The night sky has long captured the imagination of humanity, sparking a sense of wonder and curiosity about the cosmos. Constellations, the patterns of stars that form recognizable shapes in the sky, have played a significant role in our history and culture. From ancient civilizations to modern astronomy, constellations have been a source of fascination and inspiration. In this article, we will explore the origins and history of constellations, delving into the ancient traditions of the Mesopotamians, Egyptians, Greeks, and Chinese. We will also uncover the role of constellations in Western culture, their mystical and cultural significance, and the future of these celestial formations. Get ready to embark on a captivating journey through the stars.
Contents
- What are Constellations?
- Ancient Civilizations and Early Constellations
- Constellations in Western Culture
- Mystical and Cultural Significance of Constellations
- Future of Constellations
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the oldest known constellation?
- How many constellations are officially recognized?
- Do all cultures see the same constellations?
- Can constellations change over time?
- Are constellations made up of stars within close proximity?
- How were constellations used for navigation in the past?
- What is the significance of zodiac constellations?
- Are there any new constellations that have been discovered recently?
- Do constellations have different meanings across cultures?
- Can I see constellations from both the northern and southern hemispheres?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- How did ancient civilizations identify and name constellations?
- Were constellations the same in different ancient civilizations?
- What role did constellations play in navigation?
- Why were constellations important in astrology?
- How have constellations been depicted in art and literature?
- What is the significance of the constellation Orion?
- Do constellations have scientific relevance today?
- Are there any new constellations discovered in recent times?
- Can constellations change over time?
- What are some popular modern constellations?
- References
- Read More
What are Constellations?
Constellations are patterns of stars that appear to form shapes or figures in the night sky. These celestial formations have captured the imagination of humans throughout history. The various cultures around the world have identified and named different constellations, each with its own significance and mythology. One way to understand constellations is to imagine connecting the stars with imaginary lines, creating a recognizable shape or pattern. Some constellations are widely known, such as the Big Dipper and Orion, while others may be more obscure. The stars that make up a constellation may not be physically related or even close to each other in space. They may be at different distances from Earth and even belong to different galaxies. Yet, when viewed from our perspective on Earth, they align to create visually appealing shapes. Additionally, constellations provide astronomers with a practical way to locate and study stars and other celestial objects. By using recognizable patterns in the sky, astronomers can navigate the vastness of space and make observations. The International Astronomical Union (IAU) has defined 88 official constellations, dividing the entire sky into distinct regions. These constellations help astronomers communicate and study the night sky more effectively. Now that we have a basic understanding of what constellations are, let’s explore how they originated and their significance in different cultures and time periods.
Ancient Civilizations and Early Constellations
Ancient civilizations played a crucial role in the development and understanding of constellations. The Mesopotamians, one of the earliest known civilizations, were skilled astronomers who observed the night sky and associated certain patterns of stars with their religious beliefs and agricultural practices. They documented their observations of constellations, such as the “Great Twins” and the “Bull of Heaven,” on clay tablets. The Egyptians also had a deep connection with the stars, linking constellations to their religious and mythological beliefs. The constellation of Orion, with its three bright stars forming the hunter’s belt, held special significance in Egyptian culture. The ancient Greeks, known for their advancements in science and philosophy, made significant contributions to the study of constellations. Figures from Greek mythology, such as Perseus, Hercules, and Pegasus, were immortalized in the night sky as constellations. In Chinese astronomy, constellations were associated with celestial, mythical animals or gods. These ancient civilizations laid the foundation for our understanding of constellations and their significance, intertwining myth, religion, and the observation of the night sky. Through their observations and cultural interpretations, they passed down a rich celestial heritage that continues to fascinate us to this day.
