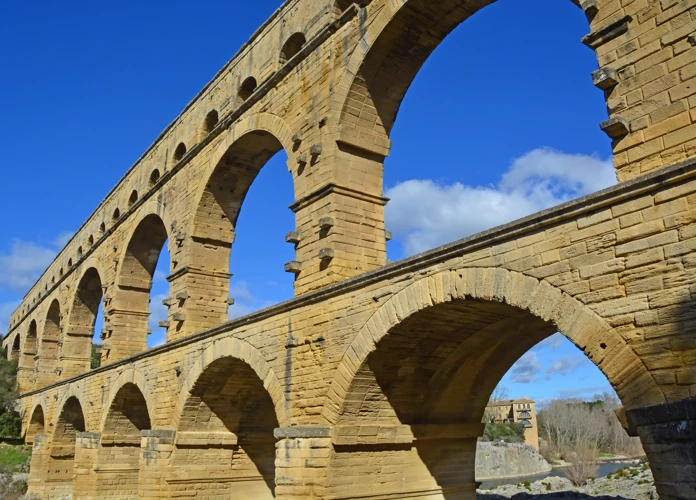
For thousands of years, civilizations have been advancing and developing their engineering skills to create remarkable structures that stand the test of time. One such civilization that is renowned for its engineering marvels is ancient Rome. From its magnificent aqueducts to its extensive road network and impressive infrastructure, the Romans left behind a legacy that still astounds us today. In this article, we will delve into the world of Roman engineering and explore the intricacies of their aqueducts, roads, and infrastructure. Join us as we uncover the secrets behind the design, construction techniques, and societal impact of these incredible feats of engineering.
Contents
- Aqueducts
- Roads
- Infrastructure
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- How did Roman aqueducts work?
- What materials were used to construct Roman aqueducts?
- How were Roman aqueducts built on uneven terrain?
- What was the purpose of Roman aqueducts?
- How did the construction of aqueducts impact Roman society?
- Were Roman aqueducts only built in Italy?
- Who designed and supervised the construction of Roman aqueducts?
- What technology did the Romans use for water filtration in aqueducts?
- Do any Roman aqueducts still exist today?
- How did the fall of the Roman Empire impact the aqueducts?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How did Roman aqueducts work?
- 2. What materials were used in the construction of Roman aqueducts?
- 3. How were Roman roads built?
- 4. Why were Roman roads so important?
- 5. What engineering techniques were used in the construction of Roman roads?
- 6. What were some of the public buildings and structures in ancient Rome?
- 7. How did the Romans manage their water supply and sewage systems?
- 8. What impact did Roman infrastructure have on society?
- 9. Were the Roman aqueducts and roads unique to the Roman Empire?
- 10. Why are Roman engineering marvels considered an important part of history?
- References
- Read More
Aqueducts
The Roman aqueducts were an engineering marvel that showcased the ingenuity and innovation of ancient Rome. These impressive structures were designed to transport water from distant sources to cities, ensuring a reliable water supply for public baths, fountains, and private residences. The aqueducts were constructed using a combination of arches, tunnels, and channels, skillfully navigating natural obstacles such as hills and valleys. The use of strong materials like stone and concrete ensured the durability of the aqueducts, some of which still stand today. The impact of these aqueducts on Roman society cannot be overstated, as they not only provided vital resources but also demonstrated the power and grandeur of the empire. The aqueducts are a testament to the remarkable engineering prowess of the Romans and their commitment to enhancing the quality of life for their citizens.
Aqueduct Design and Function
Aqueduct design and function were crucial elements in the success of the Roman water supply system. The primary purpose of aqueducts was to transport water from sources located outside cities to where it was needed most. The design of these structures incorporated a combination of engineering techniques and architectural brilliance.
Aqueduct Design: Roman aqueducts were meticulously planned to ensure the steady flow of water over long distances. They utilized a sloping gradient called the “downward gradient principle” to maintain a constant flow of water. This meant that the source of the water, such as a spring or river, had to be at a higher elevation than the destination. To achieve this, aqueducts often spanned across valleys and hills, utilizing elevated channels supported by rows of sturdy arches. The use of arches not only provided structural stability but also allowed the aqueducts to blend seamlessly into the landscape.
