The artistic virtuosity of the Inca civilization is a remarkable testament to their ingenuity and creativity. From their awe-inspiring architecture to their intricately designed pottery and textiles, the Inca left behind a rich cultural legacy that continues to captivate and inspire. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of Inca art, exploring their architectural marvels, the aesthetic excellence of their pottery, and the mastery of symbolic representation in their textiles. Join us on a journey through time as we uncover the beauty and artistic prowess of the Inca civilization.
Contents
- Inca Architecture
- Inca Pottery
- Inca Textiles
- Influence and Legacy
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What materials did the Inca use in their architecture?
- 2. How did the Inca transport the massive stones for their construction?
- 3. What was the significance of Machu Picchu?
- 4. Did the Inca incorporate astronomy into their architecture?
- 5. Were all Inca structures made from stone?
- 6. How did the Inca ensure their structures were earthquake-resistant?
- 7. Why did the Inca incorporate natural features into their architecture?
- 8. What tools did the Inca use for their stone masonry?
- 9. Did the Inca have any architectural techniques to combat the harsh Andean climate?
- 10. How did the Inca ensure the preservation of their architectural achievements?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is Inca architecture?
- How did the Inca create their architectural marvels?
- What are some examples of Inca architecture?
- What were the sacred sites built by the Inca?
- What characterized Inca pottery?
- What was the purpose of Inca pottery?
- What techniques did Inca potters use?
- What makes Inca textiles unique?
- What materials were used in Inca textile production?
- How did the Inca influence modern artisans?
- References
- Read More
Inca Architecture
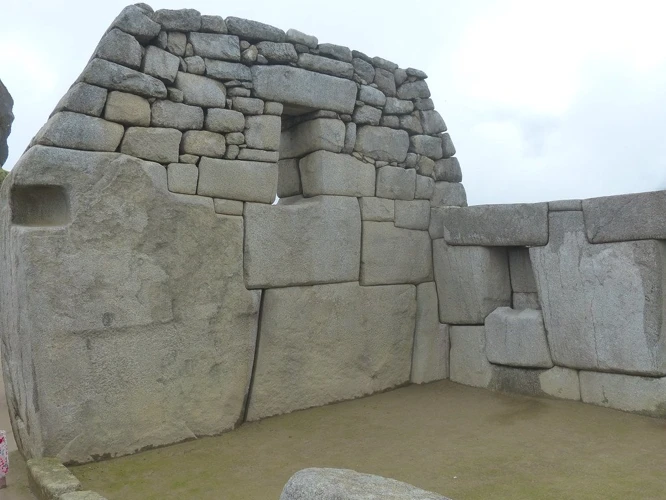

The Inca were renowned for their extraordinary architectural achievements, showcasing their advanced engineering skills and deep understanding of the natural environment. Their architectural marvels were not only functional but also deeply symbolic, reflecting their spiritual beliefs and social hierarchy. Let’s explore some of the key aspects of Inca architecture:
The Inca ingeniously designed and constructed impressive structures using massive stones that fit together perfectly, without the use of mortar. The most famous example of their engineering prowess is Machu Picchu, an ancient citadel nestled high in the Andes Mountains. This archaeological masterpiece showcases precise stone masonry, with each stone expertly carved to fit seamlessly with its neighbors. The intricacy and precision of Inca construction still leave archaeologists and engineers in awe to this day.
Inca architecture comprised a wide range of monumental structures, including temples, fortresses, and administrative buildings. One of the most notable examples is Sacsayhuaman, an imposing fortress located above the city of Cusco. The massive stone walls, some weighing up to 300 tons, were skillfully shaped and fitted together, exhibiting the Inca’s mastery of stonework. These monumental structures not only served practical purposes but also served as symbols of power and authority.
The Inca believed in the sacredness of their surroundings, and their architecture reflected their reverence for the natural world. They constructed temples and sacred sites in harmony with the landscape, integrating natural features such as mountains, caves, and springs into their designs. The most sacred site of all was Coricancha, the Temple of the Sun, in the heart of Cusco. Its walls were once covered in gold, and its construction showcased the Inca’s ability to blend their architecture with the surrounding environment.
The Inca’s architectural achievements continue to captivate visitors from around the world, revealing the depth of their artistic and engineering skills. Now, let’s delve into the intriguing world of Inca pottery and explore the aesthetic excellence that this ancient civilization achieved.
1.1 Engineering Marvels
Inca architecture is renowned for its engineering marvels, showcasing the incredible skills and ingenuity of the Inca civilization. The Inca’s ability to construct monumental structures with remarkable precision without the use of mortar still leaves experts astounded. One notable example is the complex and intricate stonework found in the ancient citadel of Machu Picchu. The seamless integration of massive stones, some weighing several tons, is a testament to the Inca’s mastery of stone masonry. The stones were expertly carved and fitted together, creating walls and structures that have withstood the test of time. The engineering prowess of the Inca is also evident in the construction of extensive road networks, which connected their vast empire. These roads, built with meticulous attention to detail, traversed diverse terrains, including mountains, valleys, and rivers. The precision and sophistication of Inca engineering continue to amaze modern architects and engineers, inspiring awe and admiration for their ingenuity and technical knowledge.
