Navigation and Timekeeping Through the Stars: The Role of Constellations
Embarking on a journey through the vastness of the universe, humans have long relied on the mesmerizing beauty of constellations to navigate and keep track of time. As we delve into the history of these celestial patterns and their profound impact on our understanding of the world, we uncover the ancient techniques used by seafarers and explorers to traverse the oceans. Fast forward to the present day, and we witness the continued relevance of constellations in modern navigation systems. These captivating arrangements of stars have played a pivotal role in the development of calendars and the precise measurement of time. Join us on this celestial voyage as we explore the fascinating world of constellations and their enduring importance in our lives today.
Contents
- The History of Constellations
- Constellations and Navigation
- Constellations and Timekeeping
- The Astronomical Clocks
- The Importance of Constellations Today
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How do constellations assist in navigation?
- 2. Which constellations are commonly used for navigation?
- 3. Why are constellations important for modern navigation?
- 4. How were constellations used in ancient navigation techniques?
- 5. Do different cultures have different constellations for navigation?
- 6. How were constellations used for timekeeping in ancient civilizations?
- 7. Can constellations be used to create calendar systems?
- 8. What are astronomical clocks and how do they relate to constellations?
- 9. Are there any famous examples of astronomical clocks from history?
- 10. How are constellations relevant in today’s modern world?
- References
- Read More
The History of Constellations
The history of constellations is as old as human civilization itself. From the earliest recorded cultures to the present day, constellations have captivated our imaginations and played a crucial role in our understanding of the night sky. Ancient civilizations such as the Egyptians, Mesopotamians, and Greeks all developed their own constellations based on their cultural and mythological beliefs. These early sky watchers used the stars to navigate the seas, mark the changing of seasons, and tell stories about the gods and heroes they worshipped. The Greeks in particular made significant contributions to the study of constellations, with figures like Ptolemy cataloging over 1,000 constellations in his influential work the Almagest. As we move through history, we see the influence of constellations spreading to different parts of the world, with unique constellations and legends emerging in the southern hemisphere. Today, astronomers continue to study and map the stars, unraveling the mysteries of the universe, including the fascinating phenomenon of black hole mergers. The history of constellations is not just a story of stars and patterns; it’s a journey through time, culture, and our enduring fascination with the night sky. (Link: southern hemisphere constellations legends)
Constellations have served as invaluable tools for navigation throughout human history. Ancient civilizations devised various techniques to navigate the seas using the stars. One such technique was celestial navigation, which involved aligning certain constellations with specific compass directions to determine the ship’s position. Navigators learned to observe the position and movement of constellations like the Big Dipper, Orion, and the Southern Cross to plot their course. The use of constellations also helped seafarers identify landmarks and navigate along coastlines. Today, modern navigation systems still rely on constellations, but in a different way. Satellites in space, such as the Global Positioning System (GPS), utilize a network of satellites that transmit signals to receivers on Earth, enabling precise positioning and navigation. However, understanding the role of constellations in navigation allows us to appreciate the rich history and ingenuity of our ancestors in their quest to explore the world. (Link: unraveling the mystery of black hole mergers)
Ancient civilizations navigated the vast seas using various ingenious techniques that relied heavily on their understanding of the stars and constellations. One of the earliest methods was celestial navigation, which involved using the positions and movements of celestial bodies to determine direction and location. Sailors would use a device called an astrolabe to measure the angle between the horizon and a specific star. This information, along with the time of observation, would allow them to calculate their latitude. Another method was dead reckoning, where sailors would estimate their position based on their last known location, speed, and direction of travel. However, due to the lack of accurate timekeeping devices, longitude remained a challenge to determine accurately. To overcome this limitation, sailors often relied on landmarks, currents, and other natural phenomena to complement their celestial navigation. The ancient Polynesians, for example, used a technique known as “wayfinding,” where they studied the movement of ocean swells, birds, and stars like the constellation Cygnus, to navigate vast distances across the open ocean. These ancient navigation techniques required a deep understanding and observation of the natural world, including the motion of constellations in the night sky. (Link: cracking code cygnus constellation guide northern cross)
In modern navigation, constellations continue to play a vital role in guiding us across land, air, and sea. Through advancements in technology and the use of Global Positioning System (GPS), constellations are utilized to determine precise locations around the globe. The GPS system relies on a network of satellites that transmit signals to receivers on Earth, enabling accurate positioning. These satellites are strategically placed in specific orbits, with each one synchronized with atomic clocks. By measuring the time it takes for signals to travel from multiple satellites to a receiver, the GPS receiver can triangulate its exact position.