Aqueduct Function: Aqueducts served a variety of functions within Roman society. They were crucial for providing a consistent water supply to cities, enabling the construction of public baths, fountains, and even private residences. The aqueducts also played a significant role in supporting Roman agriculture by providing irrigation for farmlands. This, in turn, contributed to the empire’s economic prosperity and food security. Additionally, the water transported through aqueducts was essential for sanitation purposes, helping to improve public health and hygiene.
It is worth noting that the Romans developed advanced techniques to ensure the optimal functionality of aqueducts. These techniques included the use of settling tanks, which allowed sediment to settle before the water entered the main channels, and the inclusion of inspection chambers to monitor and maintain the flow of water.
The design and function of Roman aqueducts were a testament to the engineering brilliance of the civilization. These remarkable structures not only provided a reliable water supply but also showcased the Romans’ ability to harmoniously blend engineering and architecture to create enduring infrastructure. Their ingenuity and dedication to enhancing the quality of life for their citizens continue to inspire awe and admiration centuries later.
[Link to Ophiuchus Rising: New Zodiac Sign](/ophiuchus-rising-new-zodiac-sign/)
Construction Techniques
Construction Techniques used in the building of Roman aqueducts were both innovative and effective. The Romans employed various methods and technologies to ensure the success and longevity of these remarkable structures. One of the key techniques utilized was the use of arches, which distributed weight evenly and allowed for the creation of large, open spaces. The arches were made using stone or concrete blocks held together by mortar. The Romans also employed the use of piers, which provided additional support and stability to the aqueducts. The building materials used, such as brick and concrete, were carefully selected for their durability and strength. In addition to arches and piers, the Romans used channels and tunnels to navigate difficult terrain. The channels were typically made of stone or concrete and served as conduits for the flowing water. Tunnels were constructed through hills and mountains, utilizing advanced engineering techniques. To prevent leaks, the aqueducts were lined with a waterproof coating made from a mix of lime, crushed pottery, and volcanic ash. These construction techniques allowed the Romans to overcome geographical obstacles and create aqueducts that could span long distances and deliver water to even the most challenging locations. The meticulous planning and craftsmanship involved in the construction of Roman aqueducts truly demonstrate the engineering prowess of the ancient Romans.
Impact on Roman Society
The aqueducts had a profound impact on Roman society, transforming the way people lived and shaping the development of cities. The reliable water supply provided by the aqueducts enabled the construction of magnificent public baths, where Romans could gather to socialize, relax, and cleanse themselves. These communal spaces became central hubs for social interaction and played a significant role in promoting a sense of community and well-being.
The aqueducts allowed for the establishment of ornate fountains that adorned public squares and private estates, serving as symbols of wealth and power. These beautifully designed fountains, often featuring statues and intricate water displays, added to the aesthetic appeal of the cities and elevated the Roman’s appreciation for art and beauty.
The availability of clean water facilitated improvements in sanitation and hygiene, leading to a decrease in waterborne diseases and an overall improvement in public health. The aqueducts enabled the development of sophisticated sewage systems, effectively removing waste from the cities and reducing the risk of outbreaks and epidemics.
The impact of the aqueducts extended beyond the immediate benefits of water supply and sanitation. The construction of these massive structures required a significant workforce, providing employment opportunities and stimulating the local economy. The aqueducts also showcased the grandeur and power of Roman engineering, reflecting the empire’s wealth and prosperity.
The aqueducts played a vital role in enhancing the quality of life for the Romans, improving public health, promoting social interaction, and contributing to the overall development and advancement of Roman society. Their influence can still be seen and appreciated today through the remnants of these engineering marvels scattered across the former Roman Empire.
