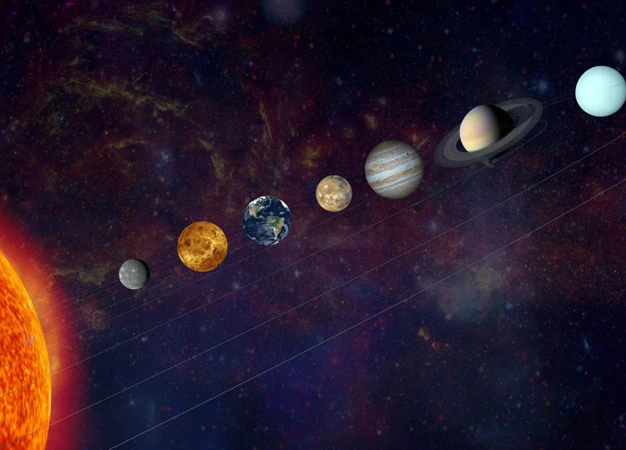
The wonders of the universe have captivated humanity for centuries, inspiring us to explore the mysteries that lie beyond our planet. One phenomenon that has intrigued astronomers, astrophysicists, and even the general public is planetary alignments. These rare occurrences, where the planets of our solar system appear to line up in a straight line, have sparked curiosity and speculation throughout history. In this article, we will delve into the scientific explanation behind planetary alignments, exploring the role of gravitational forces, the influence of celestial bodies, and the impact on our Earth. Join us on this voyage of discovery as we unravel the secrets of these celestial alignments and separate fact from fiction.
Contents
- The Solar System and Planetary Orbits
- What are Planetary Alignments?
- The Role of Gravitational Forces
- Astrophysics and Planetary Alignments
- Historical Significance of Planetary Alignments
- Misconceptions and Superstitions Surrounding Planetary Alignments
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How often do planetary alignments occur?
- 2. Can planetary alignments cause catastrophic events on Earth?
- 3. Can planetary alignments affect human behavior or emotions?
- 4. Do all planets in the solar system align perfectly in a straight line during planetary alignments?
- 5. How long do planetary alignments usually last?
- 6. Can we predict when planetary alignments will occur?
- 7. Are planetary alignments useful for space exploration?
- 8. Are there any upcoming notable planetary alignments?
- 9. Does Earth itself take part in planetary alignments?
- 10. Are there any historical or cultural significance attached to planetary alignments?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How do planetary alignments occur?
- 2. Are planetary alignments a rare occurrence?
- 3. Can planetary alignments affect Earth’s climate?
- 4. Do planetary alignments have any impact on human behavior?
- 5. Can planetary alignments cause natural disasters?
- 6. Do all planets in the solar system align at the same time?
- 7. How long do planetary alignments last?
- 8. Can we predict when planetary alignments will occur?
- 9. Are there any significant historical events associated with planetary alignments?
- 10. What tools or techniques are used to study and observe planetary alignments?
- References
- Read More
The Solar System and Planetary Orbits
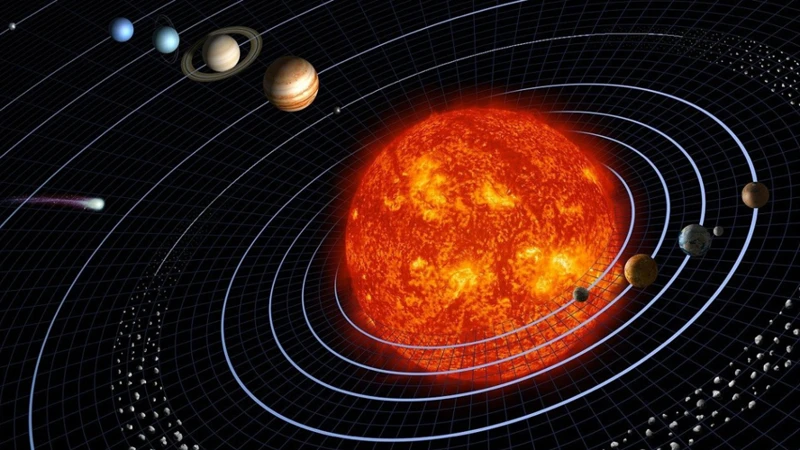
The Solar System is a complex and fascinating collection of celestial bodies, with the Sun at its center. Planetary orbits, or the paths that planets follow as they revolve around the Sun, play a crucial role in understanding the dynamics of our solar system. Each planet has its own unique orbit, determined by its distance from the Sun and its interaction with gravitational forces. Understanding these orbits is essential in unraveling the mysteries of planetary alignments.
The Sun, a mighty star at the heart of our solar system, holds everything in its gravitational embrace. It provides light, heat, and energy to all the planets that orbit around it. Without the Sun, life as we know it would not be possible on Earth.
