For centuries, the constellation of Orion has captivated and bewildered stargazers. With its distinctive pattern of stars resembling a mighty hunter wielding a sword and shield, Orion has sparked the imagination of people around the world. In this article, we embark on a journey to unravel the mysteries surrounding Orion, delving into the ancient myths and legends that intertwine with this celestial figure. From his cosmic origins to his connections in Greek mythology and other cultures, we will explore the fascinating tales and symbolism that have made Orion a celestial marvel. Join us as we uncover the enigmatic stories and cultural significance behind the celestial hunter.
Contents
- The Hunter’s Origins
- Mythological Connections
- The Stellar Showcase
- Legends and Legends Transcending Time
- Contemporary Cultural References
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the significance of Orion in Greek mythology?
- Which other cultures have myths and legends about Orion?
- What stars make up the constellation of Orion?
- Why is Orion so prominent in the night sky?
- What is the story behind Orion and Artemis?
- How is Orion connected to Taurus and the Pleiades?
- What does Orion’s role in astrology entail?
- How has Orion been represented in literature and art?
- How does Orion feature in modern popular culture?
- What does Orion teach us about the vastness of the universe?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How did Orion become a constellation in Greek mythology?
- 2. What were Orion’s pursuits as a hunter?
- 3. How does Orion feature in Greek mythology?
- 4. Which other cultures have myths or legends featuring Orion?
- 5. Why is Orion so prominent in the night sky?
- 6. Which stars make up the constellation of Orion?
- 7. What is the story of Orion and Artemis?
- 8. How is Orion connected to the constellation Taurus and the Pleiades?
- 9. What is Orion’s role in astrology?
- 10. How has Orion been depicted in literature and art?
- References
- Read More
The Hunter’s Origins
Legend has it that Orion’s journey began through a tale of cosmic birth. According to ancient Greek mythology, Orion’s Origins can be traced back to the union of the sea god Poseidon and the Pleiad nymph, Euryale. From their union, a son named Orion was born. However, other cultures have different interpretations of Orion’s origins. In Mayan mythology, Orion was believed to represent the Maize God, who played a vital role in the cycle of life and agriculture. This connection highlights the diverse cultural significance and varied interpretations of Orion throughout history. As we explore further, we will discover more about Orion’s pursuits and the captivating tales that unfold around this celestial hunter.
The Birth of Orion
The Birth of Orion is a tale steeped in Greek mythology and holds various iterations across ancient texts and oral traditions. In one version, it is said that Orion was the result of a divine union between the sea god Poseidon and the Pleiad nymph, Euryale. From their union, Orion, a mighty and formidable figure, was born. Another account suggests that Orion was the son of the god Apollo, who fashioned him from a gigantic bronze bull. This association with celestial and divine lineage brings an air of awe and power to Orion’s story. Regardless of the specific version, the birth of Orion is always shrouded in a sense of magnificence and wonder. The various interpretations of his origins serve as a testament to the ancient fascination with connecting celestial phenomena to the intricate tapestry of human existence.
The Hunter’s Pursuits
Throughout mythology, Orion’s pursuits have been depicted in various tales and legends. One of the most famous stories involving is his encounter with the mythical creature known as the Scorpion. According to Greek mythology, Orion boasted of his hunting skills and claimed that no creature could defeat him. As a result, the Earth goddess Gaia sent a gigantic scorpion to challenge him. In a fierce battle, the scorpion and Orion fought relentlessly, each trying to gain the upper hand. However, the scorpion managed to strike a fatal blow, stinging Orion with its poisonous tail. As a result, Zeus placed both Orion and the scorpion in the night sky as constellations, forever locked in a cosmic duel. This tale of Orion’s pursuit serves as a reminder of the hunter’s hubris and the lessons learned through his encounters with formidable foes. To explore the symbolism and deeper meanings behind Orion’s pursuits, let’s delve into the astrological and mythological connections that surround this celestial figure. To learn about the astrological influence of Orion and its connection to personality traits, check out our article on how astrological houses influence personality.
Mythological Connections
Orion’s mythological connections span across different cultures, but it is in Greek mythology that his presence is deeply ingrained. Orion in Greek Mythology is often depicted as a skilled hunter, known for his immense strength and bravery. One popular tale tells of Orion’s encounter with the goddess Artemis. In this story, Orion’s arrogance led to a challenge against Artemis, who was known as the goddess of the hunt. However, Artemis, with her mastery over the wilderness, tricked Orion into wading too far into the sea, where he met his demise. This myth reflects the power struggle between mortals and gods, as well as the consequences of hubris. In other cultures, such as Mayan mythology, Orion’s significance takes on a different form. For the Maya, Orion was associated with the Maize God and played a crucial role in agricultural symbolism. This diverse range of mythological connections showcases how Orion’s celestial presence has influenced and inspired ancient cultures throughout history.
