The night sky has always fascinated and perplexed humanity throughout history. Ancient cultures looked up at the stars and sought to make sense of their patterns and movements. They observed constellations, or groups of stars that form recognizable shapes, and used them for both practical and mythical purposes. From ancient astronomy to navigation and mythology, constellations played a crucial role in shaping various aspects of human civilization. Let’s delve into the captivating world of constellations and explore their significance in ancient times and their enduring impact in the modern world.
Contents
- Ancient Astronomy
- Ancient Navigation
- Constellation Mythology
- Modern-Day Significance
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What is the significance of constellations in ancient astronomy?
- 2. How did ancient civilizations use constellations for navigation?
- 3. Did different ancient cultures have different constellations?
- 4. How did ancient cultures explain the origins of constellations?
- 5. What was the cultural significance of constellations in ancient times?
- 6. How do constellations continue to be relevant in modern astronomy research?
- 7. Can constellations be used for navigation in modern times?
- 8. How have constellations influenced cultural references in art and literature?
- 9. Can anyone spot constellations without using special tools?
- 10. Are constellations fixed or do they change over time?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is ancient astronomy?
- How did ancient civilizations map the night sky?
- Why were constellations culturally significant in ancient times?
- What is celestial navigation?
- How did ancient sailors use Polaris and other stars for navigation?
- What did ancient civilizations mean by “zoning the seas” in navigation?
- What is the significance of Greek mythology in constellation lore?
- How did ancient Egyptians incorporate constellations into their mythology?
- What is the role of Chinese mythology in constellation culture?
- How are constellations relevant in modern-day astronomy and navigation?
- References
- Read More
Ancient Astronomy
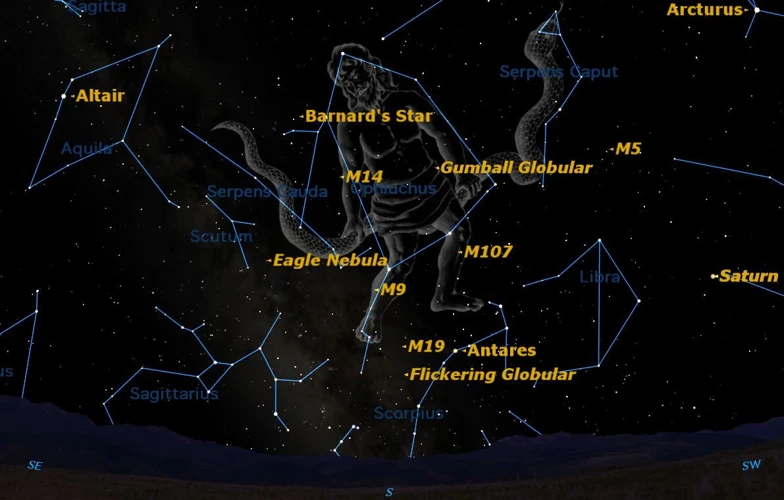
Ancient astronomy is a captivating field that unveils the wonders of the celestial realm as observed by our ancestors. Early observations of the night sky allowed ancient civilizations to track the movements of celestial bodies and gain insights into the changing seasons and navigation. They noticed patterns among the stars and identified constellations with unique names and shapes. Mapping the night sky was an essential aspect of ancient astronomy, as it enabled early astronomers to chart the positions of stars and develop methods for celestial navigation. These observations were not merely scientific pursuits; they held profound cultural significance as well. In ancient cultures, the stars were seen as a divine link between the heavens and the earthly realm, and their movements were believed to hold deep spiritual meanings. This blend of scientific knowledge and mythological storytelling created a rich tapestry of understanding the cosmos, shaping both knowledge and cultural beliefs. To this day, the study of ancient astronomy continues to fascinate and inspire our exploration and understanding of the universe.
