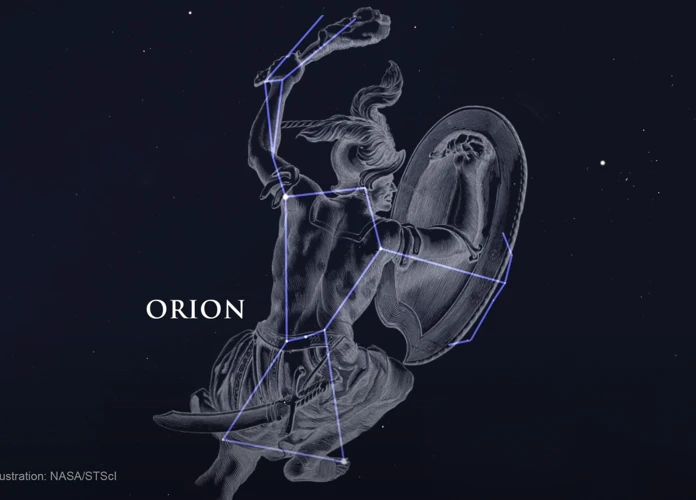
The Orion constellation has captivated the curiosity and wonder of humans for centuries. Its dazzling stars and mythical origins have sparked our imagination and left us in awe of the vastness of the universe. In this article, we will delve into the history and origins of Orion, exploring the ancient mythology surrounding it, the observations and nomenclature associated with it, its astronomical significance, notable stars and objects within the constellation, as well as the misconceptions and legends that have emerged over time. Journey with us as we unravel the mysteries of the Orion constellation and discover the secrets it holds.
Contents
- Ancient Mythology
- Observations and Nomenclature
- Astronomical Significance
- Notable Stars and Objects
- Misconceptions and Legends
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What is the significance of the Orion constellation in ancient Greek mythology?
- 2. How did the Egyptians interpret the Orion constellation?
- 3. Were there any variations in the interpretation of the Orion constellation among different ancient cultures?
- 4. Can the Orion constellation be seen from all parts of the world?
- 5. What is the significance of the Orion Nebula within the constellation?
- 6. Has the Orion constellation been used for navigation throughout history?
- 7. Are there any notable stars within the Orion constellation?
- 8. What is the Orion’s Sword and the Great Orion Nebula?
- 9. Are there any other observable features within the Orion constellation?
- 10. How has the Orion constellation influenced fiction and pop culture?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How did the Orion constellation get its name?
- 2. What is the significance of the Orion constellation in ancient cultures?
- 3. Is Orion visible from both hemispheres?
- 4. How far away is the Orion Nebula?
- 5. Are there any famous stars within the Orion constellation?
- 6. What is the Hunter’s Belt in the Orion constellation?
- 7. How did ancient cultures interpret the Orion constellation?
- 8. Can the Orion constellation be used for navigation?
- 9. Are there any myths or legends associated with the Orion constellation?
- 10. How has the Orion constellation influenced popular culture?
- References
- Read More
Ancient Mythology
The ancient mythology surrounding the Orion constellation is rich and varied, with tales passed down through generations. In Greek mythology, Orion was believed to be a great hunter, known for his exceptional strength and prowess. According to one legend, Orion’s arrogance led him to challenge the gods, who in turn sent a scorpion to kill him. This led to the creation of the constellation Scorpius, forever locked in a cosmic battle with Orion. Other ancient cultures also had their own interpretations of Orion. The Egyptians associated it with the god Osiris, while the Babylonians saw it as a shepherd. These myths highlight the enduring fascination humans have had with the stars and the role they played in shaping ancient belief systems.
1.1 Greek Mythology
In Greek mythology, the Orion constellation holds a prominent place in the celestial narratives. According to the ancient Greeks, Orion was a mighty hunter, known for his incredible strength and skills. The most popular myth surrounding Orion is his ill-fated encounter with a scorpion. Orion’s hubris and boastfulness led him to challenge the gods, who then sent a giant scorpion to ultimately defeat him. As the story goes, Orion was stung and killed by the scorpion, which was placed in the sky as the constellation Scorpius. Orion’s placement among the stars is often portrayed with his raised arm outstretched, holding a club and a lion’s pelt. This depiction aligns with his role as a hunter and warrior in Greek mythology. The Greek myths associated with Orion showcase the importance of this constellation in their culture and the enduring legacy of their beliefs in the heavens. For more information about the constellation system and its historical importance, you can read our article here.