When it comes to planetary orbits, each planet has its own specific distance from the Sun. The inner planets, Mercury and Venus, have smaller orbits closer to the Sun, while the outer planets, such as Jupiter and Saturn, have larger orbits farther away. This distinction in distances is crucial in understanding how planetary alignments occur.
To visualize the planetary orbits, imagine a table or list showcasing each planet and its distance from the Sun. The innermost planet, Mercury, has an average distance of about 36 million miles from the Sun. Venus follows at around 67 million miles, with Earth a bit further at approximately 93 million miles. Mars, the fourth planet from the Sun, is around 142 million miles away. Then, we have Jupiter at a remarkable distance of about 484 million miles, followed by Saturn at around 886 million miles. Uranus and Neptune, the furthest planets from the Sun, are approximately 1.78 billion miles and 2.79 billion miles away, respectively.
These varying distances are crucial in understanding how planetary alignments occur. As the planets move along their orbits, they occasionally line up in relation to each other and the Sun. This alignment can create the illusion of a straight line, giving birth to the concept of planetary alignments.
Understanding the intricacies of the Solar System and the planetary orbits is fundamental in comprehending the scientific explanation behind planetary alignments. It sets the stage for further exploration into the gravitational forces, celestial bodies, and the impact these alignments have on Earth. So, let us delve deeper into this captivating topic and unlock the secrets hidden within our solar system.
The Sun: The Center of Our Solar System
The Sun, our mighty star, takes center stage in our solar system. It is a colossal ball of hot plasma, radiating light and heat that sustains life on Earth. The Sun’s gravitational pull keeps all the planets, moons, asteroids, and comets in orbit around it, forming a harmonious dance in space.
With a diameter of about 1.4 million kilometers, the Sun is so massive that it accounts for approximately 99.86% of the total mass in our solar system. Its immense gravitational force dictates the movements of celestial bodies in its vicinity, including the planets. This force of gravity is what keeps the planets from drifting into the depths of space and ensures their stability within the solar system.
The Sun’s core is a tremendous powerhouse, where immense pressure and heat generate nuclear fusion, converting hydrogen into helium and releasing vast amounts of energy. This energy radiates outwards, illuminating the solar system and providing warmth and light to Earth.
The Sun’s position at the center of our solar system is integral to the formation and stabilization of planetary orbits. Its gravitational pull keeps the planets tethered to it, guiding them along their respective paths. Each planet’s distance from the Sun is a delicate balance of gravitational force and centrifugal force, preventing them from either falling into the Sun or escaping into space.
Understanding the significance of the Sun as the center of our solar system is essential in comprehending planetary alignments. Its gravitational influence plays a crucial role in determining the positioning and interactions between the planets, culminating in mesmerizing celestial phenomena. So, let us continue our cosmic journey as we explore the profound impact of planetary alignments and the forces that govern our vast universe.
Planetary Orbits and Their Distances from the Sun
Understanding the intricate details of planetary orbits and their distances from the Sun is key to unraveling the mysteries of planetary alignments. Each planet in our solar system has its own unique orbit and distance from the Sun, creating a dynamic and diverse celestial dance. Let’s explore these planetary orbits and their distances in more detail.
Mercury: The closest planet to the Sun, Mercury, has an average distance of about 36 million miles. It completes its orbit in just 88 Earth days, making it the fastest planet in our solar system.
Venus: Following Mercury, we have Venus, the second planet from the Sun. Venus has an average distance of approximately 67 million miles. It takes Venus around 225 Earth days to complete one orbit around the Sun.
Earth: Our home planet, Earth, sits at an average distance of approximately 93 million miles from the Sun. It takes Earth approximately 365.25 days, or one year, to complete a full orbit around the Sun.
Mars: Mars, often called the “Red Planet,” is the fourth planet from the Sun. It has an average distance of about 142 million miles. Mars takes roughly 687 Earth days to complete one orbit around the Sun.
Jupiter: Moving into the outer regions, we encounter Jupiter, the largest planet in our solar system. Jupiter is around 484 million miles from the Sun. Due to its substantial distance, Jupiter takes approximately 11.86 Earth years to complete its orbit.
Saturn: Known for its enchanting rings, Saturn is situated around 886 million miles from the Sun. It takes Saturn approximately 29.5 Earth years to complete an orbit, making it a slow-moving planet in comparison to the inner planets.
Uranus: Moving further outward, we reach Uranus, a gas giant planet located approximately 1.78 billion miles away from the Sun. Uranus takes about 84 Earth years to complete a single orbit.
