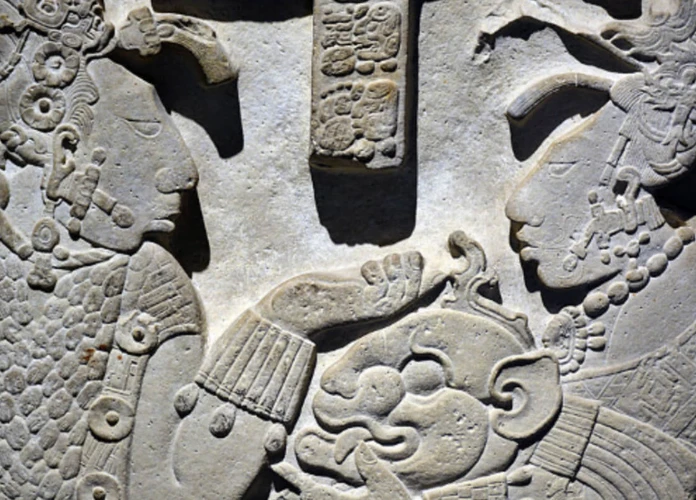
In the rich tapestry of Mayan mythology, shamans and priests play significant roles as intermediaries between the human and spiritual realms. Their unique abilities, rituals, and influence make them integral to the Mayan society. While shamans connect with the spirit world to provide guidance and healing, priests hold prestigious responsibilities in conducting religious ceremonies and offering sacrifices to appease the gods. This article delves into the fascinating world of Mayan mythology, exploring the distinct characteristics of shamans and priests, their overlapping roles, and the profound impact they have on the social, cultural, and religious practices of the Mayan people. Join us on a journey to unravel the mysteries surrounding these revered figures and uncover the essence of their contributions in Mayan society.
Contents
- Shamans in Mayan Mythology
- Priests in Mayan Mythology
- Shamans and Priests: Similarities and Differences
- The Influence of Shamans and Priests in Mayan Society
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What is the role of shamans in Mayan mythology?
- 2. How are shamans different from priests in Mayan mythology?
- 3. What rituals and practices do Mayan shamans perform?
- 4. Who can become a shaman in Mayan culture?
- 5. What are the responsibilities of Mayan priests?
- 6. How do Mayan priests gain their knowledge and training?
- 7. What is the significance of shamans and priests in Mayan society?
- 8. How do Mayan shamans and priests influence governance?
- 9. How does Mayan mythology view the power of shamans and priests?
- 10. How does the role of shamans and priests in Mayan mythology continue to influence modern Mayan culture?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What is the role of shamans in Mayan mythology?
- 2. What are the characteristics of Mayan shamans?
- 3. How do shamans connect with the spiritual world in Mayan mythology?
- 4. What kinds of rituals and healing practices do Mayan shamans perform?
- 5. What is the role and responsibilities of priests in Mayan mythology?
- 6. What are the ritualistic ceremonies and offerings performed by Mayan priests?
- 7. How do shamans and priests differ in Mayan mythology?
- 8. What are some overlapping spiritual roles of shamans and priests in Mayan mythology?
- 9. How do shamans and priests influence Mayan society?
- 10. What is the impact of shamans and priests on Mayan governance?
