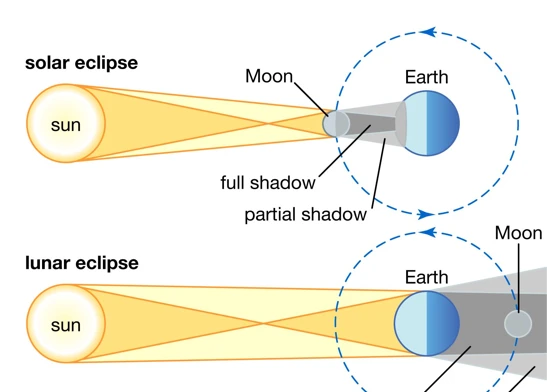
Solar Eclipses vs. Lunar Eclipses: What’s the Difference? Have you ever looked up at the sky and wondered about the celestial events that occur beyond our earthly realm? Solar and lunar eclipses are two captivating phenomena that have fascinated humans for centuries. From the mesmerizing alignment of the sun, moon, and earth to the breathtaking visual displays, these celestial events have sparked our curiosity and ignited our imagination. In this article, we will explore the distinctions between solar and lunar eclipses, shedding light on their definitions, occurrences, types, visual phenomena, and even their historical and cultural significance. So strap in and get ready to embark on a journey through the cosmos as we demystify the enigmatic world of solar and lunar eclipses.
Contents
- Understanding Solar Eclipses
- Lunar Eclipses Demystified
- Comparing Solar and Lunar Eclipses
- Preparing for Eclipse Viewing
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is a solar eclipse?
- What is a lunar eclipse?
- How often do solar eclipses happen?
- How often do lunar eclipses happen?
- Why are solar eclipses more rare than lunar eclipses?
- Can you look directly at a solar eclipse?
- Can you watch a lunar eclipse without any special equipment?
- What causes the different types of solar eclipses?
- What causes the reddish color of the Moon during a lunar eclipse?
- Are there any cultural or historical significances associated with eclipses?
- References
- Read More
Understanding Solar Eclipses
A solar eclipse occurs when the moon passes between the sun and the Earth, casting a shadow on our planet. This alignment is made possible by the fact that the moon and sun appear to be roughly the same size when observed from Earth due to a peculiar cosmic coincidence. Solar eclipses are relatively rare events, happening only when the moon’s orbit intersects with the plane of the Earth’s orbit around the sun. On average, a solar eclipse occurs somewhere on Earth every 18 months, but specific regions may experience multiple eclipses in a lifetime. It’s a mind-boggling spectacle that awes both scientists and skygazers alike.
Solar eclipses can be classified into three main types: total, partial, and annular. A total solar eclipse occurs when the moon completely blocks the sun, and the sky darkens dramatically for a few minutes. This is the most awe-inspiring type of eclipse, as it unveils the sun’s outer atmosphere known as the corona. A partial solar eclipse occurs when the moon only partially covers the sun, resulting in a crescent-shaped sun. In contrast, an annular solar eclipse happens when the moon is at its farthest point from Earth and appears smaller than the sun, causing a ring of light to surround the darkened center.
During a total solar eclipse, several phases can be observed. The first phase is the partial eclipse, where the moon starts to block the sun’s disk, gradually reducing its size. As the moon moves further along its path, the sky dims significantly, and the air cools. The next phase is the diamond ring effect, where a small burst of sunlight appears as a shining diamond on the edge of the moon just before totality. Then, in the mesmerizing moments of totality, the sun is completely covered, revealing the ethereal corona, which can be seen streaming outward like a celestial crown. This breathtaking display is only visible to those within the narrow path of totality. After the coveted minutes of totality, the moon continues its journey, gradually unveiling the sun once again in reverse order.
Now that we’ve delved into the intriguing realm of solar eclipses, let’s shift our focus to another celestial spectacle – lunar eclipses. (Link to: /unveiling-zodiac-compatibility/)
Definition and Occurrence
A lunar eclipse, just like a solar eclipse, is a captivating celestial event that occurs when the Earth aligns between the sun and the moon, casting its shadow on the lunar surface. Unlike solar eclipses, lunar eclipses are visible from anywhere on Earth where the moon is above the horizon during the event. This means that a lunar eclipse can be observed by a much larger portion of the world’s population. The occurrence of lunar eclipses is also more frequent than solar eclipses, with approximately two to four lunar eclipses happening each year.