The Mesopotamians
The Mesopotamians, one of the earliest civilizations in history, played a crucial role in the development of constellations. They were inhabitants of the region known as Mesopotamia, located in what is now present-day Iraq. The Mesopotamians believed that the stars in the sky were the gods themselves, and they assigned divine significance to these celestial bodies. They meticulously observed the night sky and documented the movements and positions of the stars and planets. The Mesopotamians developed an advanced system of astronomy, creating the basis for our understanding of constellations today. They divided the sky into various sections and identified specific constellations within each region. One of their most notable contributions was the creation of the zodiac, a band of constellations that lie along the path of the Sun, Moon, and planets. The zodiac was divided into twelve equal parts, each represented by a different constellation. This system allowed the Mesopotamians to track the movements of celestial bodies and make predictions about the future. The Mesopotamians believed that the positions of the stars and planets influenced human destiny and used astrology as a means of divination. They believed that the movement of the constellations and celestial bodies corresponded to events on Earth, shaping individual lives and the course of civilizations. The knowledge and understanding of constellations held immense importance in Mesopotamian society, serving as a guide for agriculture, navigation, and religious rituals. The Mesopotamians’ contribution to the study of constellations laid the foundation for future civilizations and cultures to explore and interpret the night sky. Their legacy lives on in the field of astronomy, where their observations and discoveries continue to shape our understanding of the universe.
The Egyptians
The Egyptians, an ancient civilization known for their rich mythology and astronomical knowledge, also had their own constellations. They believed that the stars in the sky were the dwelling place of their gods and had a significant influence on their daily lives. The Egyptians identified certain groupings of stars as representations of their deities and incorporated them into their religious practices. One prominent constellation in Egyptian culture was Orion, which they associated with the god Osiris. They believed that Osiris became the constellation after his death and that it was a symbol of rebirth and the afterlife. The Egyptians also recognized the constellation Ursa Major, which they referred to as “The Thigh,” and associated it with their god Seth. They believed that the movement of this constellation across the sky had an impact on the flooding of the Nile River, which was crucial for their agricultural livelihood. These Egyptian constellations played a significant role in their religious ceremonies, calendar systems, and agricultural practices. The alignment of certain constellations with specific events such as the flooding of the Nile served as a guide for their agricultural activities. The Egyptians’ understanding and interpretation of the constellations reflect their deep connection to the natural world and the celestial realm.
The Greeks
The Greeks made significant contributions to the study and understanding of constellations. Ancient Greek astronomers believed that the gods themselves were responsible for the placement of the stars in the night sky. They saw constellations as representations of mythical figures and creatures from their rich mythology. One of the most famous Greek constellations is Orion, a hunter who was placed among the stars after his death. The Greeks also named constellations after their heroes, such as Perseus and Hercules. They used these celestial formations not only for navigation but also to tell stories and transmit cultural knowledge. Greek astronomer Ptolemy, in the 2nd century AD, cataloged and described 48 constellations in his influential work called the Almagest. These constellations formed the basis for Western astronomy for several centuries. The Greeks’ belief in the divine origin of constellations influenced the naming and interpretation of these celestial patterns. Their contributions laid the foundation for the study of constellations and their mythology, which continues to fascinate and inspire us today. To learn more about the influence of constellations on astrology, you can read our guide on Decoding Birth Chart: A Guide to Understanding Natal Astrology.
The Chinese
The Chinese civilization has a rich history of studying and utilizing constellations. Ancient Chinese astronomers took great interest in observing the stars and mapping out the night sky. They developed their own unique system of constellations, known as the Chinese zodiac or Shí-èr Shēngxiāo. The Chinese zodiac consists of twelve main constellations, each associated with a particular animal. These animals include the Rat, Ox, Tiger, Rabbit, Dragon, Snake, Horse, Sheep, Monkey, Rooster, Dog, and Pig. The Chinese zodiac was not only used for astronomical purposes but also played a significant role in astrology and cultural beliefs. The Chinese believed that the animal associated with a person’s birth year influenced their personality traits and destiny. This belief continues to be popular in Chinese culture today and is used for matchmaking, fortune-telling, and personality analysis. In addition to the Chinese zodiac, Chinese astronomers also grouped other stars into constellations representing various objects and animals from Chinese mythology. For example, the constellation Qi Xi represents the mythical story of the Cowherd and the Weaver Girl and is associated with the annual Qixi Festival. The Chinese constellations often differ from those recognized in Western astronomy, leading to unique cultural interpretations of the night sky. The Chinese culture’s fascination with the stars and their connection to astrology and mythology has had a lasting impact on their perception and understanding of constellations. To delve deeper into the mysteries of the Chinese zodiac and its influence, read our article on /ophiuchus-enigma-mystery-serpent-bearer/.