(Internal link: Snake Bearer: Unraveling the Mysteries of Ophiuchus Mythology)
1.2 Monumental Structures
Monumental structures played a significant role in Inca architecture, serving as symbols of power, religious devotion, and social hierarchy. These grand edifices showcased the Inca’s exceptional engineering skills and their ability to create awe-inspiring structures that stood the test of time. Let’s explore some of the remarkable examples of Inca monumental structures:
1. Coricancha: Known as the “Golden Enclosure,” Coricancha was the most sacred site in the Inca Empire. Located in the heart of Cusco, Peru, Coricancha was dedicated to the worship of the sun god Inti. The temple’s walls were once adorned with sheets of gold, symbolizing the Inca’s wealth and devotion to their deity.
2. Sacsayhuaman: Situated on the outskirts of Cusco, Sacsayhuaman is a fortress-like structure that showcases the Inca’s mastery of stone masonry. The complex features massive, meticulously fitted stone walls, some weighing up to 300 tons. Sacsayhuaman was not only a defensive stronghold but also a site for religious ceremonies and celebrations.
3. Ollantaytambo: Located in the Sacred Valley of Peru, Ollantaytambo was both a fortress and a ceremonial center. The site’s massive stone terraces and intricate stone walls demonstrate the Inca’s ability to integrate natural terrain into their architectural designs. Ollantaytambo also served as a strategic military stronghold during the resistance against Spanish colonizers.
4. Pisac: Situated on a mountainside, Pisac boasts impressive agricultural terraces and finely crafted stone structures. The site served as a religious complex, featuring temples, plazas, and ceremonial baths. Pisac offers breathtaking views of the surrounding valleys and showcases the Inca’s harmonious integration of nature and architecture.
5. Choquequirao: Known as the “sister city” to Machu Picchu, Choquequirao remains relatively untouched and less visited. This remote archaeological site showcases incredible Inca terraces, ceremonial centers, and residential areas nestled in the mountains. Choquequirao provides a glimpse into the Inca’s rural infrastructure and their ability to adapt their architectural designs to challenging terrains.
The monumental structures of the Inca civilization stand as a testament to their architectural ingenuity, cultural significance, and enduring legacy. Now, let’s continue our exploration and uncover the secrets of Inca pottery.
1.3 Sacred Sites
Sacred sites held immense significance in the Inca culture, serving as places of worship, ceremony, and connection with the divine. These sites were carefully chosen and constructed to harmonize with the natural landscape, further emphasizing the Inca’s deep spirituality. Here are some examples of the sacred sites that showcase the artistic virtuosity of the Inca:
Machu Picchu: This ancient citadel, nestled high in the Andes Mountains, is not only an engineering marvel but also a sacred site. It is believed to have been a sacred retreat for Inca emperors and their priests, a place where they could connect with the spiritual realm. The precise placement of its terraces, temples, and fountains demonstrates the Inca’s understanding of the sacred geography and their ability to blend their architecture with the natural surroundings.
Ollantaytambo: Situated in the Sacred Valley, Ollantaytambo is another remarkable sacred site that showcases the Inca’s architectural prowess. Its massive stone terraces, temples, and ceremonial centers are aligned with astronomical events, reflecting the Inca’s deep connection to the celestial realm. The complex layout and intricate stonework of Ollantaytambo demonstrate the Inca’s dedication to creating sacred spaces in harmony with nature.
Coricancha: Located in the heart of Cusco, Coricancha was the most sacred site in the Inca Empire. It was the Temple of the Sun, dedicated to the Inca sun god Inti. The temple’s walls were adorned with gold and precious stones, reflecting the Inca’s reverence for the deity. Coricancha was not only a place of worship but also an architectural masterpiece that showcased the Inca’s ability to create sacred spaces infused with beauty and spiritual significance.
These sacred sites serve as a testament to the Inca’s artistic virtuosity and their deep spiritual beliefs. Their understanding of architecture as a means to connect with the divine is evident in the precise planning, craftsmanship, and integration with nature that is characteristic of Inca sacred sites. Now, let’s explore the aesthetic excellence of Inca pottery and discover the unique styles and techniques that distinguish this art form.