1. Early Observations
Ancient astronomers made remarkable early observations of the night sky, laying the foundation for our understanding of the cosmos. By closely studying the stars, they noticed recurring patterns and realized that certain stars moved in regular patterns across the sky. These observations allowed them to track the changing seasons, predict celestial events, and navigate their surroundings. One of the most notable early observations was the discovery that the Mesopotamians made of the precession of the equinoxes. They noticed that over a long period, the position of the stars would gradually shift, indicating that the Earth’s axis undergoes a slow rotation. This observation helped establish the concept of time measurement and led to the development of early calendars. With their keen eyes and patient observations, ancient astronomers not only laid the groundwork for future astronomical discoveries but also connected humanity to the vastness of the universe. Through their insights, ancient civilizations were able to navigate the seas, predict celestial events, and develop an awe-inspired understanding of the night sky. This knowledge would later become the building blocks for the development of modern astronomy and our ongoing exploration of the cosmos.
2. Mapping the Night Sky
Mapping the night sky was a crucial aspect of ancient astronomy, allowing early astronomers to gain a deeper understanding of the celestial realm. These early stargazers carefully observed the positions and movements of stars, constellations, and other celestial objects. By charting the positions of various stars in relation to each other and to the Earth, they created maps of the night sky. These maps served as valuable guides for navigation, agriculture, and religious ceremonies.
One notable example of ancient sky mapping is the Ptolemaic star catalog developed by the Greek astronomer Claudius Ptolemy in the second century. Ptolemy’s influential work, Almagest, included detailed charts and tables that mapped the positions of over a thousand stars in relation to each other. These maps profoundly influenced Western astronomy and navigational practices for centuries to come. Similarly, ancient Chinese astronomers developed their own star maps, such as the Dunhuang Star Atlas dating back to the Tang Dynasty. These maps not only depicted the positions of stars but also incorporated symbols and information about celestial events.
In addition to mapping celestial objects, ancient astronomers also observed the movement of stars over time. They noticed that certain stars appeared to move in predictable patterns, such as the circumpolar stars which never dip below the horizon. One such notable star is Polaris, also known as the North Star, which remains almost stationary in the sky and served as a reliable navigational marker for ancient seafarers. By observing and understanding the apparent motion of stars and constellations, ancient astronomers were able to create maps that aided in navigation, helping sailors find their way across vast oceans.
Through meticulous observations and map-making endeavors, ancient astronomers enriched their understanding of the night sky and contributed to the development of navigational techniques that shaped the course of human history. Today, we continue to study and appreciate the maps created by our ancient predecessors for their historical significance and their role in our ongoing exploration of the cosmos.
3. Cultural Significance
The cultural significance of constellations in ancient times cannot be overstated. These celestial patterns were not just seen as random arrangements of stars; they held deep cultural and mythological meanings. In many ancient civilizations, constellations were associated with gods, heroes, and mythical creatures that played significant roles in their belief systems. For example, in Greek mythology, the constellation Orion was tied to the legendary hunter, while Ursa Major, or the Great Bear, was connected to the nymph Callisto. These celestial figures were believed to have influenced human lives and actions. The cultural significance of constellations extended beyond mythology as well. They were used as guides for agriculture and seasonal activities. By observing the positions and movements of specific constellations, ancient societies could determine the right time for planting crops and harvesting. They provided a celestial calendar, guiding cultural practices and ensuring the survival and prosperity of their communities. Constellations were influential in ancient art, music, and storytelling. They inspired intricate constellation maps and celestial motifs in various forms of artistic expression. Ancient people imbued these celestial patterns with symbolic and spiritual significance, incorporating them into their daily lives and cultural traditions. Today, the remnants of this cultural significance can still be seen in the countless references to constellations in literature, art, and popular culture worldwide.

Ancient navigation relied heavily on the observation of celestial bodies, particularly stars and constellations, to navigate across vast oceans and uncharted territories. One of the key methods of navigation was celestial navigation, where sailors used the positions of stars and other celestial objects as reference points to determine their location and course. By observing the movement of the stars throughout the night, sailors could calculate their latitude and, to some extent, their longitude. One star that played a vital role in ancient navigation was Polaris, also known as the North Star. Located almost directly above the North Pole, Polaris remained relatively fixed in the night sky, providing a reliable guide for navigators to determine their northward direction. Additionally, different constellations served as markers for specific regions and seasons, helping sailors zone the seas and navigate their way through treacherous waters. The deep connection between ancient navigation and the stars revolutionized exploration and trade, paving the way for the expansion of civilizations across the globe.