Neptune: The farthest planet from the Sun in our solar system, Neptune, is roughly 2.79 billion miles away. It takes Neptune approximately 164.8 Earth years to complete an orbit, making it the slowest-moving planet in our solar system.
By visualizing the varying distances of each planet from the Sun, we can better understand the mechanics behind planetary alignments. These unique orbits and distances contribute to the mesmerizing dance of the planets and the potential for them to align in incredible ways. Exploring the significance of these alignments and their impact on Earth will lead us to a deeper understanding of our place in the universe.
For further intriguing insights into the secrets of the cosmos, you might be interested in the article “Pandora’s Box: Unveiling Dark Secrets”, where we delve into the mysteries of the universe and explore the enigmatic phenomena that lie beyond our planet.
What are Planetary Alignments?
Planetary alignments are celestial events in which the planets of our solar system appear to align in a straight line from our perspective on Earth. These alignments occur when the planets align themselves along a certain arc or a specific axis. It is important to note that these alignments are purely observational and do not refer to the actual physical alignment of the planets in space. Rather, they are a result of the planets’ positions in relation to one another as seen from our vantage point.
Planetary alignments can range from simple alignments involving two planets to more complex alignments that involve multiple planets. For example, a common alignment is the conjunction, where two planets appear close together in the sky. This often occurs when the planets are on the same side of the Sun and their orbits bring them near each other. This phenomenon can result in stunning celestial displays and is often sought after by astronomers and stargazers alike.
It is important to understand that planetary alignments are relatively rare events due to the complexities of the planets’ orbits. The planets orbit the Sun at different speeds and on different planes, making it unlikely for them to align precisely in a straight line on a regular basis. However, when they do align, it can be a captivating sight.
While planetary alignments have captivated the imaginations of humans for centuries, it is crucial to approach them with a scientific lens. These events have no direct influence on Earth or its inhabitants, contrary to certain misconceptions and superstitions. Planetary alignments are simply a result of the motions and positions of the planets in our solar system. They provide us with an opportunity to appreciate the wonders of the universe and the intricate dance of the celestial bodies. So, keep an eye out for these enchanting alignments and embrace the beauty and fascination they bring.
The Role of Gravitational Forces

Gravitational forces play a crucial role in shaping the movements of celestial bodies, including planets, and are an essential factor in understanding planetary alignments. Gravity is the force that holds the universe together, exerting a pull on all objects with mass. In the context of planetary alignments, the gravitational forces between the Sun, planets, and other celestial bodies come into play.
The Sun’s immense gravitational force is what keeps the planets bound to it in their respective orbits. Each planet also possesses its own gravitational force, although significantly weaker compared to the Sun’s. These gravitational forces allow the planets to maintain their orbits around the Sun while interacting with each other.
As the planets revolve around the Sun, their gravitational forces influence one another. This is particularly evident when multiple planets align. When two or more planets come into alignment, their gravitational forces interact with each other, creating a delicate dance of attraction and repulsion.
It is important to note that while the alignment may appear straight from our perspective, the actual alignment is not perfectly linear. Instead, it can be seen as an alignment of the planets along a particular arc or curve in their orbits. This is due to the elliptical nature of planetary orbits, where the distance between the planets and the Sun varies throughout their journey.
This gravitational dance between the planets during alignments can have an impact on their orbits. The gravitational forces exerted by one planet on another can slightly alter their paths, leading to subtle changes in their orbital parameters over time. These variations contribute to the intricate dynamics of the Solar System and can influence planetary alignments in the future.
Understanding the role of gravitational forces in planetary alignments is essential for unraveling the scientific explanation behind this phenomenon. It highlights the intricate interplay between celestial bodies, their masses, and the forces that govern their movements. By exploring the gravitational forces at work, we gain a deeper understanding of the mysteries that lie within our cosmos.
So, let us continue our journey and explore the fascinating world of astrophysics and planetary alignments. In the next section, we will delve into the influence of celestial bodies on these alignments, shedding light on the positions of planets in relation to each other.
Gravity: The Force That Holds the Universe Together
Gravity is a fundamental force that plays a central role in the workings of the universe. It is the force that holds celestial bodies, including planets, stars, and galaxies, together. Without gravity, the planets would not orbit the Sun, and galaxies would not cluster together. Understanding gravity is crucial in comprehending the scientific explanation behind planetary alignments.
Gravity, as described by Isaac Newton, is a force of attraction between two objects that depends on their masses and the distance between them. The greater the mass of an object, the stronger its gravitational pull. This means that the Sun, with its immense mass, exerts a powerful gravitational force on the planets, keeping them in their orbits.
In the context of planetary alignments, gravity plays a significant role. As the planets move along their orbits, their gravitational interactions with each other can cause them to align in a particular configuration. The gravitational pull between the planets influences their positions in relation to one another, creating the potential for alignment.
