
Scientific studies and hypotheses have been instrumental in unraveling the mysteries surrounding the unexplained phenomena associated with meteor showers. Researchers have explored various theories to explain these enigmatic occurrences. One hypothesis focuses on ionization and plasma effects generated by the passage of meteors through Earth’s atmosphere. As meteors collide with atmospheric particles, the high-speed impact creates a plasma trail, which can persist long after the meteor has passed. This phenomenon may explain the persistent meteor trails observed during meteor showers. Another hypothesis suggests that electric fields and interactions with Earth’s atmosphere play a role in the sudden flares of meteors. These flares, which result in a temporary increase in brightness, could be caused by electrical discharges or interactions with charged particles in the atmosphere. Additionally, sonic boom explanations propose that the sounds and vibrations associated with meteor showers are caused by shockwaves generated by the rapid movement of meteors through the air. As they collide with molecules, the resulting pressure waves can produce audible sounds and seismic vibrations. The composition and mineralogy of meteorites also present an avenue for investigation. Researchers study the elemental makeup and characteristics of meteorites to gain insights into their origin and the processes that occur during their entry into Earth’s atmosphere. With ongoing scientific research and advancements, our understanding of the unexplained phenomena connected to meteor showers continues to evolve, bringing us closer to unraveling the secrets of these celestial spectacles (source).
1. Ionization and Plasma Effects
The phenomenon of ionization and plasma effects during meteor showers adds an extra layer of intrigue to these cosmic events. As meteors streak through the Earth’s atmosphere, they encounter molecules and atoms, causing them to collide and release energy. This energy leads to the ionization of air particles, creating a glowing trail that can last for several seconds or even minutes after the meteor has passed. This ionization process produces a trail of charged particles that can interact with Earth’s magnetic field, resulting in the creation of plasma. Plasma, often referred to as the fourth state of matter, is a highly energetic and electrically charged gas. The interaction between the meteor and the Earth’s atmosphere creates complex electromagnetic processes, generating fascinating visual displays and amplifying the energy released during meteor showers. These ionization and plasma effects contribute to the ethereal beauty and enigmatic nature of meteor showers, captivating observers and providing an opportunity for scientific study and exploration (source).
2. Electric Fields and Atmospheric Interactions
Electric fields and atmospheric interactions play a significant role in the phenomena associated with meteor showers. As meteors travel through Earth’s atmosphere, they create ionized trails due to the intense heat generated by their entry. These ionized trails can cause disruptions in the Earth’s electric field, leading to various atmospheric effects. The interaction between the electric field and the ionized particles can result in the production of glowing plasma, which gives rise to the brilliant streaks of light we observe during meteor showers. The movement of charged particles in the ionized trails can also induce electromagnetic disturbances in the surrounding atmosphere. These disturbances can manifest as changes in local magnetic fields or the creation of atmospheric ripples. Scientists are still studying the complex relationship between electric fields and meteor phenomena to gain a deeper understanding of these atmospheric interactions. By investigating the electrical properties of meteor trails and their impact on the surrounding environment, researchers hope to unravel the mysteries behind the unexplained phenomena observed during meteor showers. The study of electric fields and atmospheric interactions is a fascinating area of research that sheds light on the intricate workings of Earth’s atmosphere and its interaction with cosmic phenomena.
3. Sonic Boom Explanations
One of the explanations for the unexplained phenomena associated with meteor showers involves sonic booms. When a meteor enters the Earth’s atmosphere, it generates a tremendous amount of energy and heat due to friction. As the meteor travels at incredible speeds, it creates a shockwave in front of it. When this shockwave reaches the ground, it is heard as a loud explosion or a sonic boom. These booming sounds can be startling and are sometimes mistaken for thunder or even an explosion nearby. However, unlike thunder, which is caused by the rapid expansion of air due to lightning, the sonic booms associated with meteors are the result of the intense heat and energy released during their entry into the atmosphere. The sonic booms can be particularly loud and intense if the meteor is large enough and traveling at a high velocity. In some cases, witnesses have reported feeling vibrations or even their windows rattling as a result of the sonic boom. Scientists study these sonic booms to better understand the properties of meteors and their interactions with the Earth’s atmosphere. By analyzing the sounds and vibrations associated with meteor showers, researchers hope to gain further insights into their composition, velocity, and entry angle. This knowledge can contribute to our understanding of the origins and characteristics of these celestial visitors (source). While sonic booms offer a plausible explanation for some of the unexplained phenomena witnessed during meteor showers, they are just one piece of the puzzle in unraveling the mysteries of these cosmic events.
