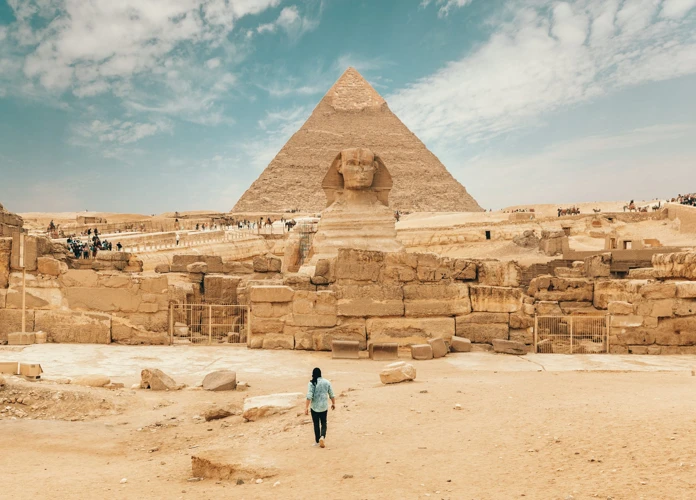
Imagine standing at the edge of the vast desert, the golden sands stretching into the distance, and in the midst of this barren landscape, towering majestic and enigmatic, are the Pyramids of Egypt. These ancient structures, hailing from a time long past, have captivated the human imagination for centuries. The mythology behind the pyramids adds another layer of intrigue to their already awe-inspiring presence. Exploring the religious significance, mythical connections, and theories surrounding these age-old marvels, we delve into a world where gods and mortals intertwined, and where the secrets of the afterlife were believed to be unlocked. Join us on a journey to unravel the mysteries of the Pyramids of Egypt and discover the enchanting mythology that surrounds them.
Contents
- The Ancient Egyptian Cosmology
- Religious Significance of Pyramids
- Mythical Connections: Gods and the Afterlife
- The Pyramid Texts
- Pyramids as Heavenly Stairways
- The Sphinx: Guardian of the Pyramids
- The Enigma of the Ophiuchus Zodiac Sign
- Theories and Speculations
- Modern Fascination and Pop Culture Influences
- Legacy of the Pyramids
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How were the Pyramids of Egypt built?
- 2. Why were the Pyramids built in the shape of a pyramid?
- 3. How long did it take to build a pyramid?
- 4. Were the pyramids built as tombs?
- 5. How were the pyramids aligned with celestial bodies?
- 6. What rituals and ceremonies took place at the pyramids?
- 7. Did all pharaohs have pyramids built for them?
- 8. What was the purpose of the small pyramids surrounding the main pyramids?
- 9. How were the pyramids protected against grave robbers?
- 10. What is the significance of the pyramid’s numerical proportions?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. Can we visit the inside of the pyramids?
- 2. How long did it take to build a pyramid?
- 3. Were the pyramids built by slaves?
- 4. How were the pyramids aligned with the stars?
- 5. What is the significance of the pyramid shape?
- 6. Were there any treasures buried inside the pyramids?
- 7. How were the pyramids built without modern technology?
- 8. Were there any curses associated with the pyramids?
- 9. How were the pyramid texts discovered?
- 10. Do the pyramids still align with astronomical events today?
- References
- Read More
The Ancient Egyptian Cosmology

The Ancient Egyptian cosmology forms the foundation of the mythology surrounding the Pyramids of Egypt. According to their beliefs, the universe was divided into three main realms: the sky, the earth, and the underworld. The sky was represented by the goddess Nut, who arched over the earth like a protective canopy. The earth was personified by the god Geb, while the underworld was ruled by Osiris, the god of the afterlife. This cosmological framework was intricately connected to the construction of the pyramids. It was believed that these monumental structures were the earthly representations of the primordial mound, the place where creation first took place. The pyramids were seen as a means to bridge the gap between the earthly realm and the divine, serving as a conduit for the pharaoh’s journey to the afterlife. This cosmological understanding also influenced the alignment of the pyramids with the celestial bodies, such as the Orion constellation, in an attempt to align the earthly and heavenly realms. The Ancient Egyptian cosmology not only provided a spiritual backdrop for the construction of the pyramids but also shaped their architectural design and astronomical significance. It is through this cosmological lens that we begin to unravel the fascinating mythology surrounding these ancient structures.
