From ancient civilizations to modern horoscopes, astrology has captivated and intrigued humanity for centuries. But have you ever wondered about the origins of the zodiac? In this article, we delve into the rich history of the zodiac, tracing its roots back to the Mesopotamian contributions. Mesopotamia, the cradle of civilization, gave birth to many significant advancements that would shape the world as we know it today, and astrology was no exception. By exploring the early beginnings, development of celestial observations, and birth of the zodiac, we unravel the mysteries surrounding this ancient astrological system and shed light on its enduring influence. So join us on this celestial journey and discover the Mesopotamian origins of the zodiac.
Contents
- Mesopotamian Astrology
- The Mesopotamian Zodiac
- Spread and Evolution of the Mesopotamian Zodiac
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What is astrology?
- 2. When did astrology originate?
- 3. What is the difference between astronomy and astrology?
- 4. How did Mesopotamians contribute to astrology?
- 5. What is the significance of the zodiac?
- 6. Do the Mesopotamian constellations match the modern zodiac signs?
- 7. Did the Mesopotamians believe in the power of astrology?
- 8. How did Mesopotamian astrology influence other cultures?
- 9. Is Mesopotamian astrology still relevant today?
- 10. How can one apply Mesopotamian astrology in daily life?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the significance of Mesopotamian astrology in the history of zodiac?
- How did celestial observations develop in Mesopotamia?
- What led to the birth of the Zodiac in Mesopotamia?
- Which constellations were part of the Mesopotamian Zodiac?
- What was the significance of celestial figures in Mesopotamian astrology?
- How did the gods influence the Mesopotamian Zodiac?
- How did the Mesopotamian Zodiac spread to other cultures?
- How did the integration and transformation of the Mesopotamian Zodiac occur?
- What impact did the Mesopotamian Zodiac have on modern astrology?
- What can we learn from the Mesopotamian Zodiac today?
- References
- Read More
Mesopotamian Astrology
Mesopotamian astrology holds a significant place in the history of human understanding of the celestial sphere. Its origins lie in the ancient civilization that inhabited the region, where early astronomers and priests observed the heavens with awe and curiosity. The Mesopotamians believed that the movements and alignments of the stars and planets held immense power and influence over daily life and destiny. Their astrological practices and beliefs laid the foundation for the development of astrology in later cultures. These ancient astronomers meticulously recorded celestial observations, calculating the patterns and cycles of the stars and planets. These observations formed the basis for the creation of the zodiac and the subsequent understanding of cosmic influences on human lives. To learn more about the mythological stories behind the zodiac signs, visit this link.
Early Beginnings
The early beginnings of astrology in Mesopotamia can be traced back to as early as the 3rd millennium BCE. The Mesopotamians had a deep fascination with the sky and believed that it held profound significance and divine power. They observed celestial events such as equinoxes, solstices, and eclipses, noting their relationship to the changing seasons and agricultural cycles. These observations formed the basis for their astrological beliefs and practices. The Mesopotamians believed that the gods communicated their intentions and messages through celestial phenomena, which influenced human affairs. They saw a connection between earthly events and the movements of celestial bodies, and this notion laid the groundwork for the development of astrology.
The Sumerians, one of the earliest civilizations in Mesopotamia, devoted special attention to celestial observations. They built observatories and temples called ziggurats, which served as sacred spaces where they could connect with the divine. These ziggurats had platforms that provided an elevated vantage point for observing the sky. The Sumerians meticulously charted the movements of stars and planets, creating elaborate records known as star catalogues. These catalogues served as references for future celestial observations and calculations.
The Babylonians, who succeeded the Sumerians, further advanced the field of astrology. They developed a system of omens, which linked celestial events to specific earthly outcomes. These omens were meticulously recorded in literature such as the Enuma Anu Enlil, a collection of tablets that documented celestial phenomena and their interpretations. The Babylonians believed that interpreting these omens could provide insight into the future and help humans make informed decisions.
To understand more about the mysterious prophecies of the Oracle of Delphi, you can read about it in detail by visiting this link.
Development of Celestial Observations
The development of celestial observations played a crucial role in the advancement of Mesopotamian astrology. Mesopotamian astronomers dedicated themselves to studying the movements of celestial bodies, meticulously noting the patterns and cycles of the stars and planets. They believed that these observations could reveal profound insights into the nature of the cosmos and its influence on human existence. By charting the positions of celestial bodies over extended periods, such as months and years, they were able to identify recurring patterns and cycles. These observations formed the basis for understanding the concept of zodiacal divisions and the characteristics associated with each constellation. The Mesopotamians carefully recorded celestial observations on clay tablets and created astronomical texts known as “mul.APIN,” which included detailed information about constellations, lunar observations, and solar events. The accuracy and precision of their observations paved the way for the development of an intricate astrological system that would continue to evolve throughout history. To explore the astrological significance of Ophiuchus in modern astrology, click on this link.