- References
- Read More
Shamans in Mayan Mythology
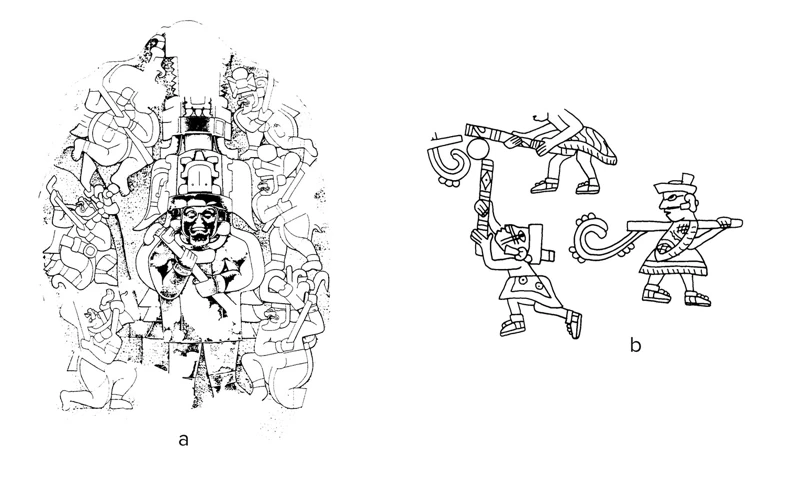
Shamans in Mayan mythology hold a deeply revered and intricate role within the spiritual fabric of the culture. These spiritual leaders possess distinctive characteristics that set them apart from other members of Mayan society. Shamans are believed to have a special connection with the spirits, acting as intermediaries between the human and supernatural realms. Through their rituals and practices, they channel cosmic forces and tap into the wisdom of the ancestors. Their abilities encompass divination, healing, and the interpretation of signs and symbols. With their gift of insight, shamans guide individuals and communities in making important decisions, resolving conflicts, and maintaining spiritual balance. It is in their hands that the spiritual welfare of the Mayan people lies, embodying wisdom, power, and the ability to bridge the gap between the seen and unseen worlds. (anchor link: astrological significance of the Ophiuchus symbol)
1. Definition and Characteristics of Shamans
Shamans in Mayan mythology are individuals who possess unique characteristics and fulfill specific roles within their society. The definition of shamans varies across different Mayan communities, but they are generally regarded as spiritual leaders and intermediaries between the human and spirit realms. Shamans are believed to have been chosen by the gods or spirits due to their innate abilities and qualities such as intuition, empathy, and a deep connection to nature. These chosen individuals undergo rigorous training and initiations to prepare themselves for their sacred role. They acquire knowledge of ancient rituals, medicinal herbs, and spiritual practices, allowing them to serve as healers, seers, and guides. The characteristics of shamans often include exceptional communication with the spirit world through dreams, visions, or altered states of consciousness induced by rituals or natural substances. Their immense wisdom and insights into the spiritual realm make them crucial figures in the Mayan community, sought after for divination, healing, and spiritual guidance. (anchor link: history of the Orion constellation)
2. Connection with the Spiritual World
Shamans in Mayan mythology have an extraordinary connection with the spiritual world. They are deeply attuned to the energies and entities that exist beyond the physical realm. Through sacred rituals, trance-like states, and the use of herbal remedies, shamans commune with supernatural beings, ancestors, and deities. This connection allows them to access spiritual guidance, receive prophetic visions, and gain insights into the hidden aspects of reality. The Mayan shamans believe that the spiritual world is intricately intertwined with the physical world, and by bridging these realms, they can bring about healing, restoration, and balance. The connection with the spiritual world is the cornerstone of a shaman’s power and effectiveness. It provides them with the ability to understand the messages of the gods and spirits, interpret omens, and navigate the complex web of cosmic forces. This deep relationship with the spiritual realm empowers the shamans to serve as conduits of divine knowledge and to guide their communities towards spiritual enlightenment and well-being. (anchor link: intriguing history of the Cassiopeia constellation)
3. Rituals and Healing Practices
Shamans in Mayan mythology are renowned for their profound rituals and powerful healing practices. These rituals serve as a means of establishing a connection with the spiritual realm and harnessing its energies for the betterment of individuals and the community as a whole. One such ritual is the “Sacred Ceremony of the Four Directions.” In this ritual, the shaman invokes the forces of the four cardinal directions – north, south, east, and west – to create balance and harmony. Through the use of sacred herbs, chants, and dance, the shaman navigates through the spiritual realm, seeking guidance and healing for those in need. The Mayans also practiced “Soul Retrieval,” a therapeutic technique wherein the shaman would journey into the spirit world to locate and retrieve lost or fragmented souls of individuals who have experienced trauma or illness. This ritualistic healing practice aims to restore wholeness and spiritual equilibrium. Additionally, the “Sweat Lodge Ceremony” played a vital role in purifying the mind, body, and spirit. Participants would enter a small enclosed space, symbolizing the womb of Mother Earth, to cleanse themselves through intense heat and steam. These rituals and healing practices demonstrate the shaman’s ability to tap into spiritual forces, address physical and emotional afflictions, and restore harmony within individuals and the community.