Religious Significance of Pyramids

The pyramids held immense religious significance in ancient Egyptian culture. These awe-inspiring structures were considered as sacred sites, symbolizing the connection between the earthly realm and the realm of the gods. The Egyptians believed that the pharaohs were divine beings and the intermediaries between the mortal world and the gods. The construction and design of the pyramids were aligned with religious rituals and beliefs, reflecting the divine nature of the pharaohs and their journey into the afterlife. The pyramids served as monumental tombs for the pharaohs, where their bodies were preserved and prepared for the afterlife. The rituals performed within these sacred structures included purification ceremonies, offerings to the gods, and the recitation of spells and prayers. The pyramids also housed elaborate burial chambers and intricate passageways, symbolizing the journey of the pharaoh’s soul to join the gods in the celestial realm. The religious significance of the pyramids cannot be overstated, as they represented the ultimate link between humanity and the divine. Through these monumental structures, the ancient Egyptians sought to eternalize their relationship with the gods and ensure the pharaoh’s successful transition to the realm of the immortals. To explore more about the afterlife beliefs in different cultures, you can check out our article Exploring Afterlife in Japanese Mythology.
1. The Pyramids as Sacred Structures
The Pyramids of Egypt were not merely architectural marvels; they held a sacred and spiritual significance for the ancient Egyptians. These monumental structures were believed to be the earthly homes of the pharaohs, who were considered divine beings. The pyramids served as the final resting place for the pharaohs, preserving their physical bodies for eternity while also ensuring their smooth transition into the afterlife. The careful construction and alignment of the pyramids were essential in maintaining the balance between the earthly realm and the divine. The pyramids were built with precise measurements and orientations, aligning them with the cardinal directions and astronomical phenomena. The ancient Egyptians believed that such precision allowed the pharaoh’s soul to ascend to the heavens, joining the gods in eternal bliss. The pyramids’ sacredness extended beyond the pharaohs themselves, acting as powerful symbols of divine presence and protection. The grandeur and imposing nature of the pyramids were seen as reflections of the gods’ power on Earth. The Pyramids of Egypt were not just magnificent structures; they were spiritual conduits connecting humans to the divine realm. They embodied the complex web of beliefs and symbolism that defined ancient Egyptian religion and mythology. Exploring the pyramids as sacred structures allows us to delve into the deep spiritual significance they held for the ancient Egyptians and the eternal legacy they left behind.
2. Symbolism and Rituals Associated with Pyramids
Symbolism played a crucial role in the construction of the pyramids and the rituals associated with them. The shape of the pyramid itself held deep significance, representing the rays of the sun extending downwards and connecting the earthly and divine realms. The pyramid’s four triangular sides were believed to symbolize the four cardinal directions, emphasizing the structure’s alignment with cosmic forces. The pyramid’s apex, reaching towards the heavens, was seen as a direct pathway to the gods. Another symbolism associated with the pyramids was their alignment with specific celestial bodies, such as the Orion constellation. These alignments were believed to facilitate the pharaoh’s transition to the afterlife and ensure their divine transformation. Rituals performed inside the pyramids involved offerings to the deceased pharaoh, invoking the gods for protection and guidance on their journey. These rituals often included the recitation of prayers and the burning of incense. The inner chambers of the pyramids were adorned with intricate artwork depicting religious scenes and hieroglyphic inscriptions, further enhancing their sacred nature. The symbolism and rituals associated with the pyramids reflected the Ancient Egyptians’ deep connection to the divine realm and their belief in the pharaoh’s access to the gods in the afterlife.