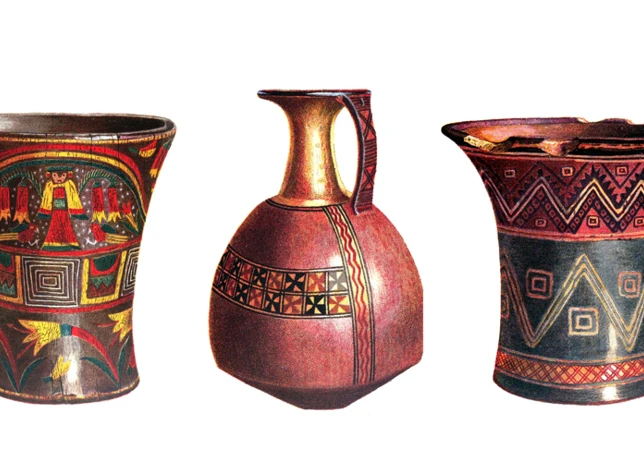
Inca Pottery

Inca pottery is a testament to the artistic excellence and craftsmanship of this ancient civilization. The pottery created by the Inca not only showcased their aesthetic sensibilities but also served practical and symbolic purposes. Here are some key aspects of Inca pottery:
Aesthetic Excellence: Inca pottery exhibits a remarkable level of artistry and attention to detail. The ceramics were often adorned with intricate designs, stylized figures, and geometric patterns. The Inca artisans displayed a mastery of form and balance, creating vessels with elegant shapes and proportions. The use of vibrant colors, such as red, black, and white, added to the visual appeal of the pottery.
Symbolism and Functionality: Inca pottery was not just decorative; it had significant symbolic and functional value. Many vessels were created for religious and ceremonial purposes, reflecting the Inca’s spiritual beliefs and rituals. For example, certain pottery forms, such as the ‘huaco’ (a ceremonial vessel), were used in rituals associated with offerings and libations. Other pottery served practical functions, such as storing food and water, cooking, and serving.
Unique Styles and Techniques: Inca pottery encompassed a wide range of styles and techniques, showcasing the diversity of the Inca civilization. One distinctive style is known as ‘Tiahuanaco-Huari’, characterized by bold geometric designs and abstract motifs. Another notable technique is the use of ‘stirrup spouts’ on many vessels, where the spout resembles a stirrup, allowing for controlled pouring of liquids. The Inca also developed innovative glazing and firing techniques, resulting in pottery with a smooth and lustrous finish.
Inca pottery provides valuable insights into the cultural and artistic heritage of this ancient civilization. The intricate designs and skilled craftsmanship of these ceramics continue to captivate art enthusiasts and archaeologists alike. Now, let’s delve into the world of Inca textiles and explore the mastery of symbolic representation in their woven creations. (source: /ophiuchus-symbol-impact-astrological-charts/)
2.1 Aesthetic Excellence
Inca pottery is renowned for its aesthetic excellence, displaying a remarkable level of skill and artistry. The Inca people had a keen eye for design and incorporated intricate details into their pottery, resulting in visually stunning pieces that are admired to this day.
One notable aspect of Inca pottery is its diverse range of forms and shapes. The Inca artisans skillfully crafted vessels of various sizes and purposes, including plates, bowls, jars, and figurines. Each form was carefully shaped, taking into consideration both functionality and aesthetics. The attention to detail in the proportions and symmetry of the pottery is evident, highlighting the Inca’s commitment to creating visually pleasing pieces.
The Inca also showcased their artistic talent through the intricate decoration and designs adorning their pottery. They used a variety of techniques, such as incising, stamping, and painting, to embellish the surfaces of their vessels. Geometric patterns, animal motifs, and anthropomorphic figures were commonly depicted, each with its own symbolic meaning. These designs not only added to the visual appeal of the pottery but also conveyed cultural and religious narratives.
The color palette of Inca pottery further enhanced its aesthetic value. Rich earth tones, vibrant reds, deep blues, and bright yellows were utilized to create striking contrasts and highlight the intricate designs. The use of these colors, along with meticulous attention to detail, resulted in pottery that truly showcased the artistic brilliance of the Inca civilization.
The beauty and aesthetic excellence of Inca pottery continue to captivate art enthusiasts and archaeologists alike. Its intricate designs, diverse forms, and vibrant colors are a testament to the skill and creativity of the Inca artisans. Now, let’s explore the fascinating symbolism and functionality of Inca pottery in the next section.
2.2 Symbolism and Functionality
Symbolism and functionality played a significant role in Inca pottery. Each ceramic piece was meticulously crafted with purpose and meaning, reflecting the Inca’s rich cultural traditions. Here are some key aspects of the symbolism and functionality of Inca pottery:
1. Ritual and Ceremonial Significance: Inca pottery was often used in religious rituals and ceremonies. The designs and motifs on the ceramics were intricately linked to their spiritual beliefs and practices. For example, vessels adorned with geometric patterns represented the cosmos and the interconnectedness of all things. Animal and plant designs symbolized deities, natural forces, and the cycle of life.
2. Social Hierarchy and Status: Inca pottery also served as a marker of social status and hierarchy. Elaborate and finely crafted pottery was often reserved for the elite, while simpler designs were used by commoners. The size, shape, and decoration of a ceramic vessel could indicate the importance of its owner and their position in society.