The GPS satellites themselves are equipped with atomic clocks that are synchronized to an extremely high level of accuracy. This synchronization is achieved by using the signals from multiple atomic clocks on Earth. By comparing the time signals from the atomic clocks on the satellites with the atomic clocks on the ground, any discrepancies can be corrected. This ensures that the signals transmitted by the satellites are as precise as possible.
The GPS system relies on constellations of satellites, including the popular Global Positioning System (GPS) and the emerging Galileo and GLONASS systems. Each constellation consists of multiple satellites positioned in orbit around the Earth, forming a network that provides global coverage. These satellites are constantly moving, maintaining their positions relative to each other and the Earth’s surface.
With the help of precise calculations and position fixing techniques, the GPS receiver can determine its latitude, longitude, and elevation, allowing for accurate navigation. Whether it’s guiding ships through treacherous waters, guiding aircraft through the skies, or helping hikers find their way in the wilderness, constellations and their satellite networks have revolutionized modern navigation. (Link: unraveling the mystery of black hole mergers)
Constellations and Timekeeping
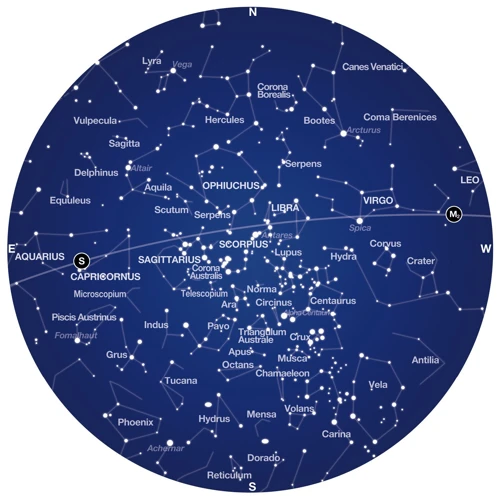
The connection between constellations and timekeeping goes beyond navigation. Constellations have played a fundamental role in determining the passage of time and understanding celestial movements. The concept of time is intricately linked to the celestial sphere, an imaginary sphere surrounding the Earth that contains the stars and constellations. Observing the movement of constellations allowed ancient civilizations to devise calendar systems based on the changing positions of stars throughout the year. By tracking the rising and setting of specific constellations, early astronomers were able to predict the seasons and mark important celestial events. Through the ages, constellations have been used to create intricate calendar systems, such as the Chinese zodiac and the Mayan Long Count calendar. Today, we continue to rely on constellations to keep time, although modern technology provides more precise methods. The relationship between constellations and timekeeping is a testament to humanity’s ongoing quest to understand the universe and mark the passage of our own existence.
The Celestial Sphere and Time
The Celestial Sphere and Time
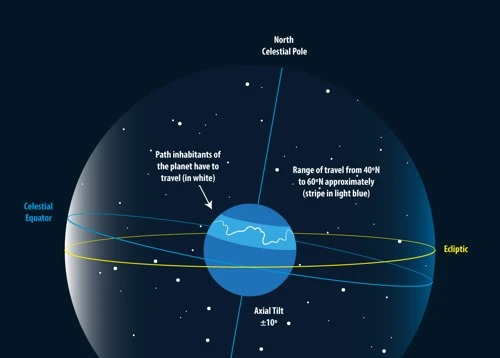
Understanding the relationship between the celestial sphere and time is crucial to comprehend how constellations help keep track of time. The celestial sphere is an abstract concept used to map stars and other celestial objects onto a spherical surface surrounding Earth. In this model, the Earth is at the center, and the stars are imagined to be fixed on the inner surface of this imaginary sphere. As the Earth rotates on its axis, the stars appear to move across the celestial sphere, creating the illusion of a rotating sky.
