When it comes to iconic structures that have stood the test of time, the Colosseum and the Pantheon take center stage as magnificent examples of Roman architecture. These architectural wonders continue to captivate visitors with their grandeur and mystery. Step back in time and explore the secrets and engineering marvels that lie within the walls of the Colosseum, an ancient amphitheater that once hosted gladiatorial contests and spectacles. Then, marvel at the architectural brilliance of the Pantheon, with its perfect dome and rich history. From the underground tunnels of the Colosseum to the cultural significance of these structures, join us as we unveil the secrets and uncover the legacy of these remarkable Roman constructions.
Contents
- The Colosseum: A Grand Amphitheater
- The Pantheon: An Architectural Wonder
- Secrets and Mysteries
- Legacy and Significance
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How long did it take to build the Colosseum?
- 2. How many spectators could the Colosseum hold?
- 3. What materials were used in the construction of the Colosseum?
- 4. What types of events were held at the Colosseum?
- 5. What was the purpose of the underground tunnels in the Colosseum?
- 6. How were the spectators seated in the Colosseum?
- 7. Did the Colosseum have any protective features for the audience?
- 8. Were the events at the Colosseum violent?
- 9. Who funded and oversaw the construction of the Colosseum?
- 10. Is the Colosseum still standing today?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How long did it take to build the Colosseum?
- 2. What materials were used to construct the Pantheon?
- 3. How big is the Colosseum?
- 4. Who designed the Pantheon?
- 5. What was the purpose of the underground tunnels in the Colosseum?
- 6. How was the dome of the Pantheon constructed?
- 7. Can you still visit the Colosseum today?
- 8. What are some of the unique features of the Colosseum?
- 9. What is the significance of the Pantheon in Roman history?
- 10. How were the events and spectacles organized at the Colosseum?
- References
- Read More
The Colosseum: A Grand Amphitheater
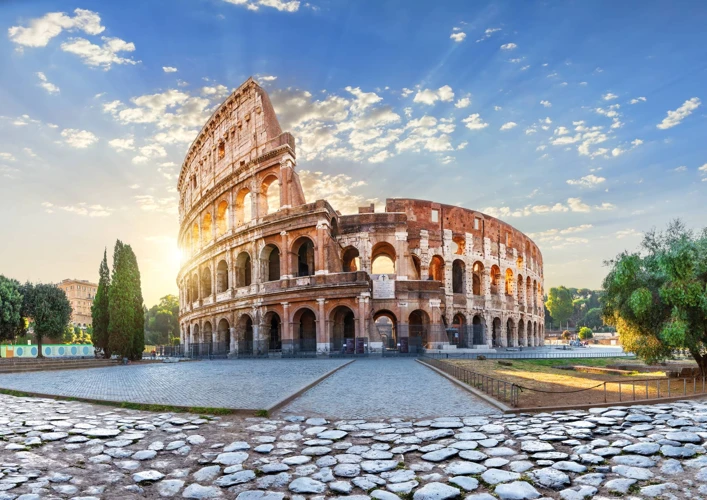

The Colosseum, also known as the Flavian Amphitheater, stands as an enduring symbol of the grandeur and power of ancient Rome. Construction of this monumental structure began in 72 AD and was completed in 80 AD under the rule of the Flavian emperors: Vespasian and Titus. The purpose of the Colosseum was to serve as a venue for various types of spectacles, including gladiatorial contests, animal hunts, and mock naval battles. These events were highly entertaining and drew massive crowds, with the capacity to hold up to 50,000 spectators. The Colosseum quickly became an important part of Roman culture and a demonstration of imperial might.
The Colosseum was an architectural marvel of its time, featuring a unique design that allowed for efficient crowd management and awe-inspiring spectacles. Built primarily using concrete and stone, the amphitheater stands four stories tall and covers an area of approximately six acres. Its elliptical shape, with a length of 189 meters and a width of 156 meters, made it the largest amphitheater in the Roman Empire. The exterior facade showcases a series of arches, columns, and statues, highlighting the Romans’ mastery of architectural embellishment. The seating arrangement consisted of different tiers, with the higher tiers designated for commoners and the lower tiers reserved for the elite. The design also included multiple entrances and exits, ensuring smooth entry and exit for the large crowds.