Orion in Greek Mythology
In Greek mythology, holds a prominent place among the celestial figures. He is often depicted as a mighty hunter, renowned for his exceptional strength, bravery, and skills. One of the well-known tales associated with Orion revolves around his encounter with the goddess Artemis, the twin sister of Apollo. According to the myth, Orion’s boastful nature led him to claim that he could hunt and kill all the creatures on Earth, which angered the goddess. To teach him a lesson, Artemis sent a giant scorpion to confront Orion. The scorpion stung him, and despite his mighty strength, Orion was ultimately defeated. The gods immortalized both Orion and the scorpion by placing them in the night sky as constellations, Orion being visible in the winter sky, while the scorpion became the constellation Scorpius. This myth of Orion’s downfall serves as a reminder of the consequences of hubris and the balance of power in Greek mythology. So, we see that Orion’s mythological connections are not limited to Greek mythology alone; other cultures also have their unique interpretations of this celebrated celestial figure.
Orion in Other Cultures
Orion’s celestial prominence extends far beyond Greek mythology. Various cultures around the world have woven their own unique narratives around this iconic constellation. In Egyptian mythology, Orion was associated with the god Osiris, the ruler of the afterlife. The alignment of Orion’s belt with the pyramids of Giza was believed to hold symbolic significance in connecting the earth and the heavens. In Norse mythology, Orion was associated with the legendary hero known as Skathi. Skathi, who was also a mighty hunter, was often depicted alongside the constellation Orion. Similarly, the Dogon people of Mali in West Africa revered Orion as the foundation of their religious beliefs. They believed that the star Sirius, which is part of the constellation Canis Major and connected to Orion, played a significant role in their cosmology. These diverse cultural interpretations of Orion showcase the universal fascination and reverence for the celestial realms across time and geography. Discovering these connections helps us unravel the enduring legacy of Orion in other cultures and their rich mythologies.
The Stellar Showcase
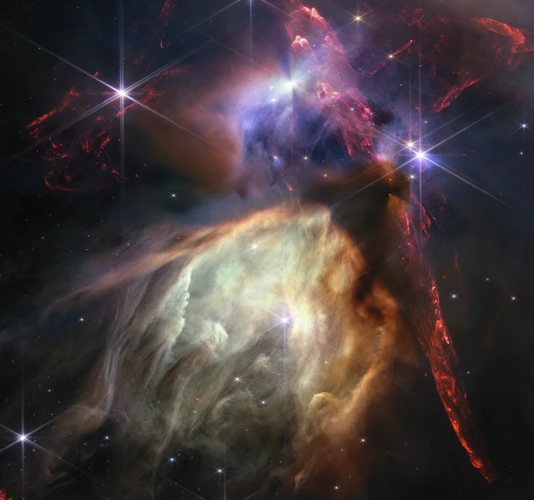

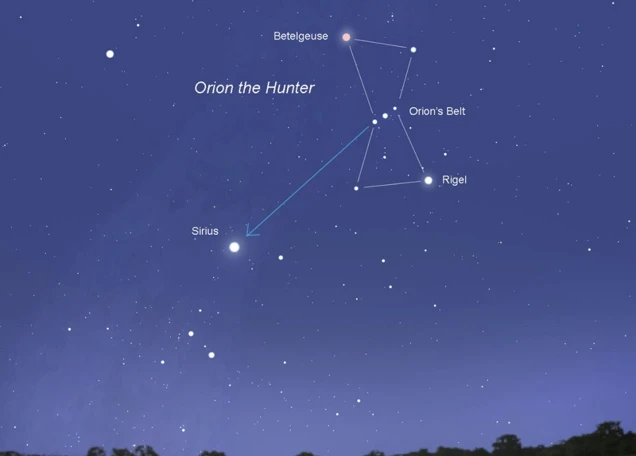
In the vast expanse of the night sky, Orion holds a significant place as a Stellar Showcase. The constellation of Orion is easily recognizable with its prominent three-star belt, which aligns with the celestial equator. This positioning gives Orion a commanding presence in the Northern Hemisphere during the winter months. Among the stars that comprise Orion, the most notable are the bright blue supergiant, Rigel, and the red supergiant, Betelgeuse. These stars not only contribute to Orion’s striking appearance but also hold astronomical importance. Rigel, located at Orion’s foot, is one of the brightest stars in the night sky, while Betelgeuse, at Orion’s shoulder, is a massive star nearing the end of its life. Their brilliance and celestial stature add to the allure of Orion’s stellar showcase, captivating both astronomers and stargazers alike.