3. Functionality and Practicality: While pottery was laden with symbolism, it also had practical uses in Inca society. Vessels were created to store and transport food and beverages. The pottery’s design and structure made it suitable for various purposes, including cooking, serving, and storing liquids. The ceramics were crafted with high levels of skill and precision to ensure functionality and durability.
4. Ancestral Connections: Inca pottery often depicted ancestral figures and mythological creatures, linking the present to the past. These representations served as a connection to the ancestors and the Inca’s belief in their guidance and protection. The inclusion of these ancestral figures on ceramics displayed the deep reverence and respect the Inca held for their lineage.
The symbolism and functionality of Inca pottery reflect the intricate cultural and religious beliefs of the civilization. Each ceramic piece tells a story, carrying both practical and spiritual significance. As we uncover the unique styles and techniques used in Inca pottery, we gain a deeper appreciation for the artistic virtuosity of this ancient civilization.
2.3 Unique Styles and Techniques
When it comes to Inca pottery, one cannot overlook the unique styles and techniques that set their ceramics apart. The Inca artisans developed a distinct aesthetic that blended both tradition and innovation, resulting in pottery that showcased their exceptional craftsmanship and artistic vision.
One notable style of Inca pottery is known as “Cuzco Ware.” This type of pottery is characterized by its bold geometric patterns and vibrant colors, often featuring intricate designs of animals, plants, and human figures. The craftsmen achieved these intricate patterns through a variety of techniques, including incising, carving, and painting with mineral-based pigments. The use of contrasting colors, such as black against a white background, further emphasized the intricacy of the designs.
Another distinctive style is called “Mochica Ware,” named after an earlier civilization that the Inca had absorbed into their empire. Mochica Ware is known for its realistic and detailed representations of everyday life, including depictions of people engaged in various activities, such as farming, fishing, or weaving. The Mochica people were skilled at portraying expressions and emotions, adding a sense of liveliness to their pottery.
In addition to these specific styles, the Inca artisans also employed unique techniques in their pottery production. One notable technique is called “double firing.” After an initial firing, the pottery was painted and then fired once again to achieve a vibrant and long-lasting finish. This meticulous process required great skill and attention to detail.
The Inca utilized molds and molds with multiple parts to create pottery with intricate shapes and designs. They also employed the technique of burnishing, which involved polishing the surface of the pottery to achieve a smooth and shiny finish. This technique not only enhanced the visual appeal but also helped to seal the pottery, making it more resistant to moisture.
The unique styles and techniques employed by Inca pottery artisans resulted in pieces that were not only functional but also stunning works of art. Their mastery of form, color, and intricate detailing speaks to the artistic virtuosity of this ancient civilization. Now, let’s move on to explore the fascinating world of Inca textiles and their mastery of symbolic representation.
Inca Textiles
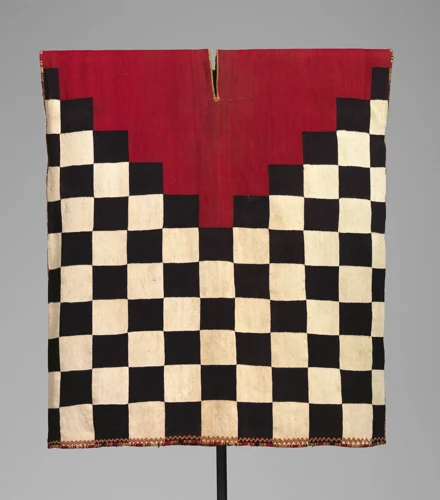

Inca textiles are a testament to the mastery of symbolic representation and the intricate weaving techniques of the Inca people. Their textiles served multiple purposes, including clothing, ceremonial items, and status symbols. Let’s delve into the fascinating world of Inca textiles:
1. Mastery of Symbolic Representation: Inca textiles were not merely decorative; they were rich in symbolism, reflecting the social and spiritual beliefs of the Inca civilization. Each pattern and motif conveyed deep cultural meanings and stories. For example, the Chakana, or Inca Cross, represented the three realms of existence: the underworld, the present world, and the upper world. These symbolic representations were carefully woven into textiles, creating a visual language unique to the Inca.
2. Intricate Weaving Techniques: The Inca displayed impressive skills in textile production, utilizing various weaving techniques to create intricate and durable fabrics. They employed backstrap looms, where tension was achieved using body weight, allowing for the precise manipulation of threads. Inca weavers used natural fibers such as alpaca, llama, and cotton, which they spun and dyed with vibrant colors derived from plants and minerals. This meticulous attention to detail and craftsmanship resulted in textiles that could withstand the test of time.
3. Colors and Patterns: Inca textiles were renowned for their vibrant colors and intricate patterns. The colors were derived from natural dyes and represented different aspects of the Inca society. For instance, red symbolized power and prosperity, while yellow represented the sun and gold. Patterns included geometric shapes, stylized animals, and human figures, all of which conveyed specific meanings. Each textile was a work of art, combining harmonious colors and patterns to produce visually stunning and culturally significant pieces.
