Throughout history, astronomers have been fascinated by the alignments of celestial bodies and the impact they have on our understanding of the universe. The study of planetary alignments has played a crucial role in shaping astronomical discoveries, from ancient civilizations to modern space exploration. By observing and documenting the movements and relationships between planets, astronomers have been able to uncover fundamental laws of physics, make groundbreaking discoveries, and push the boundaries of our knowledge. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating journey of how planetary alignments have shaped astronomical discoveries throughout history, spanning ancient observations to the Copernican Revolution, technological advancements, and modern space exploration. So fasten your seatbelt and get ready for a celestial journey through time and space.
Contents
- Ancient Observations
- The Copernican Revolution
- New Discoveries with Technological Advancements
- Modern Space Exploration
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How did ancient civilizations track planetary alignments?
- 2. Why were planetary alignments important to ancient civilizations?
- 3. How did the Copernican Revolution change our understanding of planetary alignments?
- 4. What are Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion?
- 5. How did Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation contribute to our understanding of planetary alignments?
- 6. Which technological advancements led to the discovery of Uranus and Neptune?
- 7. Why did the search for Pluto involve the study of perturbations?
- 8. How did the Voyager missions contribute to our understanding of planetary alignments?
- 9. What recent planetary alignments have led to significant discoveries?
- 10. How do modern astronomers track and study planetary alignments?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How did ancient civilizations observe and interpret celestial events?
- 2. How did the Copernican Revolution change our understanding of planetary alignments?
- 3. What were Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion and how did they shape our understanding of celestial alignments?
- 4. How did Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation contribute to our understanding of planetary alignments?
- 5. How were Uranus and Neptune discovered through advancements in technology?
- 6. What role did perturbations play in the search for Pluto?
- 7. How did the Voyager missions contribute to our understanding of planetary alignments?
- 8. What recent planetary alignments have led to significant discoveries?
- 9. How do planetary alignments affect space exploration missions?
- 10. How have advancements in digital imaging technology improved our ability to study planetary alignments?
- References
- Read More
Ancient Observations

Ancient civilizations were keen observers of the night sky, and their observations of planetary alignments played a pivotal role in shaping our understanding of astronomy. In Mesopotamia, the cradle of civilization, astronomers meticulously recorded and interpreted celestial events, including planetary alignments, on clay tablets known as cuneiform texts. These texts reveal the Mesopotamians’ belief in the connection between celestial phenomena and earthly affairs. They recognized the cyclical patterns of planetary alignments and associated them with significant events such as the rise and fall of empires. Similarly, the Mayans, known for their sophisticated calendar system, closely monitored planetary alignments, particularly those involving Venus. They considered Venus as a celestial deity and believed its movements were linked to important aspects of their culture and religious practices. The Mayans also observed and documented other celestial events like eclipses and meteor showers, understanding the intricate relationship between the cosmos and their daily lives. These ancient observations highlight the rich history of planetary alignments and the profound impact they had on shaping the beliefs and knowledge of ancient civilizations.
1. Mesopotamian Astronomy
Mesopotamian astronomy holds a significant place in the history of planetary alignments. Ancient civilizations in Mesopotamia, such as the Babylonians and Assyrians, were pioneers in observing and documenting celestial events. Through their careful observations and recording on clay tablets known as cuneiform texts, they developed a deep understanding of planetary alignments and their association with earthly affairs.
Tablet collections like the Enuma Anu Enlil and the Mul.Apin texts provide valuable insights into the Mesopotamians’ astronomical knowledge. These texts contain detailed information about planetary positions, phases, and movements. The Mesopotamians observed the motion of the planets against the backdrop of fixed stars and recognized their cyclical patterns.
One of the key celestial events the Mesopotamians focused on was the planetary conjunctions. Conjunctions occur when two or more planets align in close proximity to each other in the night sky. These conjunctions were seen as significant omens, believed to foretell events of great importance. The Mesopotamians associated certain planetary alignments with the rise and fall of empires, wars, and natural disasters. They believed that the positioning and relationships of celestial bodies had a direct impact on events unfolding on Earth.
The Mesopotamians also closely observed the movements of planets like Venus. Venus was particularly important to them, and they associated it with their deities. They found that Venus followed a distinct pattern, appearing as both a morning and evening star at different times of the year. These observations allowed them to develop precise calendars and make predictions about future celestial events.
