Imagine a world where the sun’s brilliant rays are suddenly blocked, and darkness descends upon the Earth. The phenomenon of an eclipse has captivated humanity for centuries, igniting curiosity and sparking scientific advancements. In this article, we delve into the scientific significance of studying eclipses, exploring the historical, astronomical, and exploratory insights they offer. From ancient observations to the frontiers of exoplanet discoveries, eclipses unveil the secrets of our celestial surroundings and shed light on the fascinating interplay between the Earth, Moon, and Sun. Join us on this journey of cosmic exploration as we explore the wonders hidden within these rare celestial events.
Contents
- 1. Historical Significance
- 2. Astronomical Insights
- 3. Earth-Moon-Sun Interactions
- 4. Solar System Exploration
- 5. Exoplanet Discoveries
- 6. Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How often do solar eclipses occur?
- 2. Can solar eclipses be harmful to the eyes?
- 3. How long does a total solar eclipse last?
- 4. What causes the different types of eclipses?
- 5. Are there any cultural significance attached to eclipses?
- 6. Can lunar eclipses affect people’s emotions or behavior?
- 7. How do astronomers study eclipses?
- 8. Why are accurate predictions of eclipses important?
- 9. Can eclipses provide insights into other planets and moons?
- 10. Are there any upcoming significant eclipse events?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What is the historical significance of studying eclipses?
- 2. How did ancient civilizations observe eclipses?
- 3. What knowledge has been gained through the study of eclipses?
- 4. What insights do solar eclipses provide?
- 5. How do lunar eclipses contribute to scientific understanding?
- 6. How do eclipses help us understand celestial mechanics?
- 7. Can eclipses be accurately predicted?
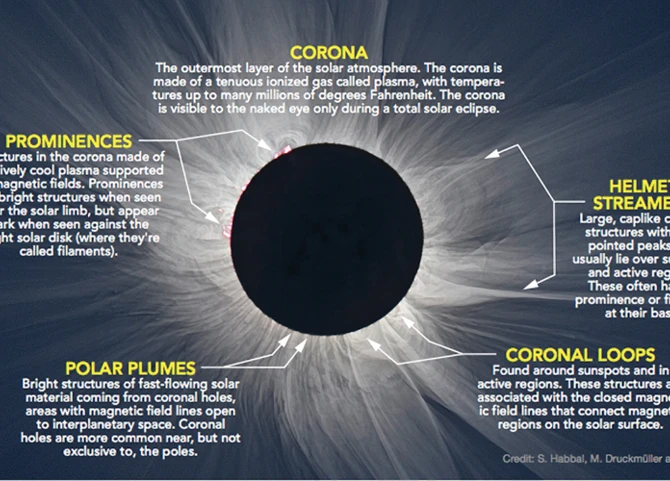
- 8. How do scientists study the Sun’s corona during solar eclipses?
- 9. What can studying the Moon’s surface during eclipses reveal?
- 10. How have eclipses contributed to the discovery of exoplanets?
- References
- Read More
1. Historical Significance
The historical significance of studying eclipses spans across cultures and civilizations, leaving behind a rich tapestry of observations and interpretations. Ancient civilizations, such as the Egyptians, Greeks, and Mesopotamians, recognized the profound influence of eclipses on their societies. They believed that these celestial events were omens, often associated with major events like the birth or death of a ruler. In fact, the ancient Greeks derived the word “eclipse” from the word “ekleipsis,” meaning abandonment or disappearance. The observation of eclipses played a crucial role in the development of early astronomy, allowing early astronomers to refine their understanding of celestial motions and unlock the secrets of the universe. For example, the Chinese astronomer, Zhang Heng, accurately predicted and documented a solar eclipse in 130 CE, showcasing the advancement of astronomical knowledge during ancient times. Eclipses also have deep mythological and symbolic significance, with cultures like the Mayans associating them with cosmic battles between deities and the haunting figure of the celestial serpent known as Ophiuchus. Throughout history, the study of eclipses has intertwined with various aspects of human culture and knowledge, laying the foundation for our understanding of the cosmos.
