The Role of Women in Mayan Society has been a subject of intrigue and fascination for historians and scholars alike. The ancient Mayan civilization, known for its advanced knowledge and intricate culture, held women in high regard, recognizing their valuable contributions in various aspects of society. From their involvement in the household and religious life to their role in the economy and politics, women played a crucial role in shaping Mayan society. Through this article, we will explore the multifaceted roles and responsibilities of women in Mayan society, shedding light on their significance and the influence they exerted in this captivating civilization.
Contents
- Women in Mayan Household
- Women in Mayan Religious Life
- Women in Mayan Economy
- Women in Mayan Politics
- Women’s Status and Roles in Society
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What were the primary responsibilities of women in Mayan households?
- 2. Did Mayan women have any roles in religious life?
- 3. What was the significance of Mayan priestesses?
- 4. Were women involved in agriculture and farming?
- 5. Did Mayan women participate in trade and commerce?
- 6. Were there any Mayan Queen Regents?
- 7. What was the role of noblewomen in Mayan politics?
- 8. How were women positioned in Mayan social hierarchies?
- 9. Did Mayan women have access to education and knowledge?
- 10. In what ways did Mayan women express themselves artistically?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How did women contribute to Mayan agriculture and farming?
- 2. What were the responsibilities of Mayan women in their households?
- 3. Did Mayan women have any decision-making power in their households?
- 4. Did Mayan women have any role in Mayan religious life?
- 5. How did Mayan women contribute to the Mayan economy?
- 6. Did Mayan women hold any positions of power in Mayan politics?
- 7. Were there social hierarchies that affected the status of Mayan women?
- 8. What opportunities did Mayan women have for education and knowledge?
- 9. Did Mayan women have opportunities for artistic expression?
- 10. How did the roles and status of Mayan women contribute to the overall Mayan society?
- References
- Read More
Women in Mayan Household

Women played a central role in the Mayan household, assuming various responsibilities that were vital for the smooth functioning of their families. Responsibilities included tasks such as cooking, cleaning, and weaving textiles, which were essential for the well-being of the family unit. Additionally, women were responsible for managing the household finances and ensuring the procurement of necessary supplies. They also oversaw the upbringing and education of children, passing down cultural traditions, myths, and values to future generations. With their expertise in agricultural practices, women played an active role in cultivating crops and ensuring food security for their families. Their dedication and hard work within the household laid the foundation for a thriving Mayan society.
1. Responsibilities
In Mayan society, women had a multitude of responsibilities within the household. They were primarily in charge of domestic affairs, including cooking and preparing meals for the family. The art of cooking was highly valued among Mayans, and women took great pride in their culinary skills. They would gather and prepare ingredients, often using traditional methods and recipes passed down through generations. In addition to cooking, women were also responsible for maintaining cleanliness and order in the household. This involved tasks such as cleaning, sweeping, and organizing the living space. Another important responsibility of women was textile production. Mayan women were skilled weavers and would create intricate textiles using techniques like backstrap weaving. These textiles served both practical and cultural purposes, as they were used for clothing, blankets, and ceremonial offerings. Women also played a crucial role in ensuring the financial stability of the household. They managed the budget, purchased necessary supplies, and oversaw the distribution of resources. Their meticulous attention to detail and financial acumen contributed to the overall prosperity and well-being of the family unit.
2. Childcare and Education
Women in Mayan society played a crucial role in childcare and education, ensuring the proper upbringing and instruction of children. Childcare was primarily the responsibility of women, who tenderly cared for infants and young children. They provided nurturing environments, ensuring the physical and emotional well-being of the children. Mothers would breastfeed their infants and carry them on their backs using cloth slings, allowing them to continue with other tasks while keeping their children close. As children grew older, women, particularly mothers and grandmothers, took charge of their education. They taught essential skills such as farming, weaving, and cooking, passing down valuable knowledge from one generation to the next. Education was not limited to practical skills; women also shared cultural traditions, myths, and stories that helped shape the children’s understanding of their heritage. By imparting knowledge and instilling cultural values, women in Mayan society played a vital role in the intellectual and cultural development of their communities.