Roads

The roads of ancient Rome were a remarkable feat of engineering and played a pivotal role in the development and expansion of the Roman Empire. The Romans were renowned for their well-constructed and meticulously planned road network, which stretched across thousands of miles. These roads were built to withstand heavy traffic and provide efficient transportation for both military and civilian purposes. The construction of Roman roads involved several engineering techniques, such as using a layered approach with a foundation of packed soil, followed by layers of gravel and paving stones. The roads were typically wide enough to accommodate two chariots passing each other and featured well-drained surfaces to ensure durability. These roads connected major cities, forts, and provinces, facilitating trade, communication, and military campaigns. The Roman road network had a profound impact on the empire, enhancing commerce, enabling quicker troop movement, and allowing for the efficient governance of distant territories. It is no surprise that the legacy of these Roman roads can still be seen today, with some sections still in use or serving as the foundation for modern roads.
Roman Road Construction
Roman road construction was a remarkable feat of engineering, known for its durability and efficiency. The construction process involved several key steps, each contributing to the overall strength and longevity of the roads. Firstly, the Romans would clear and level the ground where the road was to be built. This ensured a solid foundation for the road. Then, a layer of large stones, known as the “statumen,” was laid down to provide stability and prevent sinking. On top of the statumen, a layer of smaller stones, known as the “rudus,” was compacted to form a sturdy base. Next, a layer of concrete, called the “nucleus,” was added, providing additional strength. Finally, a top layer of carefully fitted and tightly packed stones, called the “summa crusta,” was added to create a smooth and durable surface. The Romans also incorporated drainage systems such as ditches and culverts to prevent water damage. This meticulous construction process resulted in roads that could withstand heavy traffic, harsh weather conditions, and the test of time. Roman roads were crucial for the efficient movement of troops, goods, and people throughout the vast empire, contributing to its economic and military success. This exceptional engineering achievement paved the way for modern road construction techniques and continues to inspire us today.
Importance of Roman Roads
The Roman roads played a vital role in the overall infrastructure of the ancient empire and held immense importance in various aspects of Roman life. Firstly, these roads facilitated efficient transportation and communication throughout the vast expanse of the empire. With a well-connected network of roads spanning thousands of miles, the Romans were able to transport goods, troops, and information swiftly and reliably. This enhanced trade, facilitated economic growth, and allowed for the rapid expansion and stabilization of the Roman territories.
The roads also played a crucial role in the military dominance of the Roman Empire. They provided strategic routes for the movement of armies, enabling the quick deployment of troops to various regions. Additionally, the roads allowed for easy and efficient supply chains, ensuring that provisions could reach soldiers stationed in distant parts of the empire without delay. This not only helped secure Roman control over conquered territories but also allowed for a rapid response to any potential threats or uprisings.
The presence of well-maintained roads fostered a sense of unity and Roman identity among the citizens. Travel became easier and safer, encouraging cultural exchange and bringing people from various regions closer together. The roads also provided a means for the dissemination of Roman culture, law, and language throughout the empire, further solidifying the dominance of Roman civilization.
In terms of governance and administration, the roads played a pivotal role. They facilitated the movement of government officials, allowing them to efficiently oversee the regions under Roman control. The network of roads also aided in the collection of taxes, as tax collectors could easily access different areas and ensure the empire received its due revenue.
The importance of Roman roads cannot be overstated. These impressive engineering feats played a significant role in the growth, stability, and dominance of the Roman Empire. They facilitated trade, military operations, cultural exchange, and efficient governance, leaving a lasting legacy that continues to awe and inspire to this day.
Engineering Techniques
The engineering techniques employed by the Romans in the construction of their roads were incredibly advanced for their time and played a crucial role in the longevity and effectiveness of these transportation networks. One key technique used by the Romans was the concept of a solid foundation. They understood that a strong foundation was essential for the durability of the roads, especially in areas with varying terrains and weather conditions. To achieve this, they would excavate the ground and create a sub-base composed of layers of different materials, such as stones, gravel, and sand, compacted together to form a solid base. This technique allowed for better load distribution and prevented the road surface from deteriorating rapidly.