1.1 Ancient Observations
In the realm of ancient observations, eclipses held great significance and were often seen as celestial events that bridged the gap between the heavens and the Earth. Various ancient civilizations meticulously recorded their observations, leaving behind valuable astronomical records that continue to intrigue modern researchers. In ancient China, for example, the Book of Zhou documents solar eclipses as early as the 8th century BCE. The Chinese not only recorded the timing and duration of eclipses but also noted the colors, shapes, and patterns observed during these extraordinary moments. Similarly, the ancient Greeks were fascinated by eclipses and sought to understand their patterns and mechanisms. Early Greek astronomer Geodekidis compiled an extensive catalog of solar eclipses, while Hipparchus, known as the “father of trigonometry,” made significant contributions to understanding celestial motions and predicting lunar eclipses. These ancient observations not only provide a glimpse into the intellectual curiosity of past cultures but also lay the foundation for the advancements in the field of astronomy that we enjoy today. To learn more about the mythology and symbolism surrounding eclipses, explore the fascinating tale of the celestial serpent Ophiuchus.
1.2 Advancement of Knowledge
The study of eclipses has been instrumental in the advancement of knowledge in various scientific disciplines. One key aspect of this advancement lies in the field of astronomy. Eclipses provide scientists with unique opportunities to observe and analyze celestial phenomena that are not visible under normal circumstances. Solar eclipses, for instance, offer scientists the chance to study the Sun’s corona, the outermost layer of its atmosphere, which is normally too faint to observe. By carefully analyzing the corona during eclipses, scientists have been able to gain valuable insights into the Sun’s magnetic field, solar wind, and other solar phenomena. Lunar eclipses, on the other hand, provide scientists with opportunities to study the Earth’s atmosphere. The way the Earth’s atmosphere refracts sunlight during a lunar eclipse can reveal information about the composition and density of our planet’s atmosphere. Additionally, the study of eclipses has also contributed to our understanding of celestial mechanics and the precise motions of the Earth, Moon, and Sun. This knowledge has paved the way for accurately predicting future eclipses and has played a crucial role in the development of navigation and timekeeping systems. Thus, the scientific study of eclipses not only deepens our understanding of the universe but also has practical applications that impact various scientific fields.
2. Astronomical Insights
Astronomical insights gained from the study of eclipses provide invaluable information about our universe. Solar eclipses, for instance, offer a rare opportunity to observe the Sun’s outer atmosphere, known as the corona. This wispy, ethereal region is typically hidden from view due to the Sun’s intense brightness. During a total solar eclipse, when the Moon aligns perfectly between the Earth and the Sun, the corona becomes visible /unlocking-secrets-universe-planetary-alignments/— revealing intricate structures and unleashing a wealth of knowledge about the physics and dynamics of the Sun’s outer layers. By studying the corona during different stages of eclipses, scientists can better understand phenomena such as solar flares, coronal mass ejections, and the Sun’s magnetic field.
Similarly, lunar eclipses provide astronomers with a unique opportunity to explore our own planet’s influence on the Moon. As the Earth casts its shadow on the Moon, its reddish glow reveals the presence of Earth’s atmosphere. This phenomenon offers valuable insights into the composition of our atmosphere and how it affects the scattering of light. Lunar eclipses provide a chance to study the Moon’s surface in a different light (pun intended). As sunlight passes through the Earth’s atmosphere, it gets refracted, filtering out certain colors and allowing only red light to reach the Moon. This can alter the way we perceive the lunar landscape, emphasizing different geological features and providing astronomers with a fresh perspective on lunar geology.
By closely observing both solar and lunar eclipses, scientists can gain deeper understandings of celestial bodies, their interplay, and their impact on our understanding of the universe. These astronomical insights contribute to ongoing research and advancements in fields such as stellar physics, planetary science, and cosmology, pushing the boundaries of human knowledge further into the depths of the cosmos.
