Many mysteries surround the formation of planets in our vast universe. One captivating aspect is the role played by asteroids and comets, celestial bodies that have fascinated scientists and explorers for centuries. These enigmatic objects, originating from the depths of space, hold valuable clues about the evolution of our solar system. In this article, we will delve into the captivating world of asteroids and comets, exploring their composition, origin, and the pivotal role they play in planet formation. Join us in uncovering the secrets of these celestial wanderers as we embark on a journey through the cosmos.
Contents
- Asteroids: Building Blocks of Planets
- Comets: Ancient Messengers from Space
- Comparison: Asteroids vs. Comets
- Interaction with Planets: Effects and Significance
- Current Research and Future Missions
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. Are all asteroids located in the asteroid belt?
- 2. How many asteroids have been discovered so far?
- 3. Can asteroids collide with planets?
- 4. Are all asteroids made of the same materials?
- 5. Are asteroids a threat to Earth?
- 6. Can asteroids contain water?
- 7. Are there any missions to study asteroids up close?
- 8. Can asteroids be used as stepping stones for space exploration?
- 9. How do scientists determine the composition of asteroids?
- 10. What can studying asteroids tell us about the formation of the solar system?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How did asteroids and comets form in the solar system?
- 2. What are the differences in composition between asteroids and comets?
- 3. How do asteroids contribute to the formation of planets?
- 4. What is the significance of comets in the process of planet formation?
- 5. How do asteroids and comets interact with planets?
- 6. What is the role of asteroids and comets in delivering volatile elements and water?
- 7. What are the ongoing studies focused on asteroids and comets?
- 8. Which upcoming missions are planned for exploring asteroids and comets?
- 9. How do asteroids and comets contribute to orbital dynamics and stability?
- 10. What is the significance of studying asteroids and comets for understanding the formation of the universe?
- References
- Read More
Asteroids: Building Blocks of Planets

Asteroids are fascinating celestial objects that play a crucial role in the formation of planets. These rocky remnants from the early days of our solar system are often referred to as the “building blocks” of planets. Composition and Origin of Asteroids
1. Composition and Origin of Asteroids
Asteroids are composed of various minerals, primarily rocky and metallic materials. They differ in size, with some being as small as boulders while others can span hundreds of kilometers in diameter. These ancient bodies originated from the protoplanetary disk, a rotating disk of gas and dust that surrounded the young Sun during the early stages of our solar system’s formation.
2. Role of Asteroids in Planet Formation
Asteroids played a pivotal role in the accretion process, where small particles collided and stuck together, eventually forming planets. They are considered the building blocks of planets because they contain substantial amounts of volatiles such as water, carbon, nitrogen, and other organic compounds. These volatiles are crucial for the development of life as we know it. Additionally, asteroids contain valuable resources such as precious metals and rare earth elements, making them potential targets for future mining endeavors.
Understanding the composition and origin of asteroids provides valuable insights into the early solar system dynamics and the formation of planets. Studying these rocky remnants helps scientists piece together the puzzle of our solar system’s evolution and enables us to gain a deeper understanding of the conditions that led to the emergence of life on Earth.
Continue reading to further explore the topic of asteroids in our article, where we will uncover the intriguing connection between comets and stardust that further enhances our understanding of these enigmatic celestial objects.
1. Composition and Origin of Asteroids
1. Composition and Origin of Asteroids
Asteroids, those mysterious celestial objects, come in various sizes and compositions, shedding light on the fascinating world of planetary formation. As remnants from the early solar system, asteroids are primarily composed of rocky and metallic materials. They are often considered the leftovers from the protoplanetary disk, a swirling disk of gas and dust that surrounded the young Sun billions of years ago. Although there is no one-size-fits-all answer concerning their origin, scientists believe that asteroids could have formed through a variety of mechanisms. One hypothesis suggests that asteroids formed from the initial stages of planet formation when the rocky building blocks collided and stuck together. Another possibility is that they are fragments of larger differentiated objects, like planets or moons, that were shattered due to violent collisions. Regardless of their specific origin, the study of asteroids provides valuable insights into the composition and dynamics of our early solar system. To learn more about the intriguing realm of near-Earth asteroids, check out our article on key facts about near-Earth asteroids.
2. Role of Asteroids in Planet Formation
2. Role of Asteroids in Planet Formation
Asteroids play a crucial role in the formation of planets through several key processes.