Orion’s Prominence in the Night Sky
Orion’s Prominence in the Night Sky is undeniable, captivating both professional astronomers and amateur stargazers alike. This constellation dominates the winter sky in the northern hemisphere, displaying its splendor from November to February. Its visibility is due in part to its position along the celestial equator, allowing Orion to be seen from various regions around the world. The distinct pattern formed by its stars, including the bright stars Betelgeuse and Rigel, further adds to its visibility and recognition. Betelgeuse, a red supergiant located in the upper left of Orion, holds the title of being one of the largest known stars in our galaxy. Its dazzling presence contributes to Orion’s overall allure and makes it readily identifiable even to those new to stargazing. The prominent position of Orion in the night sky, coupled with its easily recognizable star pattern, has made it one of the most famous and beloved constellations throughout human history. Its brightness and accessibility make it a wonderful starting point for those venturing into the wonders of stargazing. So, on a clear winter night, take a moment to look up and marvel at the prominent figure of Orion glistening above, igniting a sense of wonder and inspiration. Who knows, you might even catch a glimpse of other celestial wonders while exploring Orion’s domain. If you’re a fan of zodiac signs and interested in the influences of astrology, you might find it fascinating to delve into the connection between Orion’s prominence and its effect on personalities, such as the earthy and determined traits attributed to the constellation of Capricorn, which can be explored further through astrological houses. The influence of astronomy on cultures throughout history, like the Mayans, also adds another layer to the prominence of Orion in the night sky, as it explores the interconnectedness of celestial bodies and myths, as seen in Mayan mythology. So, next time you gaze up at the heavens, let Orion guide your eyes to the wonders of the cosmos.
The Stars that Comprise Orion
The stars that comprise Orion form a magnificent and easily recognizable constellation in the night sky. Let’s take a closer look at each of these celestial gems:
1. Betelgeuse: This bright, red supergiant star marks Orion’s right shoulder. It is one of the largest known stars in the universe and shines with a distinct reddish glow.
2. Rigel: Positioned at Orion’s left knee, Rigel is a blue-white supergiant and one of the brightest stars in the night sky. Its luminosity and brilliance add to the constellation’s allure.
3. Bellatrix: Found in Orion’s left shoulder, Bellatrix shines with a blue-white radiance. Its name translates to “female warrior” in Latin, reflecting its role as a prominent member of the Orion constellation.
4. Mintaka: This star is the westernmost of the three stars forming Orion’s belt. Mintaka is a multiple star system consisting of at least four stars, providing a fascinating spectacle in the night sky.
5. Alnitak: Positioned at the eastern end of Orion’s belt, Alnitak is a triple-star system. Its name translates to “the girdle” in Arabic, symbolizing its location in the constellation’s belt.
6. Saiph: Located at Orion’s right knee, Saiph is a blue supergiant star that adds to the constellation’s brilliance. Its name comes from the Arabic word for “sword,” tying into the celestial hunter’s iconic weapon.
These stars, along with others in the Orion constellation, come together to form a striking pattern recognized and studied by astronomers and stargazers alike. As we delve deeper into the mysteries and legends surrounding Orion, we will gain a deeper understanding of its importance and cultural significance throughout history.
Legends and Legends Transcending Time

Legends surrounding Orion have transcended time, captivating the imaginations of people across different cultures and eras. One of the most famous tales is the enduring love story between Orion and Artemis, the Greek goddess of hunting and the moon. In this myth, Orion was a skilled hunter who caught the attention of Artemis. However, her twin brother Apollo became jealous and tricked Artemis into shooting Orion, leading to his tragic demise. Another significant legend involving Orion is the tale of his encounter with the bull known as Taurus and the cluster of stars called the Pleiades. In this story, Orion was a relentless hunter who pursued the Pleiades, and Taurus intervened to protect them. This conflict resulted in the placement of the constellations Orion and Taurus in close proximity in the night sky. Beyond mythology, Orion’s influence extends into astrology, where it is associated with traits such as strength, ambition, and perseverance. These rich and captivating legends have left an indelible mark on human culture and continue to inspire artists, writers, and astronomers to this day.