Constellations in Western Culture
In Western culture, constellations have played a prominent role throughout history, influencing both scientific exploration and cultural symbolism. During the Renaissance period, there was a resurgence of interest in astronomy, leading to the birth of modern astronomy. Astronomers such as Nicolaus Copernicus and Johannes Kepler made groundbreaking discoveries by studying the movements of celestial bodies, including the stars in constellations. Exploration and new discoveries in the field of astronomy further expanded our knowledge of constellations. In contemporary astronomy, constellations continue to serve as a reference system for locating and classifying stars, galaxies, and other celestial objects. They provide a framework for mapping the night sky and facilitating astronomical research. Constellations have infiltrated various aspects of Western culture, from art to literature and even astrology. Artists have been inspired by the beauty of constellations, incorporating them into their artwork, while writers have woven tales and legends around these celestial patterns. Additionally, in astrology, specific constellations, known as zodiac constellations, are associated with personality traits and astrological signs. The cultural significance of constellations in Western society continues to thrive, representing both scientific curiosity and creative imagination. (source: sagittarius-aries-rising-compatibility)
The Renaissance and the Birth of Modern Astronomy
The Renaissance period marked a significant turning point in the study of astronomy and the understanding of constellations. During this time, there was a revival of intellectual pursuits and an increased emphasis on empirical observation and scientific enquiry. Pioneering astronomers like Nicolaus Copernicus, Tycho Brahe, and Johannes Kepler made groundbreaking discoveries that challenged the geocentric view of the universe.
Nicolaus Copernicus, a Polish astronomer, proposed the heliocentric model of the solar system, which placed the Sun at the center instead of the Earth. This revolutionary idea challenged the long-held belief that the Earth was the center of the universe and opened up new possibilities for the study of celestial objects, including constellations.
Tycho Brahe, a Danish astronomer, meticulously observed the sky and compiled detailed data on the positions of stars and planets. His observations laid the foundation for future advancements in the field of astronomy. Brahe’s observations provided valuable insights into the movements of celestial bodies, including the stars that formed constellations.
Johannes Kepler, a German astronomer and mathematician, built upon the work of Copernicus and Brahe. Using Brahe’s data, Kepler formulated his laws of planetary motion, which described how planets moved in elliptical orbits around the Sun. Kepler’s discoveries contributed to a more accurate understanding of the positions and movements of stars and constellations in the night sky.
During the Renaissance, there was also a renewed interest in mapping the night sky. Astronomical instruments like the telescope and the astrolabe were developed, enabling astronomers to make more precise observations and measurements. These advancements in technology allowed for the identification and cataloging of a greater number of constellations.
The Renaissance period was a pivotal time in the history of astronomy and the study of constellations. The groundbreaking discoveries and advancements in observational techniques paved the way for the birth of modern astronomy, leading to a more comprehensive understanding of the stars and the constellations they form.
Exploration and New Discoveries
Exploration and new discoveries in the field of astronomy have greatly expanded our knowledge of constellations and the universe as a whole. With advancements in technology and space exploration, astronomers have been able to study the stars and celestial objects in unprecedented detail. Satellites and telescopes have been sent into space to observe distant galaxies, allowing scientists to map and identify new constellations. One such example is the discovery of the constellation Ophiuchus, also known as the Serpent Bearer. Ophiuchus was not officially recognized as a constellation by the International Astronomical Union until 1930, despite its presence in ancient texts and depictions. This discovery and recognition shed light on the rich history and mythology associated with this constellation. Alongside new discoveries, astronomers continue to study and understand existing constellations. Technology such as spectroscopy has revealed intricate details about the composition and behavior of stars within constellations. It has also provided insights into stellar evolution and the formation of galaxies. The exploration and observations of constellations are ongoing, with astronomers and scientists constantly pushing the boundaries of our understanding of the universe. These new discoveries not only deepen our knowledge of constellations but also contribute to our understanding of the vastness and complexity of the cosmos.