Lunar eclipses can be categorized into three main types: total, partial, and penumbral. A total lunar eclipse takes place when the Earth completely blocks the direct sunlight from reaching the moon, resulting in the moon turning a deep red or coppery color. This phenomenon, often referred to as a “blood moon,” occurs due to the filtering effect of Earth’s atmosphere, which scatters shorter wavelengths of light while allowing longer wavelengths, such as red and orange, to pass through.
During a partial lunar eclipse, only a portion of the moon is covered by the Earth’s shadow, resulting in a crescent or half-moon shape. Lastly, a penumbral lunar eclipse occurs when the moon passes through the Earth’s penumbra, the outer part of its shadow. This type of lunar eclipse is more subtle, with only a slight darkening of the moon’s surface.
The occurrence of a lunar eclipse is dependent on the alignment of the sun, Earth, and moon. It happens when the moon is in its full moon phase and is in or near Earth’s orbital plane. Due to the tilt of the moon’s orbit relative to the Earth’s orbit around the sun, lunar eclipses do not occur during every full moon. However, they are more frequent than solar eclipses, and their mesmerizing beauty has captivated humans throughout history.
As we continue our exploration of lunar eclipses, we will delve into the different types and visual phenomena associated with these celestial events. (Link to: /red-giants-stellar-evolution/)
Types of Solar Eclipses
There are three main types of solar eclipses: total, partial, and annular. Let’s take a closer look at each one:
1. Total Solar Eclipse: During a total solar eclipse, the moon completely blocks the sun, casting a shadow on Earth. This rare and awe-inspiring event allows us to witness the beautiful corona surrounding the sun. The path of totality, where the moon completely covers the sun, is relatively narrow and only visible to those lucky enough to be in its trajectory.
2. Partial Solar Eclipse: In a partial solar eclipse, the moon only partially covers the sun, resulting in a crescent shape. This type of eclipse is more common since the alignment does not need to be perfect for it to occur. People outside the path of totality can still witness a partial eclipse depending on their location.
3. Annular Solar Eclipse: An annular solar eclipse occurs when the moon is at its farthest point from Earth in its elliptical orbit. As a result, the moon appears smaller than the sun, leaving a ring of sunlight visible around the edges of the moon. This creates a mesmerizing “ring of fire” effect, which is truly a sight to behold.
It’s fascinating to observe the different types of solar eclipses and marvel at the celestial dance between the sun, moon, and Earth. (Link to: /ophiuchus-literature-books-characters/)
Phases and Visual Phenomena
The phases and visual phenomena associated with solar eclipses are truly awe-inspiring. Let’s break down the sequence of events that occurs during a total solar eclipse.
1. Contact and Partial Eclipse: The moon begins to move in front of the sun, gradually covering a portion of its disk. This initial stage is known as the partial eclipse. As more of the sun is obscured, the sky dims, and the overall lighting conditions change.
2. Diamond Ring Effect and Baily’s Beads: As the moon continues its journey across the sun, a remarkable phenomenon called the diamond ring effect occurs. It happens when a small burst of sunlight appears as a shining diamond on the edge of the moon, creating a stunning visual effect. Additionally, during this phase, Baily’s beads may be observed, which are tiny points of sunlight shining through the moon’s valleys and mountains.
3. Totality: The pinnacle of a total solar eclipse is the phase of totality. At this moment, the moon completely covers the sun, creating a unique spectacle for those fortunate enough to be within the path of totality. The surrounding sky darkens, and stars may become visible. The corona, the sun’s outer atmosphere, becomes visible as a delicate, ethereal white glow encircling the moon. The corona extends millions of kilometers into space and showcases intricate structures created by magnetic fields.
4. Prominences and Solar Flares: During totality, solar prominences, which are immense arcs and loops of glowing gases, may become visible on the sun’s surface. These majestic structures are formed by the sun’s magnetic fields and add to the jaw-dropping beauty of the phenomenon. In certain instances, solar flares, which are massive explosions on the sun’s surface, might also occur, producing additional visual interest and complexity.