3. Household Decision-making
Women in Mayan society held a significant role in household decision-making. While men often took the lead in external affairs, it was the women who had the final say in matters that directly impacted the family. Their opinions and input were valued and respected, and they actively participated in discussions and deliberations regarding issues such as major purchases, familial obligations, and community matters. Women were considered the cornerstone of the family unit and were regarded as wise and knowledgeable in matters concerning the household. Their insights and judgment carried weight, and they played an instrumental role in shaping the direction of the family’s well-being. It was common for women to have a strong influence in family dynamics and interpersonal relationships, providing guidance and nurturing to maintain harmony and balance within the household. The ability of women to contribute to important decision-making processes demonstrated the respect and empowerment they held within Mayan society.
Women in Mayan Religious Life
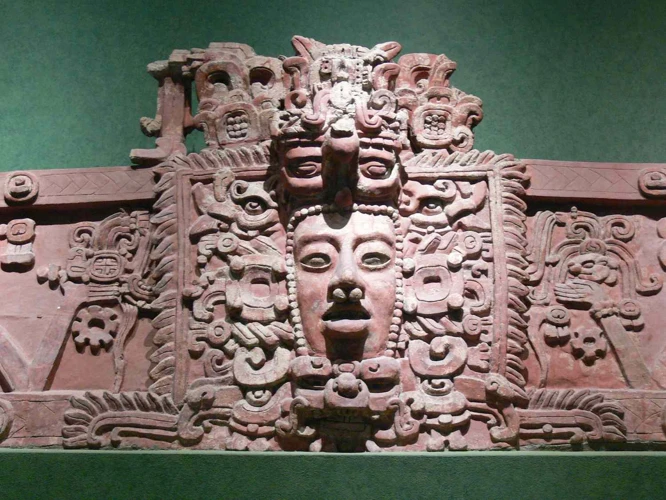

Women in Mayan society held significant roles in the religious life of their community. They served as priestesses, acting as intermediaries between the mortal world and the divine realm. These priestesses played a crucial role in performing rituals and ceremonies, often held in temples and sacred spaces. They led spiritual practices, offered prayers and sacrifices to the gods, and interpreted omens and signs believed to hold religious significance. Mayan women also partook in rituals and ceremonies that were specific to their gender, such as fertility rites and birthing rituals. Through their active participation in religious life, women contributed to the spiritual and cultural fabric of the Mayan civilization, fostering a deep connection with the divine.
1. Priestesses
Priestesses held a prominent and influential position in Mayan society. As spiritual leaders, they played a crucial role in religious ceremonies and rituals. These women were esteemed for their wisdom and connection to the divine. They were responsible for conducting rituals and offering sacrifices to the Mayan gods in order to maintain a harmonious relationship between the earthly realm and the supernatural. Priestesses acted as intermediaries between the human world and the spiritual realm, interpreting omens, performing divination, and providing guidance to the community. Their deep understanding of astrology and astronomy allowed them to accurately predict celestial events, which held great significance in Mayan culture. The priestesses were highly respected and revered for their knowledge and were often consulted by rulers and nobles for their insights. Through their divine connection, the priestesses played a crucial role in maintaining the spiritual well-being of the Mayan society.
2. Rituals and Ceremonies
Rituals and ceremonies held significant importance in Mayan society, and women were actively involved in these religious practices. As priestesses, they played a pivotal role in conducting and overseeing various rituals and ceremonies. They were responsible for performing religious rites, making offerings, and communing with the gods. The Mayans believed that women had a special connection to the spiritual realm and possessed the ability to communicate with deities. These rituals and ceremonies often took place in sacred temples and were marked by elaborate dances, music, and processions. Women’s participation in these religious activities demonstrated their integral role in upholding the spiritual fabric of Mayan society. Their deep understanding of sacred traditions and their ability to act as intermediaries between the human and divine realms made them highly respected figures within the community. (For more information on the role of women in Mayan religion, you can visit /mythology-origins-ophiuchus-constellation/).
Women in Mayan Economy

Women in Mayan society had a significant presence in the economy, contributing through various means to the prosperity of the civilization. One of the key roles women undertook was in agriculture and farming. They actively participated in planting and harvesting crops, such as maize, beans, and squash, which formed the staple diet of the Mayans. Through their knowledge of agricultural techniques and their diligent work in the fields, they ensured the sustenance of their families and communities. Additionally, women also played a role in trade and commerce. They engaged in the production of intricate textiles, pottery, and other handicrafts, which were highly valued commodities. Women traders would travel to nearby settlements and marketplaces to exchange their goods for other essential resources. Their involvement in economic activities showcased their independence and entrepreneurial spirit, contributing to the thriving Mayan economy.