Celestial navigation refers to the ancient practice of using the stars and other celestial bodies to navigate vast oceans and unknown territories. Sailors and explorers relied on the positions of stars, particularly the Polaris, also known as the North Star, to determine their direction at sea. By observing the height and direction of the North Star in relation to the horizon, sailors could establish their latitude and align their course accordingly. The concept of celestial navigation was developed by various ancient civilizations, such as the Phoenicians, Greeks, and Polynesians. They devised ingenious tools like astrolabes and quadrant to measure angles and calculate positions of celestial bodies. Additionally, constellations played a vital role in celestial navigation. Sailors identified specific constellations, such as the Big Dipper and Orion, which served as guideposts or “sailing stars.” By aligning their course with these constellations and monitoring their positions over time, sailors could accurately navigate the seas, even without sophisticated instruments or modern technology. The reliance on celestial navigation was especially crucial during long voyages or in areas where landmarks were scarce. It allowed ancient sailors to traverse vast distances and explore uncharted territories, pushing the boundaries of human knowledge and discovery. Today, celestial navigation techniques are still taught in select naval institutions and continue to be of historical and navigational interest.
2. Polaris and Other Stars
Polaris, also known as the North Star, has played a significant role in ancient navigation, guiding sailors and explorers through the vast expanses of the sea. Located almost directly above the North Pole, Polaris remains relatively stationary in the night sky while other stars appear to rotate around it. This steadfastness made it an invaluable point of reference for mariners who could determine their latitude by measuring the angle between the horizon and Polaris. Additionally, ancient cultures across the world identified different stars and constellations that aided in navigation. For example, the Southern Cross, a constellation visible in the southern hemisphere, guided sailors in the southern seas. These celestial markers served as guiding lights in the darkness, helping seafarers traverse vast oceans and navigate treacherous waters. The knowledge of these stars and their positions allowed ancient mariners to explore new territories, establish trade routes, and expand civilization. Today, while advancements in technology have reduced reliance on stellar navigation, the legacy of Polaris and other guiding stars in ancient navigation still holds significance in our understanding of early seafaring practices and the interconnectedness of civilizations throughout history.
3. Zoning the Seas
Zoning the seas was an integral part of ancient navigation, and constellations played a crucial role in this practice. Sailors relied on the stars to determine their position and navigate vast oceans. By identifying specific constellations and their positions in the night sky, mariners were able to divide the seas into distinct zones. One of the most significant techniques used was celestial navigation, where the position of celestial bodies, including stars and planets, was used to determine the ship’s location. Sailors would look for specific constellations such as the Southern Cross in the Southern Hemisphere or the Big Dipper in the Northern Hemisphere to guide their course. These constellations acted as reference points, allowing sailors to pinpoint their location and stay on course during long voyages. The ability to navigate the seas using constellations was a remarkable feat in ancient times, showcasing the ingenuity and resourcefulness of early explorers. This method of celestial navigation not only ensured safe passage but also paved the way for extensive exploration and trade across vast oceans centuries ago. Today, while modern navigation methods rely on advanced technology, the practice of using constellations as a navigational tool holds a historical and cultural significance in the maritime world.
To learn more about celestial references in different cultures, check out our article on the symbolism of animals in Japanese mythology.