Birth of the Zodiac
The marks a pivotal moment in the history of astrology. The concept of the zodiac, as we know it today, emerged in ancient Mesopotamia during the 5th century BCE. It was during this time that the Babylonians began to develop a system that divided the ecliptic, the apparent path of the Sun across the sky, into twelve equal sections, each corresponding to a specific constellation. This division was based on the observation that the Sun’s position against the backdrop of the stars changed throughout the year. These twelve sections eventually became associated with particular months, forming the foundation of the zodiac we recognize today.
The Mesopotamian astrologers believed that the positions of the celestial bodies at the time of a person’s birth influenced their personality traits, characteristics, and even future events. They believed that by studying the stars and their movements, they could unlock the mysteries of human life and destiny.
The Babylonians assigned specific constellations to each of these twelve divisions. The constellations, including Aries, Taurus, Gemini, Cancer, Leo, Virgo, Libra, Scorpio, Sagittarius, Capricorn, Aquarius, and Pisces, became the foundation of the zodiac system. Each constellation was associated with specific qualities and attributes that were thought to affect individuals born during that particular period.
It is important to note that while the Babylonians established the groundwork for the zodiac, their system differed from the one widely used in modern astrology. For instance, their zodiac did not include the constellation Ophiuchus, which is now known as the 13th zodiac sign. To learn more about the astrological significance of Ophiuchus in modern times, visit this link.
The Mesopotamian contributions to the birth of the zodiac set the stage for the development of astrology in other cultures. The knowledge, observations, and beliefs surrounding the zodiac spread throughout the ancient world, shaping different astrological practices. This diffusion and transformation of the zodiac further fueled its influence on various civilizations, eventually leading to its integration and evolution into the astrology we know today.
The Mesopotamian Zodiac
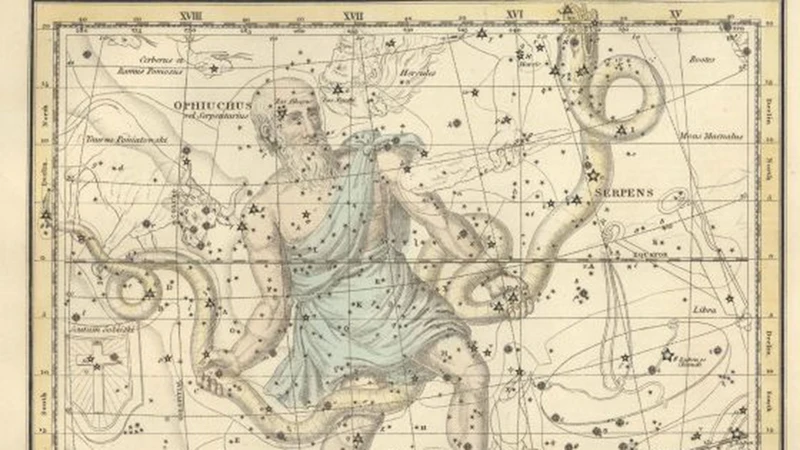
The Mesopotamian Zodiac played a crucial role in shaping astrological systems that followed. It consisted of a set of twelve constellations, each associated with different periods throughout the year. These constellations, also known as the “Signs of the Zodiac,” held symbolic meanings and were believed to influence various aspects of life. The Mesopotamians assigned celestial figures to each sign, such as the Ram, Bull, and Twins. These representations added a visual element to the zodiac, making it easier for observers to identify and track the movement of the stars. The significance of these celestial figures was steeped in mythology, with each figure representing a powerful deity or mythological character. Thus, the Mesopotamian Zodiac not only served as a tool for measuring time but also conveyed divine associations and the belief in a cosmic order. To learn more about the astrological significance of Ophiuchus today, you can visit this link.
Constellations in Mesopotamian Astrology
In Mesopotamian astrology, the constellations played a vital role in understanding and interpreting celestial phenomena. These ancient astronomers identified and named various constellations based on the patterns they observed in the night sky. Some of the well-known constellations in Mesopotamian astrology include:
1. The Great Bull (Taurus): The constellation of Taurus symbolized the primeval bull that played a significant role in Mesopotamian mythology. It represented the divine power and fertility associated with nature.