1. Agriculture and Farming
In the Mayan society, women played a significant role in agriculture and farming, contributing to the sustenance and prosperity of their communities. They possessed valuable knowledge about planting, harvesting, and the cultivation of various crops, which they passed down through generations. Women skillfully cultivated staple crops such as maize, beans, and squash, which formed the backbone of the Mayan diet. They utilized agricultural techniques like slash-and-burn farming, terrace cultivation, and the construction of irrigation systems to maximize crop yields. Women were also involved in the collection of medicinal plants and herbs, utilizing their knowledge of herbal medicine for the well-being of their families. Their labor-intensive work in the fields demonstrated their dedication and the critical role they played in ensuring food security and the overall stability of the Mayan society. In many ways, women were the backbone of agricultural practices, contributing to the thriving civilization.
2. Trade and Commerce
Women in Mayan society were actively involved in trade and commerce, playing a significant role in economic activities. They participated in local markets, where they bartered and traded goods such as textiles, pottery, and food items. Mayan women were skilled weavers, and their vibrant textiles were highly sought after in regional trade networks. Some women even traveled long distances to engage in commercial exchanges. They acted as intermediaries, facilitating trade relations between different Mayan city-states. Their involvement in commerce extended beyond domestic trade, as they also engaged in long-distance trade networks that reached other Mesoamerican societies and even distant regions. This participation in trade not only contributed to the economic prosperity of Mayan communities but also allowed women to gain social and cultural connections beyond their immediate surroundings. Their entrepreneurial spirit and expertise in commerce played a crucial role in shaping the economic landscape of the Mayan civilization.
Women in Mayan Politics

In Mayan society, women had a notable presence in the political domain, making significant contributions to governance and leadership. Queen Regnants held prominent positions of power, ruling over Mayan city-states and making key decisions that influenced the welfare of their people. These influential queens were not only involved in political matters but were also responsible for religious rituals and ceremonies, symbolizing the close association between politics and spirituality in Mayan culture. Additionally, noblewomen played a crucial role in supporting the ruling elite and maintaining social stability. They had access to education, allowing them to develop skills in diplomacy and the arts, which further empowered them in matters of politics and governance. The participation of women in Mayan politics showcases the society’s recognition of their capabilities and expertise in shaping the destiny of their civilization.
1. Queen Regnants
Queen regnants were a remarkable aspect of Mayan society, showcasing the high regard in which women were held. Queens ascended to the throne as rulers in their own right, wielding significant power and authority. These powerful women exhibited strong leadership qualities and made crucial decisions that impacted the well-being of their communities. They governed over territories, oversaw the administration of justice, and engaged in diplomatic relations with neighboring regions. Queen regnants also played a crucial role in religious ceremonies, maintaining a divine connection between the earthly and spiritual realms. One prominent example of a Mayan queen regnant is the powerful Lady Yohl Ik’nal, who ruled the city-state of Palenque during the Classical period. She proved her prowess and led with wisdom, solidifying her place as a respected ruler in Mayan history. The reign of queen regnants served as a testament to the elevated status of women in Mayan society, challenging traditional gender roles and breaking barriers of patriarchy.
2. Noblewomen
Noblewomen in Mayan society held positions of power and influence. They were often members of the ruling elite and played a significant role in the political affairs of the civilization. These noblewomen had the privilege of receiving education in fields such as politics, religion, and administration. They were well versed in diplomatic matters and played a key role in forming alliances through intermarriages. Noblewomen participated in important decision-making processes alongside their male counterparts, and their opinions and counsel were highly valued. They also had the responsibility of preserving cultural traditions and passing down knowledge to future generations. These powerful women often wore elaborate clothing and adorned themselves with intricate jewelry, highlighting their elevated status in society. The lives of noblewomen were complex and fascinating, and their contributions helped shape the Mayan civilization.