Orion and Artemis
In the realm of Greek mythology, the story of Orion and Artemis intertwines in a tale of friendship, love, and tragedy. were renowned hunting partners and close companions. Artemis, the goddess of the hunt and the moon, took a particular liking to Orion due to his incredible hunting prowess. Their bond grew so strong that some even whispered of a romantic connection between the two. However, it is essential to note that interpretations of their relationship may vary across different sources and myths. One version of the story tells of Orion’s boastful nature, claiming that he could slay any beast on Earth. Artemis, seeking to teach him a lesson, created a giant scorpion to challenge Orion’s strength. In a tragic turn of events, Orion was stung by the creature and succumbed to its venom. Distraught with grief, Artemis placed Orion among the stars, immortalizing him as the constellation we know today. Their mythical union showcases the power of friendship, the fragility of life, and the enduring presence of Orion in the night sky.
Orion, Taurus, and the Pleiades
Orion, Taurus, and the Pleiades have long been connected in mythologies and legends across various cultures. In Greek mythology, the story goes that the Pleiades, a group of seven sisters, caught the eye of Orion. Enchanted by their beauty, Orion pursued them relentlessly. However, the sisters sought protection and found solace in the mighty bull, Taurus. Taurus fiercely defended the Pleiades, standing between them and Orion.
This tale of Orion, Taurus, and the Pleiades has been immortalized in the night sky. In the celestial realm, the Pleiades cluster is located on the shoulder of the Taurus constellation, with Orion positioned nearby. The stars of the Pleiades can be seen as a small cluster of bright lights while the stars of Orion form the well-known figure of the hunter.
The relationship between Orion, Taurus, and the Pleiades has inspired countless interpretations throughout history. In astrology, this alignment is believed to hold significant influence over individual personalities. Those born under the sign of Taurus are said to possess the determination and strength of the bull, while the presence of Orion and the Pleiades may enhance their sense of adventure and curiosity.
This celestial trio has also found its way into various works of literature, art, and popular culture. From novels and paintings to movies and songs, their timeless connection has continued to captivate and inspire. It serves as a reminder of the enduring power of mythology and the influence of the night sky on human imagination and creativity.
The intertwined story of Orion, Taurus, and the Pleiades weaves together themes of pursuit, protection, and celestial beauty. The connection between these celestial bodies transcends time and culture, leaving an indelible mark on human mythology and artistic expression.
Orion’s Role in Astrology
Orion’s Role in Astrology:
Orion holds a unique place in the realm of astrology, despite not being officially recognized as a zodiac constellation. Astrologers and enthusiasts have attributed significant symbolism and meaning to Orion’s presence in the night sky. Aligning with the elements of fire and air, Orion embodies qualities of passion, ambition, and intellectual prowess. Those born under the influence of Orion may possess an innate sense of adventure, a desire for exploration, and a strong will to achieve their goals.
In astrology, Orion is often associated with strength, courage, and determination, reflecting the hunter’s legendary tenacity. People inspired by Orion may exhibit leadership qualities, fearlessness, and a natural ability to inspire others. Orion’s placement in an astrological chart can provide insights into one’s personality, highlighting their assertiveness, willingness to take risks, and capacity for success.
It is important to note that Orion’s influence in astrology goes beyond the classical zodiac system. Astrologers delve into various aspects of celestial bodies and their alignments to gain a holistic understanding of an individual’s character and destiny. While not officially recognized as a zodiac sign, Orion’s mythical and symbolic significance continues to capture the imaginations of astrologers and individuals seeking insight into their personality traits and life’s purpose.
Contemporary Cultural References

Orion’s enduring presence and rich mythology have not only captivated ancient civilizations but continue to inspire contemporary culture as well. In , we see Orion’s influence seep into various forms of art and literature. From classic pieces like Dante’s Divine Comedy, where Orion is mentioned as a prominent constellation in the heavens, to modern movies and novels that draw inspiration from his heroic figure and constellation, Orion has left an indelible mark on the artistic world. Additionally, in astrology, Orion’s position in the sky and its alignment with certain zodiac signs are believed to have an influence on personality traits and character. The connection between the celestial hunter and human behavior adds another dimension to Orion’s cultural significance. With such diverse cultural references, it’s evident that Orion’s legacy persists in the modern world, transcending time and fascinating both creators and admirers alike.