Constellations in Contemporary Astronomy
Constellations continue to play a vital role in contemporary astronomy, aiding scientists in their exploration and understanding of the universe. In modern times, constellations serve as reference points for identifying and locating celestial objects in the night sky. Astronomers use these patterns to navigate and map out the vastness of space. The International Astronomical Union (IAU) has standardized the official list of constellations, providing a common framework for astronomers worldwide. These constellations serve as a celestial coordinate system, allowing astronomers to pinpoint the exact location of stars, galaxies, and other celestial phenomena.
In addition to their navigational significance, constellations in contemporary astronomy also play a role in astronomical research and discovery. By studying the distribution and arrangement of stars within a constellation, scientists can gain insights into stellar evolution, the formation of galaxies, and even the nature of dark matter. Constellations provide astronomers with a shared language and framework for communication. When discussing observations or discoveries, referring to specific constellations helps ensure clarity and precision in scientific discourse.
Advancements in technology, such as powerful telescopes and computer simulations, have further enhanced our understanding of constellations in contemporary astronomy. Through high-resolution imaging and spectroscopic analysis, astronomers can explore the intricate details of stars within constellations, unraveling their composition, temperature, and distance from Earth. These findings contribute to our broader knowledge of the cosmos and our place within it.
The concept of constellations has extended beyond traditional star patterns. With the discovery of exoplanets and the emergence of the field of astrobiology, astronomers have begun to identify and map constellations based on the presence of potential habitable worlds. These newly defined “exoplanet constellations” represent regions in the sky where exoplanets have been discovered, encouraging further exploration and the search for extraterrestrial life.
Constellations remain an integral part of contemporary astronomy, serving as a foundation for observation, research, and discovery. As technology and scientific understanding continue to evolve, these celestial formations will undoubtedly continue to shape and inspire our exploration of the universe.
Mystical and Cultural Significance of Constellations
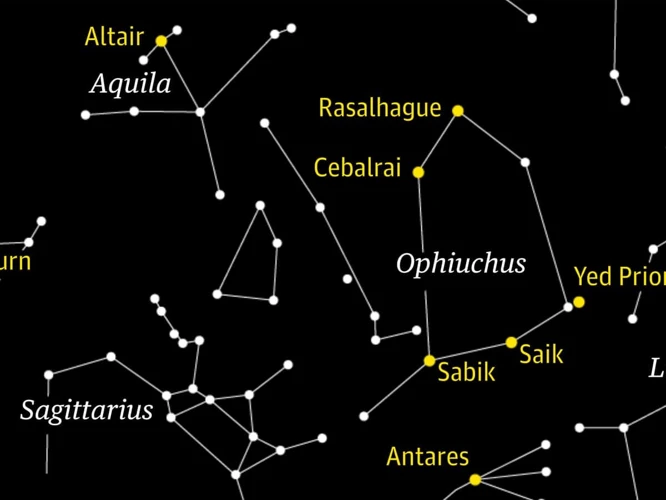
Constellations hold great mystical and cultural significance throughout history, intertwining with mythological stories, astrology, art, and literature. These beautiful patterns in the sky have inspired countless tales and legends, connecting the celestial realms to human existence. Mythological stories surrounding constellations often explain the origins of stars and their connection to gods and heroes. For instance, the Greek myth of Orion portrays the mighty hunter who was placed among the stars after his death. Astrology, on the other hand, assigns meaning and personality traits to zodiac constellations, linking them to an individual’s birth chart and horoscope. The constellations’ influence extends beyond mythology and astrology into art and literature, where they serve as symbols of beauty, adventure, and the limitless expanse of the universe. From Van Gogh’s Starry Night to Shakespeare’s references to the “twinkling of constellations,” these celestial formations have evoked wonder and inspiration for creative minds throughout the ages. Today, constellations continue to captivate our imagination, and their deep cultural significance enriches our understanding of the cosmos and our place within it.