The Colosseum boasted several notable features that contributed to its grandeur and functionality. One such feature was the sophisticated system of underground tunnels, known as hypogeum, which allowed for the movement of gladiators, animals, and props without interrupting the flow of the events. This intricate network of tunnels and chambers consisted of ramps, lifts, and trapdoors, providing a captivating spectacle for the audience. Additionally, the Colosseum had an elaborate system of awnings, called velarium, that could be extended to provide shade and protection from the elements. This innovation demonstrated the Romans’ concern for the comfort and well-being of the spectators. The combination of architectural innovation, grand design, and remarkable features solidified the Colosseum’s status as a grand amphitheater and a legendary testament to Roman engineering prowess.
1. Historical Background
The historical background of the Colosseum is deeply intertwined with the political and social dynamics of ancient Rome. Its construction was initiated by Emperor Vespasian, who ruled Rome from 69 AD to 79 AD. Vespasian sought to solidify his power and gain favor among the Roman people, which had been significantly weakened in the aftermath of the chaotic Year of the Four Emperors. The Colosseum was built on the site of Nero’s grand palace, the Domus Aurea, which had been destroyed after Nero’s death, signifying the end of his despotic rule.
Vespasian’s decision to construct a vast amphitheater in its place was a strategic move to boost his popularity. The building project also served as a means to showcase Rome’s wealth and demonstrate the power of the Flavian dynasty. Upon Vespasian’s death, his son Titus took over the completion of the Colosseum, overseeing its inauguration in 80 AD with a series of splendid games and spectacles that lasted for 100 days. These lavish spectacles were intended to celebrate the newly constructed amphitheater and to commemorate the Roman Empire’s military triumphs.
The Colosseum’s completion marked a significant moment in Roman history. It not only represented the strength and stability of the Flavian dynasty, but it also signified Rome’s ability to recover and rebuild after a period of political unrest. The grandeur and magnificence of the Colosseum became a symbol of Roman power and imperial dominance, influencing subsequent generations and leaving a lasting impact on Western culture.
Today, the Colosseum stands as a testament to the grandeur and architectural prowess of ancient Rome. It serves as a reminder of the historical events and societal values that shaped the Roman Empire. Visitors from around the world continue to be captivated by its splendor and the historical significance it holds. The Colosseum remains a timeless icon, offering a glimpse into the rich history and culture of ancient Rome.
2. Construction and Design
The construction and design of the Colosseum showcased the ingenuity and engineering expertise of the ancient Romans. The architects and engineers employed innovative techniques and materials to create this monumental structure. The foundation of the Colosseum was built on a solid base of concrete, a revolutionary Roman invention known for its strength and durability. The outer walls were constructed using travertine stone, held together with iron clamps, and adorned with decorative elements such as statues and reliefs. The elliptical shape of the Colosseum allowed for optimal crowd visibility and efficient circulation within the amphitheater. To support the vast weight of the structure, a series of massive arches and vaults were incorporated into the design. These arches and vaults, made possible by the Romans’ expertise in engineering and construction, distributed the weight evenly and added stability to the Colosseum’s overall structure. The Colosseum’s design combined functionality with architectural splendor, showcasing the Romans’ ability to create awe-inspiring structures that still inspire wonder to this day.
3. Notable Features
Notable features of the Colosseum include its advanced architectural elements and the technological innovations incorporated into its construction. One prominent feature is the complex system of tunnels and chambers known as the hypogeum. This underground network allowed for the transportation of gladiators, animals, and props, enhancing the dramatic effect of the spectacles. The hypogeum consisted of ramps, lifts, and trapdoors to facilitate the movement of these elements seamlessly, captivating the audience with the element of surprise. Another remarkable feature is the velarium, an elaborate awning system that could be extended to provide shade and shelter to the spectators. The velarium was designed using advanced pulley mechanisms, allowing for optimal coverage as per the sun’s position. This attention to detail showcased the Romans’ ingenuity and their commitment to the comfort of their spectators. Additionally, the Colosseum boasted an impressive seating arrangement, with different sections designated for social classes. The seating tiers offered a clear view of the arena, ensuring an immersive experience for everyone present. This intentional segregation further emphasized the social hierarchy of Roman society. The combination of these notable features contributed to the Colosseum’s reputation as an architectural marvel and a testament to the engineering prowess of ancient Rome.