Inca textiles continue to inspire and captivate people around the world. Their influence can be seen in contemporary textile art, and their cultural significance is preserved through efforts to document and protect these ancient works. The legacy of Inca textiles remains an important part of our shared human history. Now, let’s move on to explore the influence and legacy of the Inca civilization, and how their artistic achievements continue to resonate with modern artisans.
3.1 Mastery of Symbolic Representation
Inca textiles were not just woven fabrics; they were intricate pieces of art that conveyed profound symbolic meanings. The Inca mastered the art of symbolic representation, using textiles as a visual language to communicate their religious beliefs, social status, and cultural identity. Every pattern, color, and motif told a story and held deep significance.
One of the ways the Inca showcased their mastery of symbolic representation was through the use of geometric designs. These intricate patterns, often featuring repetitive shapes and symbols, conveyed a range of meanings. For example, the chakana (or Inca cross) was a prominent symbol in Inca textiles. It represented cosmic order, with its four steps symbolizing the underworld, the earth’s surface, and the heavens above. The geometric designs also expressed the connection between the spiritual and physical realms.
Another way the Inca demonstrated their skill in symbolic representation was through the use of animal motifs in their textiles. Each animal held specific significance and was associated with different qualities or realms of existence. The condor, for instance, symbolized the heavenly realm, representing power and divinity. The snake, on the other hand, was associated with the underworld and represented transformation and rebirth. By incorporating these animal motifs into their textiles, the Inca visually communicated their religious and cosmological beliefs.
The color choices in Inca textiles were intentional and meaningful. The Inca used natural dyes derived from plants, minerals, and even insects to create an array of vibrant colors. Red symbolized power and vitality, while yellow represented gold and the sun. Blue was associated with water and the sky, and green symbolized fertility and abundance. These colors were strategically used to enhance the symbolic narratives depicted in the textiles.
The Inca’s mastery of symbolic representation in their textiles is evident in the intricate designs and careful use of colors. Each textile was a work of art that conveyed a complex story and served as a visual representation of the Inca’s rich cultural heritage. Now, let’s explore the fascinating world of Inca pottery and discover the aesthetic excellence that this ancient civilization achieved.
3.2 Intricate Weaving Techniques
Inca textiles are renowned for their intricate weaving techniques, demonstrating the skill and artistry of the Inca people. Weaving was a highly regarded craft in Inca society, and textiles held great cultural, social, and economic significance. The Inca employed various weaving methods to create their textiles, showcasing their mastery of the craft.
One of the techniques used by the Inca was backstrap weaving, a method that involved attaching one end of the loom to a fixed object and the other end to a strap worn around the weaver’s back. This technique allowed for incredible precision and control over the weaving process, as the tension could be easily adjusted. The backstrap loom enabled weavers to produce intricate patterns and designs, resulting in textiles of exceptional beauty.
Another notable weaving technique utilized by the Inca was tapestry weaving. This method involved weaving different-colored threads to create intricate pictorial designs. The Inca were skilled at incorporating symbolic representations into their textiles, often depicting elements from the natural world, animals, and important cultural motifs. These tapestries served as visual narratives, conveying stories and conveying information about the Inca’s religious and social beliefs.
The Inca also employed a technique known as discontinuous warp and weft or cross-knit looping. This technique involved using a single strand of thread to create intricate patterns and designs by looping it through the warp threads. The resulting textiles had a distinctive texture and were highly valued for their complexity and beauty.
The highly skilled weavers of the Inca empire produced textiles of exceptional quality and artistry. Their intricate weaving techniques allowed them to create textiles that not only served practical purposes but also embodied the cultural and spiritual essence of the Inca civilization. These masterpieces continue to be appreciated and studied today, offering us a glimpse into the skill and creativity of the Inca people. Now, let’s move on to explore the captivating colors and patterns found in Inca textiles.
3.3 Colors and Patterns
Inca textiles are renowned for their vibrant colors and intricate patterns, revealing the mastery of the ancient Inca weavers. The Inca utilized a wide range of natural dyes to create a stunning palette of colors, including vibrant reds, deep blues, rich yellows, and earthy browns. These colors were derived from various sources such as plants, insects, and minerals, each carefully chosen to achieve the desired hue. The bold use of color in Inca textiles served both decorative and symbolic purposes, with specific colors representing different themes and meanings.
Patterns played a crucial role in Inca textiles, showcasing the artistic skill and cultural significance of the civilization. The patterns incorporated in the textiles often depicted elements from nature, such as animals, plants, and celestial bodies. These representations carried symbolic meanings, connecting the wearer to the natural world and the cosmic realm. Additionally, geometric patterns, such as diamonds, triangles, and zigzags, were prevalent in Inca textiles, representing order and balance. The intricate weaving techniques employed by the Inca allowed for the precise repetition of these patterns, resulting in visually stunning and harmonious textiles.