Mythological Stories and Legends
Mythological stories and legends have played a significant role in the history and interpretation of constellations. Various ancient civilizations wove intricate tales around the patterns of stars they observed in the night sky. These stories often involved gods, heroes, and mythical creatures, providing explanations for the origins and meaning of constellations. For example, in Greek mythology, the constellation Orion represents a mighty hunter. The story goes that Orion’s boastfulness angered the gods, who then placed him in the heavens as a constellation. Similarly, the constellation Ursa Major, also known as the Great Bear, has its origin in Greek mythology. It is said to represent Callisto, a nymph whom Zeus transformed into a bear to protect her from his jealous wife Hera. The stories surrounding constellations not only served as entertainment but also helped ancient civilizations navigate and understand the natural world around them. They provided a way to remember and pass down knowledge of the stars and their movements, as well as the cultural and moral values associated with them. Today, these mythological stories continue to fascinate and inspire, connecting us to our ancient past and the wonders of the cosmos.
Astrology and Zodiac Constellations
Astrology, an ancient practice that has its roots in the belief that the positions and movements of celestial bodies can influence human behavior and personality, is closely intertwined with constellations. Astrologers have long associated specific constellations with different personality traits and the events that occur during specific times of the year. These constellations are known as the Zodiac constellations. The Zodiac is a band in the sky made up of twelve constellations that lie along the ecliptic path, which is the apparent path of the Sun across the sky throughout the year. Each of these Zodiac constellations is associated with a specific time period, known as a zodiac sign. These signs include Aries, Taurus, Gemini, Cancer, Leo, Virgo, Libra, Scorpio, Sagittarius, Capricorn, Aquarius, and Pisces. Astrologers believe that the position of the Sun, Moon, and planets in relation to these zodiac constellations at the time of a person’s birth can provide insights into their personality traits and future events. For example, individuals born under the sign of Leo are often associated with qualities such as confidence, leadership, and creativity, while those born under the sign of Libra are often seen as diplomatic, balanced, and harmonious. Astrology enthusiasts consult birth charts, which map the positions of these celestial bodies at the time of birth, to gain a deeper understanding of themselves and their destiny. While astrology and its connection to zodiac constellations have been met with skepticism by the scientific community, they continue to be a source of fascination and study for many people around the world, offering insights into the complexities of human nature and the interplay between the celestial and terrestrial realms.
Constellations in Art and Literature
Constellations have not only captivated astronomers and ancient civilizations but have also inspired artists and writers throughout history. Their presence in art and literature is a testament to their enduring cultural significance. Artists have incorporated constellations into their works, depicting them as intricate and mesmerizing patterns of stars. Paintings, sculptures, and tapestries have showcased constellations as a way of connecting the earthly realm with the celestial sphere. In literature, constellations have often been used as metaphors or symbols, representing various concepts such as destiny, enlightenment, and interconnectedness. They have served as a source of inspiration for poets, allowing them to evoke a sense of wonder and awe. One example is the famous constellation of Orion, which has been referenced in countless poems and epic tales. Additionally, constellations have had an impact on astrology, where they are seen as significant markers in interpreting and understanding individual personalities, relationships, and life events. The zodiac constellations, in particular, play a central role in astrology, revealing insights into one’s character traits and compatibility with others. Constellations have a versatile and enduring presence in the realms of art and literature, continuing to inspire and ignite the human imagination.
Future of Constellations
The future of constellations holds exciting possibilities for both scientific exploration and cultural significance. Advancements in technology, particularly in the field of astronomy, continue to shape our understanding of the cosmos. With the development of more powerful telescopes and space exploration missions, we can expect to uncover new constellations and gain deeper insights into existing ones. Scientists are constantly discovering new stars, galaxies, and celestial objects, which may lead to the creation of additional constellations in the future. Advancements in virtual reality and augmented reality technologies offer new ways to experience and interact with constellations. These technologies allow us to project and visualize constellations in immersive ways, enhancing our understanding and connection to the stars. In addition to scientific advancements, constellations will continue to hold cultural and symbolic significance. They serve as a source of inspiration in various art forms, literature, and even astrology. As our society evolves, so too will our interpretation and use of constellations. Whether they continue to be a navigational tool, a source of storytelling, or a symbol of cultural identity, constellations will undoubtedly remain an integral part of our collective human experience. The future of constellations is a journey of endless exploration, discovery, and imagination.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the origins and history of constellations showcase the deep connection between humanity and the stars. Across ancient civilizations such as the Mesopotamians, Egyptians, Greeks, and Chinese, constellations served as navigational guides, storytelling tools, and sources of cultural and mystical significance. As Western astronomy evolved during the Renaissance and modern era, constellations played a pivotal role in mapping the night sky and making groundbreaking discoveries. Today, constellations continue to inspire and captivate us, from their presence in mythology and astrology to their representation in art and literature. While our understanding of the universe has expanded, constellations remain a timeless reminder of our place in the cosmos. As we gaze up at the night sky, we can’t help but wonder about the countless stories hidden among the stars. So, let us continue to explore and appreciate the beauty and mystery of constellations, allowing them to guide our celestial journeys and fuel our curiosity for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions

What is the oldest known constellation?