1. Accretion: During the early stages of planet formation, small asteroids collide and merge, gradually building up larger bodies known as planetesimals. These planetesimals serve as the foundation for the formation of planets. Through continued accretion, these planetesimals gather more and more material, eventually growing into full-fledged planets.
2. Delivery of Volatiles: Asteroids contain a significant amount of volatiles, including water and organic compounds. These volatiles are essential for the development of habitable environments and the emergence of life. As asteroids collide with young planets, they can deliver these volatiles to the planetary surface, enriching the planet’s composition and potentially providing the necessary ingredients for life to thrive.
3. Impact Events: Large asteroids can create dramatic impact events when they collide with a planet. These impacts can have far-reaching effects on the planet’s surface, altering its geology and even triggering mass extinctions. As such, the impact of asteroids in planet formation is not limited to their role as building blocks but also includes their influence on shaping the planetary landscape.
By studying asteroids and their impact on planet formation, scientists gain a deeper understanding of the dynamics and processes involved in the early stages of our solar system’s evolution. The significance of asteroids in planet formation cannot be understated, as they provide valuable insights into the conditions that allowed our own Earth to develop and sustain life.
Learn more about fascinating legends related to celestial objects like the Feathered Serpent Quetzalcoatl from Mayan mythology, further highlighting the diverse cultural perspectives surrounding celestial phenomena.
Comets: Ancient Messengers from Space
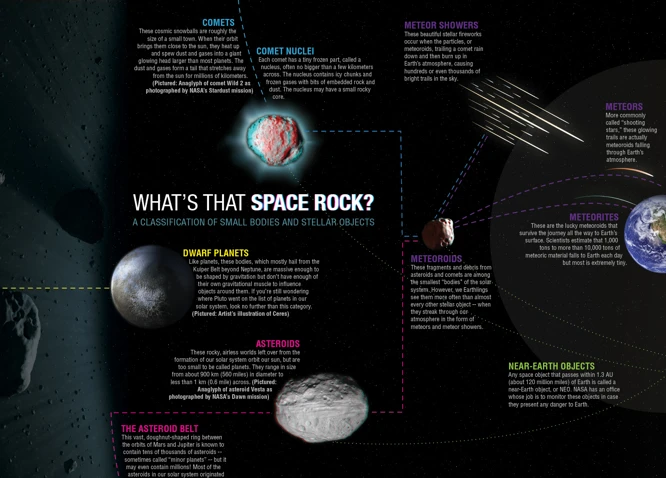
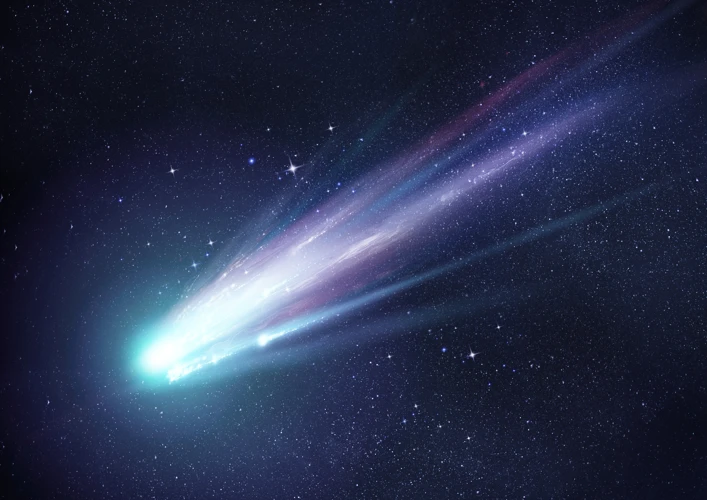
Comets, often referred to as ancient messengers from space, are captivating celestial objects that have fascinated astronomers for centuries. These icy wanderers originate from the outer regions of the solar system and carry valuable information about the early history of our cosmic neighborhood.
1. Composition and Origin of Comets
Comets are primarily composed of ice, dust, and small rocky particles. This composition gives them a distinct appearance, with a glowing nucleus surrounded by a glowing coma and often a tail that stretches millions of kilometers when the comet approaches the Sun. The origin of comets can be traced back to the Oort Cloud and the Kuiper Belt, two regions located in the outer reaches of the solar system. These regions are believed to be home to countless comets waiting to make their approach towards the Sun.
2. Impact of Comets in Planet Formation
Comets played a significant role in the formation of planets and the delivery of essential elements. When comets approach the Sun, the heat causes the icy nucleus to vaporize, releasing gas and dust into space. This process creates a glowing coma around the nucleus, and the pressure of sunlight pushes the dust and gas away, forming a magnificent tail. Comets carry complex organic molecules, including amino acids, which are the building blocks of life. When comets collide with young planets, they deliver these organic materials, water, and other volatiles, providing the necessary ingredients for the emergence of life.