The influence of gravity on planetary alignments can be seen in the phenomenon known as the “grand tack.” According to this hypothesis, early in the history of the solar system, Jupiter migrated inward and then outward due to gravitational interactions with Saturn. This movement caused a chain reaction that affected the orbits of other planets, leading to planetary alignments at certain points in time.
The concept of gravity extends beyond planetary alignments and encompasses the entire universe. It is the force that holds galaxies together in clusters, giving rise to breathtaking structures such as galaxy filaments and superclusters. Gravity is responsible for shaping the cosmos as we know it.
Understanding gravity opens up a world of possibilities for exploring the mysteries of planetary alignments. By studying the gravitational interactions between celestial bodies, scientists can gain insights into the mechanisms behind these alignments and their significance in the cosmic dance of the universe. So, let us continue our exploration, guided by the force that holds the universe together.
Gravitational Interactions Between Planets
Gravitational interactions between planets play a crucial role in understanding planetary alignments. Gravity, the force that holds the universe together, is responsible for the movements and interactions of celestial bodies in our solar system. As each planet orbits the Sun, their gravitational fields exert a pull on each other, resulting in complex movements and occasional alignments.
To comprehend the gravitational interactions between planets, let’s imagine a table or list featuring the planets and their respective masses. The Sun, as the most massive object in our solar system, holds the planets in its gravitational grip. However, the planets also have their gravitational influence on each other, albeit to a lesser extent.
For instance, let’s consider the gravitational interaction between Earth and its closest neighbor, the Moon. The Moon’s gravitational pull tugs on the Earth, causing the ocean tides and influencing various natural phenomena. Similarly, the gravitational forces between planets impact their orbits. For example, the massive planet Jupiter has a significant gravitational influence on the other planets, particularly those closer to it like Mars and Earth.
These gravitational interactions can influence the alignment of planets, especially when multiple planets align with the Sun. The gravitational tugs between different planets, combined with the Sun’s gravitational pull, can create unique geometric arrangements. These configurations, in turn, give rise to the striking visual phenomenon of planetary alignments.
Understanding the intricacies of gravitational interactions between planets is a vital part of comprehending planetary alignments. These interactions shape the paths and movements of the planets, leading to occasional instances of alignment. By studying these interactions, astronomers and scientists can further unravel the mysteries of celestial mechanics and deepen our understanding of the universe we inhabit. So, let’s continue our exploration of planetary alignments and the scientific explanations that underlie this awe-inspiring phenomenon.
Astrophysics and Planetary Alignments
Astrophysics plays a crucial role in understanding the phenomenon of planetary alignments. It helps us delve deeper into the scientific principles behind these celestial events and provides insight into the influence of celestial bodies on planetary alignments. By studying the positions of planets in relation to each other and the gravitational interactions between them, astrophysicists have been able to uncover the mechanisms that drive planetary alignments.
One key aspect of astrophysics in relation to planetary alignments is the influence of celestial bodies. Not only do the planets interact with each other, but they also interact with other celestial objects such as asteroids, comets, and even distant stars. These interactions can affect the orbital paths of the planets and contribute to the occurrence of alignments. By studying these interactions, astronomers gain a deeper understanding of the dynamics of planetary motion and alignment patterns.
The positions of the planets in relation to each other also play a significant role in planetary alignments. As the planets orbit the Sun at different speeds, their relative positions constantly change. Sometimes, these positions align in such a way that they appear to form a straight line from our vantage point on Earth. This alignment can span just a few planets or, in rare cases, several planets in a row. Astrophysicists analyze these alignments to determine their frequency, duration, and predictability, shedding light on the patterns and probabilities of planetary alignments.
The field of astrophysics also encompasses the study of the impact of planetary alignments on Earth. While some claim that planetary alignments have significant effects on Earth, such as natural disasters or changes in climate, scientific research has not provided conclusive evidence to support these claims. Astrophysics helps us separate fact from fiction when it comes to the impact of planetary alignments on our planet.
Astrophysics provides the tools and knowledge necessary to unravel the mysteries of planetary alignments. It allows us to study the interactions between celestial bodies, analyze the positions of planets in relation to each other, and investigate the impact of these alignments on Earth. By delving into this branch of science, we gain a deeper understanding of the mechanics and significance of planetary alignments, guiding us towards the realms of scientific knowledge and dispelling misconceptions. So, join us on this fascinating journey as we explore the wonders of astrophysics in relation to planetary alignments.
The Influence of Celestial Bodies on Planetary Alignments
Celestial bodies, beyond the planets themselves, play a significant role in influencing planetary alignments. These celestial bodies include the Moon, other moons, asteroids, and comets. While they may be smaller in size compared to the planets, their gravitational pull can have a profound impact on the alignment of the planets.