5. Reverse Sequence: As the moon continues its journey across the sun, the phases and visual effects described above occur in reverse order. The corona fades away, the diamond ring effect reappears, and the sky gradually brightens as the moon moves away from the sun, concluding the extraordinary display of a total solar eclipse. (Link to: /ophiuchus-literature-books-characters/)
Understanding these mesmerizing phases and visual phenomena of solar eclipses helps us appreciate the sheer splendor of these celestial occurrences. Now, let’s turn our attention to exploring the phases and visual phenomena associated with lunar eclipses.
Lunar Eclipses Demystified
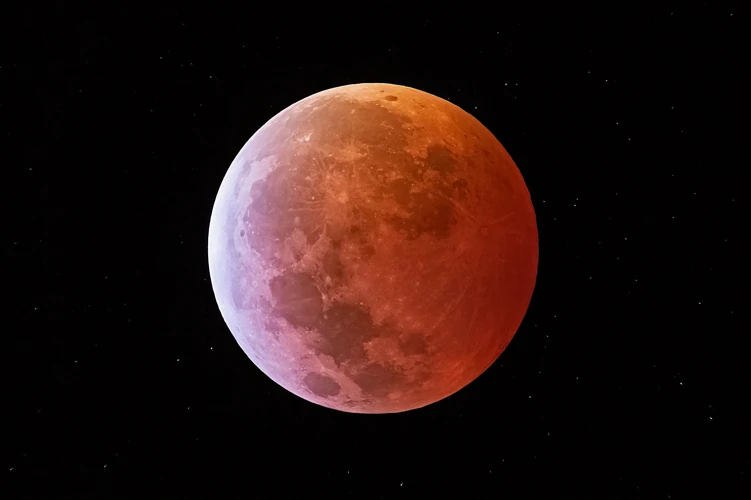

A lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth comes between the sun and the moon, causing the moon to pass through the Earth’s shadow. Unlike solar eclipses, lunar eclipses are visible from anywhere on the Earth’s night side, as long as the moon is above the horizon. This means that lunar eclipses are more frequent and can be observed by a larger portion of the population.
There are three types of lunar eclipses: total, partial, and penumbral. A total lunar eclipse is a stunning event where the moon is completely immersed in Earth’s shadow, taking on a reddish glow, often referred to as a “blood moon.” A partial lunar eclipse occurs when only a portion of the moon enters Earth’s shadow, resulting in a partial darkening of the lunar surface. Lastly, a penumbral lunar eclipse happens when the moon enters only the outer part of Earth’s shadow, causing a subtle darkening that may be difficult to notice without careful observation.
During a lunar eclipse, there are distinct phases and visual phenomena to observe. The first phase is the penumbral phase, where the moon enters the outer edge of Earth’s shadow, resulting in a subtle darkening. As the eclipse progresses, the moon moves deeper into the shadow, leading to the partial and total phases. During the total phase of a lunar eclipse, the moon may appear to turn a deep red or copper color due to the way Earth’s atmosphere bends and filters sunlight.
This phenomenon is known as “Rayleigh scattering,” where shorter wavelengths of light are scattered, leaving behind longer wavelengths such as red and orange. The intensity and shade of the lunar eclipse’s color can vary depending on atmospheric conditions on Earth.
One fascinating aspect of lunar eclipses is their cultural and historical significance. Throughout history, lunar eclipses have been seen as omens or celestial events of importance across different cultures and civilizations. From ancient folklore to religious beliefs, lunar eclipses have often been associated with spiritual or supernatural interpretations.
Now that we’ve demystified lunar eclipses, let’s explore the differences between solar and lunar eclipses in more detail. (Link to: /ophiuchus-literature-books-characters/)
Definition and Occurrence
Lunar eclipses occur when the Earth casts its shadow on the moon, causing it to darken or take on a reddish hue. Unlike solar eclipses, lunar eclipses are visible from anywhere on the night side of the Earth. This cosmic phenomenon occurs when the sun, Earth, and moon are precisely aligned, with the Earth positioned between the sun and the moon. The Earth’s atmosphere scatters the sunlight, allowing only the longer wavelengths of light such as red and orange to reach the moon. As a result, the moon takes on a captivating reddish color, leading to its nickname as the “Blood Moon.” Lunar eclipses are relatively more common than solar eclipses, occurring multiple times a year. Their occurrence depends on the moon’s position in its orbit and the inclination of its orbit relative to Earth’s orbit around the sun. This alignment creates a beautiful and mysterious interplay between the celestial bodies that captivates observers around the world. Now that we have explored the definition and occurrence of lunar eclipses, let’s dive deeper into their types and the visual phenomena they entail.