Mythical Connections: Gods and the Afterlife

In ancient Egyptian mythology, the gods and the afterlife were deeply intertwined with the construction and purpose of the pyramids. One prominent figure in this mythology is Osiris, the god of the underworld. He was believed to be the ruler of the afterlife and the judge of the deceased souls. The pyramids were built as grand tombs for the pharaohs, serving as a gateway for their journey to the afterlife and their eventual reunion with Osiris. Another significant deity is Ra, the sun god, who represented life and rebirth. The positioning of the pyramids aligned with the movement of the sun, symbolizing the pharaoh’s ascent to the heavens after death. Additionally, the sky god Horus played a vital role in the mythology surrounding the pyramids. Horus was often depicted as a falcon, and it was believed that he protected the pharaoh’s soul during its journey through the afterlife. These mythical connections between the gods and the afterlife give the pyramids a profound spiritual significance, showcasing the ancient Egyptians’ beliefs in the cycle of life, death, and rebirth. Through these connections, the pyramids became not only monumental structures but also sacred conduits to the divine realm.
1. Osiris, the God of the Underworld
Osiris, the God of the Underworld, played a crucial role in the mythology associated with the Pyramids of Egypt. In ancient Egyptian belief, Osiris was the ruler of the afterlife and the judge of the deceased. He represented the cycle of life, death, and rebirth. Osiris was depicted as a mummified figure, emphasizing his association with the realm of the dead. According to myth, Osiris was betrayed and killed by his brother Seth, who dismembered his body and scattered the pieces across Egypt. Osiris’ wife, Isis, gathered these fragments and reassembled them, allowing Osiris to be resurrected. This story of death and rebirth symbolized the eternal cycle of life and immortality. The role of Osiris in pyramid mythology is tied to the belief that pharaohs, as descendants of Osiris, would journey to the afterlife to join him. The pyramids served as the pharaoh’s final resting place and were constructed with the hope of facilitating a successful transition to the realm of Osiris. The rituals and ceremonies performed in the pyramids were aimed at ensuring the pharaoh’s judgment and ascension to immortality. The mythology surrounding Osiris and his involvement in the afterlife played a significant role in the construction, symbolism, and religious practices associated with the Pyramids of Egypt. (Source: [fascinating-relationship-constellations-astral-projection])
2. Ra, the Sun God
Ra, the Sun God, held immense significance in Ancient Egyptian mythology and played a prominent role in the symbolism and rituals associated with the pyramids. As the sun traveled across the sky, Ra was believed to be the one who brought life, light, and warmth to the world. This celestial deity was often depicted as a falcon-headed man or as a falcon with the sun disk on his head. The pyramids, with their towering height and triangular shape, were seen as representations of the rays of the sun reaching towards the heavens. The alignment of the pyramids with the sun’s movement further emphasized their connection to Ra. During the summer solstice, the sun would align perfectly with the entrance of certain pyramids, casting its rays deep into the complex. This alignment was believed to signify the presence and blessing of Ra, and it was a crucial event during religious ceremonies. The prominence of Ra in the mythology of the pyramids underscores the importance of the sun and its life-giving properties in Ancient Egyptian culture. It is through this lens that we can begin to truly understand the reverence bestowed upon the pyramids and their association with Ra, the mighty Sun God.
3. Horus, the Sky God
Horus, the Sky God, played a significant role in the mythology surrounding the Pyramids of Egypt. In ancient Egyptian mythology, Horus was often depicted as a falcon-headed god who symbolized the sky, power, and protection. He was believed to be the son of Osiris and Isis, and was regarded as the rightful heir to the throne of Egypt. As the sky god, Horus was associated with the sun and moon, representing the eternal cycle of day and night. His connection to the sky made him a prominent figure in the construction of the pyramids. The ancient Egyptians believed that Horus was responsible for ensuring the pharaoh’s safe passage into the afterlife, guiding their soul toward the heavens. The alignment of the pyramids with certain celestial bodies, such as the Orion constellation, was a manifestation of the connection between Horus, the sky god, and the journey to the divine realm. This celestial alignment not only represented the pharaoh’s ascension to the heavens but also symbolized the eternal presence of Horus watching over the pyramids and the land of Egypt. Horus’s role as the sky god further emphasized the religious significance and mythical connections associated with the pyramids, solidifying their place in ancient Egyptian cosmology.