1.2 Other Ancient Cultures
Other ancient cultures also had their own interpretations of the Orion constellation. In Egyptian mythology, Orion was associated with Osiris, the god of the afterlife and the underworld. They believed that Osiris was immortalized as Orion in the night sky. The pyramids of Giza were even aligned with the stars of Orion’s belt. The Babylonians saw the constellation as a shepherd, representing their agricultural way of life. They believed that the movement of Orion across the sky corresponded with the changing seasons and the timing of their agricultural activities. In Native American cultures, Orion was often associated with winter and the changing of the seasons. The Lakota Sioux, for example, saw the constellation as a warrior chasing a group of seven sisters, known as the Pleiades. These diverse interpretations show how different cultures found meaning and significance in the stars above, and how the Orion constellation played a role in shaping their beliefs and traditions.
Observations and Nomenclature

The observations and nomenclature associated with the Orion constellation have evolved over time, reflecting the cultural and scientific advancements of different civilizations. One of the most recognizable features of Orion is the three stars that form his “belt,” which have been observed and referenced by various cultures throughout history. In Greek astronomy, the stars of Orion’s belt were known as the “διάσκελοι” or diáskeloi, meaning “the legs” or “the crossbeam.” These stars played a significant role in celestial navigation, serving as a marker for sailors and travelers. While the ancient Greeks made significant contributions to our understanding of Orion, they were not the only ones to observe and name the constellation. Different cultures around the world have their own names and associations for the stars within Orion, adding to its rich tapestry of nomenclature and cultural significance. To learn more about the connections between astrology and the Orion constellation, check out our article on astrological houses predicting the future.
2.1 The Hunter and His Belt
In the constellation of Orion, there is a prominent feature known as “The Hunter and His Belt.” This refers to a line of three bright stars that form a distinct pattern resembling a belt around Orion’s waist. The three stars are named Alnitak, Alnilam, and Mintaka, each shining brightly in the night sky. According to mythology, these stars are said to represent the hunter’s belt or sword. Interestingly, this iconic belt can be seen from various cultures throughout history. In Greek mythology, they were believed to be the golden belt of the hunter, while in other ancient cultures, such as ancient Egypt, they were associated with Osiris’ resurrection and his role as a judge of the dead. The three stars of Orion’s belt have served as a navigational tool for centuries, with sailors and explorers using them as a marker to navigate the night sky. Today, they continue to capture the imagination of stargazers and serve as a reminder of the enduring beauty and significance of the stars above.
2.2 Variations in Different Cultures
Variations in the interpretation of the Orion constellation can be found across different ancient cultures. In Mesopotamian mythology, Orion was associated with the hero Nimrod, known for his great hunting skills. The constellation was believed to represent him and his mighty bow. Similarly, in Chinese mythology, Orion was known as Shen, the great warrior. The Chinese saw the three stars in Orion’s Belt as members of a celestial court, with the brightest star, Mintaka, representing the emperor. In Hindu mythology, the constellation was associated with Lord Murugan, the god of war and victory. The diverse interpretations of Orion in different cultures highlight the universality of human fascination with the stars and the varied ways in which they were incorporated into ancient belief systems. These cultural variations add depth to the mythology surrounding the constellation, offering insights into the different perspectives and stories that have been passed down through generations.