Mesopotamian astronomy played a pivotal role in uncovering the significance of planetary alignments. Through their meticulous observations and recording, the Mesopotamians laid the foundation for our understanding of celestial events and their connection to earthly affairs. Their contribution to the study of planetary alignments continues to inspire and fascinate astronomers today.
2. Mayan Astronomy
The Mayans were one of the most advanced ancient civilizations in terms of their understanding and knowledge of astronomy. They closely observed planetary alignments, particularly those involving Venus, which held significant importance in Mayan cosmology. Venus, known as “K’inch Ahaw” or the “Wasp Star,” played a central role in their religious and cultural practices. The Mayans believed that Venus was associated with various deities and represented different aspects of life, such as war and agriculture. They carefully tracked the movements of Venus and developed intricate calendars to accurately predict its cycles. These calendars played a crucial role in agricultural activities, determining the best times for planting and harvesting crops. The Mayans also associated Venus with matters of the heart and relationships, linking its movements to the harmony or discord in personal connections. They believed that the positions of Venus in the sky influenced love and emotions, and that understanding its alignments could provide guidance for romantic endeavors. This deep understanding of celestial alignments showcases the Mayans’ advanced astronomical knowledge and their recognition of the interconnectedness between the sky, nature, and human existence. For more information on the influence of celestial bodies on relationships, you can explore the link.
The Copernican Revolution
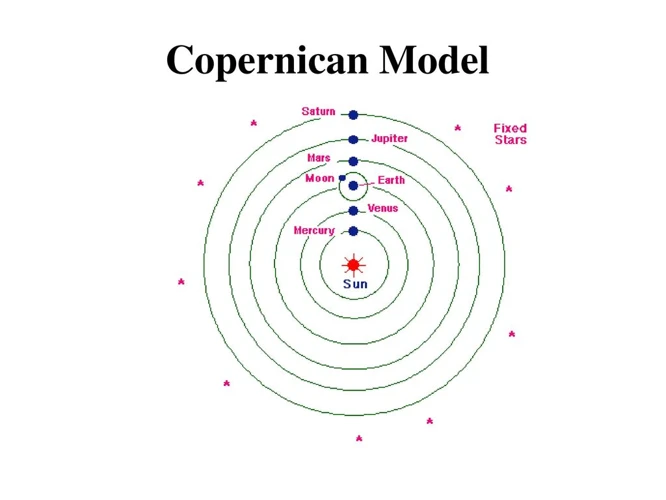
The Copernican Revolution marked a pivotal shift in our understanding of the cosmos, challenging the prevailing geocentric model and introducing the heliocentric model. In the 16th century, Nicolaus Copernicus proposed that the Sun, rather than the Earth, was at the center of the solar system, with the planets – including Earth – revolving around it. This revolutionary idea was supported by observations of planetary motion, including their apparent retrograde motion. Copernicus’s model not only simplified the understanding of planetary alignments but also provided a more accurate explanation for their observed patterns. His work laid the foundation for future advancements in astronomy and inspired other scientists to explore the nature of planetary motion. Although initially met with skepticism, Copernicus’s heliocentric model eventually gained wider acceptance as additional evidence, such as Tycho Brahe’s precise observations, supported its validity. The Copernican Revolution was a transformative period that reshaped our understanding of our place in the universe and laid the groundwork for further discoveries in astronomy and space exploration.
1. Planetary Model Shift
The Copernican Revolution marked a significant shift in our understanding of the solar system and the arrangement of planets. Prior to this revolution, the prevailing belief was the geocentric model, which placed Earth at the center of the universe and positioned the planets and the Sun in orbit around it. However, the groundbreaking work of Nicolaus Copernicus challenged this notion with his heliocentric model. According to Copernicus, the Sun, not Earth, was at the center of the solar system, and the planets, including Earth, orbited around it. This radical departure from the geocentric model ignited a scientific revolution and sparked debates that would shape astronomy for centuries to come. Copernicus’s ideas were further refined by Johannes Kepler, who proposed elliptical orbits for the planets rather than perfectly circular ones. Kepler’s laws of planetary motion provided a mathematical framework to describe the precise movements of the planets around the Sun. This planetary model shift laid the foundation for future astronomical discoveries and paved the way for a more accurate understanding of our place in the cosmos.
2. Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion
Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion revolutionized our understanding of how planets move and interact in the solar system. Johannes Kepler, a German astronomer and mathematician, formulated these laws based on his meticulous observations and calculations. Kepler’s First Law of Planetary Motion, also known as the law of ellipses, states that planets orbit the Sun in elliptical paths, with the Sun located at one of the foci of the ellipse. This law debunked the long-held belief that planetary orbits were perfect circles. Kepler’s Second Law of Planetary Motion, the law of equal areas, states that a line drawn from a planet to the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal time intervals. This means that a planet moves faster when it is closer to the Sun and slower when it is farther away, resulting in an even distribution of areas covered over time. Finally, Kepler’s Third Law of Planetary Motion, also known as the law of harmonies, establishes a mathematical relationship between a planet’s orbital period and its average distance from the Sun. This law allows astronomers to calculate the orbital period of a planet based on its distance from the Sun or vice versa. Kepler’s laws provided a mathematical framework for understanding planetary motion and laid the foundation for Isaac Newton’s later work on universal gravitation. They remain cornerstones of celestial mechanics and continue to be used in modern astronomical calculations and spacecraft missions, further advancing our knowledge of the solar system and beyond.
New Discoveries with Technological Advancements

Technological advancements in the field of astronomy have provided astronomers with new tools and methods to study planetary alignments, leading to groundbreaking discoveries. One of the most significant advancements was Sir Isaac Newton’s formulation of the Law of Universal Gravitation. Newton’s work revolutionized our understanding of planetary motion and enabled astronomers to accurately predict and explain the complex interactions between celestial bodies. With the aid of telescopes, astronomers were able to observe distant planets such as Uranus and Neptune, expanding our knowledge of the solar system. These technological advancements also led to the discovery of perturbations in the orbits of known planets, which ultimately led to the search for the elusive Planet X, later identified as Pluto. The exploration of the sixth house of the solar system, where Pluto resides, has provided valuable insights into the formation and evolution of our planetary neighborhood. Through these advancements, astronomers have not only deepened their understanding of planetary alignments but also gained insights into the broader workings of the universe.
1. Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation
Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation, formulated by Sir Isaac Newton in the 17th century, revolutionized the field of astronomy and our understanding of planetary motions. According to this law, every object in the universe attracts every other object with a force that is directly proportional to their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. This breakthrough principle provided a mathematical explanation for the observations made by astronomers regarding the motion of planets and their interactions. By applying Newton’s law, scientists could calculate the gravitational pull between celestial bodies, predict their positions in the sky, and understand how they influence each other’s orbits. This law not only validated Johannes Kepler’s laws of planetary motion but also paved the way for advancements in celestial mechanics, allowing astronomers to accurately predict future planetary alignments and determine the causes of historical celestial events. Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation laid the foundation for our modern understanding of gravity, planetary dynamics, and celestial navigation, shaping the way we explore and study the heavens to this day.
2. Discovery of Uranus and Neptune
The discovery of Uranus and Neptune stands as a testament to the power of planetary alignments and technological advancements in astronomy. In the late 18th and early 19th centuries, astronomers were able to predict the existence and location of new celestial bodies through their calculations based on observed planetary alignments. Building upon the gravitational theories proposed by Sir Isaac Newton, scientists predicted discrepancies in the observed orbits of known planets, suggesting the existence of additional planets beyond Saturn. Uranus, the first planet to be discovered through prediction, was officially recognized in 1781 by William Herschel. Its discovery challenged the existing understanding of the solar system and expanded our knowledge of celestial objects. The subsequent discovery of Neptune in 1846 by observationally predicting its location based on perturbations in Uranus’ orbit further solidified the idea that planetary alignments played a crucial role in identifying new celestial bodies. These discoveries revolutionized our understanding of the solar system and paved the way for future explorations and discoveries in the realm of outer space.