Studying comets gives us a glimpse into the early stages of the solar system’s formation and provides insights into the conditions that might exist in systems beyond our own. The exploration of comets has revealed their stunning beauty and scientific importance, solidifying their status as ancient messengers from space.
To learn more about comets and their intriguing connection to asteroids, continue reading our article, where we will compare the composition of these celestial objects and explore their impact on planet formation.
1. Composition and Origin of Comets
1. Composition and Origin of Comets
Comets, often called “dirty snowballs” or “icy dirtballs,” are fascinating celestial objects with a distinct composition and origin. Unlike asteroids, which are rocky, comets are composed mainly of ice and dust. Let’s dive into the composition and origin of these ancient messengers from space.
Composition:
Comets are primarily composed of three main components: water ice, dust particles, and various organic compounds. Water ice can make up a significant portion of a comet, sometimes accounting for up to 80% of its total mass. The dust particles found in comets are a mix of silicates, carbon, and other minerals. Organic compounds, such as methane, carbon dioxide, and ammonia, are also present on comets.
Origin:
Comets are believed to originate from two main regions within our solar system: the Kuiper Belt and the Oort Cloud. The Kuiper Belt, a disk-shaped region beyond the orbit of Neptune, is home to short-period comets that have orbital periods of less than 200 years. The Oort Cloud, a spherical region much farther from the Sun, is thought to house long-period comets that have orbital periods ranging from 200 to millions of years.
The formation of comets begins in the outer regions of the protoplanetary disk, where temperatures are extremely cold. In these frigid environments, volatile gases, water, and solid particles come together to form a nucleus, which becomes the core of the comet. As the young solar system evolves, gravitational interactions with other celestial bodies can perturb the orbits of these nuclei, leading to their journey towards the inner solar system.
Understanding the composition and origin of comets provides valuable insights into the early stages of our solar system’s formation. The intricate mix of volatile and organic compounds found in comets holds essential clues about the delivery of water and organic molecules, which may have played a crucial role in the emergence of life on Earth. As we delve deeper into the impact of comets in planet formation, we will uncover the fascinating connection between these celestial wanderers and the legends of ancient civilizations, such as the feathered serpent Quetzalcoatl in Mayan mythology.
2. Impact of Comets in Planet Formation
2. Impact of Comets in Planet Formation
Comets, often described as “ancient messengers from space,” have a significant impact on the formation of planets. These icy bodies originate from the outer regions of the solar system, specifically the Kuiper Belt and the Oort Cloud. They are composed of a mixture of water ice, dust, rock, and organic compounds.
Comets play a crucial role in planet formation through several mechanisms:
1. Delivery of Volatiles: Comets are thought to have delivered a significant amount of volatiles, including water, to young planets. During the early stages of our solar system, when terrestrial planets were still forming, comets bombarded these planets, depositing volatiles that were crucial for the emergence of life. The water delivered by comets may have contributed to the formation of oceans and provided the necessary conditions for the development of life on Earth.
2. Impact Events: Comets have been involved in numerous impact events throughout the history of our solar system. These impacts played a role in shaping the surfaces of planets, such as creating impact craters and causing significant geological disturbances. Large comet impacts may have even triggered mass extinctions on Earth, leading to significant changes in the planet’s biodiversity.
3. Seeding Planets with Organic Compounds: Comets contain a variety of organic compounds, including amino acids, the building blocks of life. When comets collide with planets, they can deposit these organic compounds, providing the necessary ingredients for the development of life.
The impact of comets in planet formation is multi-faceted. They not only deliver essential volatiles and organic compounds to young planets, but also shape the geological features of planets through their impact events. Studying comets helps scientists understand the conditions that led to the formation of planetary systems and provides insights into the origins of life in the universe.
Continue reading to discover the intriguing differences in composition between asteroids and comets, further highlighting their distinct roles in the formation and evolution of planets.
Comparison: Asteroids vs. Comets

1. Differences in Composition
Asteroids and comets may both have played significant roles in planet formation, but they have distinct differences in composition. Asteroids are primarily composed of rocky and metallic materials, while comets are made up of a mixture of rocky debris, water ice, frozen gases, and organic compounds. These differences in composition reflect their origins, with asteroids originating from the inner regions of the solar system and comets originating from the outer regions, known as the Kuiper Belt and Oort Cloud.