The Moon, Earth’s natural satellite, is one celestial body that has a noticeable influence on planetary alignments. Its gravitational pull affects the Earth’s tides and can also contribute to the alignment of the planets. The gravitational interaction between the Moon, Earth, and other planets can create a ripple effect, altering the positions of the planets and potentially leading to alignments.
In addition to the Moon, the moons of other planets within our solar system can also play a role in planetary alignments. For example, Jupiter has four large moons known as the Galilean moons: Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto. The gravitational forces exerted by these moons, along with Jupiter itself, can influence the alignment of the other planets in the solar system.
Asteroids and comets, although smaller in size, can also impact planetary alignments. As they travel through the solar system, their gravitational interactions with planets can cause perturbations in the orbits of the planets. These perturbations can, in turn, lead to changes in planetary alignments over time.
To better understand the influence of celestial bodies on planetary alignments, visualizing their positions and interactions can be helpful. Consider a table or list showcasing the planets and their respective moons, along with the distances between them. Showcasing the gravitational forces and the intricate dance between celestial bodies can shed light on how planetary alignments come to be.
The intriguing interplay between celestial bodies – the planets, moons, asteroids, and comets – adds another layer of complexity to the phenomenon of planetary alignments. By examining their roles and interactions, scientists can unravel the scientific explanation behind these alignments. Understanding how these celestial bodies contribute to planetary alignments brings us closer to comprehending the wonders and dynamics of our vast universe.
The Positions of Planets in Relation to Each Other
The positions of planets in relation to each other are crucial in determining the occurrence of planetary alignments. When observing the solar system from a vantage point, such as Earth, the arrangement of planets can vary depending on their respective orbits.
To better understand the positions of planets, let’s consider a hypothetical scenario. Suppose we are observing the solar system from Earth’s perspective. We can create a table or list highlighting the order of the planets and their positions from the Sun. Starting from the closest planet to the Sun, Mercury, we move outward to Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and finally, Neptune.
The positions of the planets in relation to each other can be seen by comparing their distances from the Sun. For example, at a specific point in time, if Earth were located between the Sun and Venus, we would observe Venus and the Sun in approximate alignment from Earth’s viewpoint. On another occasion, if Mars, Earth, and Jupiter were positioned in a straight line, we would witness an alignment of these three planets. These relative positions and alignments constantly change as the planets continue to orbit the Sun.
It is also essential to consider the concept of retrograde motion in understanding the positions of planets in relation to each other. Retrograde motion refers to the apparent backward movement of a planet in its orbit when observed from Earth. During retrograde motion, planets appear to move in the opposite direction to their usual path across the night sky. This phenomenon can affect the positions of planets in relation to each other, creating unique alignments and configurations.
Studying the positions of planets in relation to each other provides insights into the dynamics of the solar system and the occurrence of planetary alignments. By analyzing the distances, arrangements, and movements of the planets, astronomers and astrophysicists can unravel the mysteries of celestial alignments and gain a deeper understanding of the wonders of the universe.
To learn more about the fascinating celestial events that occur within our solar system, check out our article on the best viewing spots for meteor showers. Alternatively, you can explore the intriguing history and significance of the forgotten constellation Ophiuchus by reading our article on re-discovering Ophiuchus.
The Impact of Planetary Alignments on Earth
The alignment of planets in our solar system may seem like a mesmerizing cosmic event, but what impact do these alignments have on Earth? While it is true that planetary alignments can create stunning visual spectacles in the night sky, their direct effects on our planet are minimal. Contrary to popular belief, they do not cause catastrophic events or significant disruptions to our daily lives.
One important impact of planetary alignments on Earth is the influence they have on gravitational forces. When multiple planets align, their gravitational pull may slightly affect the orbits of other celestial bodies, including asteroids and comets. However, the gravitational forces exerted by planets alone are not significant enough to cause major disturbances.
Additionally, the gravitational interactions among planets during alignments have a negligible effect on Earth’s tides. Tides on our planet are primarily governed by the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon and the Sun. While planetary alignments may have some influence on these forces, the effect is generally minor and does not result in extreme tidal changes or natural disasters.
Another impact of planetary alignments relates to their significance in astronomical research. These alignments provide valuable opportunities for scientists to observe and study the positions of planets and their movements more accurately. By tracking the alignments, astronomers can gain insights into the dynamics of our solar system and refine their understanding of planetary orbits and gravitational interactions.
Planetary alignments often serve as inspiration for space exploration missions. When certain planets align favorably, it can create a so-called “gravity assist” opportunity. Spacecraft can use the gravitational pull of aligned planets to gain momentum and save fuel, allowing for more efficient space missions and enabling scientists to explore distant regions of our solar system.