The Pantheon: An Architectural Wonder

The Pantheon stands as a remarkable architectural wonder, showcasing the ingenuity and precision of Roman engineering. Originally built as a temple dedicated to all the gods of Ancient Rome, its construction dates back to 118 AD during the reign of Emperor Hadrian. The Pantheon’s design is characterized by its massive circular dome, with a diameter of 43.3 meters, making it the largest unreinforced concrete dome in the world. The dome’s ingenious design includes a series of decreasing concrete layers as it rises, reducing the overall weight and creating a stunning architectural effect. The oculus, a large circular opening in the center of the dome, serves as the primary source of light, casting a captivating and ethereal glow on the interior of the building. The dome’s perfect proportions and impeccable construction have been a source of wonder and inspiration for centuries. The Pantheon is also renowned for its meticulously constructed portico, featuring Corinthian columns made of Egyptian granite. These columns, along with the impressive bronze entrance doors, emphasize the grandeur and elegance of this architectural masterpiece. Walking into the Pantheon, visitors are greeted with a vast and open interior space, emphasizing the harmony between the design, engineering, and aesthetic elements. The circular design with its innovative architecture creates a sense of unity and balance. The Pantheon’s enduring appeal and its unmatched architectural design make it a must-visit destination for those captivated by ancient wonders.
1. Origin and History
The origin and history of the Colosseum date back to the Flavian Dynasty in ancient Rome. The construction of this impressive amphitheater was initiated by Emperor Vespasian, who saw it as a means to demonstrate his power and restore the confidence of the Roman people after the turbulent reign of Nero. The site chosen for the Colosseum was the former location of Nero’s grand palace, the Domus Aurea. By repurposing this area, Vespasian aimed to reclaim the land for the public and symbolize the transition from a lavish and extravagant era to one focused on public welfare and entertainment.
Vespasian’s son, Titus, completed the construction of the Colosseum in 80 AD, inaugurating it with a grand series of games that lasted for 100 days. These games were a spectacle of unparalleled magnitude, featuring gladiator battles, animal hunts, and mock naval engagements. The Colosseum quickly became ingrained in the fabric of Roman society, serving as a symbol of power and entertainment for the citizens.
Throughout its history, the Colosseum witnessed various modifications and transformations. It hosted numerous spectacles and events for almost four centuries until the decline of the Roman Empire. Unfortunately, the Colosseum fell into disrepair over time, with parts of its structure being dismantled and repurposed for other buildings. Natural disasters, such as earthquakes, also caused significant damage to the grand amphitheater.
However, despite the challenges it faced, the Colosseum remained a significant landmark and has been restored and preserved over the centuries. Today, it stands as a remarkable testament to the ingenuity and architectural prowess of ancient Rome, attracting millions of visitors and offering a glimpse into a bygone era. Its historical significance and awe-inspiring presence continue to intrigue and fascinate people from around the world, making it an enduring icon of Roman architecture and cultural heritage.
2. Architectural Design
The architectural design of the Colosseum is a testament to the ingenuity and engineering prowess of the ancient Romans. The elliptical shape of the amphitheater, with its well-planned proportions, allowed for optimal viewing angles from any seat within the structure. The outer facade of the Colosseum features a series of arches and columns, showcasing the Romans’ mastery of architectural embellishment. The use of concrete and stone in its construction ensured durability and stability for centuries to come. The Colosseum stands as a prime example of Roman architectural innovation, with its blend of functionality and aesthetic appeal. The seating arrangement, with different tiers designated for different social classes, allowed for efficient crowd management and provided a hierarchical structure that mirrored Roman society. The architects and engineers of the Colosseum prioritized crowd safety and comfort, implementing various entrances and exits, as well as an advanced system of awnings to provide shade and protection from the elements. The architectural design of the Colosseum continues to inspire awe and admiration, serving as a remarkable tribute to the architectural legacy of ancient Rome.
3. Unique Features
3. Unique Features
The Colosseum is renowned for its unique architectural features that set it apart from other ancient amphitheaters. One of the most remarkable features is the complex system of underground tunnels, known as the hypogeum. These tunnels provided a backstage area for performers, gladiators, and animals, as well as storage for props and equipment. The hypogeum had a series of ramps and trapdoors, allowing for the dramatic entrance of gladiators and wild animals into the arena. The intricate network of tunnels added an element of surprise and suspense to the spectacles, captivating the audience’s attention.