2. Impact on Planets
Asteroids and comets have different impacts on planets during their interactions. Due to their rocky nature, asteroids tend to cause more direct and immediate damage when they collide with planets. Their impacts can result in craters, changes in the planet’s surface, and even mass extinctions. On the other hand, comets, with their icy composition, create spectacular displays when they encounter a planet’s atmosphere. The heat from the atmosphere causes the icy nucleus to vaporize, creating a glowing coma and a tail that stretches across the sky.
While both asteroids and comets have their unique characteristics and impacts on planets, they both contribute essential elements to the formation and development of planets. Their interactions with planets provide valuable insights into the complex processes that shaped our solar system. In the next section of our article, we will explore the effects and significance of the interaction between these celestial bodies and planets, including their role in accretion events, the delivery of volatile elements and water, and the dynamics of planetary orbits. Stay tuned to unlock the secrets of these cosmic interactions.
1. Differences in Composition
1. Differences in Composition
Asteroids and comets may both contribute to the formation of planets, but they differ significantly in their composition. Asteroids are primarily composed of rocky and metallic materials, making them similar to the terrestrial planets like Earth. These rocky bodies have undergone significant heating, possibly due to collisions or radioactive decay, which has caused them to lose most of their volatile substances.
On the other hand, comets are predominantly composed of icy materials such as water, methane, ammonia, and carbon dioxide. These volatile-rich bodies originate from the outer reaches of the solar system, where temperatures are much colder. Comets are often described as “dirty snowballs” due to their icy cores covered in a layer of dust and organic compounds.
The differences in composition between asteroids and comets are attributed to their formation locations within the solar system. Asteroids formed closer to the Sun, in the inner regions of the protoplanetary disk, where it was too warm for volatile substances like water to condense. In contrast, comets formed farther away from the Sun, in the colder outer regions of the disk, allowing them to accumulate significant amounts of volatile materials.
Understanding these composition differences is crucial for comprehending the diverse nature of objects within our solar system. By studying asteroids and comets, scientists gain insights into the building blocks of planets and the formation processes that shaped our cosmic neighborhood.
2. Impact on Planets
2. Impact on Planets
Asteroids have a significant impact on the formation and evolution of planets. Their collisions with planets can have profound effects on the geological and atmospheric characteristics of celestial bodies in our solar system. Here, we will delve into the various ways in which asteroids influence planets.
One of the most evident impacts of asteroids on planets is through crater formation. When an asteroid collides with a planet’s surface, it releases an immense amount of energy, resulting in a powerful explosion. This explosion creates a crater, which can range in size from a few meters to hundreds of kilometers in diameter, depending on the size and velocity of the impacting asteroid. These craters can be found on various celestial bodies, such as the Moon, Mars, and even Earth. By studying these craters, scientists can gain insights into the size and composition of the impacting asteroid, as well as the geological history of the planet.
In addition to crater formation, asteroid impacts can also lead to significant changes in a planet’s atmosphere. When an asteroid enters a planet’s atmosphere, it experiences intense heat and pressure due to friction. This causes the asteroid to vaporize and create a shockwave that propagates through the atmosphere. As a result, the shockwave can cause widespread destruction, with the potential to alter climate patterns and atmospheric composition.
The impact of asteroids on planets can also have implications for the existence of life. Large impacts have the potential to release large amounts of dust and debris into the atmosphere, blocking sunlight and disrupting the planet’s ecosystems. On the other hand, smaller impacts can deliver organic compounds and water to a planet’s surface, providing the necessary ingredients for the emergence and sustenance of life.
As we continue to study and explore asteroids and their impact on planets, we gain a better understanding of the dynamic processes that shape the worlds within our solar system. This knowledge not only helps us comprehend the past and present of our own planet but also gives us valuable insights into the potential habitability of other celestial bodies.
Read on to the following section to explore the differences in composition between asteroids and comets, shedding further light on their unique contributions to our understanding of planet formation.
Interaction with Planets: Effects and Significance
1. Accretion and Collision Events
One of the significant effects of asteroids and comets on planets is their involvement in accretion and collision events. During the early stages of a planet’s formation, these celestial objects collide with the growing planet. These collisions result in the transfer of energy, causing intense heat and melting of the planetary surface. Over time, these repeated impacts contribute to the growth of the planet by adding additional mass. However, these events can also lead to significant alterations in the planet’s geological makeup and affect its overall structure and composition. These accretion and collision events are essential in shaping the final form and characteristics of a planet.
