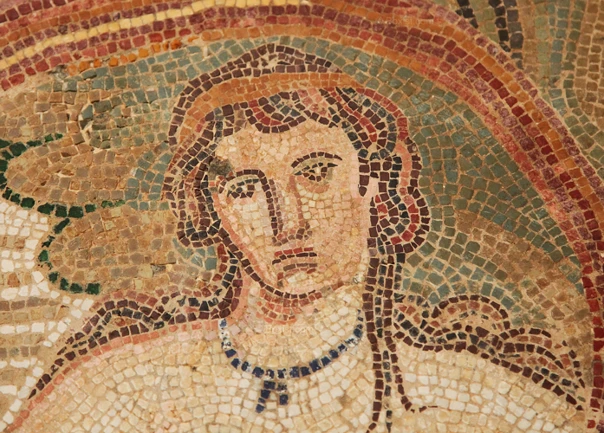
Roman art and sculpture are revered for their exquisite beauty and timeless allure. From intricate mosaics to lifelike portraits, the art of ancient Rome provides a glimpse into the rich cultural heritage of the empire. This article delves into the fascinating world of Roman art and sculpture, focusing on the captivating realms of portraits, frescoes, and mosaics. Discover the significance of portraiture in Rome, the characteristics that define Roman portraits, and explore famous examples that have captured the essence of individuals from centuries ago. Uncover the definition and significance of frescoes, delve into the themes and subjects that adorned Roman walls, and marvel at notable examples that have stood the test of time. Lastly, immerse yourself in the intricate artistry of Roman mosaics, uncover the common themes that pervade these mesmerizing artworks, and behold the beauty of iconic mosaics that continue to captivate audiences to this day.
Contents
- Roman Portraits
- Roman Frescoes
- Roman Mosaics
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What was the purpose of Roman portraits?
- 2. Who commissioned Roman portraits?
- 3. How were Roman portraits different from earlier Greek sculptures?
- 4. Were all Roman portraits of emperors and nobility?
- 5. What materials were used for creating Roman portraits?
- 6. Why were Roman portraits often accompanied by inscriptions?
- 7. Did Roman portraits influence later periods of art?
- 8. Were Roman portraits painted or left bare?
- 9. What evidence is there of hairstyles and fashion in Roman portraits?
- 10. Can Roman portraits be considered a form of propaganda?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What materials were commonly used in Roman sculpture?
- 2. Were Roman portraits always realistic?
- 3. Did Roman frescoes serve any specific purpose?
- 4. How were frescoes created in ancient Rome?
- 5. Was there a central theme in Roman mosaic designs?
- 6. What were some of the most famous Roman sculptures?
- 7. How were Roman portrait busts different from Greek sculptures?
- 8. What were the main influences on Roman art?
- 9. Were Roman mosaics primarily used in public or private spaces?
- 10. How did Roman art and sculpture survive through the ages?
- References
- Read More
Roman Portraits
Roman portraits hold immense importance in understanding the culture and society of ancient Rome. These artistic creations were not just mere representations of individuals, but rather vivid reflections of their status, achievements, and social standing. Roman portraits were highly realistic, aiming to capture every intricate detail of the subject’s features. They served as a medium for preserving the memory of prominent figures and commemorating their accomplishments. The characteristics of Roman portraits include the emphasis on individuality, idealized beauty, and a focus on realism. The artists skillfully highlighted the subject’s facial expressions, physical characteristics, and even the aging process. Notable examples of Roman portraits include the iconic busts of Julius Caesar, Augustus, and Emperor Nero. These stunning works of art offer us a glimpse into the personalities and remarkable individuals who played significant roles in ancient Roman history. (1)
1. Importance of Portraiture in Rome
The importance of portraiture in Rome cannot be overstated. Portraits served as a powerful means of communication and self-representation in Roman society. They provided a way for individuals to assert their status, lineage, and achievements. Roman portraits were not just simple likenesses; they were carefully crafted to convey a specific message or narrative. They enabled individuals to shape their public image and leave a lasting legacy. Portraits were prominently displayed in public spaces, private homes, and even in funerary contexts, symbolizing the significance of the individual and their connections to the social, political, or familial spheres. These portraits were also used as a tool for propaganda, with emperors and political figures commissioning portraits to reinforce their authority and legitimacy. This emphasis on portraiture in Rome showcases the deep-rooted desire for self-expression and the desire to be remembered. (1)
2. Characteristics of Roman Portraits
Roman portraits have distinct characteristics that set them apart from other forms of portraiture. These characteristics, carefully crafted by skilled artists, aimed to capture the essence of the subject and convey information about their status, achievements, and personality. Here are some notable characteristics of Roman portraits:
1. Realism: Roman portraits were known for their realistic portrayal of the subject’s features. Every detail, from the wrinkles and lines on their faces to the texture of their hair, was meticulously depicted. This realism aimed to immortalize the individual and provide an accurate representation of their physical appearance.