2.1 Solar Eclipses
Solar eclipses, one of the most mesmerizing astronomical events, occur when the Moon passes between the Sun and the Earth, casting a shadow on our planet. These cosmic phenomena provide scientists with invaluable opportunities for research and exploration. Studying solar eclipses allows astronomers to observe the Sun’s outer atmosphere, known as the corona, which is typically hidden from view due to the Sun’s intense brightness. During a total solar eclipse, when the Moon completely blocks the Sun, the corona becomes visible as a glowing halo surrounding the darkened Sun. This fleeting glimpse of the corona provides scientists with crucial data to understand its temperature, composition, and dynamics. Additionally, solar eclipses offer a unique opportunity to study the Sun’s magnetic fields and their influence on solar flares and eruptions. By analyzing the changes in brightness and temperature during an eclipse, researchers can enhance their understanding of our star’s behavior and its impact on Earth’s space weather. The significance of solar eclipses goes beyond scientific research; they have captivated human imagination throughout history and have been associated with celestial symbolism, like the cosmic battles mentioned in the mythology of Ophiuchus. These captivating phenomena remind us of the intricate cosmic dance that shapes our existence and inspire awe and wonder in both scientists and the general public alike.
2.2 Lunar Eclipses
Lunar eclipses, another fascinating type of eclipse, occur when the Earth passes between the Sun and the Moon, casting a shadow on the Moon’s surface. These celestial events provide valuable insights into the interactions between the Earth, Moon, and Sun. During a lunar eclipse, the Moon takes on a reddish hue, earning it the nickname “blood moon.” This phenomenon is due to the Earth’s atmosphere bending the Sun’s light, causing it to pass through our planet’s atmosphere and creating a stunning display of colors. Astronomers study lunar eclipses to better understand the Earth’s atmosphere, as the way the atmosphere filters sunlight during a lunar eclipse can provide valuable information about the quality and composition of our atmosphere. Lunar eclipses have long fascinated human cultures, with some believing them to have mystical powers and a deep connection to our emotions and intuition. Lunar eclipses have been associated with increased spiritual energy and heightened intuition, providing inspiration for art, literature, and even influencing human behavior. Their occurrence throughout history has left a mark on cultural beliefs and practices, demonstrating the powerful and enduring impact that celestial events can have on human perception and understanding.
3. Earth-Moon-Sun Interactions
The study of eclipses provides valuable insights into the intricate interactions between the Earth, Moon, and Sun, known as Earth-Moon-Sun interactions. These phenomena offer a unique opportunity to delve into the fascinating field of celestial mechanics and deepen our understanding of the forces that shape our solar system. One of the key aspects of Earth-Moon-Sun interactions is the phenomenon of celestial mechanics. By observing eclipses, scientists can analyze the precise motions and orbits of celestial bodies, including the Earth and the Moon. These observations help refine our understanding of gravitational forces and the intricate dance between these celestial bodies. The regular occurrence of eclipses allows scientists to develop accurate models for predicting future eclipses with great precision. This predictive capability not only showcases the advancements in our understanding of celestial mechanics but also serves practical purposes for astronomers and skywatchers. Additionally, the study of eclipses contributes to our understanding of the moon’s influence on Earth, including its impact on tides as well as its potential influence on human emotions and intuition. While scientific research is ongoing in these areas, there is evidence suggesting a link between lunar cycles and human experiences. By studying the intricate Earth-Moon-Sun interactions during eclipses, scientists can unravel further mysteries about our dynamic cosmos and its influence on our planet.
3.1 Understanding Celestial Mechanics
Understanding celestial mechanics is a key component in comprehending the intricate dance between the Earth, Moon, and Sun during an eclipse. The study of celestial mechanics allows scientists to decipher the motions and interactions of celestial bodies, enabling them to predict and explain the occurrence of eclipses. Eclipses occur when the Earth, Moon, and Sun align in a specific configuration, causing the shadow of one celestial body to fall upon another. By studying the orbits, rotations, and gravitational influences of these celestial bodies, scientists can calculate the precise timing and duration of eclipses. This knowledge is not only essential for astronomers seeking to observe and document eclipses, but it also contributes to our broader understanding of the dynamics of the solar system. The study of celestial mechanics has revealed the intricate beauty of the gravitational forces that govern our universe, helping us to unravel the mysteries of planetary motion and the intricate interplay between celestial bodies. Without a deep understanding of celestial mechanics, the scientific significance of studying eclipses would be greatly diminished.