—
Women’s Status and Roles in Society

The status and roles of women in Mayan society were determined by a complex system of social hierarchies. While women held significant positions within their households and communities, their influence varied depending on factors such as their familial lineage, wealth, and access to education. Noblewomen, for instance, enjoyed higher social status and had more opportunities for participation in politics and religious affairs. Education and knowledge were highly valued in Mayan society, and women who possessed intellectual prowess often held esteemed positions as priestesses or advisors to rulers. Women excelled in various forms of artistic expression, including pottery, weaving, and jewelry-making, showcasing their creativity and skill. It is important to recognize the diverse roles and contributions of women in Mayan society, as they played a crucial part in shaping the cultural and intellectual landscape of the civilization.
In Mayan society, social hierarchies played a significant role in shaping the lives of women. The societal structure was stratified, with different positions and roles assigned based on a person’s lineage, occupation, and wealth. At the top of the social hierarchy were the ruling elite, including the kings and queens, who held immense power and influence. Women belonging to the noble class held a prestigious position, often overseeing the governance of their territories and actively participating in political affairs. They were involved in decision-making processes, offering their insight and advice to the ruling elite. Artistic expressions also played a crucial role in reflecting these hierarchies, with intricate murals and sculptures depicting the divine and noble figures of Mayan society. However, not all women enjoyed the same level of status and power. Women from lower social classes, such as farmers and laborers, had limited opportunities for upward mobility. Despite these social hierarchies, women across all classes contributed to the overall functioning of Mayan society and held significant roles within their respective spheres.
2. Education and Knowledge
Mayan women had access to education and knowledge, which played a crucial role in their societal contributions. While formal education was primarily reserved for the elite, women received education through informal means within their households and communities. They were taught a wide range of skills such as weaving, pottery, and herbal medicine, which were essential to their roles in the household and society. Women also participated in religious ceremonies and were well-versed in the spiritual beliefs and practices of the Mayan civilization.
Mayan women were revered as custodians of oral tradition and passed down stories, myths, and histories through generations. Through their knowledge and storytelling abilities, they played a vital role in preserving the cultural heritage of the Mayan people. Their deep understanding of the complex Mayan calendar system allowed them to participate in timekeeping and rituals associated with important celestial events.
Additionally, women’s involvement in artistic expressions showcased another aspect of their education and knowledge. They excelled in various forms of artistic expression such as pottery, weaving intricate textiles, and creating beautiful jewelry. These skills were passed down from one generation to another, ensuring the preservation of craftsmanship and cultural identity.
Mayan women’s access to education and knowledge empowered them to contribute significantly to various fields and enriched the fabric of Mayan society through their expertise, creativity, and cultural preservation.
LINK: Cancer and Capricorn compatibility
3. Artistic Expressions
Mayan women had a significant impact on the artistic expressions of their society. They excelled in various forms of art, including pottery, weaving, jewelry making, and painting. In pottery, women showcased their creativity by sculpting intricate designs and patterns onto the vessels, which often depicted scenes from daily life or mythological stories. Weaving was another artistic expression where women displayed their skill and mastery. They used backstrap looms to create vibrant and detailed textiles, incorporating intricate patterns and symbols that held cultural significance. These textiles were not only used for clothing but also served as important items for trade and ceremonial purposes. Women were also involved in jewelry making, crafting elaborate pieces using precious metals and gemstones. These adornments were highly valued and were worn as symbols of status and beauty. Lastly, women contributed to the Mayan artistic expressions through their participation in mural painting and creating exquisite murals on the walls of temples and palaces. These murals depicted mythological scenes, religious rituals, and historical events. The artistic contributions of Mayan women greatly enriched the cultural heritage of their society and continue to captivate and inspire people to this day.
Conclusion
The role of women in Mayan society was diverse and multifaceted, spanning across the household, religious life, economy, and politics. From being the backbone of the household and assuming numerous responsibilities, women held significant power and influence. In religious life, women served as priestesses, participating in rituals and ceremonies that connected the Mayan people with the spiritual realm. Women also played a crucial role in the economy, engaging in agriculture, farming, trade, and commerce. In politics, women had the opportunity to become queen regnants or noblewomen, further highlighting their importance in governing and decision-making. Mayan society recognized and valued women’s contributions, and their status was not solely determined by social hierarchies but also by their education, knowledge, and artistic expressions. Women held knowledge and played a vital role in preserving and passing down cultural traditions. Their artistic expressions, including weaving, pottery, and painting, showcased their creativity and skill. Overall, women in Mayan society enjoyed a respected position and made significant contributions to the flourishing civilization. Their legacy continues to inspire and impress, highlighting the remarkable achievements of women in ancient times.