2. Idealized Beauty: While striving for realism, Roman portraits also incorporated elements of idealized beauty. This meant that the artists would often enhance certain features to convey an image of physical perfection. For example, they might emphasize a strong jawline or chiseled features to evoke a sense of power and authority.
3. Individuality: Roman portraits were highly individualized, capturing the unique characteristics of the subject. These works aimed to capture not only the physical appearance but also the personality and character of the individual. This individuality was achieved through careful attention to facial expressions, including subtle nuances that conveyed emotions and personality traits.
4. Aging Process: Roman portraits often depicted the subject at different stages of their life, showcasing the aging process. This unique approach enabled the audience to see the subject’s physical transformation over time and provided insight into their life story and accomplishments.
These characteristics combined to create lifelike and compelling portraits that reflected the values and aspirations of Roman society. They served as lasting reminders of the individuals they depicted, preserving their memory and contributing to the rich artistic heritage of ancient Rome. (2)
3. Famous Examples of Roman Portraits
Famous Examples of Roman Portraits:
1. Bust of Julius Caesar: One of the most renowned Roman portraits is the bust of Julius Caesar. Created during his lifetime, this marble sculpture captures the commanding presence and charisma of the great Roman dictator. The artist skillfully portrays Caesar with his trademark features, including the prominent forehead, the receding hairline, and the characteristic short beard.
2. Augustus of Prima Porta: The statue of Augustus of Prima Porta is another iconic Roman portrait. It depicts Emperor Augustus in a regal pose, wearing military attire. The statue showcases Augustus as a powerful military leader and a symbol of authority. The intricate details, such as the meticulously carved armor and the divine depiction of Cupid at his feet, emphasize his connection to the gods and his claim to divine lineage.
3. Fayum Portraits: The Fayum Portraits offer a unique glimpse into the lives of ordinary Romans during the Greco-Roman period. These portraits, painted on wooden panels, adorned the mummy casings of individuals of various social statuses. The Fayum Portraits exhibit a remarkable level of naturalism and attention to detail. The expressions and features captured in these portraits reveal the individuality and emotions of the subjects, creating a sense of intimacy with the viewer.
4. Bust of Nero: The bust of Emperor Nero is a striking example of a Roman portrait that showcases the power dynamics of the time. This magnificent marble sculpture depicts Nero as a young, idealized emperor with a youthful and handsome visage. However, behind the beautifully carved features lies the complexity of Nero’s reign, marked by controversy and infamy.