4. Meteorite Composition and Mineralogy
Meteorites, the remnants of meteoroids that survive their journey through Earth’s atmosphere and land on the surface, provide valuable insights into the composition and mineralogy of these cosmic visitors. Studying meteorites allows scientists to understand the diverse materials that exist in our solar system and beyond. These extraterrestrial rocks come in various types, including stony, iron, and stony-iron meteorites, each possessing unique characteristics (source). Analyzing their composition helps scientists determine the origin of meteorites and gain insights into the formation of our solar system. Through techniques such as X-ray diffraction, spectroscopy, and isotopic analysis, researchers can identify the minerals present in meteorites, which can vary widely depending on their type and origin. These minerals may include olivine, pyroxene, feldspar, and even rare minerals not commonly found on Earth. By comparing the mineralogy of meteorites with terrestrial rocks, scientists can also gain a better understanding of the processes that have shaped our planet over billions of years. The study of meteorite composition and mineralogy not only contributes to our scientific knowledge but also holds clues about the origins of life on Earth and the possibility of life elsewhere in the universe. It is a fascinating field of research that continues to unravel the mysteries of our cosmic neighborhood.
Experiences and Testimonies

Experiences and testimonies surrounding meteor showers contribute to the intriguing tapestry of unexplained phenomena associated with these celestial events. Countless witnesses have shared their accounts of extraordinary sightings and encounters during meteor showers. Some have reported witnessing persistent meteor trails that linger in the sky long after the initial streak of light has vanished. These trails, which can sometimes persist for several minutes, defy conventional explanations and leave observers perplexed and astounded (source). Others have described sudden meteor flares, where a meteor momentarily intensifies in brightness before fading away. These flares, often accompanied by vivid colors and unique patterns, have been documented by amateur astronomers and astrophotographers who have managed to capture these elusive moments on camera. In addition to visual phenomena, there have been reports of mysterious sounds and vibrations occurring simultaneously with meteor showers. Witnesses have described hearing crackling noises, hissing sounds, or even low-frequency rumbles that seemingly accompany the celestial display. While the origins of these sounds are still unknown, they add an eerie and otherworldly element to the already awe-inspiring event. Electromagnetic anomalies have been documented during meteor showers. These anomalies manifest as disruptions in electronic devices or fluctuations in radio reception, suggesting a potential interaction between the celestial objects and Earth’s electromagnetic field. These occurrences challenge conventional scientific understanding and continue to fuel speculation and curiosity. The experiences and testimonies shared by individuals who have witnessed meteor showers contribute to a growing body of captivating evidence that demands further investigation and exploration.
1. Witness Accounts
Witness accounts of meteor showers provide valuable firsthand experiences that contribute to the understanding of these celestial events. People from all walks of life have shared their encounters with shooting stars, describing the awe-inspiring sight of meteors streaking across the night sky. Many witnesses describe feeling a sense of wonder and amazement as they observe the radiant trails left by the meteors. Some accounts even mention witnessing rare phenomena, such as fireballs or unusually large and bright meteors. These personal testimonies are essential in corroborating scientific data and expanding our knowledge of meteor showers. If you have ever witnessed a meteor shower firsthand, you know the sense of wonder and excitement it can evoke. The vivid memories and emotions associated with these celestial spectacles are what make meteor showers such profound and magical experiences.