2. Delivery of Volatile Elements and Water
Asteroids and comets have played a vital role in delivering volatile elements and water to planets. Volatile elements can include gases such as carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and methane, which are crucial for the development and sustainability of life. Water, one of the fundamental building blocks of life, has also been delivered by these celestial bodies to planets like Earth. Comets, in particular, are rich in water ice, and when they collide with a planet, they release vast amounts of water vapor. This water then gets incorporated into the planet’s atmosphere or surface, contributing to the formation of oceans and the potential for the emergence of life.
3. Orbital Dynamics and Stability
The interaction between asteroids, comets, and planets also plays a significant role in the overall orbital dynamics and stability of a planetary system. Large celestial bodies with substantial gravitational influence, such as Jupiter, can alter the trajectories of asteroids and comets, either redirecting them towards the inner solar system or flinging them out into interstellar space. This gravitational influence helps in preventing a high number of collisions with inner planets, protecting them from potentially catastrophic impacts. The complex dance between asteroids, comets, and planets creates a delicate balance in the solar system’s dynamics, ensuring long-term stability.
Understanding the effects and significance of the interaction between asteroids, comets, and planets gives us valuable insights into the processes that drive planetary formation and evolution. By studying these interactions, scientists can better comprehend the origins of our solar system and gain a deeper understanding of the mechanisms that contribute to the creation and sustainability of habitable planets.
Continue reading to explore current research and future missions dedicated to unraveling the mysteries surrounding asteroids and comets in our upcoming sections.
1. Accretion and Collision Events
1. Accretion and Collision Events
During the early stages of planet formation, accretion and collision events involving asteroids and comets played a crucial role in shaping our solar system. As these celestial bodies traversed the chaotic environment of the protoplanetary disk, their paths occasionally intersected, leading to collisions. These collisions resulted in the merging and accumulation of mass, gradually building up the bodies that would eventually become planets.
Accretion, the process of particles sticking together due to gravity, allowed the formation of planetesimals, which were larger bodies ranging in size from kilometers to hundreds of kilometers in diameter. These planetesimals further grew by colliding with other planetesimals or by accreting smaller debris in their paths.
These collisions were not gentle encounters but rather violent events, with tremendous amounts of energy involved. The impact of these high-speed collisions released immense heat, causing the rocks to melt and partially vaporize. As the molten material cooled, it solidified to form solid structures, laying the foundation for the eventual formation of terrestrial planets like Earth.
Throughout this turbulent period of accretion and collision events, the gravitational forces exerted by larger objects, such as Jupiter, influenced the distribution and trajectories of asteroids and comets. These interactions led to the migration of asteroids from their original locations, creating a complex dance of celestial bodies within the solar system.
Studying these accretion and collision events helps scientists gain insights into the dynamics of planet formation and the structural diversity observed among celestial bodies. By examining the composition of asteroids and comets, scientists can piece together the history of these events and unravel the mysteries of how our planetary system took shape.
Continue reading to discover the significance of asteroids and comets in delivering volatile elements and water to planets, a key factor in the emergence and sustainability of life as we know it.
2. Delivery of Volatile Elements and Water
2. Delivery of Volatile Elements and Water
Asteroids have played a significant role in delivering volatile elements and water to planets in our solar system. The presence of these volatiles is essential for the development and sustainability of life as we know it.
During the early stages of planet formation, volatile elements such as water, carbon dioxide, methane, and ammonia were scarce in the inner regions of the protoplanetary disk. However, asteroids, rich in these volatiles, acted as messengers, delivering them to planets through impacts and collisions. These impacts released the trapped volatiles, enriching the atmospheres and surfaces of planets.
Water, in particular, is a crucial component for the existence of life. Scientists believe that Earth’s water originated from the impact of icy asteroids, known as carbonaceous chondrites, which carried significant amounts of water. These impacts not only delivered water to Earth but also provided the oceans that cover our planet’s surface. This delivery of water by asteroids has likely played a vital role in creating a habitable environment on our home planet.
The delivery of volatile elements by asteroids has contributed to the diversity of planetary atmospheres and surface compositions. For example, the atmosphere of Mars contains abundant traces of carbon dioxide and water vapor, possibly due to the impact of carbonaceous asteroids. Similarly, the presence of organic compounds on asteroids suggests that they have supplied the building blocks necessary for the emergence of life on other planets or moons.