2. The Lion (Leo): Representing kingship and regality, Leo was linked to the celestial lion, a symbol of power and authority. Mesopotamian astrologers saw this constellation as a representation of the sun.
3. The Scorpion (Scorpio): The constellation of Scorpio portrayed the image of a scorpion, which held immense significance in Mesopotamian astrology. It was associated with the mythological creature that played a part in many tales of their gods.
4. The Twins (Gemini): Gemini, the constellation of the twins, was seen as a symbol of duality and balance in Mesopotamian astrology. It represented the harmonious coexistence of opposites and the concept of unity.
5. The Water Bearer (Aquarius): Aquarius was depicted as a figure pouring water from a vessel, signifying the water-bringer. In Mesopotamian astrology, this constellation represented the life-giving waters that sustained civilization.
These constellations, along with many others, formed the basis for determining the signs of the zodiac and their astrological interpretations. The Mesopotamian astrologers believed that the positioning and movement of these constellations influenced individual characteristics, natural events, and the fate of nations. The intricate understanding of these celestial figures allowed them to make predictions, provide guidance, and gain insights into the complexities of human existence.
Significance of Celestial Figures
The Significance of Celestial Figures in Mesopotamian astrology cannot be overstated. To the ancient Mesopotamians, celestial bodies such as the sun, moon, and planets were not just astronomical objects but divine beings with immense power and influence. Each celestial figure was associated with a specific deity in the Mesopotamian pantheon. For example, Utu, the sun god, was closely linked with the concept of justice and played a vital role in maintaining cosmic balance. The moon was associated with the god Nanna, while Venus was associated with the goddess Inanna, symbolizing love and fertility. The movement and alignments of these celestial figures were considered meaningful omens, guiding the actions and decisions of individuals and societies alike. The Mesopotamians believed that by understanding the movements of these celestial figures, they could interpret the will of the gods and gain insight into future events. It was a deeply spiritual and interconnected belief system that shaped the lives and worldview of the Mesopotamian civilization.
The Influences of the Gods
In Mesopotamian astrology, the influences of the gods played a pivotal role in shaping the beliefs and practices of this ancient system. The Mesopotamians believed that each celestial figure within the zodiac was associated with a particular god or goddess, imbuing them with divine power and authority. These celestial deities were thought to have a direct impact on the lives and destinies of individuals born under their corresponding zodiac signs. For instance, the god Anu, known as the ruler of the heavens, was associated with the zodiac sign Taurus. It was believed that those born under Taurus would have characteristics similar to Anu, such as being steadfast, reliable, and determined. Similarly, the goddess Ishtar, associated with the planet Venus, governed the zodiac sign Libra. People born under Libra were believed to possess qualities such as charm, balance, and a love for beauty, mirroring the influence of Ishtar. These divine influences guided individuals’ personalities, behaviors, and even their futures, as the gods determined the path of each person’s life. The interplay between the gods and the zodiac was a core aspect of Mesopotamian astrology, allowing people to connect their lives to the celestial realm and seek guidance from the divine forces that governed their existence.
Spread and Evolution of the Mesopotamian Zodiac

The spread and evolution of the Mesopotamian Zodiac is a testament to its enduring significance and influence. Over time, the knowledge and practices of Mesopotamian astrology expanded beyond the borders of the region, transcending cultural boundaries. Through trade, conquest, and cultural exchanges, the Mesopotamian Zodiac found its way into other civilizations, such as the ancient Greeks and Egyptians. These cultures adapted and incorporated the Mesopotamian astrological system into their own belief systems, giving rise to new interpretations and variations. The integration and transformation of the Mesopotamian Zodiac resulted in the inclusion of additional constellations, such as Ophiuchus, which you can read more about here. As astrology continued to evolve, the Mesopotamian Zodiac played a pivotal role in shaping the foundations of modern astrology. Its principles and symbolism continue to provide insight and guidance for individuals seeking to understand their place in the cosmos.
Transmission to Other Cultures
The transmission of Mesopotamian astrology to other cultures is a fascinating chapter in the history of the zodiac. As the Babylonian empire expanded its influence, so too did their astrological knowledge. Traders, diplomats, and scholars would travel far and wide, carrying with them the wisdom and teachings of Mesopotamian astrology. One of the significant recipients of this knowledge was the Hellenistic world, particularly during the conquests of Alexander the Great. The blending of Babylonian and Greek cultures led to the synthesis of ideas, resulting in a Hellenistic astrology that incorporated the Mesopotamian zodiac. This fusion of astrological concepts also spread to the Roman Empire and became the foundation for Western astrology as it is known today. In addition to the Hellenistic influence, the diffusion of Mesopotamian astrology reached India, where it merged with existing astrological practices, eventually giving birth to Vedic astrology. The impact of Mesopotamian astrology on the development of other cultures’ astrological systems cannot be overstated, as it paved the way for the wide dissemination and continued evolution of astrological knowledge throughout history.
