Dragons have long been a fascinating and enigmatic part of Chinese mythology and culture, captivating the imagination of people around the world. These majestic creatures hold a prominent role in Chinese folklore and are deeply ingrained in the country’s history and traditions. From symbols of power and good fortune to guardians and protectors, dragons have left an indelible mark on Chinese society. They are celebrated in art, architecture, festivals, and even tattoos. Join us on a journey to explore the mesmerizing role of dragons in Chinese mythology and culture, delving into their significance, legends, various types, artistic representations, and their enduring influence in modern Chinese society.
Contents
- The Significance of Dragons
- Dragon Legends and Stories
- Different Types of Dragons
- Dragons in Chinese Art and Architecture
- Dragons in Chinese Festivals and Celebrations
- The Influence of Dragons in Modern Chinese Culture
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- What role do dragons play in Chinese mythology?
- Are dragons considered good or evil in Chinese culture?
- What is the symbolism behind dragons in Chinese culture?
- Do dragons appear in Chinese art and architecture?
- What are the different types of dragons in Chinese mythology?
- Are there any festivals in China dedicated to dragons?
- Can dragons be found in other cultures’ mythology?
- Are there any real-life creatures that inspired the concept of dragons?
- What is the significance of dragons in Chinese astrology?
- How are dragons represented in modern Chinese culture?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the significance of dragons in Chinese culture?
- What role do dragons play in Chinese mythology?
- Who are the Four Dragon Kings in Chinese mythology?
- What is the legend of the Dragon and the Pearl?
- What are Long Dragons?
- What are Winged Dragons?
- What is the Dragon Boat Festival?
- What is the significance of dragon tattoos in Chinese culture?
- How are dragons featured in Chinese New Year celebrations?
- How have dragons influenced modern Chinese culture?
- References
- Read More
The Significance of Dragons

Dragons hold immense significance in Chinese mythology and culture, embodying power, wisdom, and good fortune. They are revered as celestial beings and symbols of imperial authority. In traditional Chinese beliefs, dragons are believed to bring abundance and prosperity, making them a popular motif in various forms of art, architecture, and decorative objects. Their association with water makes them connected to the life-giving forces of rainfall and rivers, further enhancing their importance as bringers of fertility and agricultural abundance. Dragons are also considered guardians and protectors, watching over homes, temples, and other sacred spaces. In Chinese culture, dragons are deeply intertwined with the concept of yin and yang, representing the balance of cosmic forces. This duality can be seen in the dragon’s features, with the long body symbolizing the yang energy and the scales representing the yin energy. The significance of dragons resonates throughout Chinese history and continues to shape the cultural fabric of the nation to this day.
Symbols of Power and Good Fortune
Dragons are widely recognized as symbols of power and good fortune in Chinese culture. They are regarded as the highest-ranking and most auspicious of mythical creatures. The dragon’s association with power stems from its depiction as a fearsome creature capable of controlling the elements. Emperors in ancient China considered themselves to be the descendants of dragons and believed that by using dragon imagery, they could legitimize their authority and reinforce their rule. Dragons were often depicted on imperial robes, thrones, and other imperial regalia, symbolizing the emperor’s divine right to rule. The dragon’s ability to bring good fortune and blessings is believed to attract prosperity and success. Many Chinese businesses and individuals incorporate dragon imagery into their logos, hoping to harness the positive energy and luck associated with these mythical beings. Dragons also play a role in Chinese astrology and are one of the twelve animals in the Chinese zodiac. Those born in the Year of the Dragon are believed to be strong, confident, and charismatic, further emphasizing the auspicious nature of dragons in Chinese culture.