2. Astrophotography Evidence
Astrophotography has become an invaluable tool in capturing the beauty and mysteries of meteor showers. By using specialized cameras and techniques, photographers are able to capture stunning images of meteors streaking across the night sky. Astrophotography evidence not only showcases the visual spectacle of meteor showers but also provides valuable documentation for scientific research and analysis. These photographs allow astronomers to study the trajectory, velocity, and composition of meteors, providing insights into their origins and behavior. High-resolution images captured during meteor showers can also reveal intricate details such as persistent trails, sudden flares, and unique colors, shedding light on the unexplained phenomena associated with these celestial events. These photographic records serve as a visual record of the transient nature of meteor showers, reminding us of the fleeting beauty that our universe has to offer (source). As technology advances, astrophotography continues to play a crucial role in unraveling the mysteries of meteor showers and providing captivating visual evidence for both scientific research and public fascination. Whether shared on social media, displayed in galleries, or used in scientific publications, astrophotography evidence allows us to appreciate the awe-inspiring nature of meteor showers and deepens our understanding of the celestial wonders that surround us.
3. Professional Astronomer Observations
Professional astronomers play a crucial role in the study of meteor showers, providing valuable observations and insights into these celestial phenomena. With their advanced telescopes and scientific expertise, they are able to capture detailed data and analyze the behavior of meteors during these captivating events. Through their observations, astronomers have been able to identify patterns and characteristics of meteor showers, such as the radiant point from which meteors appear to originate, known as the “radiant” (source). They also use spectroscopy to study the composition of meteoroids, which can provide valuable information about their origin and nature. By documenting the number, brightness, and trajectory of meteors, professional astronomers contribute to our understanding of meteor showers and help to refine models and theories surrounding these phenomena. Their meticulous observations have also revealed rare events, such as fireballs or exceptionally bright meteors, which provide valuable data for further investigation. Thanks to the efforts of professional astronomers, our knowledge of meteor showers continues to expand, deepening our understanding of these mesmerizing celestial spectacles.
Unresolved Mysteries

Unresolved mysteries surround certain meteor shower events, leaving scientists and researchers puzzled. One of the most perplexing cases is the Tunguska Event of 1908, which occurred in a remote region of Russia. This powerful explosion, estimated to be around 1,000 times more powerful than the atomic bomb dropped on Hiroshima, flattened trees over an area of 2,000 square kilometers. The cause of this event has long been debated, with theories ranging from a meteoroid or comet fragment impact to more exotic explanations like a mini black hole or alien spacecraft (source). Another notable case is the Chelyabinsk meteor that struck Russia in 2013, injuring hundreds of people and causing widespread damage. While these incidents have been extensively studied, conclusive explanations for these events still elude researchers. Other meteor shower-related mysteries include reports of unidentified flying objects (UFOs) during meteor shower peaks and anecdotal accounts of strange phenomena coinciding with meteor showers. Despite ongoing scientific exploration and investigation, these unresolved mysteries continue to fuel our fascination with the unexplained and remind us of the boundless mysteries that lie beyond our earthly realm.
1. The Tunguska Event
The Tunguska event is one of the most infamous and perplexing mysteries associated with meteor showers. On June 30, 1908, a massive explosion occurred in the remote region of Tunguska, Siberia, with the force of up to 15 megatons of TNT. The blast flattened an estimated 80 million trees over an area of about 2,000 square kilometers, equivalent to the size of a major city (source). The cause of this event has been a subject of debate and speculation for over a century. While some theories suggest that it was caused by the impact of a meteoroid or comet, others propose more exotic explanations, such as a mini black hole or an extraterrestrial spacecraft. To this day, the exact nature and origin of the Tunguska event remain unknown, leaving scientists and researchers fascinated and perplexed by this extraordinary event that shook the Siberian wilderness and continues to baffle the world.