Integration and Transformation
During the spread of the Mesopotamian zodiac to other cultures, various civilizations integrated and transformed the astrological system to fit their own beliefs and practices. One such influential culture was ancient Egypt, which adopted the zodiac and incorporated it into their own religious and mythological framework. The Egyptians associated each zodiac sign with different deities, attributing divine qualities and characteristics to individuals born under specific signs. This integration of astrology into religious and spiritual practices continued as the zodiac spread further, reaching ancient Greece and Rome. In Greece, the zodiac became intertwined with mythology, with each sign representing mythological figures and enigmatic stories. The Romans, in turn, adopted and adapted Greek astrology, integrating their own deities and cultural references into the zodiac system. The spread and integration of the Mesopotamian zodiac not only transformed the astrological system itself but also became a catalyst for the blending and exchange of diverse cultural beliefs and traditions. It is fascinating to see how the zodiac, originating in Mesopotamia, became an integral part of various civilizations worldwide, each contributing their own unique perspectives and interpretations.
Impact on Modern Astrology
The influence of Mesopotamian astrology on modern astrology cannot be overstated. The concepts and practices developed by the Mesopotamians continue to shape our understanding and interpretation of the zodiac today. One notable impact is the continued use of the twelve zodiac signs and their correspondences to specific months of the year. These signs, derived from the Mesopotamian zodiac, still form the foundation of astrology as we know it. Additionally, the Mesopotamians assigned various meanings and characteristics to each zodiac sign, which are still employed in modern astrology to delineate personality traits and predict future events. The Mesopotamian tradition of identifying important celestial events and their significance is echoed in modern astrology’s emphasis on planetary transits, retrogrades, and cosmic alignments. The enduring legacy of Mesopotamian astrology can also be seen in the continued use of astrological symbols, such as the sun, moon, and planets, in contemporary astrological charts and discussions. Mesopotamian astrology has left an indelible mark on modern astrology, providing a strong foundation on which subsequent astrological traditions have been built. To learn more about the astrological significance of Ophiuchus in modern times, visit this link.
Conclusion

Through exploring the Mesopotamian contributions to astrology and the origins of the zodiac, we gain a deeper appreciation for the ancient wisdom that still shapes our understanding of the cosmos today. The Mesopotamians’ early beginnings in celestial observations paved the way for the development of astrology, as they meticulously recorded the movements of stars and planets. Their fascination with the heavens ultimately led to the birth of the zodiac, a celestial map that divided the sky into twelve sections, each associated with specific constellations and their mythological stories.
Significantly, the Mesopotamian zodiac was not limited to the twelve familiar signs we know today but encompassed a larger number of constellations, portraying a more comprehensive view of the celestial sphere and its influences. The celestial figures in Mesopotamian astrology also held immense significance, representing gods, goddesses, and mythical creatures that influenced the fate and destiny of individuals.
The influence of Mesopotamian astrology did not remain confined to its place of origin. It spread to other cultures, including the Greeks and Romans, who adapted and integrated their own beliefs and mythological stories into the framework of the zodiac. This integration and transformation paved the way for the zodiac to become intertwined with other religious and cultural practices, ultimately leading to its enduring impact on modern astrology.
In conclusion, the Mesopotamian contributions to astrology laid the foundation for our understanding of the zodiac and its significance in our lives. The celestial observations, the constellations associated with mythological stories, and the integration of these ideas into various cultures have shaped astrology as we know it today. As we gaze at the night sky and ponder the positions of the stars and planets, we can trace these celestial connections back to the ancient civilizations of Mesopotamia, where the seeds of this cosmic knowledge were sown.
Frequently Asked Questions

1. What is astrology?
Astrology is a belief system that suggests a connection between celestial phenomena and human experiences and personality traits.
2. When did astrology originate?
Astrology originated thousands of years ago in ancient civilizations such as Mesopotamia, Egypt, and Greece.
3. What is the difference between astronomy and astrology?
Astronomy is the scientific study of celestial objects and phenomena, while astrology focuses on interpreting those celestial movements and their influence on human behavior.
4. How did Mesopotamians contribute to astrology?
Mesopotamians made significant contributions to astrology by developing early observational techniques and creating the zodiac as a means to understand celestial events and their impact on earthly life.