Astronomical Significance
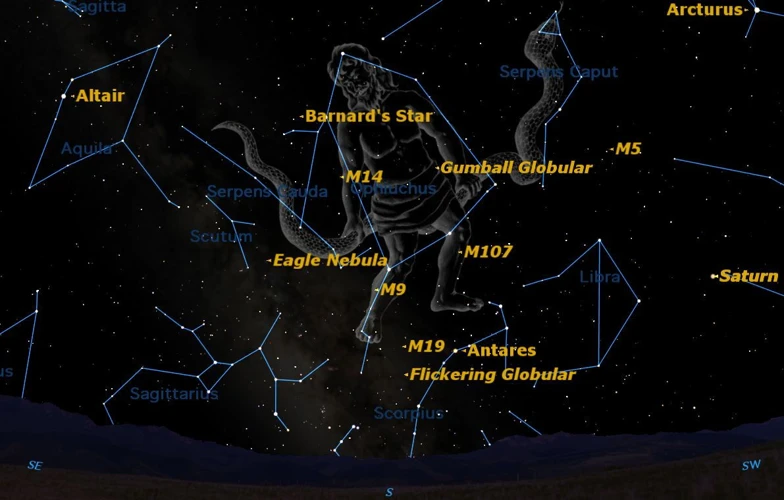
The Orion constellation holds great astronomical significance, captivating both astronomers and stargazers alike. One of its notable features is the Orion Nebula, located within Orion’s sword. This nebula is a hotbed of star formation, giving scientists valuable insights into the birth and evolution of stars. Additionally, Orion has played a crucial role in navigation throughout history. Sailors and explorers have used its distinctive belt made up of three bright stars as a guide to orient themselves in the night sky. This constellation’s prominent position and easily recognizable shape have made it an important landmark for adventurers and astronomers. The Orion constellation’s astronomical significance continues to inspire and educate, unlocking the secrets of the universe for those who dare to gaze upon it.
3.1 Orion Nebula and Star Formation
Located in the constellation of Orion, the Orion Nebula is one of the most famous and easily recognizable stellar nurseries in the night sky. It is a vast cloud of gas and dust where new stars are born. The nebula is illuminated by a cluster of young, hot stars known as the Trapezium. These stars are so bright that they ionize the surrounding gas, causing it to emit a colorful glow. The Orion Nebula is a site of active star formation, with ongoing studies and observations shedding light on the processes that give rise to new stars. At the heart of the nebula lies an intricate network of dust and gas known as the “Pillars of Creation.” These structures are massive columns of dust and gas that serve as incubators for new stars. The intense radiation from nearby stars erodes the material in these pillars, leading to the birth of new stellar objects. The Orion Nebula provides astronomers with a valuable opportunity to study the early stages of star formation in great detail. By examining the interactions between the young stars and the surrounding nebula, scientists can gain insights into the mechanisms that shape the evolution of galaxies and the formation of planetary systems. It is a testament to the beauty and complexity of the universe, reminding us of the awe-inspiring processes that shape the cosmos.
The Orion constellation has played a significant role in navigation throughout history. Sailors and travelers have relied on the position of the stars to guide them on their journeys, and Orion has been a prominent reference point for centuries. The three stars that form Orion’s Belt serve as an excellent navigational tool, especially in the northern hemisphere. By aligning their vessel’s course with the Belt, sailors could determine their direction in relation to other celestial bodies, such as the North Star. Additionally, Orion’s bright stars made it easily recognizable even in unfavorable weather conditions, providing a reliable point of reference for navigation. Today, modern navigational systems have replaced reliance on the stars, but the historical importance of Orion in navigation cannot be overstated. Its presence in the night sky served as a guiding light for explorers and adventurers across the ages.
Notable Stars and Objects
The Orion constellation is home to several notable stars and objects that have fascinated astronomers and stargazers alike. One of the most prominent stars in Orion is Betelgeuse. This red supergiant star is known for its variable brightness and is easily recognizable as the upper-left shoulder of Orion. Another significant star within the constellation is Rigel, situated at the lower-right foot of Orion. Rigel is a blue supergiant and one of the brightest stars in the night sky. The constellation also features the famous Orion’s Sword, consisting of three stars that form a line hanging from Orion’s belt. Within Orion’s Sword lies the Great Orion Nebula, a stellar nursery where new stars are born. This nebula is a stunning sight in the night sky and has captured the attention of astronomers due to its active star-forming activity. These notable stars and objects within the Orion constellation continue to inspire astronomers and spark the imagination of those who gaze upon the cosmos.