Studying the delivery of volatile elements and water by asteroids not only enhances our understanding of the formation and evolution of planets but also has significant implications for our search for life beyond Earth. By analyzing the composition of asteroids and their impact on planetary bodies, scientists can unravel the story of how the ingredients for life were disseminated throughout the solar system.
Continue reading to explore the fascinating field of orbital dynamics and stability and its importance in the study of asteroids and comets.
3. Orbital Dynamics and Stability
3. Orbital Dynamics and Stability
The orbital dynamics and stability of asteroids and comets are crucial factors in understanding their role in planet formation. These celestial bodies follow elliptical orbits around the Sun, but their paths can be influenced by various factors, such as gravitational interactions with planets and other celestial objects. Understanding these dynamics is essential for predicting potential collision events and studying the long-term stability of our solar system.
Asteroids, due to their relatively small size, are affected more prominently by gravitational forces exerted by larger celestial bodies. These forces can cause significant changes in their orbits, leading to orbital resonances, where asteroids’ orbits become synchronized with the orbital periods of planets. As a result, these resonances can lead to close encounters between asteroids and planets, increasing the likelihood of future collisions.
Comets, on the other hand, follow highly elongated orbits that take them far into the distant reaches of our solar system. These elliptical orbits are influenced by the gravitational pull of distant stars, resulting in their periodic returns to the inner regions of the solar system. The stability of comets’ orbits is crucial in determining their potential impact on planets during these periodic returns.
Studying the orbital dynamics and stability of asteroids and comets provides valuable insights into the potential risks associated with their interactions with planets, including the Earth. Understanding their paths and potential collision probabilities allows scientists to develop strategies for mitigating potential threats from near-Earth asteroids and comets. This research is essential for ensuring the long-term stability and safety of our planet.
To further explore the intriguing connection between asteroids and comets, and the impact of comets in planet formation, continue reading our article as we delve into the role of comets as ancient messengers from space.
Current Research and Future Missions

1. Ongoing Studies on Asteroids and Comets
Scientific research on asteroids and comets is a continuously evolving field, with numerous ongoing studies exploring these celestial bodies’ mysteries. Researchers employ a variety of techniques, including ground-based observations, space missions, and laboratory analyses. Spectroscopy is commonly used to determine the composition and surface characteristics of asteroids and comets, providing valuable insights into their origins and evolution. Additionally, scientists study impact craters on planets and moons to understand the role of asteroids and comets in shaping celestial bodies’ surfaces.
As technology advances, new instruments and telescopes enable scientists to gather more detailed information about these objects. The utilization of powerful telescopes, such as the Hubble Space Telescope and the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), allows for unprecedented observations of asteroids and comets. Ongoing missions like NASA’s OSIRIS-REx and JAXA’s Hayabusa2 are currently collecting samples from asteroids (such as Bennu and Ryugu, respectively) and returning them to Earth for detailed analysis. These samples hold the promise of revealing invaluable information about the early solar system’s composition and the processes that led to planet formation.
2. Upcoming Missions and Exploration
The future of asteroid and comet exploration looks promising, with several ambitious missions planned by space agencies around the world. NASA’s upcoming mission, the Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART), aims to test asteroid redirection techniques by crashing into the moon of the near-Earth asteroid Didymos, known as Dimorphos. This mission will provide valuable insights into how we can potentially mitigate the threat of hazardous asteroids colliding with Earth.
Another notable mission is the European Space Agency’s (ESA) Hera mission, which will study the impact crater of the DART mission on Dimorphos. Hera will provide detailed measurements and observations of the asteroid, enhancing our understanding of the effects of asteroid impact and the resulting changes to the celestial body.
The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) plans to launch the Martian Moons eXploration (MMX) mission, which will study the two moons of Mars, Phobos and Deimos. These moons are believed to be captured asteroids, and studying them will shed light on the relationship between Mars and asteroids.
These future missions will undoubtedly contribute to our knowledge of asteroids and comets, uncovering more secrets about their formation and impact on planetary evolution. As we continue to explore and study these fascinating celestial objects, we bring ourselves closer to unraveling the mysteries of the universe and our place within it.
1. Ongoing Studies on Asteroids and Comets
1. Ongoing Studies on Asteroids and Comets
There is a wealth of ongoing research and studies focused on understanding the intriguing nature of asteroids and comets. Scientists and space agencies around the world have embarked on missions and conducted extensive observations to gather valuable data about these celestial objects.