2. The Chelyabinsk Meteor
The Chelyabinsk meteor is one of the most notable events in recent meteor shower history. On February 15, 2013, a massive meteoroid entered the Earth’s atmosphere over the Russian city of Chelyabinsk. The spectacular event was captured on numerous cameras and witnessed by thousands of people in the area. The explosion caused by the meteoroid’s entry released an estimated 20-30 times the energy of the Hiroshima atomic bomb, resulting in a shockwave that shattered windows, damaged buildings, and injured over 1,500 people. The Chelyabinsk meteor serves as a sobering reminder of the potential danger posed by these celestial objects. It highlighted the need for increased awareness and monitoring of near-Earth objects (source). The incident also provided scientists with valuable data for studying the effects of such impacts and developing strategies for future mitigation. The Chelyabinsk meteor is a testament to the raw power and unpredictability of these cosmic phenomena, underscoring the ongoing quest to understand and protect our planet from potential cosmic hazards.
3. Other Notable Cases
3. Other Notable Cases:
While the Tunguska Event and the Chelyabinsk Meteor are among the most well-known and studied incidents related to meteor phenomena, there have been several other notable cases that have captured attention and left researchers puzzled. One such case is the 1972 Great Daylight Fireball, which occurred over the United States and Canada. This extraordinary event was witnessed by thousands of people and left a trail of debris in its wake. The fireball was estimated to be as bright as the Sun and produced a deafening sonic boom, causing windows to shatter and buildings to tremble (source). Another intriguing case is the Peekskill Meteorite, which occurred in 1992. This meteorite entered Earth’s atmosphere and fragmented, with a large piece crashing into a parked car in Peekskill, New York. The event was captured on video by several witnesses, making it one of the most documented meteorite falls in history (source). Similarly, the 1969 Allende Meteorite fall in Mexico garnered significant attention due to its scientific significance and the large number of recovered fragments, aiding researchers in understanding the composition and origins of meteorites (source). These notable cases stand as reminders of the unpredictable and awe-inspiring nature of meteor phenomena, leaving us with more questions than answers as we continue to explore the mysteries of the cosmos.
Conclusion

In conclusion, meteor showers are not only a celestial spectacle but also a source of unexplained phenomena that continue to intrigue scientists and enthusiasts alike. From persistent meteor trails and sudden flares to mysterious sounds and electromagnetic anomalies, these phenomena add an element of mystery to the already awe-inspiring displays. While scientific studies and hypotheses offer explanations for some of these phenomena, there are still unresolved mysteries surrounding meteor showers. Witness accounts, astrophotography evidence, and observations by professional astronomers further contribute to the intrigue surrounding these cosmic events. The Tunguska Event and the Chelyabinsk Meteor are just two notable cases that highlight the destructive potential of meteor showers and their impact on Earth. As we delve deeper into the world of meteor showers, we are reminded of the vastness and complexity of the universe. So the next time you find yourself gazing up at the night sky during a meteor shower, let your imagination wander and embrace the mysteries that lie beyond our comprehension (source). And who knows, perhaps one day we will unlock the secrets of these mesmerizing celestial phenomena.
Frequently Asked Questions

1. Can meteor showers be seen from anywhere on Earth?
Yes, meteor showers can be observed from various locations around the world. However, the visibility and intensity of the showers may vary depending on factors such as light pollution and weather conditions.
2. How often do meteor showers occur?
Meteor showers occur throughout the year, but the frequency and intensity vary. Some showers have regular annual appearances, while others are more sporadic and unpredictable.
3. What causes meteor showers?
Meteor showers are caused by Earth passing through the debris left behind by comets or asteroids. As these particles enter the Earth’s atmosphere, they burn up, creating the streaks of light we see as shooting stars.
4. Are meteor showers dangerous?
No, meteor showers are not dangerous. The meteoroids that cause meteor showers are typically small and burn up completely in the atmosphere before reaching the Earth’s surface.
5. Can meteor showers be predicted?
Yes, meteor showers can be predicted to some extent. Astronomers can calculate the times and locations of meteor showers based on the orbits of comets and asteroids that produce them. However, the actual visibility and intensity may vary.
6. Why do meteor showers have different names?
Meteor showers are named based on the constellation from which they appear to radiate. For example, the Perseid meteor shower appears to originate from the constellation Perseus.