4.1 Betelgeuse and Rigel
Betelgeuse and Rigel are two of the most prominent stars within the Orion constellation. Betelgeuse, located on Orion’s left shoulder, is a red supergiant and one of the largest known stars in our galaxy. Its name is derived from the Arabic phrase meaning “the armpit of the central one,” as it marks the armpit of the celestial hunter. Betelgeuse is a variable star, meaning its brightness fluctuates over time. This variability has made it an object of interest for astronomers studying stellar evolution. Despite its vast distance of approximately 640 light-years from Earth, Betelgeuse is easily visible to the naked eye due to its immense size.
On the other hand, Rigel, situated on Orion’s right foot, is a blue-white supergiant and one of the brightest stars in the night sky. Its name originates from the Arabic term for “foot,” indicating its position within the constellation. Rigel shines with an intense blue-white glow, showcasing its extreme heat and luminosity. With a distance of about 860 light-years from Earth, Rigel is a young and massive star that is evolving rapidly. It is estimated to be approximately 23 times more massive than our sun and shines over 120,000 times brighter.
Both Betelgeuse and Rigel play prominent roles in the visual appearance of Orion and have captivated the attention of astronomers and stargazers throughout history. Their distinct characteristics and positions within the constellation make them essential celestial landmarks for navigation and observation. Studying these remarkable stars offers insights into the life cycles of massive stars and the processes that drive their evolution. To learn more about celestial observations and their intersection with astrology, check out our article on the unveiling of tarot card secrets in horoscope.
4.2 Orion’s Sword and Great Orion Nebula
Orion’s Sword, located just below Orion’s Belt, is a prominent feature of the constellation. It consists of several stars and is accompanied by a well-known and visually striking nebula called the Great Orion Nebula. The Great Orion Nebula, also known as M42, is a stellar nursery where new stars are born. It is one of the most studied and photographed objects in the night sky. Within the nebula, gas and dust are compressed, triggering the formation of new stars. The nebula is illuminated by the intense radiation emitted by these young stars, creating a breathtaking display of glowing gas and intricate dust patterns. The Great Orion Nebula is visible to the naked eye and is a popular target for amateur astronomers and astrophotographers. Its proximity to Orion’s Sword makes it an easily identifiable and captivating sight in the night sky.
4.3 Other Observable Features
4.3 Other Observable Features about the Orion constellation offer a plethora of fascinating celestial objects and phenomena to explore. Among these is the Flame Nebula, a brightly illuminated patch of gas and dust located just below Alnitak, the easternmost star in Orion’s Belt. The nebula derives its name from the fiery appearance of its glowing gases. Another notable feature is the Running Man Nebula, which lies just to the southeast of the Orion Nebula. It is so named due to the shape of the gases and dust that resemble a person in motion. Additionally, there is the Horsehead Nebula, a dark nebula in the shape of a horse’s head, located in the emission nebula IC 434. While these objects may not be as prominently known as some of the other features in the constellation, they provide astronomers and enthusiasts alike with a wealth of beauty and wonder to observe and study. Exploring these other observable features further enhances our understanding and appreciation of the diverse and captivating nature of the Orion constellation.
Misconceptions and Legends

Throughout history, the Orion constellation has been the subject of various misconceptions and legends that have added to its allure. One popular misconception is the belief that the three stars of Orion’s Belt align perfectly with the pyramids of Giza, giving rise to theories of ancient extraterrestrial influence. While the alignment is not exact, it has fueled speculation about hidden connections between the constellations and Earth’s ancient civilizations. Additionally, Orion’s prominence in the night sky has made it a common point of reference in popular culture, from ancient texts to modern science fiction. It is often associated with bravery, heroism, and adventure, inspiring countless tales and legends. Its enduring presence in literature, art, and movies has cemented its place in the collective imagination. Whether through ancient mysteries or pop culture, the misconceptions and legends surrounding Orion have contributed to its enduring fascination.