Orion in Literature and Art
Orion’s majestic presence in the night sky has served as inspiration for countless works of literature and art. In literature, he often represents strength, bravery, and the pursuit of greatness. One of the most famous references to Orion can be found in Homer’s epic poem, “The Odyssey,” where he is mentioned as a symbol of a skilled hunter. His constellation also features prominently in Dante Alighieri’s “Divine Comedy,” where it is associated with an image of spiritual enlightenment.
In art, Orion is depicted in various forms, showcasing his mythical stature. From ancient Greek pottery to Renaissance paintings, artists have sought to capture his powerful presence. One notable depiction is the painting “The Hunt of Diana” by Peter Paul Rubens, where Orion can be seen alongside the goddess Artemis (or Diana in Roman mythology) and other hunters. The painting highlights Orion’s legendary hunting skills and his association with the divine.
Orion’s influence extends to modern literature as well. In J.R.R. Tolkien’s epic fantasy series, “The Lord of the Rings,” the constellation of Orion is referenced as part of Middle-earth’s lore, connecting the fictional world with the celestial realm.
Orion’s captivating presence in literature and art showcases the enduring fascination with this celestial hunter. Through the ages, his depiction has evolved, but his symbolism as a mighty and skilled hunter remains. The enduring presence of Orion in various forms of artistic expression demonstrates his timeless appeal and the inspiration he continues to provide to writers and artists alike. Whether it is through ancient mythology or contemporary works, Orion’s legacy echoes through the ages, forever immortalized in the realms of literature and art.
Orion in Popular Culture
Orion’s influence and iconic imagery have extended beyond ancient mythology and into popular culture. In movies, literature, and art, has become synonymous with strength, bravery, and adventure. Here are some notable examples:
1. Film: Orion’s character has appeared in various films, captivating audiences with his heroic persona. One famous example is the science fiction film “Men in Black” where Orion is portrayed as an alien from the Orion constellation. Additionally, in the film “The Dark Knight Rises,” Batman uses a software called “Project Orion” to track down criminals in Gotham City, symbolizing the hunter’s relentless pursuit.
2. Literature: Orion’s legend has also found its way into literature, both in adult and children’s books. He is often portrayed as a formidable figure, embarking on epic quests or serving as a guiding force for protagonists. In Rick Riordan’s “Percy Jackson” series, Orion is depicted as a powerful antagonist, adding a thrilling dynamic to the story.
3. Music: The influence of Orion can even be found in the music world. The infamous rock band Queen released a song titled “The Prophet’s Song,” which includes references to Orion and his cosmic presence. The song’s lyrics evoke a sense of wonder and mystery, mirroring the enigmatic nature of the celestial hunter.
4. Art: Artists from various eras and styles have been inspired by Orion’s striking presence. Paintings, sculptures, and murals depict the majestic constellation and its mythological associations. One famous artwork, “The Orion Nebula” by Max Ernst, showcases the mesmerizing beauty of the celestial object, capturing the imagination of viewers.
These examples illustrate how Orion continues to captivate the minds of creators and audiences alike, demonstrating his enduring popularity in contemporary culture. Whether it be in film, literature, music, or art, Orion’s significance and symbolism persist, reminding us of the timeless allure of the celestial hunter.
Conclusion

In , unraveling the mysteries of Orion has revealed a tapestry of myths, legends, and cultural significance woven into the fabric of human history. From his celestial origins as the son of Poseidon and Euryale to his prominent role in Greek mythology and connections to other cultures, Orion has remained an enduring figure that continues to captivate our imaginations. As we gaze up at the night sky and spot the distinctive pattern of stars that form the Hunter, we are reminded of the timeless stories of Orion and his pursuits. Whether it’s his legendary encounters with Artemis, his connection to Taurus and the Pleiades, or his role in astrology, Orion holds a special place in our collective consciousness. Not only has he inspired countless works of literature, art, and film, but he also serves as a reminder of our fascination with the cosmos and its ability to spark our creativity and curiosity. So, the next time you catch a glimpse of Orion in the night sky, take a moment to appreciate the rich mythology and cultural heritage that surround this illustrious celestial figure.
Frequently Asked Questions

What is the significance of Orion in Greek mythology?
In Greek mythology, Orion is a prominent figure known as a mighty hunter. He is often associated with the myth of his pursuit of the Pleiades or his tragic encounter with the goddess Artemis.
Which other cultures have myths and legends about Orion?