Types of Lunar Eclipses
Lunar eclipses, unlike solar eclipses, occur when the Earth is positioned between the sun and the moon, casting a shadow on the lunar surface. There are three main types of lunar eclipses: total, partial, and penumbral.
A total lunar eclipse happens when the moon is completely engulfed by the Earth’s dark inner shadow, known as the umbra. During this awe-inspiring event, the moon may take on a reddish hue due to the sunlight passing through the Earth’s atmosphere. This phenomenon is often referred to as a “blood moon.” Total lunar eclipses are rare occurrences and can be quite spectacular to witness.
Partial lunar eclipses occur when only a portion of the moon passes through the Earth’s umbra. In this case, only a fraction of the moon is covered by the shadow, resulting in a crescent or semicircular shape. While not as dramatic as a total lunar eclipse, partial lunar eclipses still offer a captivating sight for sky enthusiasts.
Penumbral lunar eclipses, on the other hand, occur when the moon passes through the Earth’s outer shadow, known as the penumbra. During a penumbral lunar eclipse, the moon appears slightly darker but does not take on the reddish hue characteristic of a total lunar eclipse. This type of eclipse is often more subtle and may go unnoticed to the untrained eye.
Each type of lunar eclipse offers a unique visual display, showcasing the intricate interplay between the Earth, moon, and sun. Understanding these distinctions allows us to appreciate the sheer magnitude of cosmic events that occur beyond our own planet. (Link to: /ophiuchus-literature-books-characters/)
Phases and Visual Phenomena
During a solar eclipse, several phases and visual phenomena can be observed, adding to the magical experience. As the moon starts to block the sun’s disk during a partial solar eclipse, the sun gradually reduces in size, creating a crescent-shaped appearance in the sky. This phase allows for unique photographic opportunities and a chance to witness the transformative power of celestial alignment.
One of the most mesmerizing moments of a total solar eclipse is the diamond ring effect. Just before totality, a small burst of sunlight appears as a shining diamond on the edge of the moon. This dazzling sight is caused by sunlight passing through lunar valleys and craters, creating a brief and intense glimmer.
As the moon completely covers the sun during totality, a remarkable visual phenomenon unfolds – the reveal of the sun’s corona. This outer atmosphere of the sun, which is typically invisible due to the sun’s intense brightness, becomes visible as a beautiful halo streaming outward. The corona is composed of plasma, or ionized gases, and exhibits a delicate and intricate structure. Its appearance during totality is breathtaking and has inspired awe in astronomers and stargazers throughout history.
Additionally, the sky darkens significantly during a total solar eclipse, and the air cools, offering a surreal and eerie atmosphere. Birds may stop singing, and nocturnal animals may become active, mistakenly thinking that night has fallen. The sudden transformation of the environment adds to the sense of wonder and astonishment experienced during this celestial event.
It’s important to note that observing a solar eclipse requires precaution and proper eye protection to avoid eye damage. Looking directly at the sun, even during an eclipse, can be harmful. Specialized solar filters or eclipse glasses certified to be safe for solar viewing should always be used.
Now, let’s explore another celestial marvel – lunar eclipses. (Link to: /ophiuchus-literature-books-characters/)
Comparing Solar and Lunar Eclipses

Solar and lunar eclipses may share similarities in their astronomical nature, but they possess distinct differences that set them apart. Let’s explore these variations and gain a deeper understanding of these captivating celestial events.
First and foremost, the key distinction lies in the alignment of the Earth, moon, and sun. During a solar eclipse, the moon stands between the Earth and the sun, causing a temporary shadow to fall on our planet. On the other hand, during a lunar eclipse, the Earth stands between the sun and the moon, casting a reddish hue on the lunar surface.
Another notable difference is the frequency and visibility of these phenomena. Solar eclipses are relatively rare, occurring less frequently than lunar eclipses. This scarcity results from the sun’s smaller size in comparison to the moon, which means that the moon can cast its shadow on Earth less often. Lunar eclipses, on the other hand, are more common and visible from a broader range of locations on Earth.