The Pyramid Texts

The Pyramid Texts are a collection of religious texts and spells that were inscribed on the walls of the pyramids during the Old Kingdom of Ancient Egypt. These texts, written in hieroglyphics, were meant to guide and assist the pharaoh in their journey to the afterlife. The Pyramid Texts depict a rich mythology centered around the resurrection and ascension of the pharaoh, ultimately reaching a state of eternal life among the gods. They contain spells and rituals for the pharaoh to navigate the treacherous underworld and gain favor from the gods. The texts also emphasize the divine nature of the pharaoh, highlighting their close connection to the gods and their role as a mediator between the earthly and divine realms. It is within the Pyramid Texts that we find references to mythological figures such as Osiris, Horus, and Ra, representing different aspects of the afterlife and showcasing the intricate belief system of the ancient Egyptians. The Pyramid Texts provide valuable insights into the religious and mythological beliefs of the time, shedding light on the profound significance of the pyramids and their role in the journey to the afterlife. They are a testament to the deep spiritual and mythological traditions that formed the foundation of ancient Egyptian civilization.
Pyramids as Heavenly Stairways

The Pyramids of Egypt have long been regarded as celestial structures, with their pointed apexes reaching towards the heavens. In the mythology surrounding these majestic monuments, they were believed to serve as heavenly stairways, facilitating the journey of the deceased pharaohs’ souls to the afterlife. This concept was closely tied to the Ancient Egyptian belief in the Duat, the realm of the gods and the final resting place for the righteous. The pyramids were viewed as physical portals that connected the earthly realm with the divine, bridging the gap between mortals and gods. Just as the pyramid’s construction required immense effort and precision, the journey of the pharaoh’s soul was seen as a demanding ascent towards spiritual enlightenment. The design elements of the pyramids further reinforced the notion of ascension, with their sloping sides symbolizing the gradual climb towards the heavens. This concept is exemplified by the Great Pyramid of Giza, which, at over 480 feet in height, was considered a remarkable feat of engineering and ambition. The pyramids’ alignment with certain constellations, such as Orion’s Belt, added to their celestial symbolism. This alignment was believed to facilitate the pharaoh’s transition from earthly existence to the realm of the gods. The notion of pyramids as heavenly stairways exemplifies the intricate relationship between mythology, cosmology, and the architectural marvels of ancient Egypt. By understanding this symbolism, we gain a deeper appreciation for the profound spiritual significance attributed to these monumental structures.
/table
The Sphinx: Guardian of the Pyramids
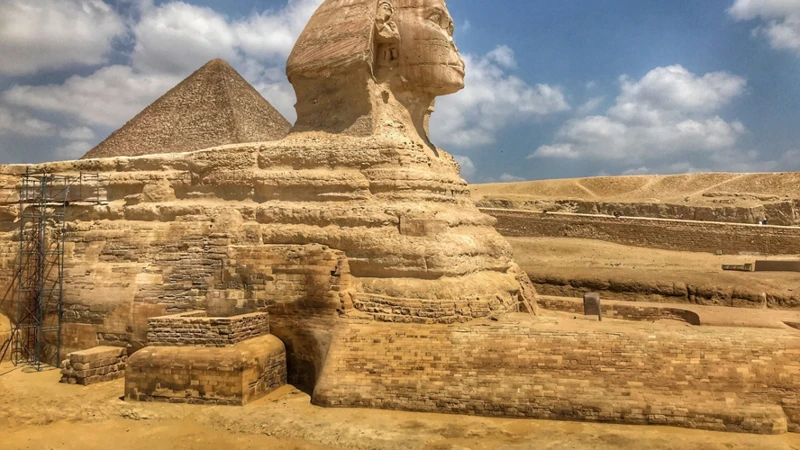

The Sphinx, with its lion’s body and human head, stands proudly near the Pyramids of Egypt, embodying a sense of mystery and guardianship. It is believed to have been constructed during the reign of pharaoh Khafre in the Old Kingdom period. The Sphinx served as a symbolic representation of royal power and protection. Its location at the entrance of the complex of pyramids gave it a prominent role in the mythology surrounding these ancient structures. The Sphinx was seen as the guardian or protector of the pyramids, warding off any evil or malicious forces that might threaten the pharaoh’s eternal resting place. The Sphinx’s association with the sun god, Ra, further solidifies its significance in Egyptian mythology. It was believed that the Sphinx was an embodiment of Ra himself and served as a manifestation of his divine power on earth. The Sphinx also became linked to the concept of resurrection and rebirth, often associated with the god Osiris. The image of the Sphinx, with its head rising above the sands, became a symbol of eternal life and the cyclical nature of existence. Its enigmatic expression further adds to its mystical appeal, leaving us with more questions than answers. To this day, the Sphinx continues to captivate the imagination, enticing visitors and researchers to uncover its secrets and decipher its role in the mythology of the pyramids.