Guardians and Protectors
In Chinese mythology, dragons are revered as guardians and protectors, playing a vital role in safeguarding important spaces and individuals. These divine creatures are believed to possess extraordinary powers and have the ability to ward off evil spirits. Dragons are often depicted as guardians of temples, palaces, and other sacred sites, with their images intricately carved into architectural structures as a sign of protection. They are also associated with the protection of emperors, symbolizing their divine authority and right to rule. The Dragon Throne, for example, is an iconic symbol of imperial power in Chinese history. Dragons are believed to bring blessings and fortune to those under their watchful gaze, shielding them from harm and misfortune. The celestial status of dragons contributes to their role as guardians, as they are seen as intermediaries between heaven and earth, ensuring harmony and balance. Their presence in Chinese culture reminds people of the need to protect and preserve the sacred and valuable aspects of life. The enduring belief in the protective nature of dragons is beautifully represented in various art forms and continues to be honored in Chinese society.
Dragon Legends and Stories

Dragon legends and stories are a prominent aspect of Chinese mythology, captivating the imaginations of generations. One of the well-known dragon legends is that of the Four Dragon Kings (龙王), who are considered the rulers of the four seas surrounding China. Each dragon king is associated with a cardinal direction and has the power to control the weather and rainfall. They are believed to reside in magnificent underwater palaces and are revered as benevolent beings.
Another popular legend revolves around the Dragon and the Pearl. In this story, a dragon is said to possess a pearl that symbolizes wisdom and enlightenment. The dragon fiercely guards this precious pearl, representing its treasured knowledge. This tale emphasizes the dragon’s role as a guardian and protector of valuable treasures.
In addition to these legends, countless stories depict dragons as either fearsome creatures or benevolent beings that interact with humans. These stories highlight the unique characteristics of dragons, including their ability to shape-shift, breathe fire, and fly. Dragons are often portrayed as wise creatures who impart wisdom and guidance to those who seek them.
Dragon legends and stories not only entertain, but they also reflect the deep-rooted beliefs and values of Chinese culture. They provide moral lessons, inspire creativity, and instill a sense of awe and reverence for these majestic creatures. Through these stories, dragons continue to hold a significant place in the hearts and minds of the Chinese people.
Four Dragon Kings
The Four Dragon Kings, also known as the Four Heavenly Kings, are legendary creatures in Chinese mythology. Each of these powerful dragons rules over a cardinal direction and is associated with specific elements and seasons. These divine beings are often depicted as protectors and guardians, safeguarding the world against evil spirits and natural disasters.
The first Dragon King, Ao Guang, rules over the East Sea and represents spring and the element of wood. He is often depicted holding a serpent-like weapon called a zhangba snake spear. The second Dragon King, Ao Qin, governs the South Sea and symbolizes summer and the element of fire. He is often portrayed holding the Pearl of Power, a symbol of abundance and strength.
The third Dragon King, Ao Run, presides over the West Sea and is associated with autumn and the element of metal. He is often shown holding a sword and is considered a deity of rainfall, ensuring a bountiful harvest. The fourth Dragon King, Ao Shun, rules the North Sea and represents winter and the element of water. He is often depicted holding a well bucket, symbolizing his ability to control the waters.
Together, the Four Dragon Kings form a powerful alliance, protecting the celestial order and maintaining balance in the natural world. Their influence extends beyond mythology and can be seen in various cultural expressions, such as artworks, temple decorations, and even in contemporary festivals. The tales of the Four Dragon Kings continue to inspire awe and reverence, reminding us of the rich mythological traditions of Chinese culture.
The Dragon and the Pearl
In Chinese mythology, the story of the Dragon and the Pearl is a captivating tale that further highlights the significance of dragons. According to the legend, dragons are known for their insatiable desire for wisdom and knowledge. They are believed to possess a precious pearl, often referred to as the Dragon’s Pearl or the Dragon’s Ball. This pearl is said to hold immense power and represents spiritual enlightenment or the ultimate truth. In many depictions, the dragon is shown chasing or holding the pearl in its claws or mouth., symbolizing the pursuit of wisdom and enlightenment. The pearl is associated with cosmic energy and the harmony of the universe. It is believed that by obtaining the pearl, the dragon gains ultimate wisdom and control over the elements. The Dragon and the Pearl are often depicted together in various forms of Chinese art, including paintings, sculptures, and embroidery. This symbolism is a testament to the Chinese reverence for knowledge and the eternal quest for wisdom that dragons embody.