Additionally, the Colosseum featured an advanced crowd-management system. The seating arrangement consisted of tiers, with each tier designated for a specific social class. The higher tiers were accessible to the commoners, while the lower tiers were reserved for the elite. This hierarchical seating arrangement ensured that everyone had a clear view of the events taking place in the arena. The Colosseum boasted an efficient entry and exit system with multiple entrances and exits strategically positioned around the amphitheater. This design allowed for the smooth flow of large crowds, minimizing congestion and ensuring the safety of the spectators.
The Colosseum had a unique technological feature called the velarium. This was a retractable awning system made of canvas or linen that could be extended to provide shade and protection from the sun or rain. The velarium was attached to a series of ropes, pulleys, and masts, allowing it to be easily raised or lowered as needed. This innovation showcased the Romans’ understanding of architectural engineering and their commitment to providing comfort for the audience, irrespective of the weather conditions.
The Colosseum’s unique features, including the hypogeum, the elaborate crowd-management system, and the retractable velarium, demonstrate the ingenuity and advanced engineering skills of the ancient Romans. These features not only enhanced the functionality of the amphitheater but also contributed to the overall spectacle and grandeur of the events held within its walls. Explore the fascinating secrets of the Colosseum, from its underground tunnels to its advanced crowd control, and gain a deeper appreciation for the architectural brilliance of this grand amphitheater.
Secrets and Mysteries

Diving into the secrets and mysteries surrounding the Colosseum and its enigmatic past reveals intriguing insights into the ancient world. One of the most fascinating aspects lies beneath the surface, in the underground tunnels that run beneath the amphitheater. These tunnels, known as hypogeum, played a crucial role in the staging of events, providing hidden passages for gladiators, animals, and props to enter and exit the arena. Exploring these subterranean levels offers a glimpse into the behind-the-scenes operations of this grand amphitheater. While the exact layout and purpose of every chamber and corridor remain somewhat mysterious, ongoing archaeological excavations continue to unearth ancient artifacts and shed light on the intricate workings of the Colosseum. In fact, recent discoveries have included ancient astrological artifacts, revealing the intersection of ancient Roman entertainment and beliefs in astrology. These artifacts provide a unique window into the cultural and spiritual significance that guided the staging of events at the Colosseum. Additionally, the Colosseum’s design and location have sparked theories about its potential alignment with planetary positions and its connection to predicting natural disasters. Some researchers speculate that the amphitheater’s orientation toward the cosmos may have been intentional and served as a tool for early astronomers. While these theories are still the subject of debate, they contribute to the ongoing fascination and mystique surrounding the Colosseum and its hidden secrets.
1. Colosseum’s Underground Tunnels
The Colosseum’s underground tunnels, known as the hypogeum, played a crucial role in the functioning and spectacle of the grand amphitheater. This intricate network of passageways and chambers was a testament to the Romans’ engineering skill and organizational prowess. The hypogeum served multiple purposes, including the movement of gladiators, animals, and props, as well as the storage of equipment and other necessities for the spectacles.
The hypogeum was a complex system that consisted of ramps, lifts, and trapdoors, allowing for the efficient transportation and staging of various elements of the shows. Gladiators would enter the arena through concealed entrances, creating an element of surprise as they emerged to face each other in combat. Animals, such as lions and tigers, were also brought up from the underground chambers to participate in the wild and thrilling hunts that took place inside the Colosseum.
The underground tunnels of the Colosseum were a marvel of Roman engineering, demonstrating their innovative use of space and logistics. The tunnels allowed for the smooth flow of events, ensuring that the spectacles remained captivating and uninterrupted. The hypogeum also provided a sense of grandeur and mystique, as the audience was able to witness the seemingly magical appearances and disappearances of gladiators and animals.
Today, visitors to the Colosseum can explore a small portion of the underground tunnels to get a glimpse into the complexity and ingenuity of this architectural feat. The hypogeum offers a unique perspective on the vast scale of the Colosseum’s operations and provides a deeper understanding of the historical significance of this iconic structure.
The Colosseum’s underground tunnels are a testament to the remarkable engineering and logistical skills of the Romans, and they add to the mystique and allure of this ancient amphitheater. Exploring these hidden depths allows us to uncover the secrets and marvel at the ingenuity that made the Colosseum an unparalleled cultural and architectural masterpiece.