Mayan shamans utilize a myriad of rituals and techniques to access the spiritual realms for guidance, healing, and restoration. Their practices are deeply rooted in ancient traditions and continue to hold significance and relevance in contemporary Mayan society.
Priests in Mayan Mythology
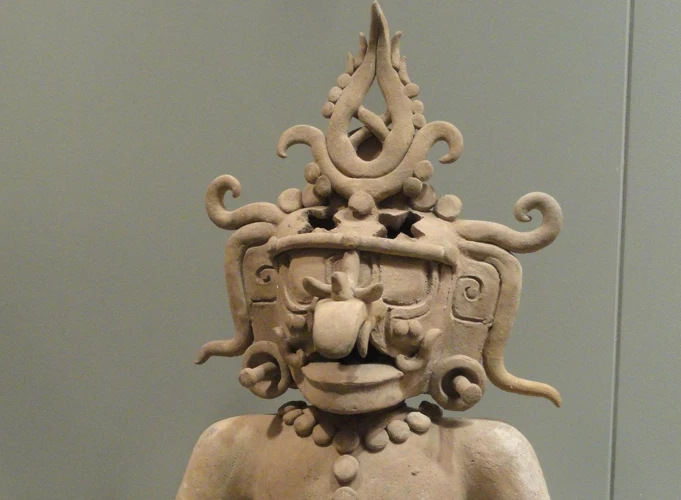

Priests hold a position of great importance within the intricate tapestry of Mayan mythology. As divinely appointed individuals, they bear the responsibility of conducting religious ceremonies and maintaining the delicate balance between mortals and deities. The role of priests transcends mere rituals and offerings; they are considered as intermediaries between the human and divine realms. Through elaborate ceremonies and sacrifices, priests strive to appease the powerful Mayan gods and ensure the prosperity and well-being of their society. These esteemed figures wield significant power and influence, representing the conduit through which the wishes and desires of the gods are communicated. Their knowledge of the sacred texts, rituals, and cosmology allows them to guide the people in aligning their lives with the divine will. The role of priests in Mayan mythology is paramount, reflecting the deep-seated religious beliefs and practices that shaped the cultural and spiritual fabric of the Mayan civilization.
1. The Role and Responsibilities of Priests
– Priests in Mayan mythology hold a position of immense importance and responsibility within the society. Their role goes beyond serving as religious leaders; they are regarded as the mediators between the mortal realm and the realm of the gods. Their primary duty is to perform rituals and ceremonies to honor and appease the deities worshipped by the Mayan people.
– The responsibilities of priests extend to the administration of religious institutions, such as temples and sacred sites. They oversee the maintenance of these sacred spaces and ensure that the proper rituals and offerings are carried out. Additionally, priests are responsible for preserving and interpreting sacred texts and mythology, passing down the knowledge and wisdom of the Mayan gods to future generations.
– Education and training form an integral part of a priest’s role. They undergo rigorous spiritual and intellectual training to gain a deep understanding of the rituals, ceremonies, and religious practices specific to Mayan mythology. This extensive knowledge allows them to lead and guide the community in matters of spirituality, provide counsel, and offer insights into cosmic principles.
– Priests are also tasked with forecasting future events and interpreting cosmic events. They observe celestial phenomena, such as solar and lunar eclipses, and interpret them as omens or messages from the gods. By interpreting these signs, priests provide guidance on matters of governance, agriculture, warfare, and other important aspects of Mayan society.
– The authority and influence wielded by priests in Mayan society are significant. They often hold positions of power within the hierarchy, advising rulers and acting as spiritual advisors to kings and nobles. Their ability to connect with the divine realm and their knowledge of the gods make them indispensable in matters of governance, ensuring the prosperity and well-being of the community.