Orion is not limited to Greek mythology. Many other cultures, such as Egyptian, Mayan, and Native American, have their own myths and legends surrounding the constellation.
What stars make up the constellation of Orion?
The constellation of Orion is composed of several notable stars, including Betelgeuse, Rigel, Bellatrix, and the three stars that form Orion’s belt: Alnitak, Alnilam, and Mintaka.
Why is Orion so prominent in the night sky?
Orion’s prominence in the night sky is due to its position on the celestial equator and its distinct pattern of stars, making it easily recognizable and visible from different parts of the world.
What is the story behind Orion and Artemis?
In Greek mythology, Orion and Artemis had a complex relationship. Some stories portray Orion as a suitor of Artemis, while others narrate his death caused by Artemis’ arrow, leading to his transformation into a constellation.
How is Orion connected to Taurus and the Pleiades?
In mythology, Orion is often depicted in pursuit of the Pleiades, a cluster of stars in the constellation of Taurus. This pursuit adds both tragedy and drama to the celestial narrative.
What does Orion’s role in astrology entail?
Orion’s role in astrology is not as prominent as other constellations. However, its presence in the night sky can influence certain zodiac signs, particularly those born between November and December.
How has Orion been represented in literature and art?
Orion has been a source of inspiration for authors and artists throughout history. He has been depicted in various literary works, such as poems, novels, and epic tales, and has been a subject of many artistic representations.
How does Orion feature in modern popular culture?
Orion continues to be referenced in popular culture, appearing in movies, TV shows, and even video games. His iconic silhouette and mythological significance make him a recognizable and captivating character.
What does Orion teach us about the vastness of the universe?
Orion’s presence in different mythologies and cultural traditions highlights the universality of our fascination with the stars and the human desire to explore and make sense of the vastness of the cosmos.
References
- Orion the Hunter | Constellation & Mythology
- Orion
- Discovering the Universe Through the Constellation Orion
Frequently Asked Questions

1. How did Orion become a constellation in Greek mythology?
According to Greek mythology, Orion was the son of Poseidon, the god of the sea, and Euryale, a mortal woman. After his death, he was placed in the sky by Zeus, the king of the gods, as a constellation to honor his legendary hunting skills.
2. What were Orion’s pursuits as a hunter?
Orion was known for his exceptional hunting abilities. His pursuits included tracking and slaying fierce beasts, such as the Nemean Lion and the Lernean Hydra. He was also said to have traveled across the land and sea in search of adventure.
3. How does Orion feature in Greek mythology?
In Greek mythology, Orion is often associated with his tragic love story with the goddess Artemis. He is also mentioned in various other myths, including his role in the tale of the hunt for the Calydonian Boar and his encounter with the giant Orionis.
4. Which other cultures have myths or legends featuring Orion?
Aside from Greek mythology, Orion appears in the mythologies of other cultures as well. He is present in Norse mythology as a giant named Hrungnir and is also associated with the Egyptian god Osiris in certain texts.
5. Why is Orion so prominent in the night sky?
One of the reasons Orion is so prominent in the night sky is due to its location on the celestial equator, allowing it to be visible from both the northern and southern hemispheres. Additionally, its distinctive shape and the brightness of its stars contribute to its visibility.
6. Which stars make up the constellation of Orion?
The constellation of Orion is composed of several bright stars, including Betelgeuse, Rigel, Bellatrix, and Saiph. These stars form the outline of the hunter’s body, with Betelgeuse representing his right shoulder and Rigel representing his left foot.
7. What is the story of Orion and Artemis?
The story of Orion and Artemis tells of a close bond between the hunter and the goddess of the hunt. Some versions depict them as hunting companions, while others suggest a romantic relationship. However, their story ends tragically when Orion is killed by a scorpion sent by Artemis.
8. How is Orion connected to the constellation Taurus and the Pleiades?
In Greek mythology, Orion is said to have pursued the Pleiades, a group of seven sisters, in an attempt to win their favor. He is also associated with the constellation Taurus, as some myths describe his demise at the hands of a giant bull, which became the constellation.
9. What is Orion’s role in astrology?
In astrology, Orion is often associated with strength, courage, and power. People born under the sign of Orion are believed to possess these qualities and are thought to be determined, adventurous, and natural-born leaders.
10. How has Orion been depicted in literature and art?
Orion has been a recurring theme in various literary works and artistic representations throughout history. He has been featured in poems, novels, and paintings, often portrayed as a fearless hunter or a symbol of masculine power and beauty.