Different Types of Dragons

Dragons in Chinese mythology come in various forms, each with its own distinctive characteristics. The two main types of dragons depicted in Chinese culture are the Long Dragons and the Winged Dragons.
1. Long Dragons: These serpentine creatures are the most commonly depicted dragons in Chinese art and folklore. Long Dragons are known for their elongated bodies, typically with four legs and no wings. They are considered the rulers of rivers, lakes, and seas, and are associated with the element of water. Long Dragons have a powerful presence and are believed to bring abundant rainfall, ensuring a bountiful harvest. In Chinese mythology, the Dragon King, also known as the Long Wang, is the ruler of all the water bodies and is often depicted with a human-like form wearing a crown. This type of dragon represents wisdom, strength, and good fortune.
2. Winged Dragons: Unlike the Long Dragons, Winged Dragons possess both wings and legs. These dragons are believed to have the ability to soar through the sky and are associated with the element of air. Winged Dragons symbolize freedom, agility, and protection. They are often depicted on rooftops and as guardians of important buildings and temples. Winged Dragons are also seen in ancient Chinese literature and are considered celestial creatures, carrying messages between the mortal realm and the divine. Their presence is believed to bring harmony and auspicious energy.
It is fascinating to explore the diverse representations of dragons in Chinese mythology and how each type holds its own symbolism and significance. Whether it be the majestic Long Dragons ruling the waters or the mythical Winged Dragons soaring through the skies, these creatures continue to capture the imagination and awe of people around the world.
Long Dragons
Long dragons, known as “long” or “lung” in Chinese, are one of the most iconic and recognizable types of dragons in Chinese mythology and culture. These dragons are typically depicted as serpentine creatures with elongated bodies covered in scales. They are believed to reside in bodies of water, such as rivers, lakes, and oceans. Long dragons are associated with auspicious qualities, representing power, strength, and good luck. They are often depicted with a pearl, said to have the power to grant wishes, in their mouths or claws. The image of the dragon chasing or holding the pearl is a common motif in Chinese art and artifacts, symbolizing the pursuit of knowledge, enlightenment, and fulfillment of desires. In Chinese folklore, it is believed that long dragons have control over weather phenomena, particularly rainfall, making them vital for agricultural prosperity. The dragon dance, a popular cultural performance during festivities, often features a long dragon puppet manipulated by a team of performers. Through its graceful and dynamic movements, the dragon dance celebrates the spirit of the long dragon and brings blessings of good fortune and prosperity to the community. The long dragon continues to be a revered and cherished symbol in Chinese culture, epitomizing the majestic and mythical qualities associated with dragons. Ophiuchus constellation
Winged Dragons
Winged dragons, also known as “Feilong” in Chinese mythology, are a fascinating and distinct type of dragon. Unlike the traditional long-bodied dragons, winged dragons possess the ability to fly, making them an awe-inspiring symbol of power and freedom. These majestic creatures are often depicted with elongated bodies, fierce facial features, and large, bat-like wings. In Chinese culture, winged dragons represent the union of heaven and earth, combining the terrestrial power of dragons with the celestial realm. They are believed to possess tremendous strength and agility, capable of soaring through the skies and traversing vast distances. Winged dragons are often associated with the element of air and are believed to have control over the weather, particularly wind and storms. Their wings are seen as a representation of their celestial nature and their ability to transcend earthly limitations. In Chinese art and mythology, winged dragons are commonly depicted in various forms, such as sculptures, paintings, and even on architecture. They continue to capture the imagination of people with their majestic and otherworldly presence.