The role and responsibilities of priests in Mayan mythology encompass spiritual leadership, preservation of traditions, education, interpretation, divination, and guidance in matters of governance. Their indispensable presence in the society and their connection to the divine realm establish them as pillars of strength and wisdom in the Mayan culture.
2. Ritualistic Ceremonies and Offerings
Ritualistic ceremonies and offerings hold a central place in the practices of Mayan priests. These ceremonies serve as conduits for communication between the mortal realm and the realm of the gods. Priests are responsible for organizing and conducting these elaborate rituals, which are often performed with precision and reverence. The ceremonies may involve various aspects such as dance, music, chanting, and the burning of incense. These elements are carefully chosen to create a sacred ambiance and to invoke the presence of the deities. Priests also play a pivotal role in offering sacrifices, which may include food, flowers, or even precious objects. These offerings are provided as gifts to the gods, expressing gratitude, seeking blessings, and appeasing the divine powers. Through the intricate choreography of the ceremonies and the careful selection of offerings, priests aim to maintain harmony and ensure the favor of the gods in the Mayan world. (No relevant link to insert.)
3. Power and Influence in Mayan Society
The power and influence of shamans and priests in Mayan society cannot be overstated. In the case of priests, their role as intermediaries between the gods and the people grants them immense authority. They are responsible for performing religious ceremonies, making sacrifices, and maintaining the connection between the mortal realm and the divine. Through their actions, priests ensure the prosperity and well-being of the community. Their words and blessings are considered sacred, and they often advise rulers on matters of governance and decision-making. Priests hold a esteemed place in society, their wisdom and guidance sought after by both the ruling elite and the common people.
Shamans, on the other hand, derive their power and influence from their ability to communicate with the spirits and access the supernatural. The Mayans believe that shamans possess a direct connection with the spiritual world, granting them the authority and knowledge to heal the sick, drive away evil spirits, and provide spiritual guidance. Their role as healers and spiritual mediators gives them a significant position of power within the community. People turn to shamans for a myriad of reasons, seeking solace, protection, and guidance in various aspects of life.
Both shamans and priests exert a considerable influence over the beliefs, practices, and values of the Mayan people. Their words and actions shape the religious and spiritual landscape, providing a moral compass for the community. The power they hold extends beyond the spiritual realm, influencing social, cultural, and even political matters. Both individuals and communal decisions are often guided by the teachings and recommendations of these revered figures. Their roles as leaders and advisors illustrate the profound impact they have in shaping the course of Mayan society as a whole. The power and influence of shamans and priests in Mayan society are an intrinsic part of their rich and complex mythology, permeating all aspects of life.
Shamans and Priests: Similarities and Differences

Shamans and priests in Mayan mythology share some similarities in their spiritual roles, yet they also have distinct attributes and duties. Both shamans and priests serve as conduits between the human and divine realms, acting as mediators and interpreters of spiritual guidance. They both conduct rituals and ceremonies, utilizing various tools and symbols to establish a connection with the supernatural. However, there are significant differences between the two. Shamans are typically chosen by spiritual forces and possess inherent mystical abilities, whereas priests are appointed by the ruling class and undergo rigorous training. Shamans focus on personal healing and guidance, often working on an individual level, while priests primarily perform religious duties for the community and the ruling elite. Shamans often engage in ecstatic trance states and visionary experiences to commune with spirits, while priests adhere to more formalized religious practices and offer sacrifices to appease the gods. Despite these contrasts, both shamans and priests hold immense spiritual authority and are indispensable in upholding the spiritual and cultural fabric of the Mayan society.
1. Overlapping Spiritual Roles
The Mayan mythology showcases a fascinating aspect of the shamans and priests’ roles – their overlapping spiritual responsibilities. While there are distinct differences between the two, they also share certain commonalities in their duties and contributions to Mayan society.