One remarkable aspect of Inca textiles is the way in which they conveyed intricate narratives and stories through their designs. Each textile was a work of art that told a unique and meaningful tale, conveying the history, mythology, and spiritual beliefs of the Inca civilization. These narratives often celebrated important events, honored deities, or depicted scenes from daily life.
The remarkable use of color and patterns in Inca textiles not only displayed the artistic virtuosity of the Inca but also served as expressions of identity, status, and cultural heritage. Today, these ancient textiles continue to captivate and inspire, showcasing the timeless beauty and rich cultural legacy of the Inca civilization. If you’re interested in exploring the compatibility of zodiac signs, you can delve into the intriguing world of astrology and discover the fascinating connections between individuals’ personality traits and astrological signs.
Influence and Legacy
The influence of Inca architecture, pottery, and textiles can be seen in various ways, even today. Their artistic legacy has left a profound impact on modern artisans and continues to inspire creativity and innovation. Let’s explore some of the significant aspects of the influence and legacy of the Inca civilization:
1. Inspirations for Modern Artisans: The intricate designs, meticulous craftsmanship, and unique styles of Inca artistry have served as a wellspring of inspiration for contemporary artisans. From architecture to pottery and textiles, artists draw upon the rich heritage of the Inca to create new works that pay homage to their techniques and aesthetics. Modern structures incorporating Inca-inspired motifs and contemporary pottery using traditional Inca designs can be found in many parts of South America and beyond.
2. Preservation Efforts: Recognizing the historical and artistic value of Inca art, there have been substantial efforts to preserve and protect these cultural treasures. Archaeologists, historians, and conservationists work diligently to maintain the integrity of Inca architectural sites, pottery collections, and textile artifacts. Museums and cultural institutions play a vital role in the conservation and exhibition of these artworks, allowing future generations to appreciate and learn from the artistic virtuosity of the Inca.
3. Appreciation Worldwide: The impact of Inca artistry extends far beyond the borders of Peru. Their architectural wonders, such as Machu Picchu and Sacsayhuaman, attract millions of visitors every year who marvel at the engineering marvels created by the Inca civilization. Inca pottery and textiles are also sought after by art collectors and enthusiasts worldwide, who value the intricate craftsmanship and cultural significance of these artifacts. The global appreciation for Inca art serves as a testament to their enduring legacy.
The influence and legacy of the Inca’s artistic virtuosity continue to thrive in various forms, inspiring artists, promoting preservation efforts, and captivating audiences worldwide. Through their architecture, pottery, and textiles, the Inca have left an indelible mark on the artistic landscape of our world. As we conclude this exploration of the Inca’s artistic legacy, let us reflect on the profound impact they have had and continue to have, shaping our understanding and appreciation of art.
4.1 Inspirations for Modern Artisans
Inca architecture continues to inspire and influence modern artisans and architects. The remarkable engineering feats and creative design of the Inca structures serve as a constant source of inspiration for contemporary craftsmen. Here are some ways in which the Inca architecture has inspired modern artisans:
1. Structural Innovation: The Inca’s mastery of stonework and their ability to create intricate and seamless structures without the use of mortar have inspired modern artisans to experiment with innovative construction techniques. Architects and engineers draw inspiration from the precision and efficiency demonstrated by the Inca, incorporating similar principles into their own designs.
2. Harmonious Integration: The Inca had a profound understanding of the natural environment and sought to integrate their structures harmoniously into the landscape. Modern artisans often emulate this approach, creating buildings that blend seamlessly with their surroundings. The use of sustainable materials and design elements that respect nature’s elements is a testament to the influence of Inca architecture.
3. Symbolic Representation: The Inca imbued their structures with deep symbolic meaning, reflecting their spiritual and cultural beliefs. Modern artisans often incorporate symbolism into their designs, drawing inspiration from the Inca’s use of architectural elements to convey important messages or values.
4. Cultural Preservation: The preservation efforts made to protect and restore Inca architectural sites have served as a model for modern artisans who are passionate about preserving cultural heritage. By studying and emulating the techniques used by the Inca, artisans contribute to the conservation and continuation of ancient building traditions.
5. Aesthetics and Decorative Elements: The intricate carvings, patterns, and motifs found in Inca architecture have inspired modern artisans in their decorative works. From sculptures to ceramics, the use of similar designs and motifs can be seen in contemporary art forms, paying homage to the artistic virtuosity of the Inca civilization.
As modern artisans continue to draw inspiration from the architectural achievements of the Inca, the legacy of this ancient civilization lives on in the innovative designs and creative works of today. Now, let’s explore the preservation efforts made to safeguard Inca artifacts and sites, ensuring their appreciation for generations to come.