Another crucial engineering technique utilized by the Romans was the construction of well-draining road surfaces. They developed a cambered shape for the roads, which means the roads were slightly elevated in the middle and sloped downward towards the edges. This design allowed rainwater to flow off the road surface and into ditches or channels at the sides, preventing the accumulation of water that could cause erosion or make the roads impassable.
Additionally, the Romans had a methodical approach to road construction, using precise measurements and leveling tools to ensure a smooth and even surface. They would use a device called a groma to measure angles and properly align the roads. Frequent use of milestones along the roads helped track distance and establish a system of navigation.
The Romans also employed different engineering techniques to reinforce the structural integrity of the roads. Stone slabs or paving stones were used to create a durable and smooth surface, especially in heavily trafficked areas. These stones were carefully cut and fitted together to form a strong and uniform road surface. They also incorporated curbstones and drainage channels along the sides of the roads to prevent erosion and provide stability.
The attention to detail and engineering prowess of the Romans in the construction of their roads is truly remarkable. These techniques ensured that the Roman roads were able to withstand heavy traffic, harsh weather conditions, and the test of time. Their dedication to quality and innovation laid the foundation for efficient transportation systems that lasted for centuries, and their engineering techniques continue to inspire modern infrastructure projects around the world.
Infrastructure
The Roman Empire was renowned for its well-planned and extensive infrastructure, which played a crucial role in the functioning of its vast empire. The Romans constructed a wide range of public buildings and structures, including amphitheaters, bathhouses, and temples, showcasing their architectural prowess and cultural achievements. These structures were not only aesthetically pleasing but also served important purposes in daily life, providing venues for entertainment, social gatherings, and religious ceremonies. The Romans were also pioneers in developing efficient water supply and sewage systems, utilizing aqueducts and underground channels to bring fresh water to cities and remove waste. This focus on infrastructure greatly improved the quality of life for the Roman people and contributed to the overall success and longevity of the empire. The legacy of Roman infrastructure can still be seen today in the remnants of ancient buildings and the inspiration it provided for future architectural styles.
Public Buildings and Structures
Public buildings and structures were an essential part of Roman infrastructure, contributing to the development and functionality of the empire. These structures served various purposes, ranging from administrative centers to entertainment venues and religious sites. One iconic example is the Colosseum in Rome, which was a massive amphitheater used for gladiatorial contests, animal hunts, and other public spectacles. The Colosseum’s innovative design featured a complex system of ramps, trapdoors, and underground tunnels that allowed for the efficient movement of people, animals, and equipment. Another notable structure is the Pantheon, which was originally built as a temple dedicated to all the gods of ancient Rome. The Pantheon’s iconic dome, made from concrete and featuring a central oculus, remains the largest unreinforced concrete dome in the world. This architectural marvel is a testament to the Romans’ advanced engineering techniques and their ability to create awe-inspiring structures. Additionally, public buildings such as basilicas, theatres, and bath complexes were constructed throughout the empire. These structures not only served practical purposes but also served as symbols of power, wealth, and civic pride. The construction of these public buildings and structures showcased the Romans’ mastery of engineering and their commitment to creating impressive architectural works that would endure for centuries.
Water Supply and Sewage Systems
Water supply and sewage systems were integral components of the Roman infrastructure, demonstrating their advanced understanding of sanitation and hygiene. The Romans recognized the importance of clean water for public health and developed an elaborate system to ensure a reliable water supply to their cities. They constructed numerous aqueducts to transport fresh water from distant sources, such as mountains or springs, to densely populated areas. These aqueducts utilized gravity to maintain a steady flow of water, often spanning long distances and overcoming challenging terrain. The water was then distributed through a network of lead or clay pipes to public fountains, baths, and private residences, improving the quality of life for the inhabitants of ancient Rome.