5. What is the significance of the zodiac?
The zodiac is a celestial coordinate system divided into twelve signs, each associated with specific personality traits and characteristics. It helps astrologers interpret the influence of celestial bodies on an individual’s life.
6. Do the Mesopotamian constellations match the modern zodiac signs?
No, the Mesopotamian constellations did not align perfectly with the zodiac signs used in modern astrology. However, both systems share common origins and ideas.
7. Did the Mesopotamians believe in the power of astrology?
Yes, the Mesopotamians believed that celestial movements and alignments had a direct influence on human affairs, and astrology played a crucial role in decision-making and understanding personal destinies.
8. How did Mesopotamian astrology influence other cultures?
The knowledge and practices of Mesopotamian astrology spread to neighboring regions such as Egypt, Greece, and Persia, where it integrated with local beliefs, further evolving and influencing astrological traditions.
9. Is Mesopotamian astrology still relevant today?
While modern astrology draws from different cultural and historical sources, the foundation laid by Mesopotamian astrology remains essential in understanding the symbolic language and meaning of the zodiac.
10. How can one apply Mesopotamian astrology in daily life?
By studying and exploring the principles of Mesopotamian astrology, individuals can gain insights into their own personalities, strengths, and weaknesses, which can help guide decision-making and self-reflection.
References
- Astrology & Astronomy in Iran and Ancient Mesopotamia
- The History of Science and Ancient Mesopotamia
Frequently Asked Questions

What is the significance of Mesopotamian astrology in the history of zodiac?
Mesopotamian astrology holds great significance in the history of the zodiac as it is believed to be one of the earliest known forms of astrology. Many concepts and practices that originated in Mesopotamia continue to shape our understanding of astrology today.
How did celestial observations develop in Mesopotamia?
Celestial observations in Mesopotamia developed over time through the meticulous recording of celestial events. Mesopotamian astronomers made detailed observations of the stars, planets, and constellations, which were carefully recorded and analyzed to uncover patterns and correlations.
What led to the birth of the Zodiac in Mesopotamia?
The birth of the Zodiac in Mesopotamia can be attributed to the need for a systematic way to track and interpret celestial movements and their relationship to earthly events. The concept of dividing the celestial sphere into specific segments, each representing a different constellation, laid the foundation for the Zodiac.
Which constellations were part of the Mesopotamian Zodiac?
The Mesopotamian Zodiac consisted of twelve main constellations, including Aries, Taurus, Gemini, Cancer, Leo, Virgo, Libra, Scorpio, Sagittarius, Capricorn, Aquarius, and Pisces. These constellations were associated with different periods throughout the year and held specific meanings within Mesopotamian astrology.
What was the significance of celestial figures in Mesopotamian astrology?
Celestial figures played a pivotal role in Mesopotamian astrology. They were seen as representations of various gods and mythical beings, each holding symbolic meanings and influences. Mesopotamian astrologers believed that the positions and alignments of these figures could provide insights into future events and influences on human life.
How did the gods influence the Mesopotamian Zodiac?
The Mesopotamian Zodiac was heavily influenced by the gods worshipped in ancient Mesopotamia. Each constellation and celestial figure was associated with a particular god or goddess, and their characteristics and stories were believed to shape the attributes and destinies of individuals born under their influence.
How did the Mesopotamian Zodiac spread to other cultures?
The spread of the Mesopotamian Zodiac to other cultures can be attributed to various factors, including trade routes, cultural exchange, and conquest. As Mesopotamian civilization interacted with neighboring regions, such as Egypt and Greece, the concepts of astrology and the Zodiac were adopted and adapted by these cultures.
How did the integration and transformation of the Mesopotamian Zodiac occur?
Integration and transformation of the Mesopotamian Zodiac took place as it spread to different cultures. Each culture interpreted and incorporated the Zodiac into their own belief systems, often assigning different names and meanings to the constellations. This led to the development of unique astrological traditions that built upon the foundations of the Mesopotamian Zodiac.
What impact did the Mesopotamian Zodiac have on modern astrology?
The Mesopotamian Zodiac laid the groundwork for modern astrology by introducing the concept of dividing the celestial sphere into twelve segments. This division forms the basis for the Western astrological system, which is widely used today. Additionally, many of the symbolic meanings and interpretations associated with the constellations in the Mesopotamian Zodiac continue to influence modern astrological practices.
What can we learn from the Mesopotamian Zodiac today?
The Mesopotamian Zodiac offers valuable insights into the ancient world’s understanding of celestial phenomena and its connection to human life. By studying the origins and development of the Zodiac, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the historical roots of astrology and the enduring fascination humans have had with the stars and their influence on our lives.