4.2 Preservation Efforts
Preservation efforts play a vital role in ensuring that the artistic legacy of the Inca civilization is safeguarded for future generations. Recognizing the significance of Inca architecture, pottery, and textiles, various initiatives have been undertaken to protect and conserve these invaluable artifacts. Here are some of the key preservation efforts:
1. Restoration and Conservation: Many historic Inca sites, such as Machu Picchu and Sacsayhuaman, have undergone extensive restoration and conservation work to preserve their structural integrity. Skilled archaeologists and restoration experts meticulously analyze the original construction techniques and materials used by the Inca to maintain the authenticity of these architectural wonders.
2. Protective Measures: Strict regulations and guidelines have been implemented to protect Inca sites from potential damage caused by tourism, weathering, and natural disasters. Restricted access, visitor management systems, and monitoring efforts help to minimize the impact of human activity while ensuring the continued enjoyment of these cultural treasures.
3. Education and Awareness: Promoting public awareness and appreciation of Inca art and architecture is crucial for its long-term preservation. Educational programs and museum exhibitions provide the opportunity for visitors to learn about the significance of Inca artistic traditions and their historical context. This fosters a sense of responsibility towards the conservation of these cultural treasures.
4. Documentation and Research: Continuous research and documentation efforts are undertaken to enhance our understanding of Inca architecture, pottery, and textiles. Archaeologists, historians, and anthropologists collaborate to uncover new insights into the construction techniques, symbolism, and cultural significance of these artistic forms. This knowledge is valuable for future restoration and preservation endeavors.
5. International Collaboration: Preservation efforts extend beyond national borders, with international organizations and cultural institutions collaborating to protect and conserve Inca artifacts. Knowledge sharing, expertise exchange, and funding support from global initiatives facilitate the sustainable preservation of these cultural treasures.
Through these preservation efforts, the artistic virtuosity of the Inca civilization continues to be safeguarded and appreciated. The legacy of the Inca serves as a testament to the importance of preserving and celebrating the rich artistic heritage of ancient cultures. Now, let’s explore the influence and legacy of the Inca’s artistic achievements on modern artisans.
4.3 Appreciation Worldwide
Appreciation for the artistic virtuosity of Inca architecture, pottery, and textiles extends far beyond the borders of their ancient empire. Today, the intricate designs and skillful craftsmanship of the Inca continue to inspire and captivate people all around the world. Here are some ways in which this appreciation is manifested:
1. Museums and Exhibitions: Museums across the globe display Inca artifacts, providing a platform for people to admire and study the beauty and cultural significance of Inca art. These exhibitions showcase the exquisite pottery, textiles, and architectural remnants, allowing visitors to gain insights into the rich artistic heritage of the Inca civilization.
2. Artistic Reproductions: Many contemporary artisans and craftsmen draw inspiration from the Inca’s artistic techniques and designs. They create reproductions of Inca pottery and textiles, paying homage to the original artistry while adding their own unique interpretations. These reproductions allow a wider audience to appreciate and own a piece of Inca art in their homes or personal collections.
3. Cultural Festivals and Events: Inca-inspired cultural festivals and events take place in various parts of the world, celebrating the artistic heritage of the Inca civilization. These events often feature traditional dances, music, and exhibitions of Inca art, bringing together people who share a fascination and admiration for the Inca’s artistic virtuosity.
4. Online Platforms and Social Media: The digital age has made it easier than ever for people to showcase and explore different art forms, including Inca art. Online platforms and social media channels dedicated to art provide a space for artists, historians, and enthusiasts to share their knowledge and appreciation for Inca architecture, pottery, and textiles.
The worldwide appreciation for Inca art demonstrates the enduring influence and fascination that this ancient civilization holds. By preserving and celebrating their artistic legacy, we can ensure that the artistic virtuosity of the Inca continues to inspire and captivate generations to come. As we conclude our exploration of the Inca’s artistic achievements, let’s reflect on the impact they have had on modern artisans and the efforts to preserve their cultural heritage.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the artistic virtuosity of the Inca civilization, particularly in their architecture, pottery, and textiles, is truly remarkable. The Inca’s engineering marvels, such as Machu Picchu and Sacsayhuaman, leave us in awe of their advanced construction techniques and attention to detail. Their monumental structures not only served practical purposes but also conveyed their power and status. The sacred sites, intricately integrated with the natural landscape, highlight the Inca’s deep spiritual connection to their environment.
The excellence of Inca pottery is evident in its aesthetic beauty, showcasing unique styles and techniques. The symbolism and functionality of their pottery reveal the diverse aspects of Inca life and culture. Meanwhile, the mastery of symbolic representation in Inca textiles is a testament to their artistic prowess, with intricate weaving techniques and vibrant colors and patterns.
The influence and legacy of the Inca’s artistic achievements can be seen in the inspiration they provide for modern artisans. Their cultural heritage continues to be preserved and appreciated worldwide. The Inca civilization’s artistic virtuosity stands as a testament to their ingenuity, creativity, and deep connection with the natural world.
Thank you for joining us on this journey through the artistry of the Inca civilization. To explore more about astrology and the impact of astrological charts, you can delve into the fascinating world of Ophiuchus and its compatibility with other zodiac signs by visiting this link.