In addition to the water supply system, the Romans also invested in comprehensive sewage systems, known as cloacae, to effectively manage wastewater and prevent the spread of diseases. The cloacae consisted of a network of underground drains and conduits that carried away liquid and solid waste from homes, public buildings, and streets. These drains were constructed using durable materials such as stone and bricks, with precise engineering techniques to ensure efficient drainage. The sewage was directed towards rivers or the sea, effectively removing waste from urban areas and minimizing the risk of contamination.
The meticulous planning and implementation of water supply and sewage systems exemplify the Romans’ commitment to public health and sanitation. These systems not only provided clean water for drinking, cooking, and bathing but also helped in the disposal of waste, significantly reducing the risk of diseases. The presence of these sophisticated systems throughout the Roman Empire is a testament to the advanced engineering and urban planning skills of the Romans.
(Source: Link)
The Importance of Roman Infrastructure
The importance of Roman infrastructure cannot be overstated. The Romans were masterful engineers and meticulously planned and constructed a wide range of public buildings and structures to support their expanding empire. These structures included amphitheaters, like the famous Colosseum, which served as venues for various forms of entertainment, including gladiatorial contests and theatrical performances. Another significant example is the Roman bathhouses, such as the Baths of Caracalla, which were not only places for hygiene but also served as social gathering spots. Additionally, the Romans developed an extensive network of roads that connected their vast territories, facilitating trade, communication, and the movement of troops. These roads were constructed with meticulous precision, featuring layered materials such as gravel, sand, and stone paving slabs, allowing for efficient transportation across the empire. The Romans implemented sophisticated water supply and sewage systems, utilizing aqueducts to transport clean water to cities and elaborate drainage systems to remove waste. The advanced infrastructure of the Romans played a crucial role in the growth and stability of their empire, enabling commerce, facilitating governance, and improving the daily lives of its citizens. It stands as a testament to their engineering expertise and dedication to creating a sustainable and prosperous society.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Roman engineering marvels of aqueducts, roads, and infrastructure have left an indelible mark on history. The aqueducts exemplified the Romans’ ability to design and construct sophisticated systems that provided essential resources to their cities. These monumental structures showcased the empire’s power and engineering prowess. Similarly, the extensive road network of ancient Rome revolutionized transportation and communication, facilitating trade, military movements, and cultural exchange. The engineering techniques employed in the construction of roads, such as the use of a solid foundation and durable materials, ensured their longevity and contributed to the cohesion of the empire. Furthermore, Roman infrastructure encompassed public buildings, water supply systems, and sewage networks, emphasizing the Romans’ commitment to enhancing the quality of life for their citizens. The efficiency and scale of Roman engineering projects were unmatched at the time, and their impact can still be seen today in the remnants of aqueducts, the enduring presence of Roman roads, and the traces of their sophisticated infrastructure systems. These remarkable achievements have solidified the Romans’ place as innovators and master engineers. As we marvel at these feats, we are reminded of the incredible legacy left behind by the Romans and the lasting impact of their engineering ingenuity.
Frequently Asked Questions

How did Roman aqueducts work?
Roman aqueducts worked by gravity, utilizing a slight slope to ensure a constant flow of water from its source to its destination. The aqueducts were designed with a series of arches and channels that directed the water over long distances, sometimes even spanning valleys.
What materials were used to construct Roman aqueducts?
The Romans used a variety of materials to construct their aqueducts, including stone, brick, and concrete. The choice of materials depended on the location and purpose of the aqueduct, with more durable materials used for longer and more important routes.
How were Roman aqueducts built on uneven terrain?
Constructing aqueducts on uneven terrain required the use of bridges, arches, and tunnels. The Romans would carefully plan the route, adjusting the elevation as needed to maintain a consistent water flow. This engineering feat showcased their skill in adapting to the natural landscape.
What was the purpose of Roman aqueducts?
The primary purpose of Roman aqueducts was to supply water to cities for various purposes, including public baths, fountains, and private residences. They played a crucial role in ensuring a reliable water supply and improving the quality of life for the citizens.
How did the construction of aqueducts impact Roman society?