The visual phenomena during these two types of eclipses also differs greatly. During a solar eclipse, observers within the path of totality can witness the dramatic darkening of the sky, the appearance of the ethereal corona, and the mesmerizing diamond ring effect. In contrast, during a lunar eclipse, the moon takes on a reddish hue due to the scattering of sunlight by the Earth’s atmosphere. This phenomenon gives the moon a enchanting coppery or blood-red appearance, often referred to as the “Blood Moon.”
The impact of solar and lunar eclipses on Earth and sky is also worth noting. Solar eclipses cast a temporary darkness on Earth, affecting both natural phenomena and human activities. Animals may exhibit strange behavior, stars and planets become visible during the day, and temperatures may drop slightly. Lunar eclipses, however, have a more subtle impact, mainly affecting the appearance of the moon and the perception of its color.
Lastly, solar and lunar eclipses hold significant historical and cultural significance. Throughout history, these celestial events have sparked curiosity, fear, and reverence in different cultures around the world. Ancient civilizations considered solar and lunar eclipses as omens, symbols of divine intervention, or moments of cosmic alignment. Today, these events continue to inspire awe and wonder, bringing people together to witness the grandeur of the universe.
As we delve deeper into the nuances of solar and lunar eclipses, it becomes clear that while they may share some similarities, they are truly distinct and captivating phenomena. From the rarity of solar eclipses to the mesmerizing red glow of lunar eclipses, each offers a unique experience that leaves observers awe-struck and appreciative of the vastness and beauty of our celestial surroundings.
Overview of Differences
To better understand the disparities between solar and lunar eclipses, let’s examine the key distinctions:
Duration: Solar eclipses are relatively short-lived spectacles, typically lasting only a few minutes during totality. In contrast, lunar eclipses are considerably longer, lasting for several hours.
Visibility: Solar eclipses can only be observed from specific regions of the Earth that fall within the path of totality. This narrow path, usually a few hundred kilometers wide, moves across the Earth’s surface as the moon’s shadow travels. Lunar eclipses, on the other hand, are visible from anywhere on Earth’s night side, assuming the moon is above the horizon.
Frequency: Solar eclipses occur less frequently than their lunar counterparts. While solar eclipses happen roughly every 18 months, lunar eclipses occur about twice a year.
Associated Events: During a solar eclipse, the sky darkens significantly for a brief period, and temperatures may drop. Additionally, observers may witness the appearance of planets and bright stars in the daytime sky. During a lunar eclipse, the moon takes on a reddish hue due to the Earth’s atmosphere bending sunlight and filtering out shorter wavelengths, which results in a phenomenon known as a “blood moon.”
These are just a few of the fundamental differences between solar and lunar eclipses. Now that we’ve explored their disparities, let’s delve into the distinct details of lunar eclipses. (Link to: /ophiuchus-literature-books-characters/)
Impact on Earth and Sky
Solar eclipses have a notable impact on both the Earth and the sky. During a total solar eclipse, the sudden darkness that descends upon the land can evoke an eerie atmosphere, with animals sometimes exhibiting confusion or altered behavior. The temperature can drop noticeably, and winds may change direction. Additionally, the corona, which becomes visible during totality, reveals the sun’s outer atmosphere, providing scientists with a unique opportunity to study its composition and behavior. These observations contribute to our understanding of the sun’s magnetic fields, solar flares, and other solar phenomena.
In terms of the sky, a solar eclipse is a mesmerizing event that captivates observers. The gradual blocking and uncovering of the sun by the moon create a visual spectacle that never fails to awe. During totality, when the sun is completely obscured, viewers lucky enough to be within the path of totality witness a surreal sight as the sky becomes dark, revealing stars and planets that are usually obscured by the sun’s bright glare. This rare occurrence gives astronomers and stargazers an opportunity to observe and appreciate the night sky in the middle of the day.
On the other hand, lunar eclipses have a different impact on the Earth and the sky. Unlike solar eclipses, which can only be seen from specific regions, lunar eclipses are visible from any location on Earth where the moon is above the horizon during the eclipse. These events are more common and can be observed by a larger audience.
During a lunar eclipse, the Earth passes between the sun and the moon, casting a reddish glow on the moon’s surface. This reddish color is caused by sunlight bending around the Earth’s atmosphere and filtering through it. The amount of atmospheric particles, such as dust and pollution, affects the color and intensity of the lunar eclipse. Additionally, the moon may appear slightly dimmer during a lunar eclipse, making fainter stars more visible in the night sky.