3.2 Predicting Future Eclipses
Predicting future eclipses is a remarkable feat that stems from our understanding of Earth-Moon-Sun interactions and celestial mechanics. Through meticulous observation and precise calculations, scientists have developed sophisticated mathematical models to forecast the occurrence of eclipses well into the future. The study of past eclipses and the patterns they follow allow astronomers to project when and where future eclipses will take place. A critical factor in predicting eclipses is the concept of a Saros cycle. A Saros cycle is a period of approximately 18 years and 11 days, after which a similar eclipse pattern repeats. This cycle facilitates the forecasting of eclipses, as it enables astronomers to determine which regions of the Earth will be in the path of totality or experience a partial eclipse. Modern advancements, such as powerful computers and advanced algorithms, aid in refining eclipse predictions even further, providing accurate information about the exact timing, duration, and visibility of upcoming eclipses. The ability to predict future eclipses not only fascinates the general public but also holds significant scientific value, allowing researchers to plan and conduct observations, experiments, and studies during these fleeting celestial events. By continually refining our predictive capabilities, we deepen our understanding of the intricate dance between the Earth, Moon, and Sun, unraveling the mysteries of the universe one eclipse at a time.
4. Solar System Exploration

The study of eclipses has not only provided insights into our own planet and its celestial companions but has also opened doors to solar system exploration. Solar eclipses, in particular, allow scientists to examine and probe the Sun’s corona, the outermost layer of the Sun’s atmosphere. During a total solar eclipse, when the Moon completely covers the Sun, scientists have the rare opportunity to observe the corona, which is otherwise hidden by the Sun’s intense brightness. These observations help researchers study the corona’s structure, magnetic fields, and phenomena such as solar flares and coronal mass ejections, which can have significant impacts on Earth. Additionally, lunar eclipses provide opportunities to study the Moon’s surface and its composition. By analyzing the changes in the Moon’s appearance during an eclipse, scientists can gather valuable data about the Moon’s geology, topography, and even potential resources. Solar system exploration, facilitated by eclipse studies, allows us to expand our knowledge of celestial bodies beyond our own and unravel the mysteries hidden within our cosmic neighborhood.
4.1 Probing the Sun’s Corona
The probing of the Sun’s corona during eclipses has been a groundbreaking avenue for scientific research and discovery. The corona, which is the outermost layer of the Sun’s atmosphere, is typically hidden from view due to the Sun’s intense brightness. However, during a total solar eclipse, when the Moon perfectly aligns with the Sun, the corona becomes visible as a shimmering halo of light surrounding the darkened disk of the Moon. This rare opportunity allows scientists to study the corona in unprecedented detail. By using special instruments and techniques, researchers can examine the corona’s temperature, magnetic fields, and plasma dynamics. These studies have provided valuable insights into the Sun’s behavior and its impact on our planet. For example, scientists have discovered that the corona’s extreme temperatures, reaching millions of degrees, are still not fully understood. Additionally, observations during eclipses have helped reveal the complex nature of solar flares and the ejection of charged particles into space, which can have significant effects on Earth’s magnetosphere and technological infrastructure. The ability to probe the Sun’s corona during eclipses has opened up new avenues for understanding the dynamics and mysteries of our closest star.
4.2 Studying the Moon’s Surface
When it comes to studying the Moon’s surface, eclipses provide a unique opportunity to gather valuable information. During a lunar eclipse, when the Earth comes between the Sun and the Moon, the Moon appears darkened and reddish due to the scattering of sunlight by the Earth’s atmosphere. By observing the details of this reddish hue, scientists can gain insights into the composition and properties of the lunar surface. The phenomenon known as “earthshine” occurs during a lunar eclipse when sunlight reflected off the Earth illuminates the non-illuminated portion of the Moon. Astronomers can analyze this earthshine to study the Moon’s surface brightness and variations, helping to reveal geological features and details like impact craters, volcanic plains, and lunar mountains. Additionally, during a total lunar eclipse, the Moon can completely disappear from view for a short period. This provides astronomers with an opportunity to study the Moon’s surface in a different light, free from the glare of the Sun. By carefully observing and measuring the changes in the Moon’s appearance during a lunar eclipse, scientists can further our understanding of the Moon’s geology, its history, and its relation to Earth. Through these innovative means, eclipses continue to offer windows of exploration and open doors to the mysteries of celestial bodies like the Moon.