The construction of aqueducts had a profound impact on Roman society. It not only provided essential water resources but also symbolized the greatness and power of the empire. The presence of aqueducts demonstrated the ability of the Romans to harness and control nature, showcasing their advanced engineering skills.
Were Roman aqueducts only built in Italy?
No, Roman aqueducts were not limited to Italy. The Romans built aqueduct systems across their vast empire, including regions such as France, Spain, and North Africa. Many of these aqueducts were constructed to supply water to newly conquered cities and colonies.
Who designed and supervised the construction of Roman aqueducts?
Roman aqueducts were designed and supervised by skilled engineers and architects. These professionals, known as “aqueduct architects” or “aquarii,” were responsible for planning the route, calculating elevation changes, and overseeing the construction process.
What technology did the Romans use for water filtration in aqueducts?
The Romans used several techniques for water filtration in their aqueducts. This included the use of settling tanks, which allowed sediments to settle before the water was further transported. Additionally, different layers of gravel, sand, and charcoal were used to filter impurities as the water flowed through the aqueducts.
Do any Roman aqueducts still exist today?
Yes, several Roman aqueducts are still standing today, serving as remarkable remnants of their engineering prowess. Examples include the Pont du Gard in France, the Aqueduct of Segovia in Spain, and the Aqueduct of Le Pont du Gard in Tunisia.
How did the fall of the Roman Empire impact the aqueducts?
The fall of the Roman Empire led to a decline in the maintenance and repair of aqueducts. With the decline in social and economic stability, many aqueducts fell into disrepair, leading to decreased water supply and the eventual abandonment of these once vital structures.
References
- 10 Cool Engineering Tricks the Romans Taught Us
- Ancient Rome: An Engineering Marvel | UT Austin Executive …
Frequently Asked Questions

1. How did Roman aqueducts work?
Roman aqueducts used a clever system of gravity to transport water across long distances. The aqueducts were built with a gentle incline, allowing water to flow downhill from a higher source to a lower destination.
2. What materials were used in the construction of Roman aqueducts?
Roman aqueducts were constructed using a variety of materials, including stone, concrete, and clay pipes. The use of durable materials ensured the longevity and efficiency of the aqueducts.
3. How were Roman roads built?
Roman roads were built using a layered approach. The foundation consisted of compacted soil or gravel, followed by layers of larger stones and finally a layer of smaller stones or gravel. This construction method ensured the roads were durable and able to withstand heavy traffic.
4. Why were Roman roads so important?
Roman roads played a vital role in connecting different parts of the Roman Empire and facilitating trade, communication, and military movements. They helped to unify the empire and promote economic growth.
5. What engineering techniques were used in the construction of Roman roads?
Roman engineers employed several techniques to ensure the durability and stability of their roads. These included the use of drainage systems, curbs, and multiple layers of carefully selected materials.
6. What were some of the public buildings and structures in ancient Rome?
Ancient Rome boasted a wide range of impressive public buildings and structures, including amphitheaters, temples, bathhouses, forums, and aqueducts. These structures were a testament to Roman engineering and architectural prowess.
7. How did the Romans manage their water supply and sewage systems?
The Romans were highly skilled at managing their water supply and sewage systems. They built intricate networks of aqueducts, reservoirs, and public fountains to ensure a reliable water supply. Waste management was achieved through the use of sewers and public latrines.
8. What impact did Roman infrastructure have on society?
Roman infrastructure had a profound impact on society, promoting economic growth, facilitating trade and transportation, and improving quality of life for Roman citizens. It helped create a sense of unity and identity within the empire.
9. Were the Roman aqueducts and roads unique to the Roman Empire?
The construction of aqueducts and roads was not unique to the Romans. However, the scale and efficiency of Roman engineering surpass many other ancient civilizations. Roman techniques and engineering principles continue to influence infrastructure development to this day.
10. Why are Roman engineering marvels considered an important part of history?
Roman engineering marvels are considered important because they showcase the advanced engineering and craftsmanship of the ancient Romans. They serve as a lasting testament to their technological advancements and continue to inspire engineers and architects today.