The Enigma of the Ophiuchus Zodiac Sign

The enigma of the Ophiuchus Zodiac sign adds an intriguing layer to the mythology surrounding the Pyramids of Egypt. Ophiuchus, also known as the Serpent Bearer, is a lesser-known constellation that lies along the ecliptic, the path the sun appears to take across the sky. In ancient times, this constellation was disregarded in the development of the traditional zodiac system consisting of twelve signs. However, in recent years, there has been a renewed interest in Ophiuchus and its astrological significance. Some believe that Ophiuchus should be recognized as the thirteenth zodiac sign, challenging the traditional astrological stereotypes. This newfound attention has sparked debates and speculation about the influence of Ophiuchus on individuals born under this sign. While the connection between Ophiuchus and the Pyramids of Egypt may seem tenuous, it is emblematic of the fascinating relationship between constellations and human beliefs. Exploring the physical characteristics of Ophiuchus and debunking astrological stereotypes can shed light on the significance of this mysterious constellation and its potential impact on our lives. Whether Ophiuchus truly has a place in the zodiac or remains an enigmatic outlier, its association with the Pyramids of Egypt reminds us of the intricate and ever-evolving relationship between the celestial realm and human understanding. [Link: /physical-characteristics-ophiuchus-debunking-astrological-stereotypes/]
Theories and Speculations
Theories and speculations surrounding the Pyramids of Egypt have sparked intense fascination and debate over the years. One prominent theory is the Extraterrestrial Influence Theory, suggesting that the construction of the pyramids was aided by advanced beings from outer space. This theory posits that the precision and complexity of the pyramids’ design go beyond the capabilities of ancient civilizations, pointing to the possibility of extraterrestrial involvement. Another intriguing theory is the Advanced Ancient Civilization Theory, proposing that an advanced civilization predating the known ancient Egyptian civilization was responsible for the construction of the pyramids. This theory speculates that this lost civilization possessed knowledge and technology far beyond what was previously believed. While these theories may remain speculative, they add an air of mystery and wonder to the mythology surrounding the pyramids, leaving us with more questions than answers. (Reference: fascinating-relationship-constellations-astral-projection)
1. Extraterrestrial Influence Theory
The Extraterrestrial Influence Theory suggests that the construction of the Pyramids of Egypt may have been influenced or aided by beings from other planets. According to proponents of this theory, the advanced knowledge and precision required to build such monumental and mathematically precise structures could not have been achieved by ancient humans alone. They argue that these ancient civilizations may have received assistance, guidance, or even technology from extraterrestrial beings.
Evidence supporting this theory:
1. Advanced architectural and engineering techniques: The construction of the pyramids exhibits remarkable precision and engineering skills that seem beyond the capabilities of the ancient Egyptians. The perfect alignment, precise measurements, and complex mathematical calculations involved in their construction have led some to believe that these techniques could only have been provided by more advanced beings.