The movement of stars across the celestial sphere allows us to measure time. By observing the position of a specific constellation or star at a particular moment, we can determine the time of the night or day. For example, the position of the North Star, Polaris, in relation to the North Celestial Pole indicates the direction of true north and helps in determining the time for navigational purposes.
The celestial sphere is divided into various celestial coordinate systems, such as the equatorial and ecliptic coordinate systems, which assist in precise positioning of celestial objects. Time is incorporated into these coordinates, allowing us to calculate the exact position of stars and objects at any given time.
To track time, astronomers use sidereal time, which is based on the rotation of the Earth in relation to the stars. Sidereal days are approximately 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4 seconds long, reflecting the time it takes for the Earth to complete one rotation in relation to a distant star. This is slightly shorter than a solar day, which is based on the Earth’s rotation in relation to the Sun.
The celestial sphere serves as a reference for measuring time, allowing astronomers and navigators to keep track of the hours, days, and years. The movement of constellations across the celestial sphere helps in timekeeping and navigation, enabling us to understand our position in both space and time.
Using Constellations for Calendar Systems
Using constellations as a basis for calendar systems has been a practice dating back to ancient times. The movement of constellations across the night sky provided a natural way to track the passing of time and mark the seasons. In many cultures, the rising and setting of specific constellations would coincide with important agricultural events, such as the planting and harvesting of crops. For example, the ancient Egyptians used the annual rising of the star Sirius, known as the “Dog Star,” as a key marker for the onset of the Nile flood, which was crucial for their agricultural cycle. Similarly, the ancient Mayans of Central America developed an intricate calendar system that incorporated the movements of various constellations to track the cycles of the Sun, Moon, and planets. This calendrical knowledge was essential for their religious ceremonies, agricultural practices, and predictions of celestial events. Today, constellations continue to play a significant role in our modern calendar systems. Astronomers and scientists use the changing positions of the constellations to calculate the precise timing of solstices, equinoxes, and other astronomical events. The use of constellations as a foundation for calendar systems connects us to the ancient knowledge and wisdom of civilizations that came before us, reminding us of the enduring connection between the celestial and terrestrial realms.
The Astronomical Clocks
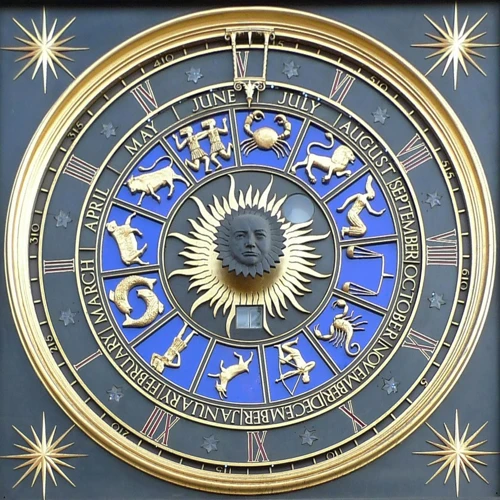

Astronomical clocks, a marvel of human ingenuity, have played a significant role in our understanding and measurement of time. These timekeeping devices, adorned with intricate mechanisms, combine the art of horology with the science of astronomy. Throughout history, these clocks have been instrumental in a variety of ways. In ancient times, astronomical clocks were used to predict celestial events, such as eclipses and planetary alignments. They served as a valuable tool for astronomers to track and study the movements of celestial bodies. In modern times, astronomical clocks have evolved into sophisticated timepieces that not only display the time but also provide information about the positions of celestial objects. From the early examples of astronomical clocks, such as the Antikythera Mechanism, to the masterpieces found in cathedrals and observatories, these clocks serve as a reminder of our fascination with the cosmos and our desire to capture its essence in the measurement of time. (Link: astronomical clocks in modern times)
Early Examples of Astronomical Clocks
Early examples of astronomical clocks showcase the ingenuity and astronomical knowledge of ancient civilizations. One notable example is the Antikythera Mechanism, an ancient Greek device dating back to the 2nd century BCE. Discovered in a shipwreck off the coast of the Greek island of Antikythera, this complex mechanical device was used for astronomical and calendrical purposes. It was composed of intricate gears and dials that accurately predicted the positions of celestial bodies, such as the sun, moon, and planets. The Antikythera Mechanism was a technological marvel of its time, demonstrating a deep understanding of astronomical phenomena. Another remarkable early example of an astronomical clock is the Dunhuang Star Chart, which originated from medieval China. This star chart, painted on a scroll, depicted a detailed representation of the night sky, including constellations, stars, and planets. It served as a practical tool for astronomers in tracking the movements of celestial bodies. These early examples of astronomical clocks highlight the astronomical expertise and mathematical prowess of ancient civilizations, contributing to the development of timekeeping and celestial observation techniques.