One of the most notable ongoing studies is the NASA OSIRIS-REx mission, which aims to retrieve samples from the asteroid Bennu and bring them back to Earth. This mission provides an unprecedented opportunity to study the composition of an asteroid up close and gain insights into the early solar system. The Hayabusa2 mission by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) also successfully collected samples from the asteroid Ryugu and is set to return them to Earth.
In addition to sample return missions, telescopic observations continue to provide valuable information about asteroids. The NEOWISE (Near-Earth Object Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer) mission, a NASA space telescope, surveys the sky to discover and characterize near-Earth asteroids. These observations help us better understand the population, size, and orbit of asteroids that could potentially pose a hazard to our planet.
Comets are also subjects of ongoing studies. The European Space Agency’s Rosetta mission made history by rendezvousing with the comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko and deploying a lander, Philae, to its surface. The mission provided valuable data about the composition and structure of comets, shedding light on their role in the early solar system.
Ground-based observatories and space telescopes such as Hubble and Spitzer continue to capture images and data about asteroids and comets, adding to our knowledge of these fascinating objects. These ongoing studies contribute towards expanding our understanding of the formation, composition, and dynamics of asteroids and comets, ultimately advancing our knowledge of the universe as a whole.
In the next section of the article, we will explore the upcoming missions and explorations that are set to further enhance our understanding of asteroids and comets. Stay tuned to discover the cutting-edge research that lies ahead!
2. Upcoming Missions and Exploration
2. Upcoming Missions and Exploration
As our understanding of asteroids and comets continues to evolve, scientists and space agencies are planning and preparing for upcoming missions and explorations to unravel more secrets about these celestial objects.
One of the exciting upcoming missions is NASA’s Lucy mission, set to launch in 2021. Lucy will visit multiple Trojan asteroids, which are located in the orbit of Jupiter. These asteroids are believed to be remnants of the early solar system and can provide valuable insights into the processes that led to planet formation.
Another intriguing mission is the European Space Agency’s (ESA) Hera mission, scheduled to launch in 2024. Hera will investigate the nature and properties of asteroids, particularly one named Didymos. Hera will also study the impact of the NASA-led DART (Double Asteroid Redirection Test) mission on Didymos. This joint effort aims to explore the feasibility of deflecting potentially hazardous asteroids away from Earth.
NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission, which arrived at the asteroid Bennu in 2018, is an ongoing exploration endeavor. The spacecraft is currently studying Bennu’s surface and will collect a sample for return to Earth in 2023. The sample will provide invaluable data about the composition and origin of asteroids, enhancing our understanding of their role in planet formation.
These upcoming missions and explorations will undoubtedly expand our knowledge of asteroids and comets, allowing us to delve deeper into their composition, origins, and their impact on the formation of planets. As technology continues to advance, we can look forward to even more ambitious missions that will bring us closer to unlocking the mysteries of our cosmic neighborhood.
Conclusion

Conclusion
Asteroids and comets have long captivated our curiosity and played a crucial role in the formation of planets. These celestial wanderers, composed of various minerals and carrying volatiles and precious resources, have left their mark on our solar system’s evolution. By studying the composition, origin, and impact of asteroids and comets, scientists have gained valuable insights into the processes that shaped our planet and the potential for extraterrestrial life.
Through ongoing research and upcoming missions, we will continue to unravel the mysteries surrounding these cosmic bodies. Ongoing studies on asteroids and comets delve deeper into their origins, structures, and dynamics, shedding light on their formation and the role they play in planet formation. Furthermore, ongoing missions aim to explore and sample these celestial objects, providing us with valuable information about their composition and history.
In the ever-expanding field of planetary science, researchers are constantly pushing boundaries to understand how asteroids and comets contributed to the intricate process of planet formation. The knowledge gained from these studies will not only enhance our understanding of our own solar system but also inform our search for habitable worlds beyond.
As we eagerly await the results of future missions and advancements in scientific research, we can only imagine the wealth of knowledge that lies ahead. The study of asteroids and comets continues to fuel our sense of wonder and fascination, reminding us of the vastness and complexity of the universe in which we exist.
Frequently Asked Questions

1. Are all asteroids located in the asteroid belt?
No, while the asteroid belt located between Mars and Jupiter is a primary source of asteroids, they can also be found in other regions of the solar system, such as near Earth, in Trojan asteroid clusters, and even in the outer regions beyond Neptune.
2. How many asteroids have been discovered so far?
Thousands of asteroids have been discovered to date, with the number constantly increasing as more advanced telescopes and space missions are launched to explore and study these celestial objects.