2. Anomalies in construction: Certain elements of the pyramids, such as the precision in the placement of the stones or the intricate internal structures, have raised eyebrows among researchers. Some argue that these anomalies suggest the involvement of extraterrestrial knowledge and technologies.
3. Astronomical alignments: The alignment of the pyramids with celestial bodies, such as Orion’s Belt, has been interpreted by some as evidence of extraterrestrial influence. They propose that this alignment could have been a deliberate message or signal from ancient aliens.
4. Ancient texts and artwork: Some ancient texts and artwork depict what appear to be extraterrestrial-like beings or advanced technologies. For example, the Egyptian hieroglyphs show depictions of beings with elongated heads or flying vehicles, which some interpret as evidence of extraterrestrial involvement.
Despite these claims, the Extraterrestrial Influence Theory remains highly controversial and is widely criticized in mainstream archaeology. Skeptics argue that the advanced knowledge and techniques employed in the construction of the pyramids can be attributed to the ingenuity and skills of the ancient Egyptians themselves, supported by evidence of their architectural and engineering practices.
It is important to note that while the Extraterrestrial Influence Theory remains speculative and lacks concrete evidence, it continues to captivate the imagination of many and adds an element of mystery to the mythology surrounding the Pyramids of Egypt.
2. Advanced Ancient Civilization Theory
The Advanced Ancient Civilization Theory proposes that the construction of the Pyramids of Egypt was not solely the result of human labor and ingenuity. Instead, it suggests the involvement of a highly advanced civilization or even extraterrestrial beings. Proponents of this theory point to the sheer size, precision, and alignment of the pyramids, which they argue would have required an intricate knowledge of mathematics, engineering, and astronomy that surpasses the capabilities of ancient Egypt. Some even suggest that the pyramids may have served as power plants or beacons for extraterrestrial communication due to their unique architecture and placement. This theory may seem far-fetched, but it raises thought-provoking questions about the true origins and capabilities of ancient civilizations. While mainstream archaeology dismisses such claims as pseudoscience, proponents argue that there are still unresolved mysteries surrounding the pyramids that warrant further investigation.
Modern Fascination and Pop Culture Influences
Modern societies continue to be fascinated by the Pyramids of Egypt, with their iconic status reaching far beyond ancient mythology. These magnificent structures have captured the imagination of people around the world, inspiring countless books, movies, and even video games. Pop culture has embraced the enigmatic allure of the pyramids, incorporating them into various forms of media. One example of this is the popular “Indiana Jones” film franchise, where the pyramids play a prominent role in the adventurous quests of the main character. The pyramids have also been depicted in animated films like “The Prince of Egypt,” adding to their legendary status. Additionally, the pyramids have become a popular subject in conspiracy theories, with claims of extraterrestrial involvement or hidden chambers yet to be discovered. This modern fascination with the pyramids reflects our ongoing intrigue with ancient civilizations and their architectural wonders. These structures serve as a testament to human ingenuity and continue to spark curiosity and imagination in the public consciousness. Whether we see them as symbols of power, mysteries waiting to be uncovered, or simply as awe-inspiring feats of engineering, the Pyramids of Egypt have left an indelible mark on our modern culture.
Legacy of the Pyramids

The legacy of the pyramids extends far beyond their original construction and the mythology surrounding them. These magnificent structures have left an indelible mark on history, art, architecture, and even popular culture.
1. Architectural Marvels: The pyramids of Egypt are awe-inspiring examples of ancient engineering and architectural prowess. Their monumental size, precise construction, and use of advanced building techniques continue to astound scholars and visitors alike. The pyramids have inspired architects throughout the ages, with their iconic shape and grandeur serving as a testament to the ingenuity of the ancient Egyptians.
2. Tourist Attractions: Today, the pyramids are major tourist attractions, drawing millions of visitors from around the world. Travelers flock to witness these ancient wonders and to experience the mystique that surrounds them. The pyramids, with their rich history and enduring allure, contribute significantly to Egypt’s tourism industry, generating revenue and promoting cultural exchange.