3. Perturbations and the Search for Pluto
Perturbations in the movements of celestial bodies have often been crucial in uncovering hidden worlds and expanding our knowledge of the universe. In the early 19th century, astronomers noticed irregularities in the orbit of Uranus that couldn’t be explained by known gravitational forces. These perturbations hinted at the existence of an undiscovered planet beyond Uranus. Leveraging mathematical calculations and predictions, astronomers embarked on a search for this mysterious planet. Percival Lowell, an American astronomer, played a key role in this search. He founded the Lowell Observatory in Arizona and dedicated many years to studying the perturbations and predicting the position of the unseen planet. Despite his efforts, Lowell passed away before the discovery could be made. It wasn’t until 1930 that Clyde Tombaugh, a young astronomer working at Lowell Observatory, finally spotted the distant planet through meticulous observations. The discovery of Pluto, named after the Roman god of the underworld, was a testament to the power of perturbations in unravelling the mysteries of the cosmos. However, in recent years, Pluto’s classification as a planet has been controversial. In 2006, it was reclassified as a “dwarf planet” due to its size and its orbit crossing that of Neptune. Nevertheless, the search for Pluto and its eventual discovery remains a significant milestone in the history of planetary alignments and celestial exploration.
Modern Space Exploration

In the realm of modern space exploration, planetary alignments continue to play a crucial role in guiding missions and uncovering new discoveries. The Voyager missions, for example, took advantage of a unique alignment of the outer planets in the late 1970s and early 1980s to conduct a historic Grand Tour of the solar system. Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 capitalized on the alignment to visit and closely study Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. These missions provided unprecedented insights into the characteristics and dynamics of these distant worlds, capturing stunning images and gathering valuable scientific data. More recently, planetary alignments have also aided in the discovery of exoplanets, planets outside our solar system. By monitoring the slight gravitational pull and subtle changes in the brightness of stars during planetary transits, astronomers have been able to identify and characterize numerous exoplanets, expanding our understanding of the vastness and diversity of the universe. The study of planetary alignments continues to push the boundaries of modern exploration, opening new avenues for scientific investigation and fueling our curiosity about the cosmos.
1. Voyager Missions and the Grand Tour
The Voyager missions, launched by NASA in the late 1970s, marked a new era in space exploration and provided unprecedented insights into the outer planets of our solar system. The Grand Tour, as it was famously called, involved two spacecraft, Voyager 1 and Voyager 2, embarking on a remarkable journey to explore Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
Voyager 1, launched in 1977, conducted a flyby of Jupiter in 1979, capturing mesmerizing images of the planet’s turbulent atmosphere, its intricate ring system, and its captivating moons such as Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto. The mission revealed the dynamic nature of these celestial bodies, with Europa, in particular, garnering significant attention due to its potential for hosting extraterrestrial life. The discoveries made by Voyager 1 at Jupiter set the stage for the subsequent encounters with Saturn and beyond.
Voyager 2, launched just two weeks earlier than Voyager 1, had its own incredible discoveries. The spacecraft reached Saturn in 1981, providing detailed images of the planet’s iconic rings, its intricate moon system, and the stormy atmospheres of Saturn and its moon, Titan. Voyager 2 then continued its journey to become the only spacecraft to fly by Uranus in 1986 and Neptune in 1989. These flybys offered the first-ever close-up views of these distant gas giants and their unique features, including Uranus’ tilted magnetic field and Neptune’s Great Dark Spot.
The Voyager missions not only revolutionized our understanding of the outer planets but also provided valuable data on the interplanetary medium and the outer boundaries of our solar system. Both spacecraft continue to transmit valuable data as they venture into deep space, exploring the uncharted territories beyond the planets. The Voyager missions truly exemplify the spirit of exploration and the insatiable curiosity of humanity to unravel the mysteries of the cosmos.
To learn more about the incredible world of meteors and their significance in astronomy and space exploration, click here: Meteors: Astronomy and Space Exploration.