The impact of lunar eclipses on Earth and the sky is more subtle compared to solar eclipses. While lunar eclipses do not cause significant changes in temperature or behavior, they provide a stunning celestial display for enthusiasts and photographers. The sight of the moon gradually dimming and taking on a reddish hue is an enchanting experience that connects us to the vastness of the universe.
In the next section, we will explore the historical and cultural significance of solar and lunar eclipses.
Historical and Cultural Significance
Throughout history, solar eclipses have held great historical and cultural significance. Ancient civilizations, such as the Egyptians and Mesopotamians, viewed solar eclipses as celestial omens, often interpreting them as harbingers of impending doom or important events. These celestial events were seen as messages from the gods and were closely tied to religious beliefs and superstitions. Some cultures even believed that mythical creatures or celestial deities were responsible for causing solar eclipses. In ancient China, for example, it was believed that a celestial dragon was devouring the sun during an eclipse, prompting people to make loud noises and bang drums to scare away the dragon.
The historical and cultural significance of solar eclipses can also be seen in various myths and legends. In Norse mythology, it was said that the sun and moon were being chased by two wolves, Skoll and Hati, and during an eclipse, they would catch their prey, temporarily swallowing them and causing darkness. These myths not only provide fascinating explanations for the phenomenon but also reflect the awe and wonder that solar eclipses inspired in people throughout history.
In more modern times, solar eclipses continue to captivate and unite people from different cultures around the world. They are often celebrated as unique and rare cosmic events, attracting tourists and enthusiasts from far and wide to witness their splendor. Eclipse-chasing has become a popular activity among adventure seekers and amateur astronomers who travel to different locations to experience the sheer beauty and grandeur of a total solar eclipse. The shared experience of witnessing this celestial marvel has the power to bring people together, fostering a sense of awe and unity in our vast and mysterious universe.
The historical and cultural significance of solar eclipses serves as a testament to the enduring fascination and reverence that we as humans have for the wonders of the cosmos. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of the universe, these celestial events remind us of our place in the cosmos and inspire us to explore, discover, and connect with the vastness beyond our planet. (Link to: /ophiuchus-literature-books-characters/)
Preparing for Eclipse Viewing
When it comes to experiencing the awe-inspiring phenomenon of an eclipse, preparation is key. To ensure a safe and memorable viewing experience, it is important to have the right equipment and take necessary safety precautions.
One of the most essential items for eclipse viewing is a pair of solar viewing glasses. These specialized glasses are designed to block out harmful ultraviolet and infrared rays, allowing you to safely look at the sun during a partial solar eclipse. It is crucial to choose glasses that meet the recommended safety standards to protect your eyes from potential damage. Always check for certifications such as ISO 12312-2 to ensure the authenticity and effectiveness of the glasses.
Another popular method for eclipse observation is using a solar filter on a telescope or camera lens. This allows for a more detailed and magnified view of the eclipse. However, it is important to note that regular sunglasses or homemade filters should never be used for eclipse viewing, as they do not provide adequate protection.
In addition to eye protection, it is important to take safety precautions to avoid damaging your equipment. Directly focusing the unfiltered sun through a telescope without proper safety measures can lead to irreversible damage to the optics. Always use approved solar filters or dedicated solar telescopes designed for safe solar observation.
Choosing the right location for eclipse viewing is also crucial. Ideally, you’ll want to find a spot with a clear view of the sky and minimal light pollution. Parks, open fields, and mountaintops often make great viewing locations. Be sure to check if there are any local events or organized gatherings for eclipse viewing in your area, as these can provide a unique and communal experience.
It’s also a good idea to plan for any weather conditions that may impact your view. Keep an eye on weather forecasts and have alternate locations in mind if necessary. Sometimes, cloud cover can add an interesting dimension to the eclipse viewing experience, but it can also obstruct the view entirely. Remember to pack essentials such as water, snacks, and comfortable seating arrangements to ensure you can stay for the duration of the eclipse.
By taking these preparation steps, you’ll be well-equipped to fully immerse yourself in the extraordinary spectacle of an eclipse. So gather your equipment, find a suitable location, and get ready to witness the wonders of the cosmos firsthand.