Dragons in Chinese Art and Architecture

Dragons have left an indelible mark on Chinese art and architecture, with their powerful and majestic presence adorning countless masterpieces. In traditional Chinese paintings, dragons are often depicted as sinuous creatures, with swirling bodies, sharp claws, and fierce expressions. They are often painted in vibrant colors, representing their mythical nature and fiery energy. These artworks showcase the Chinese belief in the auspicious power of dragons, with their presence conveying good fortune and prosperity. The dragon motif can also be found in architectural designs, particularly on rooftops, where dragon-shaped tiles called “chiwen” are placed to ward off evil spirits and protect the building. Chinese palaces and temples are often adorned with intricately carved dragon sculptures, symbolizing the grandeur and majesty of the structures. Dragons are also prominently featured in the famous Dragon and Phoenix motif, where the dragon represents the Yang energy and the phoenix represents the Yin energy, symbolizing harmony and unity. From intricate brushwork to stunning architectural details, dragons continue to inspire and influence Chinese art and architecture, serving as a testament to their enduring significance in the cultural landscape.
Dragon Boat Festival
Dragon Boat Festival, also known as Duanwu Festival, is a vibrant and lively celebration that pays homage to dragons in Chinese culture. This annual event is held on the fifth day of the fifth lunar month, usually falling in June. The festival has historical roots dating back over 2,000 years and is steeped in legend and folklore. One of the highlights of the Dragon Boat Festival is the exhilarating dragon boat races, where teams paddle in long, narrow boats adorned with intricately designed dragon heads and tails. The festival is accompanied by drumming and cheering as participants compete to cross the finish line first. The origins of this tradition can be traced back to the legend of Qu Yuan, a patriotic poet and statesman of ancient China. Qu Yuan drowned himself in a river due to political turmoil, and the local people raced their boats to find and rescue him. Today, dragon boat races symbolize the spirit of teamwork, perseverance, and the attempt to ward off evil spirits. It is also a time when people consume delicious sticky rice dumplings, known as zongzi, which are wrapped in bamboo leaves and filled with various ingredients. The Dragon Boat Festival is a lively and culturally significant event that showcases the deep-rooted connection between dragons and the Chinese people. Whether racing dragon boats or enjoying zongzi, this festival is a celebration of Chinese traditions and the enduring symbolism of dragons.
Dragon and Phoenix
The Dragon and Phoenix are revered creatures in Chinese mythology and are often depicted together as a symbol of balance, harmony, and unity. The Dragon represents the yang energy, symbolizing power, strength, and good fortune, while the Phoenix embodies the yin energy associated with grace, elegance, and prosperity. The union of these two mythical creatures is seen as a representation of marital bliss and the perfect balance between masculine and feminine forces. In Chinese culture, the Dragon and Phoenix are often used as motifs in wedding decorations and gifts, symbolizing a harmonious and successful marriage. This pairing also signifies the Emperor and Empress in imperial contexts, representing their supreme authority and divine connection. The Dragon and Phoenix symbolism can be observed in various aspects of Chinese art and architecture, including intricate carvings, paintings, and sculptures. Their presence in Chinese folklore and culture highlights the deep-rooted belief in auspiciousness and the power of unity.
Dragons in Chinese Festivals and Celebrations
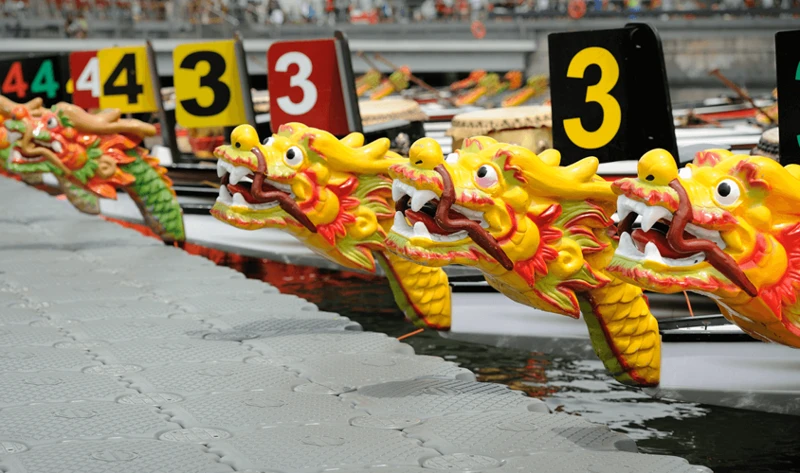

Dragons play a prominent role in Chinese festivals and celebrations, adding a touch of awe-inspiring spectacle and cultural richness. One of the most significant festivals where dragons take center stage is the Chinese New Year, also known as the Spring Festival. During this festive time, elaborate dragon dances are performed in the streets, accompanied by the rhythmic beating of drums and clashing cymbals. The dragon dance is believed to bring good luck and prosperity for the upcoming year. Another important celebration that features dragons is the Duanwu Festival, also known as the Dragon Boat Festival. This festival commemorates the ancient poet Qu Yuan and involves dragon boat races, where elaborately decorated boats resembling dragons race across rivers and lakes. These dragon boat races are not only a thrilling and competitive sport but also a way to pay homage to dragons and ensure their protection and blessings. Dragons in Chinese festivals and celebrations symbolize the spiritual connection between humans and these mythical creatures, fostering a sense of unity, cultural pride, and reverence for the awe-inspiring power they represent. Their presence adds an extra layer of enchantment and excitement to these joyous occasions, making them truly unforgettable experiences.