Constellation Mythology
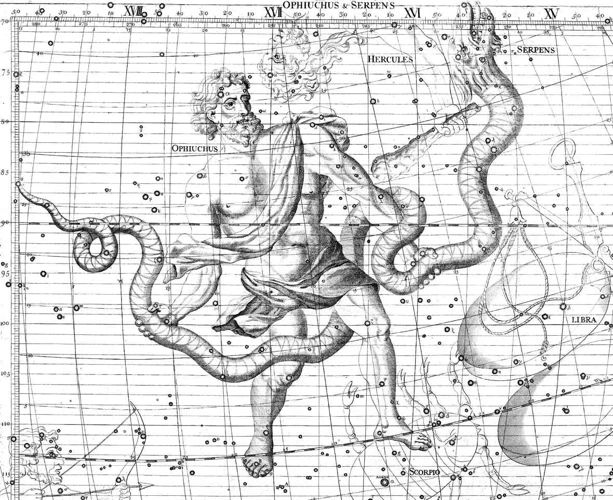
Constellation mythology is a fascinating aspect of ancient cultures, where the night sky served as a canvas for captivating stories and rich symbolism. Greek mythology is filled with tales of heroes, gods, and creatures immortalized in the stars. From Orion the Hunter to Perseus and Andromeda, these constellations bear names and legends that have been passed down through generations. One can also explore the Egyptian mythology which assigned divine significance to certain constellations like Orion and Sirius. They believed that these celestial bodies represented gods and goddesses and played a role in their religious rituals. In Chinese mythology, constellations were connected to the zodiac system, and each year corresponds to a different animal associated with specific characteristics. These ancient stories and mythologies linked the constellations to cultural beliefs, providing a sense of wonder and spiritual connection to the stars above. Exploring the mythology behind constellations offers a glimpse into the diverse ways in which ancient civilizations interpreted and revered the night sky.
1. Greek Mythology
Greek mythology is intricately intertwined with the constellations that adorn the night sky. The ancient Greeks, renowned for their rich storytelling tradition, assigned mythological figures and creatures to various constellations, creating a bridge between their folklore and the stars above. One such example is the constellation Orion, named after the mighty hunter from Greek mythology. According to the legend, Orion was a skilled hunter who eventually incurred the wrath of the gods. In the night sky, Orion is depicted as a prominent constellation, with its distinctive belt of three stars. Another famous Greek mythological figure immortalized in the stars is Cassiopeia, known for her vanity and boasting. The constellation Cassiopeia resembles a distinctive “W” or “M” shape and represents the queen from Greek mythology. The stories associated with these constellations and others served as a way to pass down cultural stories and lessons from one generation to the next. They added a touch of mystery and wonder to the night sky, making it a celestial canvas that reflected the beliefs and adventures of ancient Greek civilization. The link between Greek mythology and the constellations continues to captivate modern-day stargazers and serves as a reminder of the enduring power of storytelling.
2. Egyptian Mythology
In Egyptian mythology, the stars and constellations held great significance and were intertwined with their religious beliefs and rituals. The ancient Egyptians believed that the gods resided in the heavens and that the stars were the physical representation of these deities. They associated various constellations with their gods, assigning specific roles and attributes to each. One prominent constellation in Egyptian mythology is Orion, which was linked to the god Osiris, the ruler of the afterlife. They believed that Osiris was responsible for guiding the souls of the deceased through the Duat, the underworld. Similarly, the constellation Sirius, the brightest star in the night sky, was associated with the goddess Isis, who played a crucial role in the resurrection of Osiris. The alignment of stars also played a part in determining important celestial events such as the eclipses. The ancient Egyptians believed that during an eclipse, the sun god Ra was under attack by a serpent and required their prayers and rituals to protect him. This connection between the stars, constellations, and their pantheon of gods showcases the intricate relationship between Egyptian mythology and the night sky.