Frequently Asked Questions

1. What were the primary responsibilities of women in Mayan households?
Women in Mayan households held various responsibilities, including cooking, cleaning, weaving textiles, managing household finances, and overseeing the upbringing and education of children.
2. Did Mayan women have any roles in religious life?
Yes, Mayan women played significant roles in religious life. Some women held the esteemed position of priestesses and actively participated in rituals and ceremonies.
3. What was the significance of Mayan priestesses?
Mayan priestesses were highly respected and held significant influence in religious matters. They conducted rituals, performed ceremonies, and played key roles in connecting the Mayan people with the spiritual realm.
4. Were women involved in agriculture and farming?
Yes, women played a vital role in agriculture and farming in Mayan society. They were involved in cultivating crops, ensuring food security for their families and communities.
5. Did Mayan women participate in trade and commerce?
Absolutely, Mayan women were actively involved in trade and commerce. They engaged in various economic activities, including selling and trading goods in local markets.
6. Were there any Mayan Queen Regents?
Yes, Mayan society recognized Queen Regents who held the title of ruler during periods of interregnum or when a legitimate heir was absent or too young to rule.
7. What was the role of noblewomen in Mayan politics?
Noblewomen in Mayan politics had significant influence and power. They often played roles as advisors to rulers and were involved in political decision-making.
Mayan social hierarchies placed a strong emphasis on lineage and status. Women belonging to higher-ranking families enjoyed privileges and held more prestigious roles in society.
9. Did Mayan women have access to education and knowledge?
Mayan women had access to education and knowledge, especially within their own cultural traditions. They were taught diverse subjects, including history, mythology, and practical skills necessary for their roles.
10. In what ways did Mayan women express themselves artistically?
Mayan women expressed themselves artistically through various mediums, including pottery, weaving, and jewelry-making. Their intricate designs and craftsmanship showcased their creativity and cultural richness.
References
Frequently Asked Questions

1. How did women contribute to Mayan agriculture and farming?
Women in Mayan society played a vital role in agriculture and farming. They were responsible for tending to the crops, planting and harvesting, and ensuring the community’s food security.
2. What were the responsibilities of Mayan women in their households?
Mayan women had various responsibilities in their households, including cooking, cleaning, weaving textiles, and making pottery. They were the caretakers of their homes and the nurturers of their families.
3. Did Mayan women have any decision-making power in their households?
Yes, Mayan women had some decision-making power within their households. They were often consulted on matters concerning family matters, such as managing resources or arranging marriages.
4. Did Mayan women have any role in Mayan religious life?
Mayan women had significant roles in Mayan religious life. Some women became priestesses and actively participated in rituals and ceremonies, connecting with the spiritual realm and offering prayers and sacrifices.
5. How did Mayan women contribute to the Mayan economy?
Mayan women contributed to the Mayan economy through various means. They were involved in agricultural activities, such as cultivating crops and raising livestock. They also participated in trade and commerce, selling goods at local markets.
6. Did Mayan women hold any positions of power in Mayan politics?
Yes, some Mayan women held positions of power in Mayan politics. Queen Regnants ruled over kingdoms, and noblewomen played influential roles in their respective communities.
Yes, there were social hierarchies in Mayan society that influenced the status of women. Women from noble or ruling families held higher status compared to those from lower social classes.
8. What opportunities did Mayan women have for education and knowledge?
Mayan women had access to education and knowledge, although it varied depending on their social class. They were taught skills necessary for their roles, such as weaving or preparing herbal remedies.
9. Did Mayan women have opportunities for artistic expression?
Yes, Mayan women had opportunities for artistic expression. They excelled in various art forms, including pottery, weaving, and creating intricate jewelry. These artistic creations reflected the cultural richness of Mayan society.
10. How did the roles and status of Mayan women contribute to the overall Mayan society?
The roles and status of Mayan women were essential to the overall Mayan society. Their contributions to agriculture, household management, religious practices, economy, and politics played a vital role in the social and economic stability of their communities.