2. Pantheon’s Perfect Dome
The Pantheon, with its magnificent and awe-inspiring design, stands as a testament to the ingenuity and architectural prowess of ancient Rome. This architectural wonder is renowned for its perfect dome, which has captivated visitors for centuries. Built by Emperor Hadrian between 118 and 128 AD, the Pantheon was originally a temple dedicated to all the gods of Ancient Rome. The design of the dome is a remarkable engineering feat, showcasing the Romans’ understanding of structural stability and their mastery of concrete construction.
The Pantheon’s dome is made of concrete, with a diameter of 43.3 meters, making it the largest unreinforced concrete dome in the world. The top of the dome features an oculus, a circular opening with a diameter of 8.7 meters. This oculus serves as the main source of natural light in the building and creates a mesmerizing effect as sunlight streams into the interior, casting ethereal rays on the floor below. The dome’s dimensions perfectly align with a sphere, creating a harmonious and balanced aesthetic that is visually stunning.
What makes the dome of the Pantheon truly remarkable is its construction technique. The concrete used in the dome consists of a mixture of volcanic ash, lime, and small stones, known as pozzolana. This mixture, combined with the ingenious use of varying densities of concrete, allowed the dome to be constructed with a decreasing thickness from the base to the oculus. This architectural technique significantly reduced the weight of the dome while maintaining its structural integrity.
The Pantheon’s dome has not only stood the test of time but has also inspired countless architects throughout history. Its innovative design has influenced the construction of domes in buildings around the world, including the iconic St. Peter’s Basilica in the Vatican City. The perfect dome of the Pantheon continues to be a source of fascination and admiration, standing as a testament to the architectural brilliance of ancient Rome.
3. Engineering Marvels
The Colosseum stands as a testament to the engineering brilliance of the ancient Romans. One of the most impressive engineering achievements of the Colosseum is its innovative use of concrete. The Romans developed a special type of concrete called pozzolana, which was made by mixing volcanic ash with lime and water. This durable and versatile material allowed for the construction of massive structures like the Colosseum. The use of concrete enabled the builders to create the intricate arches and vaulted ceilings that still awe visitors today.
In addition to concrete, the Colosseum showcases the Romans’ mastery of architectural techniques, such as the use of the arch and the keystone. The arches throughout the structure not only provided stability but also distributed the weight of the building, allowing for larger and more open spaces. The keystone, which is the wedge-shaped stone at the top of an arch, helped to lock the arch in place and prevent collapse. This architectural innovation ensured the Colosseum’s longevity and structural integrity.
Another engineering marvel of the Colosseum was its advanced drainage system. With the capacity to hold tens of thousands of spectators, it was crucial to control and manage the flow of water during events. The builders designed a complex system of channels and drains that collected rainwater and efficiently carried it away from the arena, ensuring that the events were not disrupted by flooding.
The engineering feats displayed in the construction of the Colosseum continue to astound researchers and visitors alike. Studying the techniques employed in the Colosseum’s construction provides valuable insights into the architectural prowess of the ancient Romans and their ability to create enduring structures that have withstood the test of time.
Legacy and Significance

The legacy and significance of the Colosseum extend far beyond its role as a grand amphitheater. This architectural marvel has left an indelible mark on history and continues to shape our understanding of ancient Roman civilization.
From a cultural standpoint, the Colosseum holds immense importance as a symbol of Roman entertainment, power, and social hierarchy. The spectacles held within its walls served as a form of public entertainment and a means for emperors to connect with the masses, solidifying their rule and popularity. The gladiatorial contests, in particular, became an intrinsic part of Roman culture, reflecting the values of bravery, discipline, and martial skills. The amphitheater also played a significant role in reinforcing Roman social structure, as it segregated spectators based on their class and status. The seating arrangements and the elaborate rituals associated with the events highlighted the distinctions between the patricians, plebeians, and slaves, reinforcing societal divisions.
In addition to its cultural importance, the Colosseum has become a major tourist attraction, drawing millions of visitors from around the world each year. Its architectural brilliance and historical significance make it a must-visit destination for history enthusiasts, architecture lovers, and curious travelers alike. The Colosseum offers a glimpse into the grandeur of ancient Rome and allows visitors to imagine the spectacles that once took place within its walls. Exploring the amphitheater’s various levels, passages, and underground chambers provides a unique opportunity to step back in time and immerse oneself in the rich history of the Roman Empire.