These famous examples highlight the remarkable skill and artistry of Roman sculptors in capturing the essence of their subjects. Whether depicting powerful emperors or ordinary individuals, Roman portraits continue to fascinate and captivate audiences with their lifelike representations and the stories they tell. (3)
Roman Frescoes
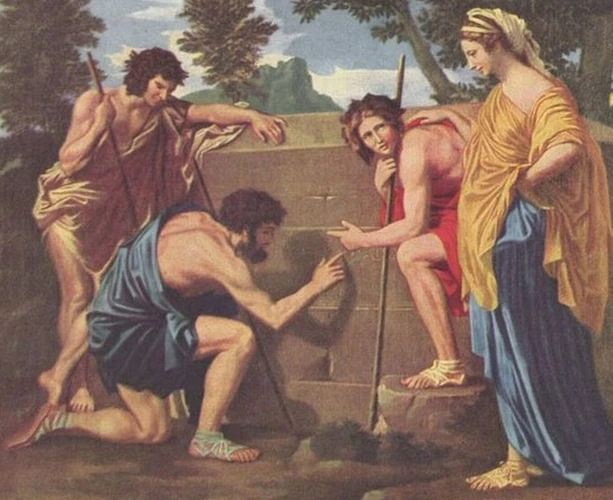

Roman frescoes are a testament to the exquisite artistic expressions of ancient Rome. These wall paintings were a popular form of decoration, adorning the interiors of grand villas, public buildings, and even tombs. Frescoes were created by applying pigments on wet plaster, allowing the colors to seep into the wall and become a permanent part of the surface. They played a significant role in Roman society, reflecting both the daily life of the Romans as well as their beliefs and mythology. Themes and subjects in Roman frescoes varied widely, ranging from mythological scenes depicting gods and goddesses to everyday scenes of domestic life, landscapes, and still life. The vibrant colors, intricate details, and skillful shading of these frescoes brought the scenes to life, captivating viewers and immersing them in the visual narratives. Notable examples of Roman frescoes include the Villa of the Mysteries in Pompeii, which features a series of enigmatic and symbolic paintings that have puzzled art historians for centuries. Delve into the world of Roman frescoes and uncover the stories and beauty they hold within their pigmented surfaces. (2)
1. Definition and Significance of Frescoes
Frescoes, an art form rich in history, played a significant role in Roman culture. A fresco refers to a technique where water-based pigments are applied to wet plaster on walls or ceilings, allowing the colors to penetrate and create a lasting image. The word “fresco” itself originates from the Italian word “affresco,” meaning “fresh.” These artworks served various purposes, from decorative elements in private homes to grand displays in public buildings and villas. The significance of frescoes lies in their ability to capture the essence of Roman life, serving as a visual narrative of the times. They depicted scenes from mythology, everyday life, and historical events, showcasing the ideals, beliefs, and aspirations of the Roman people. Not only were frescoes aesthetically pleasing, but they also provided insights into the social, political, and cultural aspects of Roman society. Through these vivid and vibrant artworks, individuals were transported to different worlds and immersed in stories that conveyed moral values, celebrated heroes, and conveyed political messages. They allowed for the preservation of history and served as a means of communication and expression for both the artist and the viewer. One notable example is the frescoes found in Pompeii, which offer a remarkable glimpse into the daily lives and customs of the ancient Romans. The significance of frescoes in Roman art cannot be overstated, as they provide a tangible connection to the past and offer a window into the rich and complex world of ancient Rome. (4)
2. Themes and Subjects in Roman Frescoes
Themes and subjects in Roman frescoes varied widely, reflecting the diverse interests and values of the ancient Roman society. One prevalent theme depicted in Roman frescoes was mythology. These frescoes often portrayed mythical figures and legendary tales, bringing the ancient myths to life within the confines of the walls. Scenes from Greek mythology, such as the exploits of Hercules, the adventures of Odysseus, and the love affairs of the gods, were frequently represented. (1) Another popular subject in Roman frescoes was daily life and domestic scenes. These frescoes offered a glimpse into the everyday activities of the Romans, showcasing scenes of banquets, parties, and leisurely pursuits. They captured the essence of Roman culture, depicting the bustling streets, vibrant markets, and the simple joys of family life. Natural landscapes and gardens also served as common motifs, with images of lush gardens, serene landscapes, and majestic villas adorning the walls. (2) Religious and spiritual themes were another prominent aspect of Roman frescoes. These artworks depicted religious ceremonies, rituals, and worship, highlighting the importance of spirituality in the lives of the Romans. From scenes of sacrifices and offerings to representations of divine beings and deities, these frescoes served as a visual testament to the Romans’ deep-rooted belief systems. Additionally, historical events and military conquests were often glorified in frescoes, commemorating the achievements and victories of the Roman Empire. (3) The wide array of themes and subjects in Roman frescoes showcases the diverse interests and cultural significance attached to this form of artistic expression in ancient Rome. The frescoes not only adorned the walls of private residences, but they also transformed public spaces, such as temples, basilicas, and amphitheaters, into vivid and captivating visual experiences, providing a lasting testament to the artistic prowess and cultural richness of Roman civilization.