3. Chinese Mythology
Chinese mythology is rich with fascinating tales surrounding constellations and their significance. In Chinese culture, the Three Enclosures or San Yuan played a crucial role in astronomy and astrology. These enclosures are known as the Purple Forbidden Enclosure, the Supreme Palace Enclosure, and the Heavenly Market Enclosure. Each enclosure contains various constellations, representing different aspects of Chinese mythology and astrology. The Beidou (Northern Dipper) is one of the most well-known constellations in Chinese mythology. It consists of seven stars that represent the seven sons of the Emperor of Heaven. The Beidou is considered a symbol of good fortune, longevity, and prosperity. Another prominent constellation is the Qi Xi, which represents the legendary love story of the Cowherd and the Weaver Girl, celebrated during the Qixi Festival. The Chinese believed that the stars of Qi Xi were actually the couple themselves, reunited once a year on this special occasion. Additionally, the Chinese zodiac is closely tied to constellations. Each year is associated with a specific animal sign, with twelve animals representing the twelve-year cycle. These animal signs are deeply rooted in Chinese mythology and astrology, shaping beliefs about compatibility, personalities, and fortune-telling. The captivating myths and symbols associated with constellations in Chinese mythology continue to be celebrated and revered in modern-day China, offering insight into ancient beliefs and cultural traditions.
Modern-Day Significance
The significance of constellations in modern times extends beyond their historical and cultural value. In the field of astronomy research, constellations provide astronomers with a framework for studying and understanding the vastness of the universe. Scientists rely on the knowledge passed down from ancient astronomers to locate and observe celestial objects. Additionally, constellations play a crucial role in stellar navigation, aiding sailors, pilots, and explorers in determining their position and course. By identifying key constellations or using celestial bodies such as Polaris as reference points, navigators can navigate with remarkable precision. Constellations continue to inspire cultural references in literature, art, and popular culture, capturing the imagination of people worldwide. The timeless tales and myths associated with constellations are retold in various forms, contributing to the preservation and celebration of ancient wisdom and our connection to the celestial realm. The enduring significance of constellations in modern times is a testament to their lasting impact on humanity’s exploration, understanding, and appreciation of the cosmos.
1. Astronomy Research
Astronomy research is a dynamic field that continues to push the boundaries of human knowledge about the universe. It involves the scientific study of celestial objects, such as stars, galaxies, planets, and other astronomical phenomena. Astronomers utilize advanced telescopes, satellites, and computational models to observe and analyze various aspects of the cosmos. This research encompasses a wide range of topics, including stellar evolution, galaxy formation, cosmology, and the search for extraterrestrial life.
One area of astronomy research focuses on understanding the dynamic nature of celestial bodies. Astronomers study how stars evolve over time, from their formation to their eventual demise. They investigate the process of stellar birth, the fusion reactions that power stars, and the mechanisms by which stars end their life cycles. This research helps scientists gain insights into the fundamental processes that shape the universe.
Another aspect of astronomy research involves studying the interactions between different celestial objects. For example, astronomers examine the impact of massive galaxy clusters on the surrounding cosmic environment. They investigate how galaxies merge and interact, leading to the formation of new structures in the universe. Astronomers explore the relationship between black holes and their host galaxies, unraveling the mysteries of these enigmatic cosmic entities.
Additionally, astronomy research plays a crucial role in advancing our understanding of the origins and evolution of the universe itself. Scientists investigate the cosmic microwave background radiation, which provides valuable insights into the early stages of the universe, shortly after the Big Bang. They also study the distribution of matter and the large-scale structure of the universe, seeking to unravel the mysteries of dark matter and dark energy.
In recent years, advancements in technology and data analysis have revolutionized astronomy research. The use of big data techniques has allowed astronomers to process vast amounts of observational data and make significant discoveries. Additionally, collaborations between different observatories and international research institutions have paved the way for groundbreaking discoveries and fostered a global community of astronomers.
Continued astronomy research not only expands our knowledge of the universe, but it also has broader implications for fields such as astrophysics, cosmology, and even astrological compatibility. By studying the celestial objects and phenomena that have fascinated humans for centuries, astronomers contribute to our collective understanding of the cosmos and inspire future generations to explore the wonders of the universe.