5. Exoplanet Discoveries

In the realm of exoplanet discoveries, eclipses play a crucial role in helping scientists detect and study distant worlds beyond our solar system. The transit method, a widely used technique for identifying exoplanets, relies on the observation of regular dimming of a star’s light when a planet passes in front of it. This periodic dimming during an eclipse provides valuable data about the exoplanet’s size, orbit, and distance from its host star. By studying multiple eclipses and the patterns they create, astronomers can infer the existence of planets within these systems. These transiting exoplanets offer a unique opportunity to study their atmospheres, composition, and even potential for supporting life. Additionally, eclipses provide insights into the concept of habitable zones – the range of distances from a star where conditions may be favorable for the existence of liquid water and potentially life. As scientists study eclipses caused by exoplanets passing in front of their host stars, they can better understand the characteristics and dynamics of these alien worlds, expanding our knowledge of the countless possibilities that exist beyond our own cosmic neighborhood.
5.1 Transiting Exoplanets
Among the exciting advancements in astronomy, the study of transiting exoplanets has emerged as a revolutionary field. When a planet passes in front of its host star, it creates a slight dimming of the star’s light. This phenomenon, known as a transit, allows astronomers to detect and study exoplanets, which are planets located outside our solar system. Transiting exoplanets provide valuable insights into the characteristics of these distant worlds. By measuring the duration and depth of a transit, astronomers can determine the size and orbit of the exoplanet. Additionally, studying the atmosphere of a transiting exoplanet through spectroscopy can reveal valuable information about its composition. This method has enabled the discovery of numerous exoplanets, including those located in the habitable zones of their star systems. The study of transiting exoplanets is crucial in our quest to understand the prevalence and diversity of planets beyond our own solar system, offering valuable data that can inform our search for extraterrestrial life. The information gathered from studying transiting exoplanets contributes to a greater understanding of the vastness and complexity of the universe, propelling humanity closer to unraveling its mysteries.
5.2 Habitable Zones
Within the realm of exoplanet discoveries, the exploration of habitable zones is of utmost importance. Habitable zones, also known as Goldilocks zones, refer to the region around a star where conditions may be just right for the existence of liquid water on a planet’s surface. As we study eclipses, we gain valuable insights into the composition and characteristics of exoplanets, including their potential for habitability. By observing exoplanet transits during a solar eclipse, scientists can gather data on the planet’s size, orbit, atmosphere, and potential for hosting life-sustaining conditions. This information helps in identifying prime candidates for further investigation and potentially discovering habitable exoplanets. The study of eclipses has enhanced our understanding of habitable zones by precisely determining the distances necessary for a planet to maintain liquid water, an essential ingredient for life as we know it. As we continue to explore the cosmos, the study of eclipses offers a window into the possibility of finding other habitable worlds among the vast expanse of the universe.
6. Conclusion
In conclusion, the scientific significance of studying eclipses is undeniable. From their historical importance, as witnessed through ancient observations and the advancement of knowledge, to the astronomical insights they offer, eclipses provide a unique glimpse into the workings of our celestial surroundings. The study of eclipses allows us to delve into the intricate interactions between the Earth, Moon, and Sun, leading to a deeper understanding of celestial mechanics and the ability to predict future eclipses. Eclipses have played a pivotal role in solar system exploration, enabling scientists to probe the Sun’s corona and study the Moon’s surface with greater precision. The discovery of transiting exoplanets and the identification of habitable zones owe much to the insights gained from studying eclipses. As we continue to explore the wonders of our universe, eclipses remain a captivating and scientifically significant phenomenon, one that continues to inspire awe and fuel our pursuit of knowledge. By unraveling the mysteries of eclipses, we unlock a deeper understanding of the cosmos and our place within it. So, let us keep our eyes to the sky, for the next eclipse promises another opportunity to expand our scientific understanding and marvel at the beauty of the universe.