Astronomical Clocks in Modern Times
Astronomical clocks have evolved significantly in modern times, combining the precision of timekeeping with the wonders of celestial mechanics. While traditional astronomical clocks focused primarily on local time and astronomical events, modern designs incorporate advanced technologies and intricate mechanisms. One notable example is the Prague Astronomical Clock, located in Prague, Czech Republic. This magnificent clock, dating back to the 15th century, not only displays the local time but also includes a series of animated figures and astronomical features. It showcases the positions of the Sun, Moon, and other celestial bodies, as well as zodiac signs. Additionally, many modern astronomical clocks integrate complex astronomical calculations and can accurately predict astronomical events such as eclipses and equinoxes. For instance, the Christiaan Huygens Astronomical Clock in The Hague, Netherlands, combines clockwork mechanics with precise astronomical calculations to accurately display celestial phenomena. These clocks not only serve as elegant timekeeping pieces but also inspire wonder and awe, reminding us of our place within the vast cosmos.
The Importance of Constellations Today
The importance of constellations in the modern world cannot be overstated. While advancements in technology have given us GPS systems and satellite navigation, constellations continue to play a vital role in our lives. In navigation, constellations provide a reliable backup when other systems fail. Astronauts and pilots still learn to identify key constellations as part of their training. Astronomers rely on constellations to locate and study celestial objects and phenomena. They use them to determine coordinates, track the movement of stars and planets, and make scientific observations. Additionally, constellations continue to inspire and connect us to our cultural heritage. They have become symbols of identity and sources of inspiration for artists and writers, reminding us of our place in the vast cosmos. The study of constellations has led to important discoveries, such as the identification of new stars and the understanding of stellar evolution. With their enduring significance in various fields, constellations remain an integral part of our lives, bridging the gap between ancient wisdom and modern technology.
Conclusion

In conclusion, constellations have played a vital role in navigation and timekeeping throughout human history. From ancient seafarers using the stars to guide their journeys to modern-day GPS systems that rely on celestial navigation algorithms, constellations have provided us with a celestial roadmap to explore and understand our world. Moreover, constellations have served as a cultural and mythological touchstone, reflecting the beliefs and stories of different civilizations. They have inspired astronomers to unravel the mysteries of the universe, guiding their studies on everything from the origins of stars to the collisions of black holes. Today, despite the advancements in technology, constellations continue to hold significance in our lives, reminding us of our connection to the cosmos and the vastness of the universe. Whether it’s finding familiar patterns in the night sky or using constellations to mark the passage of time, these celestial wonders continue to inspire and captivate us. So, next time you gaze up at the stars, take a moment to appreciate the rich history and ongoing importance of constellations in our world.
Frequently Asked Questions

FAQs About Constellations
1. What exactly is a constellation?
A constellation is a group of stars that appears to form a pattern when viewed from Earth. These patterns are often based on mythological characters, animals, or objects.