Stellar navigation, also known as astronavigation, is a method of determining one’s position on Earth using celestial bodies, particularly stars. In ancient times, before the invention of modern navigation tools, sailors and explorers relied on the stars for guidance during their journeys. By observing the positions of specific stars, such as Polaris, sailors were able to determine their latitude or north-south position. Polaris, also known as the North Star, served as a reliable reference point because it remained relatively fixed in the northern sky, aligned with the Earth’s axis. Sailors could also refer to other prominent stars and constellations to navigate across different regions.
To navigate using the stars, sailors used tools such as astrolabes and sextants to measure the angles between stars and the horizon. By comparing these measurements with known stellar positions recorded in navigational charts, they could calculate their position in the vast expanse of the open seas. This method of navigation was particularly valuable during cloudy or foggy weather when other forms of landmarks or navigation aids were obscured.
Stellar navigation was not limited to sailors alone; it also played a crucial role in overland travel, allowing ancient civilizations to navigate deserts, mountains, and vast landscapes. By understanding the positions of specific stars or constellations relative to the Earth’s horizon, travelers could find their direction and maintain a relatively accurate course.
Today, while modern technology has greatly surpassed the need for stellar navigation in most contexts, it still holds significance in certain professions and hobbies. Astronomers, astronomers, and explorers often rely on celestial objects for orientation and measurement in remote locations where traditional navigation tools may not be accessible or reliable. Stargazing enthusiasts and amateur astronomers continue to gain a sense of wonder and perspective by navigating the celestial realm using the knowledge passed down from ancient stellar navigation techniques. The legacy of stellar navigation continues to shine brightly in our modern world, connecting us to the stars and our ancient past.
3. Cultural References
Cultural references to constellations can be found throughout human history, illustrating the enduring impact of these celestial formations. In ancient Greek mythology, astronomical figures like Orion, Cassiopeia, and Ursa Major were believed to represent gods, heroes, and mythical creatures. These constellations became intertwined with legendary tales, enhancing the cultural significance and providing a basis for storytelling and artistic representations. Similarly, in Egyptian mythology, Osiris, the god of the afterlife, was associated with the constellation Orion, symbolizing resurrection and eternal life. The Chinese culture developed a unique system of constellations, known as the 28 Mansions or Lunar Mansions, which were used in astrology and agricultural practices. Each mansion represented a specific region of the sky and had its own cultural interpretations and references. These cultural connections to constellations illustrate how ancient societies viewed the stars as more than scientific objects – they were intertwined with religious, artistic, and practical aspects of their daily lives. Today, these cultural references continue to influence various aspects of contemporary society, from astrology to literature, showcasing the enduring fascination and impact of constellations throughout human history.
Conclusion

In conclusion, constellations have played a significant role in ancient astronomy, navigation, mythology, and continue to have a profound impact on our modern world. The early observations and mapping of the night sky allowed ancient civilizations to navigate the seas, track seasons, and understand cosmological phenomena. Constellations were not only scientific tools but also held deep cultural and spiritual significance, influencing art, literature, and religious beliefs. The mythology surrounding constellations, such as the Greek, Egyptian, and Chinese mythologies, added richness and meaning to their interpretations. In modern times, constellations still hold importance in various aspects. They continue to inspire astronomical research, contribute to stellar navigation systems, and are referenced in popular culture, literature, and even astrology. The study of constellations connects us to our ancient roots and reminds us of our place in the vast cosmos. Exploring the mysteries and beauty of constellations allows us to seek a deeper understanding of the universe and our own existence.
Overall, the role of constellations in ancient times and their continuing significance today serves as a testament to the enduring human curiosity and fascination with the celestial heavens. It reminds us that looking up at the stars is not just an act of observation, but an exploration of our shared history, culture, and connection to the cosmos. Whether we are navigating by the stars, studying the origins of the universe, or finding inspiration in ancient mythologies, constellations remain a source of wonder and a pathway to expanding our knowledge of the universe and ourselves.
Frequently Asked Questions

1. What is the significance of constellations in ancient astronomy?
Constellations played a crucial role in ancient astronomy as they helped early astronomers map and navigate the night sky, track celestial movements, and understand the changing seasons.