The Shaman’s Overlapping Spiritual Roles:
1. Ritualistic Performances: Both shamans and priests engage in elaborate ritualistic performances to commune with the spirits and deities. While priests often conduct these ceremonies in public temples, shamans perform rituals in more intimate settings, such as homes or sacred natural spaces.
2. Spiritual Guidance: Shamans and priests alike provide spiritual guidance to individuals and the community. They offer advice, interpretations, and solutions to spiritual dilemmas or challenges faced by the people. Both figures play a vital role in helping individuals navigate the complexities of the spirit world.
3. Healing Practices: Shamans and priests possess the power to heal both physical and spiritual ailments. Shamans use sacred plants, rituals, and energy manipulation, while priests often employ prayer, offerings, and sacred objects to facilitate healing.
4. Divination: The ability to see beyond the material world and foretell events is a shared skill of shamans and priests. Through various techniques such as scrying, dream interpretation, or the reading of omens, they provide insights into the future and seek guidance from the spiritual realm.
5. Connection to Nature: Both shamans and priests acknowledge the sacredness of nature and its connection to the divine. They perform rituals and ceremonies to honor and communicate with the natural elements, seeking harmony and balance between the human and spiritual realms.
The unique attributes of shamanism:
– Shamans often possess innate spiritual abilities, which are sometimes inherited or acquired through intense training and initiation.
– Shamans are known for their visionary experiences, where they journey into different realms of consciousness to gain knowledge, guidance, and power.
– They often serve as intermediaries between the human world and the realm of spirits, bridging the gap between the two through their unique abilities and rituals.
The distinctive attributes of priesthood:
– Priests hold formal positions within the religious hierarchy of Mayan society, often ordained through specific rituals and ceremonies.
– They are responsible for maintaining the temples and conducting public ceremonies, ensuring proper adherence to religious practices and protocols.
– Priests act as mediators between the people and the gods, offering prayers, sacrifices, and ceremonial offerings on behalf of the community.
While shamans and priests in Mayan mythology have different roles and methods, they share common ground in their spiritual practices and contributions to the Mayan society. Their overlapping spiritual roles demonstrate the intricate web of beliefs and rituals that shape the rich tapestry of Mayan mythology.
2. Distinctive Attributes and Duties
In Mayan mythology, both shamans and priests possess unique attributes and fulfill distinct duties within their respective roles.
Shamans:
1. Intuitive Abilities: Shamans are known for their heightened intuition and ability to perceive the spiritual realm. They possess a deep understanding of the natural world and connect with various spiritual entities, including deities, ancestors, and animal spirits.
2. Healing Practices: A prominent aspect of the shaman’s duty is healing. They employ a variety of techniques such as herbal medicine, energy work, and ritualistic practices to restore physical, emotional, and spiritual ailments. By communing with spirits and tapping into the unseen energies, shamans bring balance and harmony to individuals and communities.
3. Cosmic Guidance: Shamans interpret celestial patterns, such as the movement of stars and planets, to provide insights and guidance to the community. They observe the cosmos to predict favorable times for important events and ceremonies, ensuring the alignment of human activities with cosmic energies.
Priests:
1. Ritualistic Ceremonies: Priests take center stage in performing religious ceremonies and rituals in Mayan society. They meticulously follow ancient traditions, offering sacrifices and conducting prayers to appease and communicate with the gods. Through these rituals, they aim to maintain harmony in the earthly realm and seek divine blessings.
2. Keeper of Sacred Knowledge: Priests are the custodians of sacred texts, historical records, and profound spiritual knowledge. They preserve and pass down this wisdom from one generation to another, ensuring the longevity of Mayan traditions and beliefs.
3. Social Advisors: Beyond their religious roles, priests hold influence and serve as trusted advisors to rulers and community leaders. Their counsel is sought in matters of governance, warfare, agriculture, and other important aspects of Mayan society. They play a pivotal role in shaping the political, social, and cultural landscape of the Mayan civilization.
The distinctive attributes and duties of shamans and priests contribute to the intricate tapestry of Mayan mythology, strengthening the connection between the mortal realm and the divine forces that govern it.