2. How were constellations named in ancient times?
Ancient civilizations named constellations based on the mythological or cultural significance associated with them. They often drew upon the stories and characters from their religious or historical texts.
3. Are constellations visible from both hemispheres?
No, constellations can vary depending on your location. Some constellations are visible only from the northern hemisphere, while others are exclusive to the southern hemisphere.
4. Can constellations change over time?
While the patterns of stars themselves do not change, the ways in which we interpret and categorize constellations can evolve. Over time, new constellations have been added, and some older ones have been reinterpreted or discontinued.
5. How were constellations used for navigation in ancient times?
Ancient navigators used constellations as a guide for determining their position and direction at sea. By observing the position of certain constellations, they could estimate latitude and rely on them as reliable markers for navigation.
6. How were natural time markers incorporated into constellations?
Ancient civilizations integrated natural time markers, such as the rising and setting of specific constellations, into their calendar systems. These markers helped them determine the changing of seasons and agricultural cycles.
7. Can we still use constellations for navigation today?
While modern navigation systems rely on advanced technology, constellations still play a role in celestial navigation. Many sailors and aviators learn to identify specific constellations to orient themselves in the night sky.
8. How do astronomers determine the boundaries of constellations?
Astronomical organizations have established defined boundaries for constellations based on the celestial coordinates of the stars within them. These boundaries help astronomers accurately identify and study specific constellations.
9. Are there any famous constellations apart from the zodiac signs?
Apart from the well-known zodiac constellations, there are several famous constellations that have captured our collective imagination, such as Orion, Ursa Major (the Big Dipper), and the Southern Cross.
10. Can everyone see the same constellations at the same time?
No, the constellations visible in the night sky vary depending on your location and the time of year. Different constellations are visible in different seasons and in different parts of the world.
References
Frequently Asked Questions

Constellations have been used for centuries as a guide for navigation, helping sailors and explorers to determine their position and direction. By observing the positions of specific constellations in the night sky, navigators can determine their latitude and approximate their longitude.
The constellations most commonly used for navigation include the Big Dipper (part of the Ursa Major constellation), Cassiopeia, and the Southern Cross. These constellations are easily identifiable and have distinct patterns that can be used as reference points.
Even with the advancements in modern technology, constellations still play a crucial role in navigation. They act as a backup in case of GPS failures or other technical malfunctions. Additionally, their usage promotes a deeper understanding and connection to the natural world.
Ancient mariners relied heavily on constellations for navigation. They would use the position of certain stars in relation to the horizon to determine their direction and latitude. By observing how these stars rose and set over time, they could estimate their longitude as well.
Yes, different cultures have their own set of constellations used for navigation. For example, Polynesian navigators used a technique called “wayfinding” and relied on constellations such as Orion’s Belt and the Pleiades to navigate across vast oceans.
6. How were constellations used for timekeeping in ancient civilizations?
In ancient civilizations, constellations were used to mark the passage of time. As the Earth rotates, different constellations become visible at specific times of the year, allowing people to track the progression of seasons and the length of days and nights.
7. Can constellations be used to create calendar systems?
Absolutely! Many ancient civilizations developed calendar systems based on the movements of constellations. For example, the Mayan calendar was intricately tied to the motions of constellations, enabling them to predict celestial events with remarkable accuracy.
8. What are astronomical clocks and how do they relate to constellations?
Astronomical clocks are intricate timekeeping devices that display information about celestial events such as the positions of the sun, moon, and stars. These clocks often incorporate constellations in their design, further highlighting the connection between timekeeping and the night sky.
9. Are there any famous examples of astronomical clocks from history?
One famous example is the Prague Astronomical Clock, located in the Czech Republic. This medieval clock not only displays the time but also astronomical information such as the positions of the sun and moon, zodiac signs, and the movement of planets.
10. How are constellations relevant in today’s modern world?
Although technology has advanced, constellations continue to be relevant in various fields. They are used in astronomy to study the universe, in navigation to aid in emergency situations, and in cultural and educational contexts to inspire awe and curiosity about the cosmos.