The oldest known constellation is the constellation of Ursa Major, also known as the Great Bear. It has been recognized and named since ancient times, with its distinct shape resembling a bear.
How many constellations are officially recognized?
There are 88 officially recognized constellations by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). These constellations divide the entire sky into distinct regions for easier study and navigation.
Do all cultures see the same constellations?
No, different cultures have identified and named different constellations based on their unique perspectives and mythology. While some constellations are shared across cultures, many have variations in their interpretation and names.
Can constellations change over time?
Constellations appear to shift over long periods of time due to a phenomenon known as precession. This occurs because the Earth’s axis slowly wobbles, causing the positions of stars to change relative to our perspective.
Are constellations made up of stars within close proximity?
Not necessarily. Constellations are formed by connecting stars that appear close to each other from our viewpoint on Earth. However, these stars may be at different distances and belong to different galaxies.
Ancient civilizations used constellations as navigational aids. By observing the positions of certain constellations and their movements throughout the night, sailors and travelers could determine directions and time.
What is the significance of zodiac constellations?
Zodiac constellations are a specific group of constellations that lie along the ecliptic, the apparent path of the Sun across the sky. They are used in astrology and are associated with different personality traits and horoscopes.
Are there any new constellations that have been discovered recently?
While there are no new official constellations, astronomers continue to discover and name individual stars and star systems. These discoveries contribute to our understanding of the universe but do not necessarily create new constellations.
Do constellations have different meanings across cultures?
Yes, constellations can have different meanings and interpretations across cultures. They often reflect the specific mythology, beliefs, and stories of each civilization.
Can I see constellations from both the northern and southern hemispheres?
Yes, constellations can be seen from both the northern and southern hemispheres. However, the specific constellations visible will vary depending on your location and the time of year.
References
Frequently Asked Questions

How did ancient civilizations identify and name constellations?
Ancient civilizations observed patterns in the stars and used them to create stories and myths. They named constellations after animals, gods, heroes, and other significant figures in their culture.
Were constellations the same in different ancient civilizations?
No, different ancient civilizations had their own unique constellations. While some constellations were similar across cultures, there were also many differences based on their respective myths and legends.
Constellations served as important navigational tools for sailors and explorers. By locating specific constellations, they could determine their position and navigate the seas.
Why were constellations important in astrology?
Constellations were considered to have astrological significance because they were believed to influence human behavior and destiny. Each zodiac sign is associated with a specific constellation.
How have constellations been depicted in art and literature?
Constellations have been depicted in various art forms such as paintings, sculptures, and literature. They have often been used as symbols of beauty, mystery, and celestial wonder.
What is the significance of the constellation Orion?
The constellation Orion holds great significance in many ancient cultures. It is associated with mythical hunters, such as the Greek hero Orion and the Maya god Hun Hunahpu.
Do constellations have scientific relevance today?
Yes, constellations still hold scientific relevance today. They provide astronomers with a framework for locating and studying celestial objects and are used in astronomical surveys and mapping.
Are there any new constellations discovered in recent times?
No, new constellations have not been officially discovered in recent times. However, astronomers have identified new celestial objects within existing constellations.
Can constellations change over time?
Constellations themselves do not change, but their positions in the sky can shift over time due to the Earth’s precession. This means that their appearance in the night sky may vary slightly over centuries.
What are some popular modern constellations?
Some popular modern constellations include Ursa Major (the Big Dipper), Orion, Canis Major (the Great Dog), and Scorpius. These constellations are known for their distinctive shapes and visibility in the night sky.