Chinese New Year
Chinese New Year, also known as Spring Festival, is one of the most important and festive celebrations in Chinese culture. It is a time when families come together to honor their ancestors and welcome the coming year with joy and auspicious customs. Dragons play a significant role in Chinese New Year celebrations. The dragon dance is a highlight of the festivities, with a vibrant and colorful dragon puppet accompanied by the rhythmic beats of drums and cymbals. The dragon, often constructed with a long flexible body that requires many dancers to manipulate, moves in a sinuous manner, believed to bring good luck and ward off evil spirits. The dragon dance is a symbol of unity, strength, and vibrant energy, and it is believed to bring prosperity and fortune for the upcoming year. The presence of dragons during Chinese New Year festivities adds an exciting and captivating element to the celebrations, captivating both young and old alike. There is a sense of anticipation and excitement as the dragon dances through the streets, bringing the community together in celebration. Chinese New Year is a time to embrace traditions and customs, where dragons take center stage and infuse the atmosphere with a sense of awe and wonder.
Duanwu Festival
The Duanwu Festival, also known as the Dragon Boat Festival, is a vibrant and exciting celebration in Chinese culture that takes place on the fifth day of the fifth lunar month. This festival has a rich history and is primarily associated with commemorating the poet and statesman Qu Yuan. During this festival, dragon boat races are held, where beautifully decorated long boats, shaped like dragons, glide through the water. These dragon boats are manned by teams of rowers who paddle in sync to the rhythm of beating drums. The festival is not only a thrilling sport but also a way to pay homage to Qu Yuan’s patriotic spirit. It is believed that the loud drumming and the racing of the dragon boats scare away evil spirits and bring good luck and protection to the participants. Another significant aspect of the Duanwu Festival is the consumption of Zongzi, sticky rice dumplings wrapped in bamboo leaves. These delicious treats are filled with various ingredients such as meats, beans, and nuts and are enjoyed by people of all ages during the festival. The Duanwu Festival is a time of lively festivities, cultural traditions, and the unity of communities as they come together to celebrate and honor their heritage.
The Influence of Dragons in Modern Chinese Culture

The influence of dragons in modern Chinese culture is undeniable, permeating various aspects of everyday life and celebrations. One prominent way that dragons are celebrated is through dragon dances and parades. These vibrant and energetic performances are often seen during important festivals and events, captivating audiences with their elaborate dragon costumes and synchronized movements. Dragon dances are believed to bring good luck and fortune, and they are a testament to the enduring cultural significance of dragons.
Dragons also play a significant role in Chinese tattoos. The intricate and detailed designs of dragon tattoos symbolize power, strength, and protection. Many people choose to ink themselves with these mythical creatures as a way to invoke the auspicious qualities associated with dragons. Dragon tattoos are considered not only a form of self-expression but also an homage to Chinese tradition and symbolism.