Ancient civilizations, such as the Greeks and Phoenicians, used constellations for celestial navigation. By observing the positions of stars in relation to the horizon, they could determine their latitude and track their course during long journeys at sea.
3. Did different ancient cultures have different constellations?
Yes, different ancient cultures had their own unique constellations. While some constellations were shared among cultures, many civilizations developed their own interpretations and names for the groupings of stars they observed in the night sky.
4. How did ancient cultures explain the origins of constellations?
Ancient cultures explained the origins of constellations through mythology and storytelling. Divine beings, heroes, and mythical creatures were often associated with specific constellations, providing a narrative context for their existence.
5. What was the cultural significance of constellations in ancient times?
Constellations held deep cultural significance in ancient times. They were believed to connect the mortal world with the divine realms and were associated with religious beliefs, astrological practices, and the stories passed down through generations.
6. How do constellations continue to be relevant in modern astronomy research?
Constellations remain relevant in modern astronomy research as they serve as reference points for astronomers to locate and study celestial objects. They aid in the identification, classification, and mapping of stars, galaxies, and other celestial phenomena.
While modern navigation relies heavily on advanced technologies like GPS, constellations still have some navigational applications. In emergency situations or when traditional navigation systems fail, sailors and pilots can use constellations to determine their approximate position and direction.
8. How have constellations influenced cultural references in art and literature?
Constellations have had a profound impact on art, literature, and cultural references throughout history. They have provided inspiration for countless works of art, served as symbols in literature, and influenced the naming and representation of characters in various storytelling traditions.
9. Can anyone spot constellations without using special tools?
Yes, anyone can spot constellations without using special tools. On a clear night, constellations can be observed with the naked eye. However, it may take some practice and familiarity with the night sky to identify and distinguish different constellations.
10. Are constellations fixed or do they change over time?
Constellations appear fixed from our perspective here on Earth, but they do slightly change over long periods of time due to the phenomenon known as precession. This gradual change is caused by the Earth’s wobbling motion as it rotates and affects the positions of stars within constellations.
References
Frequently Asked Questions

What is ancient astronomy?
Ancient astronomy refers to the study of celestial bodies and their movements by ancient civilizations. It involves observing and understanding the stars, planets, and other celestial objects, as well as their influence on earthly affairs.
How did ancient civilizations map the night sky?
Ancient civilizations mapped the night sky by observing and recording the positions of stars and constellations over time. They created star charts and celestial globes to navigate and identify key stars and constellations.
Why were constellations culturally significant in ancient times?
Constellations held cultural significance in ancient times as they were often associated with mythological or spiritual beliefs. They were used to explain natural phenomena, predict seasons, and guide navigation.
Celestial navigation is a method of navigation that uses celestial bodies, such as the sun, moon, stars, and planets, to determine the position and direction of a vessel or traveler. It was widely practiced in ancient times.
Ancient sailors used Polaris, also known as the North Star, and other stars as navigational aids. By observing the position of these stars in relation to the horizon, they could determine their latitude and direction while at sea.
“Zoning the seas” was a method used by ancient sailors to divide the oceans into different navigational regions based on the position of specific stars and constellations. This helped them navigate and locate their position while at sea.
What is the significance of Greek mythology in constellation lore?
Greek mythology plays a significant role in constellation lore. Many constellations bear names and stories from Greek mythology, serving as a way to preserve and pass on ancient mythological tales.
How did ancient Egyptians incorporate constellations into their mythology?
Ancient Egyptians incorporated constellations into their mythology, associating them with various gods and goddesses. They believed that these celestial beings influenced certain aspects of their daily lives and rituals.
What is the role of Chinese mythology in constellation culture?
Chinese mythology has a rich constellation culture. Chinese astronomers and mythologists assigned unique names and stories to constellations, often linked to their philosophical and astrological beliefs.
Constellations continue to be relevant in modern-day astronomy and navigation. Astronomers study them to better understand stellar evolution and the universe, while techniques like stellar navigation draw on the positions of constellations for precise location determination.