3. Notable Roman Frescoes
One of the most remarkable aspects of Roman art is the extensive use of frescoes, which adorned the walls of luxurious villas and public buildings. These frescoes served as a visual feast, depicting a wide range of subjects and themes. Notable Roman frescoes have captured the imagination of art enthusiasts for centuries. The Villa of the Mysteries in Pompeii is home to a series of fascinating frescoes that depict the initiation rituals of the ancient Roman cult of Bacchus. These vibrant and mysterious scenes provide a unique insight into the religious practices of the time. Another iconic Roman fresco is the Aldobrandini Wedding Feast, discovered in the Villa Aldobrandini. This grand composition portrays a lavish wedding celebration, complete with musicians, dancers, and sumptuous feasting. The fresco showcases the opulence and social life of the wealthy Roman elite. The Villa of Livia in Rome boasts frescoes featuring beautiful garden scenes, with intricate details of plants, birds, and animals. These pastoral frescoes create a serene and idyllic atmosphere, reminiscent of the harmony between humans and nature. The House of the Vettii in Pompeii is renowned for its frescoes depicting scenes from Greek mythology, such as the “Glaucus and Scylla” and “Achilles in Scyros.” These mythological narratives add a touch of storytelling and symbolism to the overall artistic ambiance. These notable Roman frescoes continue to astound viewers with their incredible preservation, vibrant colors, and impeccable craftsmanship, offering a window into the daily lives, beliefs, and aspirations of ancient Romans. (3)
Roman Mosaics
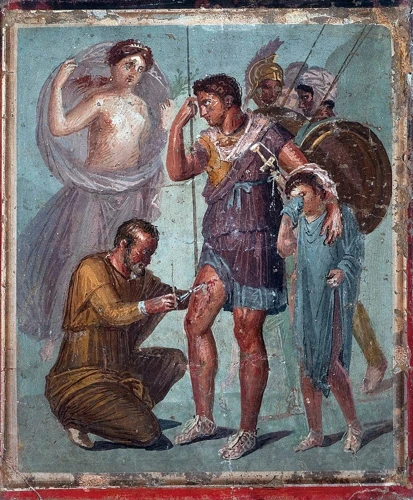

Roman mosaics are exquisite works of art that showcase the intricate artistry and skill of ancient Rome. These mosaics were created by assembling thousands of small, colored tiles called tesserae to form intricate patterns, images, and scenes. The level of detail and precision in Roman mosaics is truly remarkable, capturing a wide range of subjects including mythological figures, landscapes, and everyday life. Common themes depicted in Roman mosaics include scenes from mythology, such as the exploits of gods and heroes, as well as geometric and floral patterns. The mosaics adorned the floors and walls of Roman villas, public buildings, and even bathhouses, adding a touch of opulence and grandeur to the surroundings. One iconic Roman mosaic is the Battle of Isso, depicting the clash between Alexander the Great and Persian King Darius III. This mosaic showcases the realistic portrayal of the warriors, their intricate armor, and the fierce battle scene. Roman mosaics continue to captivate us with their vibrant colors, meticulous craftsmanship, and the stories they tell about the ancient world. (2)
1. Intricate Artistry of Roman Mosaics
Roman mosaics were a testament to the intricate artistry and craftsmanship of ancient Rome. These mosaics were created by meticulously arranging small, colored pieces of stone, glass, or tile, called tesserae, to form elaborate designs and pictorial representations. The level of detail and precision in Roman mosaics was truly remarkable. Artists carefully selected and arranged tesserae to create a wide range of colors and shading, resulting in vibrant and lifelike imagery. The mosaics adorned floors, walls, and even ceilings of important buildings, such as public baths, villas, and temples. The subjects depicted in Roman mosaics varied widely, including mythological scenes, everyday life, and even intricate geometric patterns. The mosaics served not only as decorative art but also as a means of communicating stories, beliefs, and historical events. One notable example of Roman mosaic art is the “Alexander Mosaic,” dating back to the 1st century BC, which depicts the epic battle between Alexander the Great and Persian King Darius III. This masterpiece showcases the attention to detail and the skillful use of tesserae to create a dynamic and captivating narrative. The artistry of Roman mosaics continues to awe and inspire, providing a glimpse into the aesthetic achievements of ancient Rome. (2)