Dragons continue to inspire contemporary art and design in China. Modern artists are incorporating dragon motifs into their works, merging traditional symbolism with contemporary aesthetics. The imagery of dragons can be found in various mediums, including paintings, sculptures, and even digital art. These artistic representations serve as a reminder of the deep-rooted cultural heritage and the timeless allure of dragons in Chinese society.
In addition to art, dragons have made their way into popular culture and media. They are frequently depicted in movies, anime, and video games, both in China and globally. Their portrayal often reflects their traditional attributes of wisdom and power, captivating audiences and fueling the imagination of viewers.
The influence of dragons in modern Chinese culture is a testament to their enduring relevance and impact. They continue to symbolize strength, fortune, and the rich cultural heritage of China, spanning from ancient mythology to contemporary art and entertainment.
Dragon Dances and Parades
Dragon dances and parades are vibrant and festive celebrations that showcase the cultural significance of dragons in Chinese traditions. These colorful and lively performances are commonly seen during important festivals and celebrations such as Chinese New Year and other community events. The dragon dance involves a team of dancers who work together to manipulate a long and flexible dragon puppet using poles. The dragon’s movements are choreographed to the beat of traditional music, creating a captivating spectacle for onlookers. The dances often include elaborate formations, twists, and turns, symbolizing the dragon’s power and agility. Dragon dances are believed to bring good luck and fortune for the upcoming year, and it is customary for the dragon to visit businesses and homes to bestow blessings. Parades featuring these magnificent dragons are a highlight of many cultural festivities, with participants dressed in vibrant costumes and accompanied by drummers and other musical instruments. The dragon dance and parade are not only a visual spectacle but also an expression of community unity and pride. People gather along the streets to witness and participate in these events, fostering a sense of joy and togetherness. Dragon dances and parades are a cherished tradition that continues to captivate and inspire people of all ages, symbolizing the enduring influence and cultural significance of dragons in Chinese society.
Dragon Tattoos and Symbolism
Dragon tattoos hold deep symbolism in Chinese culture and are a popular choice for body art. These intricate designs often depict dragons with vibrant colors and detailed scales, symbolizing strength, power, and good fortune. The dragon is believed to possess supernatural abilities and is associated with protection and warding off evil spirits. Many people choose to get dragon tattoos as a way to tap into the auspicious energy that dragons represent. The body placement of the tattoo can also carry significance, with some individuals opting for the dragon to wrap around their arms to symbolize protection or having it placed on their back for a sense of inner strength. Dragon tattoos can be a way for individuals to honor their Chinese heritage or simply to embrace the mystique and allure of these mythical creatures. The artistry and symbolism of dragon tattoos make them a timeless choice for those seeking a meaningful and visually captivating form of self-expression.
Conclusion
In conclusion, dragons play a significant role in Chinese mythology and culture, serving as symbols of power, good fortune, and protection. Their presence can be felt in various aspects of Chinese society, from art and architecture to festivals and celebrations. The dragon’s association with positive attributes such as abundance, fertility, and imperial authority has made it a beloved and revered creature in Chinese folklore. The legends and stories surrounding dragons further exemplify their mythical status, captivating the imaginations of both young and old. Today, dragons continue to influence modern Chinese culture, with dragon dances and parades being a highlight of important celebrations like the Chinese New Year. Additionally, dragon tattoos have become popular symbols of strength and resilience. The enduring significance of dragons in Chinese mythology and culture serves as a testament to the deep-rooted beliefs and traditions that continue to shape the country’s identity. Through their majestic presence, dragons remain a source of inspiration and awe in the hearts of many, honoring a rich and vibrant cultural heritage.
Further Reading:
Frequently Asked Questions

What role do dragons play in Chinese mythology?
Dragons hold a significant role in Chinese mythology as celestial beings associated with power, wisdom, and good fortune. They are often depicted as protectors, bringers of abundance, and symbols of imperial authority.
Are dragons considered good or evil in Chinese culture?
In Chinese culture, dragons are generally revered as benevolent beings. They are seen as bringers of prosperity, fertility, and protection. They are not associated with evil or malevolence.