2. Recent Planetary Alignments and Discoveries
In recent times, planetary alignments have continued to captivate astronomers and lead to remarkable discoveries. The advancements in technology have enabled scientists to observe and analyze these alignments with unprecedented precision. One significant recent alignment occurred in 2012 when Venus, Earth, and the Sun aligned in a rare celestial event known as the transit of Venus. This alignment allowed scientists to study Venus’ atmosphere and gather valuable data about its composition and structure. Additionally, the alignment of Mars and Earth in 2020 provided a unique opportunity for the launch of missions to the Red Planet. Several countries took advantage of this alignment to send their spacecraft to Mars, including NASA’s Perseverance rover, which successfully landed on Mars in February 2021. The study of recent planetary alignments has also contributed to our understanding of exoplanets. By observing the alignments of distant stars and their planets, astronomers can gather information about these alien worlds, such as their size, orbit, and even potential habitability. These recent alignments have pushed the boundaries of our knowledge and inspired ongoing research in planetary science and space exploration. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more exciting discoveries and insights to arise from future planetary alignments.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the study of planetary alignments throughout history has played a remarkable role in shaping the field of astronomy. Ancient civilizations recognized the significance of celestial events and their impact on earthly affairs, paving the way for the development of astronomical knowledge. The Copernican Revolution challenged the prevailing geocentric model and introduced a heliocentric view, revolutionizing our understanding of planetary motion. Technological advancements allowed for the discovery of new planets like Uranus and Neptune, while the search for Pluto highlighted the importance of perturbations caused by planetary alignments. Modern space exploration, including the Voyager missions, provided unprecedented insights into our solar system, capturing breathtaking images and expanding our understanding of planetary alignment phenomena. Today, recent planetary alignments continue to fuel scientific exploration, inspiring astronomers to uncover new discoveries and push the boundaries of our understanding of the universe. As we continue to explore the mysteries of the cosmos, it is clear that planetary alignments will remain a captivating and essential area of study in the field of astronomy.
Frequently Asked Questions

1. How did ancient civilizations track planetary alignments?
Ancient civilizations, such as the Mesopotamians and Mayans, tracked planetary alignments by carefully observing the movements of celestial bodies and recording them on clay tablets and other astronomical artifacts. They relied on elaborate systems of measurement, mathematical calculations, and astronomical tools to accurately track and predict planetary alignments.
2. Why were planetary alignments important to ancient civilizations?
Ancient civilizations believed that planetary alignments held significant meaning and had an influence on various aspects of their lives. They saw these alignments as celestial omens, which they interpreted to make predictions about events on Earth, such as the onset of seasons, agricultural cycles, or the rise and fall of dynasties. Planetary alignments also played a crucial role in their religious and cultural practices.
3. How did the Copernican Revolution change our understanding of planetary alignments?
The Copernican Revolution, spearheaded by Nicolaus Copernicus, introduced the heliocentric model of the solar system, which placed the Sun at the center instead of Earth. This revolutionary shift in thinking helped astronomers gain a more accurate understanding of planetary alignments, as they realized that the apparent motions of planets were a result of both their orbit around the Sun and Earth’s own motion.
4. What are Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion?
Johannes Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion describe how planets move in the solar system. Kepler’s First Law states that planets move in elliptical orbits around the Sun. The Second Law, also known as the Law of Equal Areas, states that a line connecting a planet to the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal time intervals. Kepler’s Third Law relates the orbital period of a planet to its distance from the Sun.
5. How did Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation contribute to our understanding of planetary alignments?
Isaac Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation provided a comprehensive explanation for the motions of celestial bodies, including planetary alignments. This law states that every object in the universe attracts every other object with a force that is directly proportional to their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. Newton’s law allowed astronomers to accurately predict and understand the gravitational interactions responsible for planetary alignments.
6. Which technological advancements led to the discovery of Uranus and Neptune?
The discovery of Uranus in 1781 and Neptune in 1846 was made possible by advancements in telescope technology. The improved telescopes allowed astronomers to observe faint celestial objects and detect the presence of these distant planets. Mathematical calculations based on observed perturbations in the orbits of other planets also played a crucial role in predicting and subsequently discovering Uranus and Neptune.
7. Why did the search for Pluto involve the study of perturbations?
The search for Pluto began due to unexplained perturbations observed in the orbit of Neptune. Astronomers hypothesized that the perturbations were caused by the gravitational pull of an unknown celestial body. Percival Lowell initiated an extensive search for this hypothetical “Planet X,” and Clyde Tombaugh eventually discovered Pluto in 1930. The study of perturbations and their impact on planetary orbits was instrumental in locating Pluto.