The Influence of Shamans and Priests in Mayan Society
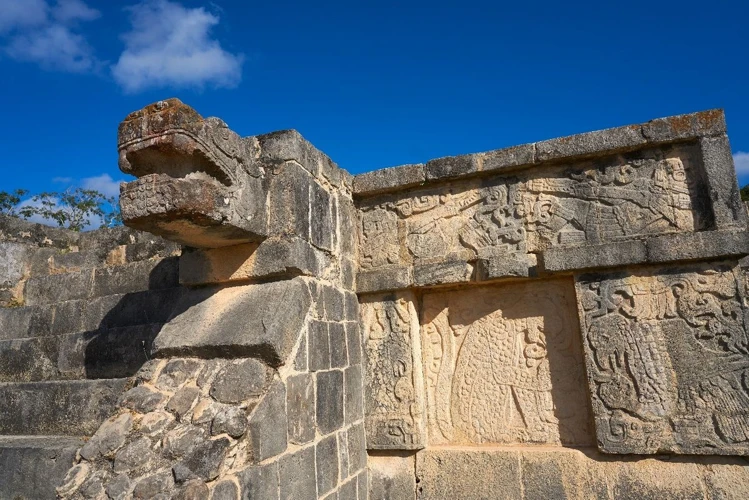

The influence of shamans and priests in Mayan society is profound and far-reaching, touching upon various aspects of social, cultural, and religious life. Both shamans and priests hold significant roles within their respective communities. Shamans, with their connection to the spiritual world, play a vital part in guiding individuals and communities through important decisions and providing healing and spiritual guidance. Through their rituals and practices, they foster a sense of unity and balance within the Mayan society. On the other hand, priests wield considerable power and influence in conducting religious ceremonies and making offerings to the gods. They are the mediators between the human and divine realms, ensuring divine favor and protection for the Mayan people. The presence of shamans and priests in Mayan society strengthens the belief system, reinforces cultural values, and serves as a unifying force among the people. Their profound impact extends beyond the spiritual realm to shaping the governance and social structures of the Mayan civilization.
The social and cultural significance of shamans and priests in Mayan society cannot be overstated. These revered figures hold important roles that extend beyond the religious realm. In the social context, shamans and priests serve as spiritual guides and advisors to individuals and communities. They offer wisdom, counsel, and healing, addressing not just physical ailments but also emotional and spiritual imbalances. Their presence and influence contribute to the cohesion and well-being of the community as a whole. Additionally, shamans and priests play a vital role in upholding Mayan cultural traditions and customs. They preserve and pass down ancestral knowledge, ensuring that the ancient beliefs, rituals, and practices are perpetuated through generations. Their rituals and ceremonies are intricately woven into the fabric of Mayan life, marking important milestones such as births, marriages, and agricultural cycles. The existence and involvement of shamans and priests in Mayan society demonstrate the deep-rooted connection between spirituality, community, and cultural identity.
2. Religious Practices and Belief System
Religion holds a paramount position in Mayan society, and the religious practices and belief system deeply shape the day-to-day lives of the people. The Mayans had a complex pantheon of gods and goddesses, each governing different aspects of the natural world and human existence. The priests, as the intermediaries between the mortal realm and the divine, played a crucial role in upholding and interpreting the religious practices.
One prominent religious practice of the Mayans was the performance of elaborate ceremonies and rituals. These ceremonies were often held in sacred temples or open plazas, involving offerings, sacrifices, music, dance, and prayer. The priests meticulously followed a prescribed ritualistic framework, ensuring that each action was performed with great precision and adherence to tradition.
One of the central beliefs in the Mayan religious system was the concept of cosmology, the understanding of the universe and its interconnectedness with human life. The Mayans believed that celestial bodies such as the sun, moon, and stars held great significance and were directly linked to their deities. Astrology played a vital role, with priests studying celestial movements, conducting observations, and interpreting celestial events to uncover divine messages and guidance for the people.