3. Cultural Symbolism: The pyramids have become synonymous with Egypt and its rich cultural heritage. They symbolize the ancient Egyptian civilization, its accomplishments, and the beliefs of the people who built them. The pyramids are an emblem of national pride and serve as a reminder of Egypt’s glorious past.
4. Archaeological Discoveries: The exploration and study of the pyramids have yielded invaluable insights into the ancient Egyptian civilization. Archaeologists have discovered intricate burial chambers, hieroglyphic inscriptions, treasures, and artifacts that provide a window into the lives of the pharaohs and their subjects. These discoveries have greatly expanded our understanding of ancient Egyptian society and continue to shed light on their mythology and religious beliefs.
5. Preservation Efforts: The preservation and conservation of the pyramids are of paramount importance to ensure their longevity and cultural significance. Various initiatives, both local and international, work towards safeguarding these architectural wonders for future generations.
The legacy of the pyramids encompasses their architectural significance, cultural symbolism, archaeological contributions, and the ongoing efforts to preserve these treasures. As we marvel at their majesty, we also recognize the enduring impact they have had on our collective human history and imagination.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the mythology behind the Pyramids of Egypt is a captivating tapestry of ancient beliefs and cosmic connections. The Ancient Egyptian cosmology, with its three realms of the sky, the earth, and the underworld, provided the framework for the construction and religious significance of the pyramids. These sacred structures served as a link between the mortal realm and the divine, symbolizing the journey of the pharaohs to the afterlife. The mythology surrounding the pyramids is intricately connected to the gods of the Egyptian pantheon, such as Osiris, Ra, and Horus, who played roles in the afterlife and solar symbolism. The Pyramid Texts, a collection of ancient religious texts, further shed light on the rituals and beliefs associated with the pyramids. The Sphinx, standing guard at the Giza Plateau, adds another layer of mystery to the pyramids, while the enigma of the Ophiuchus Zodiac sign hints at a deeper celestial connection. Various theories speculate about extraterrestrial influence and the existence of an advanced ancient civilization, adding to the allure of these structures. The modern fascination with the pyramids and their influence on pop culture showcase their enduring legacy. From ancient times to the present day, the Pyramids of Egypt continue to captivate our imagination, inviting us to unravel the secrets of their mythical origins and contemplate the profound connection between humanity and the cosmos.
Frequently Asked Questions

1. How were the Pyramids of Egypt built?
The Pyramids of Egypt were built using a technique called “corbeling,” where layers of limestone blocks were stacked on top of each other, gradually narrowing as they reached the apex. The blocks were quarried, transported, and meticulously placed by skilled laborers using simple tools and ramps.
2. Why were the Pyramids built in the shape of a pyramid?
The pyramid shape was believed to represent the sacred primordial mound, symbolizing creation and rebirth. This shape was also associated with the rays of the Sun, connecting the earthly realm with the divine and emphasizing the pharaoh’s role as a mediator between gods and humans.
3. How long did it take to build a pyramid?
The construction of a pyramid was a massive undertaking that could span several decades. The time taken depended on the pyramid’s size, complexity, and the availability of resources and labor. The Great Pyramid of Giza, for instance, took approximately 20 years to complete.
4. Were the pyramids built as tombs?
Yes, the pyramids served as tombs for the pharaohs, who were considered divine rulers. These monumental structures were intended to safeguard the pharaoh’s body and worldly possessions and facilitate their journey to the afterlife.
5. How were the pyramids aligned with celestial bodies?
The pyramids were meticulously aligned with celestial bodies, particularly the stars. Ancient Egyptians observed the movements of stars, including the Orion constellation, and adjusted the construction of the pyramids to align with these stellar formations, symbolizing the pharaoh’s ascent to the heavens.
6. What rituals and ceremonies took place at the pyramids?
The pyramids were the focal point of various religious rituals and ceremonies. These included the dedication of the pyramid to a specific deity, the “Opening of the Mouth” ceremony to revive the pharaoh’s senses, and the “Mastaba ceremony” to signify the pharaoh’s resurrection and transformation into an eternal spirit.