The Colosseum’s enduring legacy has paved the way for the preservation and study of ancient Roman architecture. Its architectural innovations, such as the use of concrete, arches, and vaults, have influenced subsequent architectural styles and techniques. The Colosseum serves as a testament to the Romans’ engineering prowess and their ability to construct massive structures that have stood the test of time.
The Colosseum’s legacy and significance extend beyond being a grand amphitheater. Its cultural importance, status as a tourist attraction, and architectural influence highlight the enduring impact of this ancient marvel. Whether it is unearthing ancient astrological artifacts, planetary alignments predicting natural disasters, or cultural significance in the constellation Cygnus, the Colosseum continues to intrigue and fascinate people from all walks of life, leaving an indelible mark on the world’s architectural and historical landscape.
1. Cultural Importance
The Colosseum holds immense cultural importance as a symbol of Roman society and its values. It served not only as an entertainment venue but also as a reflection of the political and social dynamics of the time. The spectacles held in the Colosseum were a way for emperors to gain favor with the people and demonstrate their power and wealth. The gladiatorial contests, in particular, represented the Romans’ fascination with violence and the endurance of the human spirit. These events were deeply ingrained in the cultural fabric of ancient Rome and impacted various aspects of society, including art, literature, and even religious practices. The Colosseum also became a symbol of the Roman Empire’s dominance and expansion, as captured by the Latin phrase, “bread and circuses.” The phrase refers to the practice of imperial rulers providing free food and entertainment to maintain the loyalty of the populace. Today, the Colosseum continues to be a source of inspiration and fascination, attracting millions of visitors who come to witness its historical and cultural significance firsthand.
2. Tourist Attractions
2. Tourist Attractions
The Colosseum and the Pantheon are not only architectural marvels but also popular tourist attractions that draw visitors from all over the world. The Colosseum, with its rich historical significance and grandeur, is a must-visit destination for history enthusiasts and those interested in experiencing ancient Rome. As one of the New Seven Wonders of the World, it offers a glimpse into the past and allows visitors to imagine the spectacles that took place within its walls. Guided tours provide the opportunity to explore the underground tunnels and gain a deeper understanding of the inner workings of this ancient amphitheater. The Pantheon, on the other hand, captivates visitors with its unique architectural design and the mesmerizing oculus at the center of its dome. Its impressive size and well-preserved state continue to astonish tourists and researchers. With intricate details and a rich history, the Pantheon is a testament to the ingenuity of Roman engineering. Together, these iconic structures offer an immersive experience into the ancient world and are a testament to the enduring legacy of Roman architecture and ingenuity.
When visiting the Colosseum and the Pantheon, it’s important to plan ahead to make the most of your visit. Booking guided tours in advance can provide a comprehensive understanding of the historical and architectural significance of these landmarks. Exploring the nearby archaeological sites, such as the Roman Forum and Palatine Hill, can further enrich your visit and provide a deeper insight into ancient Roman life. Don’t forget to bring comfortable shoes as both attractions require a fair amount of walking. Remember to also check the opening hours and any restrictions or regulations that might be in place. With proper planning and a sense of awe, a visit to the Colosseum and the Pantheon is sure to be a memorable experience that will transport you back in time to the grandeur of the Roman Empire.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Colosseum stands as a testament to the architectural brilliance and cultural significance of ancient Rome. This grand amphitheater continues to captivate visitors from around the world with its rich history and remarkable features. The construction and design of the Colosseum exemplify the Romans’ mastery of engineering, showcasing their ability to create massive structures that could accommodate tens of thousands of spectators. The underground tunnels, velarium, and seating arrangements all contributed to the efficient and awe-inspiring nature of the spectacles held within its walls. The Colosseum’s legacy extends far beyond its architectural marvels. It serves as a reminder of the cultural importance of entertainment and public spectacles in ancient Rome, as well as a testament to the power and grandeur of the Roman Empire. Today, the Colosseum stands as a popular tourist attraction, allowing visitors to step back in time and witness the magnificence of a bygone era. The Colosseum, along with other iconic structures like the Pantheon, continues to inspire awe and admiration for the ancient Roman civilization.
Frequently Asked Questions

1. How long did it take to build the Colosseum?
The construction of the Colosseum began in 72 AD and was completed in 80 AD, lasting a total of eight years.
2. How many spectators could the Colosseum hold?
The Colosseum had a seating capacity of up to 50,000 spectators, making it one of the largest amphitheaters in the Roman Empire.