Frequently Asked Questions

1. What materials did the Inca use in their architecture?
The Inca used primarily stone in their architecture, with a focus on fitting the stones together perfectly without the use of mortar. They also incorporated other natural materials such as wood, thatch, and adobe in some of their structures.
2. How did the Inca transport the massive stones for their construction?
The Inca ingeniously transported their massive stones using wooden rollers and ramps. They would carve a path through the mountains, allowing them to move the stones more easily. Additionally, they employed a system of labor known as “mit’a,” where communities would come together to assist in the construction efforts.
3. What was the significance of Machu Picchu?
Machu Picchu is believed to have been a royal estate for the Inca Emperor Pachacuti. It served as a center for religious, administrative, and agricultural activities. Today, it is recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site and is considered one of the New Seven Wonders of the World.
4. Did the Inca incorporate astronomy into their architecture?
Yes, the Inca had a deep understanding of astronomy and aligned many of their structures with celestial events. For example, they aligned temples and shrines with the movement of the sun, moon, and stars to mark important astronomical events.
5. Were all Inca structures made from stone?
No, while stone was the primary material used in their most significant structures, the Inca also constructed buildings using adobe, a mixture of clay, sand, and straw. Adobe was typically used for less monumental structures like homes and storage buildings.
6. How did the Inca ensure their structures were earthquake-resistant?
The Inca employed advanced architectural techniques to make their structures earthquake-resistant. They developed a trapezoidal design for walls and incorporated small stones within the structure to absorb seismic energy, allowing the buildings to withstand earthquakes.
7. Why did the Inca incorporate natural features into their architecture?
The Inca considered nature to be sacred and believed that incorporating natural features into their architecture would create harmony and balance. They saw the landscape as a reflection of the divine and sought to honor and respect it through their artistic endeavors.
8. What tools did the Inca use for their stone masonry?
The Inca used bronze and stone tools for their stone masonry, including hammers, chisels, and picks. They crafted these tools with great precision, allowing them to shape the stones with accuracy and finesse.
9. Did the Inca have any architectural techniques to combat the harsh Andean climate?
Yes, the Inca employed several techniques to combat the cold and high-altitude weather of the Andes. They constructed buildings with sloping roofs to allow for efficient drainage of rain and snow, and they built structures with thick walls and small windows to retain heat.
10. How did the Inca ensure the preservation of their architectural achievements?
The Inca built their structures with exceptional craftsmanship and durable materials, which has contributed to their preservation over the centuries. Additionally, the remote locations and natural protection of many Inca sites have helped to safeguard their architectural legacy.
References
Frequently Asked Questions

What is Inca architecture?
Inca architecture refers to the unique style of construction developed by the Inca civilization in ancient Peru. It is characterized by its precision, sophisticated engineering, and monumental structures.
How did the Inca create their architectural marvels?
The Inca employed impressive engineering techniques such as precise stone cutting, fitting, and dry-stone wall construction to create their architectural marvels. They used no mortar or cement but relied on the skillful interlocking of stones.
What are some examples of Inca architecture?
Machu Picchu, Sacsayhuaman, and Ollantaytambo are some famous examples of Inca architecture. These sites showcase the Inca’s ability to blend harmoniously with their natural surroundings and exhibit the empire’s architectural prowess.
What were the sacred sites built by the Inca?
The Inca constructed several sacred sites, such as Coricancha, also known as the “Temple of the Sun,” and the Temple of the Three Windows in Machu Picchu. These sites held great religious and spiritual significance for the Inca civilization.
What characterized Inca pottery?
Inca pottery was known for its aesthetic excellence and intricate designs. It featured a wide range of shapes, sizes, and colors, often adorned with elaborate patterns and intricate motifs.
What was the purpose of Inca pottery?
Inca pottery served both functional and ceremonial purposes. It was used for storing food and water and played a significant role in religious ceremonies, depicting deities and important cultural symbols.
What techniques did Inca potters use?
Inca potters used various techniques, including coiling, modeling, and carving, to create their pottery. They also employed distinctive polychrome and black-on-white painting styles to enhance the aesthetic appeal of their creations.
What makes Inca textiles unique?
Inca textiles are known for their mastery of symbolic representation, intricate weaving techniques, and vibrant colors. They were highly valued and used as a form of communication, expressing the social status and cultural identity of individuals.
What materials were used in Inca textile production?
The Inca used natural materials such as alpaca and llama wool, cotton, and feathers to create their textiles. The quality of the materials and their craftsmanship contributed to the durability and beauty of the finished products.
How did the Inca influence modern artisans?
The artistic virtuosity of the Inca continues to inspire modern artisans. Their architectural techniques, pottery designs, and textile weaving methods have been studied and replicated, showcasing the enduring legacy of the Inca civilization.
References
- Inca art forms: the incredibly rich creative legacy of …
- Inca Art and Why It’s Important – East India Blogging Co.