7. Did all pharaohs have pyramids built for them?
No, not all pharaohs had pyramids built for them. The construction of pyramids was limited to specific periods in ancient Egyptian history, particularly the Old and Middle Kingdoms. Pharaohs of the New Kingdom, on the other hand, were buried in hidden tombs in the Valley of the Kings.
8. What was the purpose of the small pyramids surrounding the main pyramids?
The small pyramids surrounding the main pyramids, known as the Queen’s Pyramids, were intended to house the queens and other members of the royal family. These structures, though smaller in size, were built with the same purpose of providing a final resting place for the deceased.
9. How were the pyramids protected against grave robbers?
The pyramids were protected through a combination of architectural features and security measures. These included the complex layout of the pyramid, hidden passageways, sealed chambers, and the use of traps and false doors to confuse and deter grave robbers.
10. What is the significance of the pyramid’s numerical proportions?
The numerical proportions of the pyramids held symbolic meaning in ancient Egyptian mythology. The ratio of a pyramid’s height to half its base perimeter approximates the mathematical concept of pi (π), which was associated with the divine and eternal. This numerological aspect added to the mystical nature of the pyramids.
References
- How did the Egyptian myth explain the shape of Pyramid?
- Egyptian Pyramids – Facts, Use & Construction
- Discover 15 Myths About Pyramids, Pharaohs, and Egypt
Frequently Asked Questions

1. Can we visit the inside of the pyramids?
Yes, visitors can explore the inside of some pyramids, such as the Great Pyramid of Giza. However, access to certain chambers and areas may be restricted for preservation reasons.
2. How long did it take to build a pyramid?
The construction of a pyramid typically took several decades to several centuries, depending on the size and complexity of the structure, as well as the availability of resources and labor.
3. Were the pyramids built by slaves?
The popular notion of pyramids being built solely by slaves is a misconception. While it is believed that a significant portion of the labor force comprised of skilled workers, including artisans and farmers who contributed to building the pyramids, evidence suggests that they were not slaves but rather individuals who worked on the pyramids during the yearly Nile flood when agricultural work was limited.
4. How were the pyramids aligned with the stars?
Ancient Egyptians had a deep understanding of astronomy and used celestial observations to align the pyramids with key stars and constellations, particularly the North Star and Orion’s Belt. The alignment was achieved through careful planning and design.
5. What is the significance of the pyramid shape?
The pyramid shape was symbolically associated with the sun’s rays and the process of rebirth and ascension in ancient Egyptian mythology. It represented a link between the earthly realm and the divine realm.
6. Were there any treasures buried inside the pyramids?
Yes, many pyramids were constructed as burial monuments for Egyptian pharaohs and high-ranking officials. These tombs often contained precious goods and artifacts intended to accompany the deceased into the afterlife.
7. How were the pyramids built without modern technology?
The construction of pyramids relied on the ingenuity of ancient Egyptian engineers and skilled laborers. They employed advanced techniques like quarrying, transporting massive stone blocks, and using ramps to gradually elevate the structure during the building process.
8. Were there any curses associated with the pyramids?
While popular culture has often portrayed the pyramids as cursed, there is no substantial evidence to support the existence of curses. However, superstitions and legends have emerged over time, attributing supernatural consequences to those who disturbed the resting places of the pharaohs.
9. How were the pyramid texts discovered?
The pyramid texts, ancient Egyptian funerary texts found in the pyramids, were discovered by archaeologists in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Exploration and excavation efforts uncovered burial chambers and walls adorned with hieroglyphic inscriptions that formed the pyramid texts.
10. Do the pyramids still align with astronomical events today?
Due to Earth’s axial precession over thousands of years, the alignment of the pyramids with specific astronomical events may have changed. However, the enduring design and alignment of the pyramids continue to fascinate and inspire awe, even if the specific astronomical connections may have shifted over time.
References
- Discover 15 Myths About Pyramids, Pharaohs, and Egypt
- Pyramids of Giza | National Geographic
- Dispelling Some Myths: Who built the pyramids?