3. What materials were used in the construction of the Colosseum?
The Colosseum was built primarily using concrete and stone. The exterior facade featured columns, arches, and statues, showcasing the Romans’ mastery of architectural embellishment.
4. What types of events were held at the Colosseum?
The Colosseum hosted a variety of spectacles, including gladiatorial contests, animal hunts, and mock naval battles. These events were highly entertaining and drew massive crowds.
5. What was the purpose of the underground tunnels in the Colosseum?
The underground tunnels, known as hypogeum, served as a means for the movement of gladiators, animals, and props without interrupting the flow of the events. They added an element of surprise and spectacle to the games.
6. How were the spectators seated in the Colosseum?
The seating arrangement in the Colosseum consisted of different tiers. The higher tiers were designated for commoners, while the lower tiers were reserved for the elite and important officials.
7. Did the Colosseum have any protective features for the audience?
Yes, the Colosseum had an elaborate system of awnings called velarium, which could be extended to provide shade and protection from the sun or rain, ensuring the comfort of the spectators.
8. Were the events at the Colosseum violent?
Yes, gladiatorial contests and animal hunts were indeed violent. These spectacles were meant to entertain the audience and demonstrate feats of strength, skill, and bravery.
9. Who funded and oversaw the construction of the Colosseum?
The construction of the Colosseum was funded by the spoils of war from the Jewish Revolt, and it was overseen by the Flavian emperors, Vespasian and Titus.
10. Is the Colosseum still standing today?
Yes, the Colosseum still stands as an iconic symbol of ancient Roman architecture. While parts of the structure have been damaged over time, it remains one of the most popular tourist attractions in Rome.
References
- View Article: The Colosseum: Power, Brilliance, and Brutality
- The Colosseum: A Deep Dive into Ancient Roman …
- The Colosseum Construction Techniques Still Utilized Today
Frequently Asked Questions

1. How long did it take to build the Colosseum?
The construction of the Colosseum began in 72 AD and was completed in 80 AD, which means it took approximately 8 years to build this grand amphitheater.
2. What materials were used to construct the Pantheon?
The Pantheon was built using a variety of materials. The exterior features travertine, while the interior is adorned with marble. The dome, one of its unique features, is made of concrete.
3. How big is the Colosseum?
The Colosseum is an impressive structure, measuring 189 meters long, 156 meters wide, and standing at a height of 48 meters. It could accommodate approximately 50,000 spectators.
4. Who designed the Pantheon?
The Pantheon is believed to have been designed by the Roman architects Apollodorus of Damascus and Emperor Hadrian. The exact details of the architect are still debated among experts.
5. What was the purpose of the underground tunnels in the Colosseum?
The underground tunnels, known as the hypogeum, served multiple purposes. They were used to house gladiators, animals, and equipment. They provided a means for them to enter the arena during the spectacles.
6. How was the dome of the Pantheon constructed?
The dome of the Pantheon is a remarkable feat of engineering. It was built using a combination of different types of concrete, with lighter materials used at the top and denser materials at the base. This construction technique allowed for a lighter dome and distributed the weight evenly.
7. Can you still visit the Colosseum today?
Yes, the Colosseum is open to visitors today. It is one of the most popular tourist attractions in Rome, drawing millions of visitors every year. However, it is important to note that certain areas might be restricted for safety reasons.
8. What are some of the unique features of the Colosseum?
The Colosseum has several unique features, including its elliptical shape, the elaborate system of underground tunnels, and the seating arrangement that allowed for efficient crowd control. It also had a retractable awning system known as the velarium to provide shade for the spectators.
9. What is the significance of the Pantheon in Roman history?
The Pantheon holds immense historical and cultural significance. It served as a temple dedicated to all the Roman gods and symbolized the power and grandeur of the Roman Empire. Today, it stands as a remarkable example of ancient Roman architecture and engineering.
10. How were the events and spectacles organized at the Colosseum?
The organization of events at the Colosseum was a meticulous process. The emperor or the organizing authority oversaw the planning, which involved gladiatorial fights, animal hunts, and even naval battles. The spectacles were carefully choreographed to provide entertainment and maintain the social order.
References
- The Colosseum: A Deep Dive into Ancient Roman …
- View Article: The Colosseum: Power, Brilliance, and Brutality
- The Secrets of Ancient Rome’s Buildings | History