The Mayans also had a strong belief in the cyclical nature of time. They constructed complex calendars that intertwined various astronomical cycles with religious observances and important societal events. The priests were responsible for maintaining, interpreting, and forecasting events according to these calendars. It was their duty to assess the auspicious times for agricultural activities, religious ceremonies, warfare, and even matters of governance.
It is worth noting that the religious practices and belief system of the Mayans extended beyond the realm of priests. The entire community actively participated in religious ceremonies, demonstrating their collective devotion and commitment to their deities. People made offerings, performed rituals in their homes, and visited sacred sites to seek blessings, healing, and divine intervention in their lives.
The religious practices and belief system of the Mayans played an integral role in their society. It was through these practices that the people sought to maintain harmony with the divine, ensure the well-being of their community, and navigate the cyclical nature of time. The priests, as custodians of these practices, held immense power and influence in upholding and interpreting the religious traditions that shaped the fabric of Mayan life. Their guidance and rituals not only fostered a spiritual connection but also provided a sense of purpose and direction for the Mayan people.
3. Impact on Mayan Governance
Shamans and priests had a significant impact on Mayan governance, influencing the political and social structure of the civilization. As key spiritual leaders, their opinions and guidance were sought after by rulers and decision-makers. The Mayan society believed that the divine realm directly influenced their mundane world, and the shamans and priests acted as the conduits for communication with the gods. They were often consulted on matters of state, such as war, territorial expansion, and agricultural practices. The insights provided by the shamans and priests were considered vital in making important decisions that affected the well-being and prosperity of the Mayan people. Additionally, these spiritual figures played a crucial role in maintaining social order and stability by enforcing religious laws and rituals. Their presence in the governing process helped legitimize the authority and decisions of the rulers, as they were seen as the connection between the mortal realm and the divine. Through their influence, shamans and priests held immense power and maintained a delicate balance between the spiritual and political realms. Their impact on Mayan governance ensured that the society operated in accordance with religious principles and beliefs, establishing a strong link between the divine and earthly spheres.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the role of shamans and priests in Mayan mythology holds immense significance within the Mayan society. These revered figures serve as spiritual leaders, connecting the mortal realm with the divine. Shamans, with their unique abilities and connection to the spiritual world, provide guidance, healing, and act as intermediaries between humans and spirits. On the other hand, priests hold prestigious responsibilities in conducting religious ceremonies and making offerings to appease the gods. While there are overlapping spiritual roles between shamans and priests, they also possess distinctive attributes and duties. Together, they shape the religious practices, belief system, and cultural fabric of the Mayan people. Their influence extends beyond the realms of spirituality, impacting the social structure and governance of Mayan society. The roles of shamans and priests are not only essential for the well-being and prosperity of the individual, but also for the cohesiveness and harmony of the entire Mayan community. Through their rituals, teachings, and connections to the spiritual world, shamans and priests continue to serve as pillars of strength and wisdom in the rich tapestry of Mayan mythology.
Frequently Asked Questions

1. What is the role of shamans in Mayan mythology?
Shamans in Mayan mythology are spiritual leaders who serve as intermediaries between the human and supernatural realms. They provide guidance, healing, and divination services, channeling cosmic forces and tapping into ancestral wisdom.
2. How are shamans different from priests in Mayan mythology?
While shamans focus on spiritual healing and guidance, priests in Mayan mythology primarily conduct religious ceremonies and offer sacrifices to appease the gods. Shamans have a more personal and individualized approach, while priests hold a more formal role within the religious hierarchy.
3. What rituals and practices do Mayan shamans perform?
Mayan shamans engage in a variety of rituals and practices, including trance-like journeys, purification ceremonies, and the interpretation of signs and symbols. They often use medicinal plants, chants, and drumming to enter altered states of consciousness and connect with the spirit world.
4. Who can become a shaman in Mayan culture?
In Mayan culture, becoming a shaman is typically an innate calling rather than a chosen profession. Individuals may be identified as potential shamans through dreams, visions, or by exhibiting natural spiritual abilities. Training involves apprenticeship under experienced shamans.