7. How long do meteor showers last?
Meteor showers typically last for several days, with a peak period where the activity is most intense. The duration of the peak period can vary, ranging from a few hours to a couple of days.
8. Do all meteor showers produce the same number of shooting stars?
No, the number of shooting stars produced by a meteor shower can vary. Some showers are more prolific, offering a higher number of meteors per hour, while others may be less active.
9. Can meteor showers be photographed?
Absolutely! Meteor showers are a favorite subject for astrophotographers. By using long-exposure techniques, it is possible to capture the streaks of light created by the meteors as they pass through the night sky.
10. Can meteor showers be heard?
No, meteor showers cannot be heard. The light trails we see are the result of the meteoroids burning up in the atmosphere, and they do not produce any sound waves.
References
Frequently Asked Questions

1. Can meteor showers cause damage to the Earth’s surface?
While meteor showers are a mesmerizing spectacle, they rarely pose a threat to the Earth’s surface. The majority of meteors burn up in the atmosphere before reaching the ground. However, there have been a few notable cases where larger meteorites have caused localized damage upon impact.
2. How do scientists study meteor showers?
Scientists study meteor showers through various methods, including visual observations, video and photographic recordings, radar detection, and spectroscopy. These techniques help them gather information about the speed, trajectory, composition, and other characteristics of meteors.
3. Are persistent meteor trails a common occurrence?
Persistent meteor trails, also known as “persistent trains,” are relatively rare and occur when a meteor leaves behind a glowing trail that remains visible for a few seconds or minutes. Not all meteors produce persistent trails, making them a fascinating phenomenon for astronomers and skywatchers.
4. What causes sudden meteor flares?
Sudden meteor flares, also referred to as “fireballs,” are incredibly bright meteors that appear brighter than the planet Venus. These flares occur due to larger and more massive meteors entering the Earth’s atmosphere at high speeds, causing increased friction and resulting in a dramatic burst of light.
5. Can meteor showers produce mysterious sounds and vibrations?
While meteor showers are primarily a visual experience, there have been reports of associated sounds and vibrations. Some theories suggest that these phenomena occur due to shock waves generated by larger meteors, which can travel through the atmosphere and reach the ground, causing vibrations that are audible or perceptible to humans.
6. Are there electromagnetic anomalies associated with meteor showers?
Yes, there have been reports of electromagnetic anomalies occurring during meteor showers. These anomalies include disruptions in radio communications and temporary disturbances in magnetic fields. Scientists believe that these effects are caused by the ionization of the atmosphere due to the passage of meteors.
7. What causes unusual colors in meteors?
Unusual colors observed in meteors can be attributed to the various elements present in their composition. For example, green and blue colors are often associated with meteoroids containing copper or magnesium, while red and orange colors indicate the presence of elements such as iron or nitrogen.
8. How do sonic booms relate to meteor showers?
Sonic booms occur when a meteor breaks the sound barrier as it travels through the Earth’s atmosphere. These booms produce shock waves that can create loud explosive or rumbling sounds. Sonic booms are more commonly associated with larger meteors or fireballs.
9. Can meteorites provide insights into the composition of the solar system?
Absolutely! Meteorites are valuable scientific specimens that provide valuable insights into the composition and origins of our solar system. By studying meteorites, scientists can analyze their mineralogy, isotopic compositions, and the presence of organic compounds, helping us understand the building blocks of our celestial neighborhood.
10. Are there any unsolved mysteries associated with meteor showers?
Indeed, there are several unresolved mysteries surrounding meteor showers. One notable example is the Tunguska event, where a massive explosion in 1908 demolished trees over a vast area in Siberia, with no known impact crater. The Chelyabinsk meteor in 2013 is another intriguing case that caused significant damage and injured many people. These events continue to fascinate scientists and motivate further research in the field of meteors and meteoroids.
References
- Astronomers believe we could be in for a rare meteor storm
- Researchers demystify the unusual origin of the Geminids …