While planetary alignments may capture our imagination and spark wonder, their impact on Earth is relatively minimal. They do not cause significant disruptions or catastrophic events. However, they do play a role in influencing gravitational forces and providing valuable research opportunities. So, while we continue to marvel at the beauty of planetary alignments, we can rest assured that they pose no dire consequences for our planet.
Historical Significance of Planetary Alignments
Throughout history, planetary alignments have held immense significance and intrigue for ancient civilizations and modern researchers alike. The observation of planetary alignments dates back thousands of years and has played a crucial role in shaping cultural interpretations and scientific advancements.
Ancient cultures, such as the Mayans, Egyptians, and Greeks, closely observed the night sky and recognized the rare occurrences of planetary alignments. These civilizations believed that the alignment of celestial bodies held great symbolic and spiritual meaning. They associated these celestial events with prophecies, omens, and divine messages. For example, the Mayans believed that planetary alignments signaled significant societal shifts, while the Egyptians linked them to the rising and setting of specific deities.
In addition to spiritual and symbolic interpretations, planetary alignments also influenced practical aspects of life for these ancient civilizations. They relied on the positions of the planets and stars for navigation, agriculture, and even the timing of religious ceremonies.
As scientific knowledge and understanding advanced, astronomers began to study planetary alignments with a more analytical approach. The groundbreaking work of Sir Isaac Newton in the 17th century laid the foundation for understanding the gravitational forces governing planetary motions. Newton’s laws of motion and universal gravitation revolutionized our understanding of the mechanics behind planetary alignments.
Modern researchers have continued to explore the historical significance of planetary alignments. They have studied ancient texts, archaeological remains, and astronomical records to gain insight into how various cultures perceived and interpreted these celestial phenomena. By analyzing the observations and beliefs of past civilizations, historians and scientists can unlock valuable information about the development of astronomy and the influence of planetary alignments on ancient societies.
Technological advancements have allowed scientists to observe and predict future planetary alignments with precision. These alignments continue to be of scientific interest, as they provide opportunities to study gravitational interactions, orbital mechanics, and the effects of celestial bodies on each other. Studying planetary alignments not only deepens our understanding of our own solar system but also provides insights into the workings of other planetary systems in the universe.
The historical significance of planetary alignments is multi-faceted, encompassing cultural, spiritual, and scientific aspects. From ancient civilizations’ awe and reverence to modern scientific research, planetary alignments have shaped our understanding of the cosmos and continue to inspire curiosity and exploration. By examining the historical context and cultural interpretations, we can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the enduring and captivating allure of planetary alignments.
Ancient Observations and Cultural Interpretations
Ancient civilizations across the globe were astute observers of the sky, including planetary alignments. Their interpretations of these alignments varied depending on their cultural beliefs and celestial knowledge. One notable example is the ancient Mayan civilization, renowned for their advanced understanding of astronomy. They believed that planetary alignments held significant symbolic meaning and were often associated with important events or transitions.
In Ancient Mesopotamia, the birthplace of modern astrology, planetary alignments were studied to predict and interpret celestial omens. The positions of the planets were thought to have a direct influence on earthly affairs, such as the rise and fall of kingdoms, natural disasters, and even individual destinies. These observations and interpretations were recorded in ancient texts known as cuneiform tablets, which provide valuable insights into the perceptions of planetary alignments in ancient cultures.
Across different cultures and time periods, planetary alignments were often associated with religious or mythological beliefs. In ancient Egypt, for instance, the alignment of specific planets with certain constellations was believed to signal the will of the gods. These alignments were considered auspicious or ominous, depending on the context, and played a role in the rituals and ceremonies of the Egyptian civilization.
Ancient China also had a rich tradition of observing celestial events, including planetary alignments. Chinese astronomers meticulously documented these alignments and correlated them with their astrological system. The alignments were believed to have an impact on various aspects of life, such as agriculture, weather patterns, and the fortune of the ruling dynasty. The Chinese culture placed great importance on the harmony between heaven and earth, and the observation of planetary alignments was seen as a way to understand and maintain this balance.
It is important to note that while ancient observations and interpretations of planetary alignments were deeply intertwined with cultural, religious, and mythological beliefs, they did not have a scientific understanding of the underlying mechanisms and forces at play. As our knowledge of the universe grew and scientific methods developed, we began to unravel the true scientific explanation of planetary alignments, which we will explore further in this article.
Modern Studies and Scientific Research
Modern studies and scientific research play a pivotal role in expanding our understanding of planetary alignments and their significance. Through advanced technology, sophisticated instruments, and rigorous analysis, scientists have been able to gather valuable data and insights into these celestial phenomena.