2. Common Themes in Roman Mosaics
Common themes in Roman mosaics depict a wide range of subjects that provide insights into the everyday life, culture, and beliefs of ancient Romans. One prominent theme found in Roman mosaics is mythology. These mosaics often feature scenes from Greek and Roman myths, portraying gods, goddesses, and mythological creatures in vivid detail. This fascination with mythology highlights the Romans’ admiration for the tales and legends that shaped their worldview. Another common theme is nature, where mosaics beautifully capture the flora and fauna of the Roman landscape. Floral motifs, animals, and landscapes adorned the floors and walls of Roman villas, creating a harmonious connection between the man-made spaces and the natural world. Roman mosaics also frequently depict scenes from daily life, showcasing activities such as hunting, fishing, and farming. These realistic portrayals offer glimpses into the routines and occupations of ordinary Romans. Alongside these themes, geometric patterns and abstract designs were also prevalent in Roman mosaics, showcasing the sophistication and intricacy of their artistic techniques. These patterns were often used in combination with other themes, adding depth and visual interest to the overall composition. Whether illustrating mythological narratives, celebrating nature, or capturing ordinary life, Roman mosaics reflect the diversity of the society and the artistic prowess of the time. Through these vibrant and enduring artworks, we can gain a deeper understanding of the values, beliefs, and aesthetics of ancient Rome. (2)
3. Iconic Roman Mosaics
Iconic Roman mosaics are a testament to the breathtaking artistry and craftsmanship of the ancient Romans. These intricate designs, created by meticulously placing tiny colored stones or glass pieces, adorned the floors and walls of grand villas, public buildings, and even temples. One of the most famous examples of Roman mosaics is the “Battle of Issus” mosaic, discovered in the House of the Faun in Pompeii. This remarkable artwork depicts a dramatic battle scene between Alexander the Great and King Darius III of Persia, showcasing the Romans’ fascination with historical and mythological narratives. Another notable mosaic is the “Doves of Pliny,” found in the Villa di Pollio, which portrays a vibrant and detailed image of doves perched on a fountain. The intricate tesserae work of these mosaics, with their rich colors and intricate patterns, highlight the Romans’ attention to detail and their mastery of this art form. These stunning works have not only survived the test of time but also continue to inspire and captivate audiences today. The intricate mosaics of ancient Rome are a testament to the grandeur and artistic sophistication of this ancient civilization. (3)
Conclusion
In conclusion, the art and sculpture of ancient Rome, particularly in the realms of portraits, frescoes, and mosaics, are masterpieces that continue to captivate and inspire us today. Roman portraits provide invaluable insights into the individuals and society of the time, showcasing their status, achievements, and unique characteristics. The realistic and detailed nature of these portraits allows us to connect with the past and understand the rich tapestry of Roman culture. Frescoes, on the other hand, offer glimpses into the daily lives, myths, and historical events of the Roman people. These vibrant and colorful wall paintings showcase the artistic talent and storytelling abilities of the ancient Romans. Lastly, Roman mosaics mesmerize with their intricate designs, showcasing the meticulous craftsmanship and dedication of the artists. From mythical scenes to intricate geometric patterns, these mosaics bring life and beauty to floors and walls. The beauty and significance of Roman art and sculpture cannot be understated, as they provide a window into the past and allow us to appreciate the artistic prowess and cultural heritage of ancient Rome. Dive into the world of Roman art and sculpture, and discover the wonders that have withstood the test of time.