Frequently Asked Questions

1. How often do solar eclipses occur?
Solar eclipses occur approximately every 18 months, but specific regions on Earth may not experience a solar eclipse for many years.
2. Can solar eclipses be harmful to the eyes?
Yes, viewing a solar eclipse directly without proper eye protection can cause permanent damage to the eyes. Specialized solar filters or eclipse glasses should always be used when observing the Sun during an eclipse.
3. How long does a total solar eclipse last?
A total solar eclipse typically lasts for a few minutes, with the maximum duration being around seven and a half minutes.
4. What causes the different types of eclipses?
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between the Earth and the Sun, blocking the Sun’s light. A lunar eclipse takes place when the Earth comes between the Sun and the Moon, casting a shadow on the Moon.
5. Are there any cultural significance attached to eclipses?
Absolutely! Eclipses have cultural significance in various societies. For example, in Hindu mythology, the demon Rahu is believed to swallow the Sun during a solar eclipse, while in ancient Chinese culture, the eclipse symbolizes the fight between a celestial dog and a cosmic dragon.
6. Can lunar eclipses affect people’s emotions or behavior?
While there are folklore and beliefs connecting lunar eclipses to human emotions, scientific evidence has not established a direct correlation between lunar eclipses and changes in human behavior or emotions.
7. How do astronomers study eclipses?
Astronomers study eclipses using various tools and techniques such as telescopes and spectroscopy. These observations allow them to gather data about the Sun, Moon, and Earth’s atmosphere, contributing to our knowledge of celestial bodies and their interactions.
8. Why are accurate predictions of eclipses important?
Accurate predictions of eclipses enable scientists and enthusiasts to plan observations, study the phenomenon, and gather valuable data. These predictions also help inform the public so they can safely experience and appreciate the awe-inspiring event.
9. Can eclipses provide insights into other planets and moons?
Yes, studying eclipses on other planets and moons within our solar system can provide valuable information about their atmospheres, temperatures, surface compositions, and even the presence of any potential exomoons.
10. Are there any upcoming significant eclipse events?
Yes. One notable upcoming event is the total solar eclipse that will cross parts of North America on April 8, 2024. It is expected to capture the attention of millions of people as they witness the celestial spectacle.
References
Frequently Asked Questions

1. What is the historical significance of studying eclipses?
The study of eclipses has played a crucial role in ancient cultures, shaping beliefs, and fueling advancements in knowledge.
2. How did ancient civilizations observe eclipses?
Ancient civilizations, such as the Babylonians and Egyptians, carefully observed celestial events like eclipses and recorded them on clay tablets and temple walls.
3. What knowledge has been gained through the study of eclipses?
The study of eclipses has led to advancements in understanding celestial mechanics, the Earth-Moon system, and our place in the universe. It has also contributed to the development of calendars and timekeeping systems.
4. What insights do solar eclipses provide?
Solar eclipses offer valuable insights into the Sun’s outer atmosphere, known as the corona, which is typically hidden from view due to the Sun’s intense brightness.
5. How do lunar eclipses contribute to scientific understanding?
Lunar eclipses provide scientists with an opportunity to study the Earth’s atmosphere and probe the composition of its upper layers.
6. How do eclipses help us understand celestial mechanics?
Studying the precise timing, duration, and paths of eclipses helps scientists gain a deeper understanding of the gravitational interactions between the Earth, Moon, and Sun.
7. Can eclipses be accurately predicted?
Yes, scientists can predict eclipses with remarkable accuracy using advanced mathematical models and data on the motions of celestial bodies.
8. How do scientists study the Sun’s corona during solar eclipses?
Scientists use specialized instruments and telescopes to observe the Sun’s corona during solar eclipses. These observations help unravel the mysteries of its temperature and magnetic fields.
9. What can studying the Moon’s surface during eclipses reveal?
By studying the Moon’s surface during lunar eclipses, scientists can gather important data about its geological composition, impact history, and potential resources.
10. How have eclipses contributed to the discovery of exoplanets?
Eclipses, particularly transiting exoplanets, have provided scientists with a way to detect and study planets orbiting distant stars, giving insights into the diversity and distribution of planets in the universe.