One area of modern research focuses on computer simulations and mathematical models. Using complex algorithms, scientists can simulate the movements of planets within our solar system over extended periods. These simulations help predict and analyze potential alignments, allowing researchers to study their frequency, patterns, and effects. By comparing these simulations with actual observations, scientists can validate the accuracy of their models and enhance our understanding of planetary alignments.
Advancements in telescopes, space probes, and satellite technology have provided astronomers with a wealth of data. Observatories equipped with powerful telescopes can capture detailed images, allowing scientists to observe and track the positions of planets with high precision. Space probes, such as NASA’s Voyager and New Horizons missions, have ventured into our outer solar system, capturing valuable data and images of distant planets. These technological advancements have opened new avenues for scientific exploration and enabled researchers to gather data that was once unimaginable.
Scientific research has also focused on studying the gravitational interactions between planets during alignments. By understanding the gravitational forces at play, scientists can predict the potential impact on the orbits of the planets involved. This research has revealed that while alignments may occur, their influence on planetary orbits is negligible. Despite their visual appeal, planetary alignments are not strong enough to cause significant disruptions to the planets’ regular paths around the Sun.
Scientific research has shed light on the influence of celestial bodies other than planets on planetary alignments. For example, the Moon’s gravitational pull can affect the positions of planets, leading to variations in alignments. Similarly, the Sun’s magnetic field can influence the behavior of planets and their alignments. By studying these factors, scientists gain a deeper understanding of the intricate relationships between celestial bodies and the dynamics of our solar system.
Modern studies and scientific research have transformed our understanding of planetary alignments. Through computer simulations, advanced technology, and in-depth analysis, scientists continue to uncover new insights into these captivating celestial events. As research progresses, we can expect to gain a more comprehensive understanding of planetary alignments and their role in the grand tapestry of our universe.
Misconceptions and Superstitions Surrounding Planetary Alignments

Misconceptions and superstitions often arise when it comes to the topic of planetary alignments. While there is a scientific explanation for these phenomena, some individuals have attached mystical or supernatural beliefs to them. It is important to separate fact from fiction and dispel any misconceptions surrounding planetary alignments.
One common misconception is the idea that planetary alignments can directly influence human behavior or cause catastrophic events on Earth. This belief is rooted in astrology, which associates celestial positions with personality traits and events in people’s lives. However, scientific studies have repeatedly debunked the notion that planetary alignments have any significant impact on human behavior or events on Earth.
Another misconception is the belief that planetary alignments always result in disastrous consequences. Some individuals may fear that when the planets align, natural disasters or global catastrophes are likely to occur. However, there is no scientific evidence to support this claim. Planetary alignments are purely observational phenomena and do not possess any inherent power to cause widespread destruction.
Superstitions surrounding planetary alignments have also emerged over time. Some people believe that during these alignments, negative energy is amplified, while others think it is a potent time for performing rituals or spells. These superstitions often lack a scientific basis and are rooted more in folklore and cultural beliefs than in empirical evidence.
It is important to approach planetary alignments with a scientific mindset, acknowledging that they are natural occurrences governed by the laws of physics and astronomy. While they may be visually captivating and hold astronomical significance, they do not possess any mystical or supernatural powers.
By dispelling these misconceptions and superstitions, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the scientific beauty of planetary alignments. Understanding the actual mechanisms behind these celestial phenomena allows us to truly marvel at the wonders of the universe without undue fear or misguided beliefs.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the scientific explanation of planetary alignments reveals a fascinating interplay between celestial bodies within our solar system. Through the understanding of the Solar System and planetary orbits, we can appreciate how the unique gravitational forces at work shape the movements of the planets. Planetary alignments occur when these planets line up in relation to each other and the Sun, creating a visually striking phenomenon.
Astrophysics provides valuable insights into the influence of celestial bodies on planetary alignments. The positions of the planets in relation to each other have a significant impact on the occurrence of these alignments. While planetary alignments do not directly affect Earth in a catastrophic manner, they have been known to generate small gravitational nudges, which can have subtle influences on our planet’s climate and tectonic activity.
The historical significance of planetary alignments is evident in ancient observations and cultural interpretations. Throughout history, civilizations have attributed mystical and astrological significance to these alignments. However, modern studies and scientific research have debunked many misconceptions and superstitions surrounding planetary alignments, emphasizing the importance of relying on rigorous scientific evidence.
In conclusion, planetary alignments are captivating astronomical events that continue to spark curiosity and fascination. Understanding the scientific explanation behind them allows us to appreciate the intricate workings of our Solar System and the role of gravitational forces. As we uncover more about the universe, the study of planetary alignments will undoubtedly continue to provide valuable insights into the dynamics of our celestial neighborhood.