5.1 The Orion Conspiracy
The Orion Conspiracy is a popular theory that has caught the attention of many conspiracy theorists and enthusiasts. According to this belief, there is a hidden agenda surrounding the Orion constellation, with some claiming that it holds a significant secret or knowledge that is being kept from the general public. This theory proposes that certain organizations or individuals are intentionally hiding information related to the true nature and purpose of Orion. Some suggest that ancient civilizations may have had advanced knowledge about the stars and their influence on human life, and that this knowledge is being suppressed. The Orion Conspiracy has inspired numerous books, websites, and documentaries, with proponents speculating on everything from extraterrestrial connections to hidden codes within the constellation itself. However, it is important to note that the Orion Conspiracy falls into the realm of speculation and is not supported by scientific evidence. While the mystery and allure of the Orion constellation continue to capture our imagination, it is crucial to approach such theories with a critical and rational mindset.
5.2 Orion’s Influence on Fiction and Pop Culture
Orion’s influence on fiction and pop culture is vast and far-reaching. Its prominence in mythology has translated into numerous appearances in literature, film, and art throughout history. One notable example is its inclusion in Greek tragedies and epics, such as Homer’s “Odyssey” and Aeschylus’ “Prometheus Bound,” where Orion is often depicted as a prominent character or a symbol of power and resilience. In modern literature, Orion continues to inspire and captivate readers. The constellation has been featured in science fiction novels, such as Isaac Asimov’s “Foundation” series, where it serves as a galactic hub of civilization. Orion has also made appearances in the works of J.R.R. Tolkien, where it is referenced as a guiding star or a celestial landmark. In film and television, Orion has played a prominent role as both a visual element and a source of inspiration. It has appeared in movies like “Blade Runner,” where it serves as a backdrop for futuristic cityscapes, and in the “Men in Black” franchise, where it is depicted as the headquarters of the secretive organization. Pop culture references to Orion can also be found in music, with artists like Florence and the Machine making allusions to the constellation in their lyrics. Orion’s influence on fiction and pop culture is a testament to its enduring appeal and ability to spark the imagination of creators and audiences alike.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the Orion constellation has a long and captivating history that spans across cultures and time. From the myths and legends of Greek and other ancient civilizations to its significance in navigation and astronomy, Orion has left an indelible mark on human imagination and understanding. The stars that form Orion, such as Betelgeuse and Rigel, as well as its notable objects like the Great Orion Nebula, continue to captivate stargazers and astronomers alike.
The misconceptions and legends surrounding Orion, such as the Orion Conspiracy and its influence on fiction and pop culture, showcase the enduring allure and impact of this celestial figure. While some may argue that the constellations are arbitrary human creations, there is no denying the beauty and wonder they inspire.
As we gazed at the heavens, we recognize that the constellations are more than just astronomical formations; they are stories etched onto the tapestry of the night sky. Orion, with its rich mythology and symbolism, invites us to ponder the mysteries of the universe and our place within it.
In an ever-changing world, the Orion constellation stands as a timeless reminder of our human fascination with the cosmos. It serves as a beacon of inspiration, encouraging us to explore, dream, and never cease to marvel at the wonders that await us beyond the Earth’s atmosphere. By delving into the history and origins of Orion, we not only gain a deeper appreciation of our ancient past but also a glimpse into the vastness and beauty of the universe that stretches before us.
So, next time you find yourself gazing up at the night sky, take a moment to locate Orion and let its stories and mysteries transport you to realms both mythical and scientific. Embrace the curiosity and wonder that have driven humans throughout history and continue to propel us into the future of discovery and exploration.
Frequently Asked Questions

1. What is the significance of the Orion constellation in ancient Greek mythology?
In Greek mythology, Orion was a renowned hunter known for his exceptional strength. He was said to have been placed among the stars by the gods, immortalizing his legend and serving as a reminder of his greatness.
2. How did the Egyptians interpret the Orion constellation?
The Egyptians associated the Orion constellation with their god Osiris, who was the lord of the afterlife. They believed that Osiris resided among the stars, and the appearance of Orion in the night sky marked the journey of Osiris through the underworld and his subsequent rebirth.