Frequently Asked Questions

1. What was the purpose of Roman portraits?
Roman portraits served multiple purposes. They were used to preserve the memory of prominent individuals, commemorate their achievements, and honor their status in society.
2. Who commissioned Roman portraits?
Roman portraits were typically commissioned by the wealthy elite, including emperors, senators, and other influential individuals who wanted to immortalize themselves or their loved ones.
3. How were Roman portraits different from earlier Greek sculptures?
While Greek sculptures aimed for idealized beauty and depicted figures in heroic poses, Roman portraits focused on capturing the individual’s likeness and naturalistic details, showing the effects of aging and portraying more diversity in facial expressions.
4. Were all Roman portraits of emperors and nobility?
No, Roman portraits were not limited to just emperors and nobility. There were also portraits of everyday Romans, including men, women, children, and even freed slaves.
5. What materials were used for creating Roman portraits?
Marble was the most commonly used material for Roman portraits, but other materials like bronze, terracotta, and even wood were also used depending on the artist’s preference and the client’s budget.
6. Why were Roman portraits often accompanied by inscriptions?
Inscriptions were often included with Roman portraits to provide information about the subject’s name, achievements, and sometimes even a brief biography. These inscriptions added context and enhanced the portrait’s historical significance.
7. Did Roman portraits influence later periods of art?
Absolutely. Roman portraits had a significant influence on later periods of art, particularly during the Renaissance. Artists looked to Roman portraiture as a source of inspiration for their own works, adopting the focus on realism and individuality.
8. Were Roman portraits painted or left bare?
Originally, Roman portraits were left bare, with the natural color of the material shining through. However, some portraits were later painted with vibrant colors to add a lifelike touch.
9. What evidence is there of hairstyles and fashion in Roman portraits?
Roman portraits provide valuable evidence of ancient hairstyles and fashion. Intricate hairstyles, accessories, and clothing depicted in the portraits give us insight into the trends and styles of the time.
10. Can Roman portraits be considered a form of propaganda?
Yes, Roman portraits often played a role in promoting an individual’s image or the image of the ruling class. Through portraits, rulers could project power, authority, and legitimacy, thus functioning as a form of propaganda.
References
Frequently Asked Questions

1. What materials were commonly used in Roman sculpture?
Roman sculptors primarily used marble, bronze, and terracotta for their sculptures.
2. Were Roman portraits always realistic?
While Roman portraits aimed to be realistic, they often idealized the subjects by emphasizing their virtues and omitting imperfections.
3. Did Roman frescoes serve any specific purpose?
Roman frescoes adorned the walls of homes and public buildings, serving as decorative elements and also conveying cultural, mythological, and historical narratives.
4. How were frescoes created in ancient Rome?
Roman frescoes were created by applying pigments directly onto wet plaster, allowing the colors to seep into the wall and become a permanent part of the surface.
5. Was there a central theme in Roman mosaic designs?
Although Roman mosaics encompassed various themes, common motifs included mythological scenes, intricate geometric patterns, and depictions of daily life.
6. What were some of the most famous Roman sculptures?
Famous Roman sculptures include the “Augustus of Prima Porta,” the “Laocoön and His Sons,” and the “Venus de Milo” (although discovered in Greece, it is now associated with Roman art).
7. How were Roman portrait busts different from Greek sculptures?
Roman portrait busts aimed to capture the individual’s character and likeness, whereas Greek sculptures focused more on idealized beauty and proportion.
8. What were the main influences on Roman art?
Roman art drew inspiration from Etruscan and Greek art, as well as incorporating elements from other cultures encountered through conquest and trade.
9. Were Roman mosaics primarily used in public or private spaces?
Roman mosaics were found in both public spaces (such as baths, temples, and marketplaces) and private residences, showcasing the artistry and wealth of the owners.
10. How did Roman art and sculpture survive through the ages?
The preservation of Roman art and sculpture was facilitated by the widespread adoption of Christian imagery and the repurposing of ancient buildings into churches and cathedrals.