Frequently Asked Questions

1. How often do planetary alignments occur?
Planetary alignments are relatively rare events, as they require the planets to be in specific positions in their respective orbits. Depending on the specific alignment being considered, they can occur once every few years or even decades.
2. Can planetary alignments cause catastrophic events on Earth?
No, planetary alignments do not directly cause catastrophic events on Earth. While they may have some influence on tides or gravitational interactions, their impact on our planet is negligible and cannot cause significant disturbances or disasters.
3. Can planetary alignments affect human behavior or emotions?
There is no scientific evidence to support the idea that planetary alignments have any direct influence on human behavior or emotions. The gravitational forces involved are very weak and cannot have any noticeable effects on individuals.
4. Do all planets in the solar system align perfectly in a straight line during planetary alignments?
No, planetary alignments do not require all planets to align perfectly in a straight line. The term “alignment” can refer to a configuration where planets appear close together in the sky from our perspective on Earth, but they may not be in a perfect line.
5. How long do planetary alignments usually last?
The duration of a planetary alignment depends on the specific alignment being observed. Some alignments may last for a few days, while others may extend over several weeks or even months.
6. Can we predict when planetary alignments will occur?
Yes, scientists and astronomers can predict when planetary alignments will occur based on their knowledge of planetary orbits and gravitational interactions. Advanced computer simulations and mathematical models help in forecasting these celestial events.
7. Are planetary alignments useful for space exploration?
Planetary alignments can be useful for space exploration missions, as they provide opportunities for spacecraft to travel more efficiently by utilizing the gravitational assists of multiple aligned planets. These alignments can help save fuel and time during interplanetary journeys.
8. Are there any upcoming notable planetary alignments?
Yes, there are several notable planetary alignments that astronomers and skywatchers look forward to. For example, the Great Conjunction of Jupiter and Saturn, where these two gas giants appear exceptionally close together in the sky, occurred on December 21, 2020.
9. Does Earth itself take part in planetary alignments?
Yes, Earth is often a participant in planetary alignments. As we observe the sky from our planet, we witness the other planets aligning or appearing in close proximity to each other. Earth’s position in the solar system grants us a unique perspective on these celestial events.
10. Are there any historical or cultural significance attached to planetary alignments?
Yes, throughout history, planetary alignments have held cultural and spiritual significance for different civilizations. Ancient cultures sometimes associated these alignments with sacred events or made predictions based on their observations. However, it is important to separate scientific understanding from traditional beliefs.
References
- Planetary Alignment Didn’t End the World in 1919. But One …
- Do the Planets Ever Actually Align?
- Planetary Science Standards Alignments
Frequently Asked Questions

1. How do planetary alignments occur?
Planetary alignments occur when multiple planets in our solar system align in a straight line or a specific geometric configuration.
2. Are planetary alignments a rare occurrence?
While planetary alignments are not extremely rare, they do not happen frequently either. The alignment of multiple planets in a perfect straight line is a relatively rare event.
3. Can planetary alignments affect Earth’s climate?
There is no scientific evidence to suggest that planetary alignments directly impact Earth’s climate. The Earth’s climate is influenced by various factors, such as greenhouse gases and solar radiation.
4. Do planetary alignments have any impact on human behavior?
There is no scientific evidence to support the claim that planetary alignments have any direct impact on human behavior. Human behavior is influenced by a complex interplay of biological, psychological, and social factors.
5. Can planetary alignments cause natural disasters?
There is no scientific consensus that planetary alignments can cause natural disasters. Natural disasters are typically the result of geological or atmospheric processes, such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, or severe weather conditions.
6. Do all planets in the solar system align at the same time?
No, not all planets in the solar system align at the same time. Planetary alignments occur when specific planets come into alignment, while others may not be involved in the alignment.
7. How long do planetary alignments last?
The duration of planetary alignments varies depending on the specific configuration of the planets. Some alignments may last for a few hours, while others can span several days.
8. Can we predict when planetary alignments will occur?
Scientists can predict planetary alignments to some extent based on the known planetary orbits and gravitational interactions. However, precise predictions of planetary alignments are challenging due to the complexities of celestial mechanics.
9. Are there any significant historical events associated with planetary alignments?
While some ancient civilizations believed that planetary alignments held spiritual and astrological significance, there is no scientific evidence to support any direct historical events linked to planetary alignments.
10. What tools or techniques are used to study and observe planetary alignments?
Astrophysicists and astronomers use a variety of observational tools, including telescopes, spacecraft, and computer simulations, to study and observe planetary alignments. These tools help gather data and analyze the mechanics of planetary motion in order to understand the phenomenon better.
References
- What Happens When The Planets Align? – YouTube
- Planetary Alignment Didn’t End the World in 1919. But One …
- Planetary Science Standards Alignments