Equipment and Safety Precautions
To safely view solar eclipses, proper equipment and safety precautions are of utmost importance. Looking directly at the sun during the eclipse can cause severe eye damage, so it’s essential to take the necessary steps to protect your eyesight. One of the most crucial safety tools is a pair of solar viewing glasses or solar filters. These specially designed glasses or filters block out harmful ultraviolet and infrared rays, allowing you to view the eclipse without risking eye damage. It’s important to use glasses or filters that meet the designated safety standards and have certification from reputable organizations.
Another option for safe eclipse viewing is using a solar telescope or solar binoculars with built-in solar filters. These devices provide a magnified and detailed view of the eclipse while keeping your eyes protected. However, it’s crucial to remember that regular telescopes or binoculars should never be used without appropriate solar filters, as they can intensify the sun’s rays and cause permanent eye damage.
For photography enthusiasts, capturing the beauty of a solar eclipse is an enticing endeavor. However, photographing an eclipse requires additional precautions to safeguard your eyes and equipment. To photograph a solar eclipse, you will need a solar filter specifically designed for your camera lens. This filter decreases the sun’s intensity, allowing you to capture the eclipse safely. It’s essential to follow the manufacturer’s instructions on how to attach the filter to your camera and lens properly. Additionally, using a tripod is recommended to keep your camera steady and prevent blurry images.
Remember to never use improvised or homemade filters, such as sunglasses, smoked glass, X-ray film, or CD/DVDs, as they do not offer adequate protection and can lead to eye damage.
Lastly, choosing a suitable location for observing the eclipse is crucial. Find an open area away from tall buildings and trees that may obstruct your view. Look for a spot with a clear, unobstructed view of the sky. If possible, consider traveling to areas where the total solar eclipse can be observed for the most awe-inspiring experience.
By prioritizing safety and using the right equipment, you can enjoy the wonder of a solar eclipse while protecting your eyesight. So, gather your solar viewing glasses, set up your cameras, and get ready for an unforgettable celestial experience.
Best Viewing Locations
When it comes to observing solar and lunar eclipses, the location plays a crucial role in ensuring the best viewing experience. While these celestial events can be observed from various parts of the world, certain locations offer optimal conditions for witnessing these awe-inspiring phenomena.
For solar eclipses, the ideal viewing locations are usually along the path of totality. This path is a narrow strip on Earth’s surface where the moon’s shadow falls during a total solar eclipse. To witness the dramatic moments of totality, it is essential to be within this path. Astronomers and eclipse enthusiasts often plan their travels to remote areas or specific destinations that lie along the path of totality. Some popular locations for observing solar eclipses include Chile, Argentina, the South Pacific Islands, and parts of Africa.
On the other hand, lunar eclipses can be viewed from a much wider range of locations. Unlike solar eclipses, lunar eclipses are visible from any place on Earth where the moon is above the horizon during the event. However, the visibility and the quality of the viewing experience can be influenced by factors such as light pollution, weather conditions, and obstructions like tall buildings or mountains. Choosing a location away from city lights and with a clear view of the sky is ideal for capturing the subtle beauty of a lunar eclipse.
If you are planning to witness an eclipse, it is advisable to research and consult astronomers or local sky-watching groups to identify the best viewing locations for a particular event. Additionally, equipping yourself with essential tools like solar filters for solar eclipses or binoculars for lunar eclipses can enhance your experience and allow you to observe more intricate details.
Remember, whether you choose a remote destination or simply step outside your backyard, the awe-inspiring phenomenon of an eclipse conveys the grandeur and mystery of our universe. So find the best spot, prepare your gear, and get ready to be spellbound by the wonders of nature high above in the heavens.
Conclusion

In conclusion, solar and lunar eclipses are captivating celestial events that continue to enthrall us with their awe-inspiring displays. (Link to: /red-giants-stellar-evolution/) Solar eclipses occur when the moon aligns perfectly with the sun and casts a shadow on the Earth, while lunar eclipses happen when the Earth comes between the sun and the moon, causing a shadow to fall on the moon. Understanding the differences between these two types of eclipses is essential to appreciate the unique visual phenomena and the impact they have on our planet and sky. From the rare occurrence of total solar eclipses to the stunning corona and diamond ring effects, each solar eclipse offers a mesmerizing experience. On the other hand, lunar eclipses showcase the reddish glow of the moon during totality and offer a different perspective on our celestial neighbor. Both types of eclipses have held significant historical and cultural significance throughout human civilization, inspiring myths, legends, and astronomical advancements. So, whether you’re a seasoned skywatcher or a curious novice, the allure of eclipses continues to evoke wonder and spark our imagination about the vastness of our universe.