5. What are the responsibilities of Mayan priests?
Mayan priests hold the responsibility of conducting religious ceremonies, overseeing temple rituals, and making offerings to the gods. They interpret celestial events, such as eclipses, as omens and use their knowledge to guide the community in religious matters.
6. How do Mayan priests gain their knowledge and training?
Mayan priests undergo rigorous training within established religious institutions. They learn ancient rituals, calendars, and the complex symbolism of Mayan cosmology. This knowledge is often passed down through generations.
7. What is the significance of shamans and priests in Mayan society?
Shamans and priests hold immense cultural and religious significance in Mayan society. They are the spiritual leaders who maintain the connection between the physical and spiritual realms, ensuring the well-being of the community and upholding important traditions and rituals.
8. How do Mayan shamans and priests influence governance?
Mayan shamans and priests play a role in governance by advising rulers and offering spiritual guidance for decision-making. They provide insights and interpretations of celestial events, helping to shape the direction of governance and maintaining the balance between the earthly and divine realms.
9. How does Mayan mythology view the power of shamans and priests?
In Mayan mythology, the power of shamans and priests is seen as essential for maintaining harmony and balance in the universe. They are believed to possess a direct connection with the gods and carry the responsibility of communicating with them on behalf of the community.
10. How does the role of shamans and priests in Mayan mythology continue to influence modern Mayan culture?
The role of shamans and priests continues to hold significance in modern Mayan culture. Many Mayan communities still rely on their spiritual guidance and healing practices, integrating ancient traditions into contemporary life, and honoring the wisdom passed down through generations.
References
Frequently Asked Questions

1. What is the role of shamans in Mayan mythology?
Shamans play a vital role in Mayan mythology as spiritual intermediaries between the human and spiritual realms. They act as healers, diviners, and ritual leaders.
2. What are the characteristics of Mayan shamans?
Mayan shamans possess unique spiritual abilities and often exhibit traits such as visionary experiences, extensive knowledge of sacred rituals and natural remedies, and the ability to communicate with spirits.
3. How do shamans connect with the spiritual world in Mayan mythology?
Shamans connect with the spiritual world through various means, including trance-like states induced by chanting, drumming, and the use of hallucinogenic plants. They also communicate with ancestral spirits, gods, and other supernatural entities.
4. What kinds of rituals and healing practices do Mayan shamans perform?
Mayan shamans perform a range of rituals and healing practices, which may include purification ceremonies, offerings to deities, energy cleansing, herbal medicine treatments, and soul retrievals to restore balance and well-being.
5. What is the role and responsibilities of priests in Mayan mythology?
Priests in Mayan mythology hold positions of religious authority and are responsible for carrying out ceremonies, overseeing temple rituals, interpreting divine will, and ensuring the spiritual well-being of the community.
6. What are the ritualistic ceremonies and offerings performed by Mayan priests?
Mayan priests conduct elaborate rituals and ceremonies that involve offerings of food, drink, incense, and other precious items to honor the gods and maintain the cosmic order. These ceremonies take place in grand temple complexes and sacred sites.
7. How do shamans and priests differ in Mayan mythology?
While both shamans and priests hold spiritual roles, shamans focus more on individual healing and divination, whereas priests are primarily concerned with community rituals, governance, and upholding religious traditions.
8. What are some overlapping spiritual roles of shamans and priests in Mayan mythology?
Both shamans and priests have overlapping spiritual roles, such as performing rituals, interpreting omens, communicating with deities, and guiding individuals and communities in matters of spiritual significance.
9. How do shamans and priests influence Mayan society?
Shamans and priests hold significant influence in Mayan society. They contribute to the social and cultural fabric by guiding religious practices, offering moral guidance, and playing crucial roles in governance and decision-making processes.
10. What is the impact of shamans and priests on Mayan governance?
Shamans and priests in Mayan society often have a say in governance matters as they are considered spiritual advisors to rulers and leaders. Their involvement helps integrate religious beliefs, divine guidance, and community welfare into the decision-making process.