What is the symbolism behind dragons in Chinese culture?
Dragons symbolize various aspects in Chinese culture, including imperial power, wisdom, and the forces of nature such as rain and rivers. They also represent yin and yang, signifying the balance of cosmic energies.
Do dragons appear in Chinese art and architecture?
Absolutely! Dragons are a prevalent motif in Chinese art and architecture. They can be seen in paintings, sculptures, ceramics, and even on the roofs of traditional buildings, symbolizing protection and prosperity.
What are the different types of dragons in Chinese mythology?
Chinese mythology encompasses various types of dragons. Some of the most prominent ones include the long dragon, associated with water and rain, and the winged dragon, often depicted in a more aggressive and fierce manner.
Are there any festivals in China dedicated to dragons?
Yes, there are several festivals in China that celebrate dragons. The Dragon Boat Festival, held annually, features dragon boat races in rivers, symbolizing the reverence for this mythical creature. The Chinese New Year also incorporates dragon dances as part of its festivities.
Can dragons be found in other cultures’ mythology?
While dragons are prevalent in Chinese mythology, they can also be found in the mythologies of other cultures. However, the representations and symbolism associated with dragons may differ from one culture to another.
Are there any real-life creatures that inspired the concept of dragons?
The concept of dragons in Chinese mythology is not based on any specific real-life creature. Instead, dragons are a unique and fantastical creation that emerged from the rich imaginations of ancient Chinese culture.
What is the significance of dragons in Chinese astrology?
In Chinese astrology, dragons are one of the twelve animal signs that represent different personality traits and attributes. Those born in the Year of the Dragon are believed to possess qualities such as intelligence, luck, and a strong sense of leadership.
How are dragons represented in modern Chinese culture?
In modern Chinese culture, dragons continue to hold a significant place. They are depicted in popular media, such as movies and TV shows, and play a prominent role in traditional celebrations, including dragon dances during festivals.
References
Frequently Asked Questions

What is the significance of dragons in Chinese culture?
Dragons hold great significance in Chinese culture as symbols of power, good fortune, and protection.
What role do dragons play in Chinese mythology?
In Chinese mythology, dragons are seen as guardians and protectors. They are often associated with the elements, such as water, and are believed to bring rain and control natural forces.
Who are the Four Dragon Kings in Chinese mythology?
The Four Dragon Kings are powerful and influential deities in Chinese mythology. They are believed to have control over the seas and are responsible for the distribution of rain.
What is the legend of the Dragon and the Pearl?
The legend of the Dragon and the Pearl tells the story of a dragon who guards a precious pearl. The pearl represents wisdom, power, and spiritual enlightenment.
What are Long Dragons?
Long Dragons, or “Lóng” dragons, are traditional Chinese dragons known for their long serpentine bodies. They are often depicted as benevolent creatures associated with water and rain.
What are Winged Dragons?
Winged Dragons, or “Feilong,” are Chinese dragons depicted with wings. They are believed to have the ability to fly and are associated with the sky and celestial beings.
What is the Dragon Boat Festival?
The Dragon Boat Festival, also known as Duanwu Festival, is a traditional Chinese festival celebrated to honor the memory of the poet Qu Yuan. The festival features dragon boat races and the consumption of sticky rice dumplings.
What is the significance of dragon tattoos in Chinese culture?
Dragon tattoos hold significant symbolism in Chinese culture. They are believed to bring protection, strength, and good fortune to the wearer.
How are dragons featured in Chinese New Year celebrations?
Dragons are an integral part of Chinese New Year celebrations. Dragon dances are performed to ward off evil spirits and bring good luck for the upcoming year.
How have dragons influenced modern Chinese culture?
Dragons continue to play a significant role in modern Chinese culture. Dragon dances and parades are performed during festive occasions, and dragon motifs are commonly seen in art, architecture, and even tattoos.
References
- Dragons in Chinese Culture: Overview & Mythology
- Why the Dragon is Central to Chinese Culture | Season 4 – PBS