Frequently Asked Questions

FAQs About Solar Eclipses
1. What is a solar eclipse?
A solar eclipse occurs when the moon passes between the sun and the Earth, casting a shadow on our planet.
2. How often do solar eclipses happen?
On average, a solar eclipse occurs somewhere on Earth every 18 months, but specific regions may experience multiple eclipses in a lifetime.
3. Can I look directly at a solar eclipse?
No, looking directly at a solar eclipse without proper eye protection can cause severe eye damage. Always use certified solar viewing glasses or indirect viewing methods.
4. What is the path of totality?
The path of totality refers to the narrow strip on Earth’s surface where a total solar eclipse can be observed. Outside this path, a partial eclipse is visible.
5. How long does a total solar eclipse last?
The duration of a total solar eclipse can vary, but it typically lasts for a few minutes, ranging from a few seconds to a maximum of over seven minutes.
6. What is the corona?
The corona is the outermost layer of the sun’s atmosphere. During a total solar eclipse, it becomes visible as a glowing halo surrounding the darkened disk of the sun.
7. Can animals react differently during a solar eclipse?
Yes, some animals may exhibit unusual behavior during a solar eclipse, mistaking it for an impending change in daylight and reacting accordingly.
8. Why are solar eclipses significant to scientists?
Solar eclipses provide scientists with valuable opportunities to study the sun’s physical properties, atmosphere, and magnetic fields.
9. Are solar eclipses the same all over the world?
No, the visibility and nature of a solar eclipse can vary depending on the viewer’s location. The type and extent of the eclipse depend on the observer’s position on Earth.
10. How can I photograph a solar eclipse safely?
Photographing a solar eclipse requires special equipment and techniques to protect both your camera and your eyes. Consult reliable sources for proper guidance and precautions.
References
Frequently Asked Questions

What is a solar eclipse?
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between the Sun and the Earth, temporarily blocking the Sun’s light.
What is a lunar eclipse?
A lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth comes between the Moon and the Sun, casting a shadow on the Moon and causing it to appear darkened.
How often do solar eclipses happen?
Solar eclipses are relatively rare events. On average, there are about two to five solar eclipses every year, but they can only be seen from specific locations on Earth.
How often do lunar eclipses happen?
Lunar eclipses also don’t occur frequently. On average, there are about two to four lunar eclipses each year, and they are visible from anywhere on the Earth where the Moon is above the horizon.
Why are solar eclipses more rare than lunar eclipses?
Solar eclipses are less common because the Moon’s shadow is smaller and only covers a small area on Earth during an eclipse. In contrast, the Earth casts a much larger shadow during a lunar eclipse, making it visible from a wider range of locations.
Can you look directly at a solar eclipse?
No, it is never safe to look directly at a solar eclipse without proper eye protection. The intense sunlight during an eclipse can cause permanent damage to your eyes.
Can you watch a lunar eclipse without any special equipment?
Yes, lunar eclipses are safe to watch without any special equipment. The Moon appears dimmer during a lunar eclipse, but it poses no harm to your eyes.
What causes the different types of solar eclipses?
The different types of solar eclipses are caused by the Moon’s distance from Earth and its size relative to the Sun. This affects whether the Moon fully or partially covers the Sun during an eclipse.
What causes the reddish color of the Moon during a lunar eclipse?
The reddish color of the Moon during a lunar eclipse is caused by the Earth’s atmosphere bending sunlight and filtering out shorter-wavelength blue and green light. The remaining longer-wavelength red light gets refracted onto the Moon, giving it a reddish hue.
Are there any cultural or historical significances associated with eclipses?
Yes, eclipses have held cultural and historical significances in many societies throughout history. They have often been interpreted as omens or symbols of change, with various myths, folklore, and rituals associated with them.
References
- Solar eclipse and lunar eclipse: What is the difference …
- What’s the Difference Between a Solar and a Lunar Eclipse?