3. Were there any variations in the interpretation of the Orion constellation among different ancient cultures?
Absolutely! Different ancient cultures had their own unique interpretations of Orion. The Babylonians saw it as a shepherd, emphasizing its role in guiding celestial bodies. The indigenous peoples of Australia associated the constellation with a hunter accompanied by his loyal dog.
4. Can the Orion constellation be seen from all parts of the world?
Yes, the Orion constellation is visible from most parts of the world. However, its position in the sky may vary depending on the viewer’s location and the time of year. For example, in the Northern Hemisphere, Orion is typically seen in the winter months.
5. What is the significance of the Orion Nebula within the constellation?
The Orion Nebula, also known as Messier 42, is a stunning celestial object located within the Orion constellation. It is a stellar nursery where new stars are born, and its study has provided valuable insights into the process of star formation and evolution.
Absolutely! The Orion constellation has been used by various ancient civilizations as a navigational aid. Its prominent stars, such as Betelgeuse and Rigel, have served as markers for sailors and travelers to determine their position and direction.
7. Are there any notable stars within the Orion constellation?
Yes, there are several notable stars within the Orion constellation. Betelgeuse, a red supergiant star, and Rigel, a blue supergiant star, are two of the brightest stars in the constellation. They contribute to Orion’s distinctive appearance in the night sky.
8. What is the Orion’s Sword and the Great Orion Nebula?
The Orion’s Sword is a distinctive feature within the Orion constellation. It consists of a trio of stars that appear in a straight line, resembling a celestial sword hanging from Orion’s belt. The central star in the sword is associated with the famous Great Orion Nebula, a stellar nursery and one of the most visually stunning objects in the night sky.
9. Are there any other observable features within the Orion constellation?
Yes, besides the prominent stars and nebulae, there are other observable features within the Orion constellation. It contains several star clusters, such as the Orion Nebula Cluster, which is a collection of young stars that formed from the same molecular cloud.
10. How has the Orion constellation influenced fiction and pop culture?
The intriguing mythology and striking appearance of the Orion constellation have inspired countless works of fiction and have had a significant impact on popular culture. From literature to movies, the Orion constellation continues to be featured as a symbol of bravery, adventure, and exploration.
References
Frequently Asked Questions

1. How did the Orion constellation get its name?
The Orion constellation is named after the mythological character Orion, a legendary hunter in Greek mythology who was known for his strength and size.
2. What is the significance of the Orion constellation in ancient cultures?
The Orion constellation holds great significance in various ancient cultures, representing different celestial beings such as a hunter, a shepherd, and even a god associated with the underworld.
3. Is Orion visible from both hemispheres?
Yes, the Orion constellation is visible from both the northern and southern hemispheres, making it one of the most widely recognized constellations around the world.
4. How far away is the Orion Nebula?
The Orion Nebula, located within the Orion constellation, is approximately 1,344 light-years away from Earth.
5. Are there any famous stars within the Orion constellation?
Yes, two notable stars within the Orion constellation are Betelgeuse and Rigel. Betelgeuse is a red supergiant star, while Rigel is a blue supergiant star.
6. What is the Hunter’s Belt in the Orion constellation?
The Hunter’s Belt is a distinctive feature in the Orion constellation, consisting of three bright stars that are aligned in a straight line. It represents Orion’s belt and is easily recognizable in the night sky.
7. How did ancient cultures interpret the Orion constellation?
Ancient cultures interpreted the Orion constellation differently. For example, in Egyptian mythology, Orion was associated with the god Osiris, while in Polynesian cultures, it represented a fishhook or a canoe.
Yes, the Orion constellation has been used for navigation throughout history. It served as a useful guide for sailors and travelers, particularly in the northern hemisphere.
9. Are there any myths or legends associated with the Orion constellation?
Yes, there are several myths and legends associated with the Orion constellation. One popular legend is that Orion was stung by a scorpion and was placed in the sky as both a cautionary tale and a reminder of his valor.
10. How has the Orion constellation influenced popular culture?
The Orion constellation has had a significant influence on popular culture. It has been featured in numerous books, movies, and artworks, often portraying Orion as a powerful and heroic figure, adding to his mythological legacy.