3. Can asteroids collide with planets?
Yes, asteroids can collide with planets. In fact, such collisions have occurred throughout the history of our solar system and have left impact craters on various planetary bodies, including our own Moon, Mars, and even Earth.
4. Are all asteroids made of the same materials?
No, asteroids have different compositions depending on their origins and locations. They can be made of rock, metal, or a combination of both. Some asteroids may also contain valuable minerals and resources like iron, nickel, and even precious metals.
5. Are asteroids a threat to Earth?
While the majority of asteroids pose no immediate threat to Earth, there is a small possibility of a potentially hazardous asteroid crossing paths with our planet. Scientists and space agencies actively monitor such asteroids and are working on methods to deflect or mitigate any potential impact in the future.
6. Can asteroids contain water?
Yes, many asteroids contain traces of water ice. These icy asteroids are of particular interest to scientists as they could have delivered water and other volatiles to Earth during the early stages of its formation, playing a crucial role in the development of our planet’s atmosphere and the emergence of life.
7. Are there any missions to study asteroids up close?
Yes, several space missions have been launched to study asteroids up close. Examples include Japan’s Hayabusa mission, NASA’s OSIRIS-REx, and the European Space Agency’s (ESA) Rosetta mission, which landed a probe on a comet in addition to studying asteroids.
8. Can asteroids be used as stepping stones for space exploration?
Yes, asteroids can serve as potential stepping stones for future space exploration missions. Their low gravitational pull makes it easier to land on and launch from their surfaces, which could eventually enable the establishment of mining operations or serve as refueling stations for deep space missions.
9. How do scientists determine the composition of asteroids?
Scientists determine the composition of asteroids through various methods, including spectroscopy, which analyzes the light reflected off their surfaces. By measuring the different wavelengths of light, researchers can infer the presence of certain minerals and substances on the asteroids.
10. What can studying asteroids tell us about the formation of the solar system?
Studying asteroids provides valuable insights into the early stages of our solar system’s formation. Their composition and distribution help scientists understand the processes of accretion and planet formation, shedding light on how the planets, including Earth, came into existence and how the conditions for life were established.
References
Frequently Asked Questions

1. How did asteroids and comets form in the solar system?
Asteroids and comets are remnants from the early stages of the solar system’s formation. They formed from the leftover materials of the protoplanetary disk, which was a rotating disk of gas and dust surrounding the young Sun.
2. What are the differences in composition between asteroids and comets?
Asteroids are made up of rocky and metallic materials, resembling mini-planets. Comets, on the other hand, are composed of ice, dust, and organic compounds, giving them a more volatile nature.
3. How do asteroids contribute to the formation of planets?
Asteroids play a crucial role in planet formation. They act as building blocks by colliding and merging together, gradually forming larger bodies known as protoplanets. These protoplanets then have the potential to evolve into fully-fledged planets.
4. What is the significance of comets in the process of planet formation?
Comets are believed to have delivered volatile elements and water to young planets. The impact of comets on planets during their early formation stages could have provided essential ingredients for the development of life.
5. How do asteroids and comets interact with planets?
Asteroids and comets can interact with planets through accretion and collision events. These interactions can shape the planetary surface, cause volcanic activity, and even lead to mass extinctions.
6. What is the role of asteroids and comets in delivering volatile elements and water?
Asteroids and comets contain volatile elements and water locked within their composition. When they collide with planets, these materials are delivered, enriching the planet’s inventory of resources and potentially making it habitable.
7. What are the ongoing studies focused on asteroids and comets?
Current research is aimed at understanding the composition, origins, and trajectories of asteroids and comets. Scientists are studying their physical properties, such as size, shape, and surface features, to gain insights into the early history of our solar system.
8. Which upcoming missions are planned for exploring asteroids and comets?
Future missions, such as NASA’s Lucy, ESA’s Hera, and JAXA’s DESTINY+, are focused on exploring various asteroids and comets. These missions aim to gather more data about their composition, structure, and the potential for future resource utilization.
9. How do asteroids and comets contribute to orbital dynamics and stability?
Asteroids and comets can affect the orbital dynamics of planets. Their gravitational interactions can influence the stability of a planet’s orbit, potentially causing orbital changes, gravitational perturbations, and even altering the distribution of other celestial bodies.
10. What is the significance of studying asteroids and comets for understanding the formation of the universe?
Studying asteroids and comets provides valuable insights into the early stages of our solar system’s formation. By understanding their composition, origins, and interactions with planets, scientists can unravel the mysteries of how planets, including Earth, came to be and how life as we know it emerged.