8. How did the Voyager missions contribute to our understanding of planetary alignments?
The Voyager missions, launched by NASA in the late 1970s, provided valuable data and insights into the planets of our solar system, their alignments, and their moons. The spacecraft conducted flybys of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune, capturing detailed images and collecting scientific measurements. These missions not only enhanced our understanding of planetary alignments but also revealed numerous discoveries about the composition, atmosphere, and unique characteristics of these distant worlds.
9. What recent planetary alignments have led to significant discoveries?
In recent years, planetary alignments have facilitated significant discoveries in our solar system. For instance, the alignment of Mars, Earth, and the Sun allowed for the successful landing and exploration of rovers on Mars. Additionally, the alignment of Jupiter’s moons has been crucial in studying their interactions and uncovering new information about their geological activity. These recent alignments continue to provide scientists with opportunities for groundbreaking research and exploration.
10. How do modern astronomers track and study planetary alignments?
Modern astronomers use advanced technologies such as telescopes, satellites, and space probes to track and study planetary alignments. They rely on precise measurements, computer simulations, and mathematical models to predict and understand the motions and relationships between celestial bodies. These sophisticated tools and techniques allow astronomers to explore the complex dynamics of planetary alignments and unlock the mysteries of our ever-evolving universe.
References
- A History of Astrometry – Part I Mapping the Sky From Ancient …
- Planetary Motion: The History of an Idea That Launched …
- Timeline of Solar System astronomy
Frequently Asked Questions

1. How did ancient civilizations observe and interpret celestial events?
Ancient civilizations like the Mesopotamians and Mayans used their advanced astronomical knowledge to observe celestial events, track planetary movements, and interpret their significance. They built intricate observatories and developed calendars based on celestial events.
2. How did the Copernican Revolution change our understanding of planetary alignments?
The Copernican Revolution challenged the prevailing belief that Earth was the center of the universe. Copernicus proposed that the planets, including Earth, orbited the Sun. This shift in thinking revolutionized our understanding of planetary alignments and paved the way for future discoveries.
3. What were Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion and how did they shape our understanding of celestial alignments?
Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion described the way planets move in elliptical orbits around the Sun. These laws provided a mathematical framework for understanding planetary alignments more accurately and predicting their future positions.
4. How did Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation contribute to our understanding of planetary alignments?
Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation explained how gravity influenced planetary motion. By understanding the forces acting on the planets, astronomers were able to make more precise predictions about their alignments and study their gravitational interactions.
5. How were Uranus and Neptune discovered through advancements in technology?
The discovery of Uranus and Neptune was made possible by improvements in telescope technology. Astronomers utilized more powerful telescopes and observed abnormal planetary movements, leading to the identification of these new planets in our solar system.
6. What role did perturbations play in the search for Pluto?
Perturbations, or slight deviations in the expected paths of known planets, helped astronomers predict the existence of an unknown planet beyond Neptune. This led to the discovery of Pluto in 1930 and highlighted the importance of understanding how planetary alignments can influence celestial discoveries.
7. How did the Voyager missions contribute to our understanding of planetary alignments?
The Voyager missions provided valuable insights into the outer planets of our solar system and their alignments. They conducted a “Grand Tour” that allowed scientists to study the gravitational interactions, composition, and atmospheres of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune, further expanding our knowledge of planetary alignments.
8. What recent planetary alignments have led to significant discoveries?
Recent planetary alignments have played a crucial role in the discovery of exoplanets, or planets outside our solar system. By observing the tiny dips in light caused by exoplanets passing in front of their parent stars during alignments, astronomers have identified numerous new planets in distant star systems.
9. How do planetary alignments affect space exploration missions?
Planetary alignments can influence the trajectory and timing of space exploration missions. By taking advantage of alignments, spacecraft can utilize gravity assists or perform complex maneuvers to reach their destinations more efficiently, conserving fuel and resources.
10. How have advancements in digital imaging technology improved our ability to study planetary alignments?
Advancements in digital imaging technology have allowed astronomers to capture high-resolution images of planetary alignments and analyze the data more effectively. This has enabled us to study the intricate details of planetary alignments and make new discoveries about our universe.
References
- The Birth of Modern Astronomy
- Four amazing astronomical discoveries from ancient Greece
- Early Astronomy







