The ancient civilization of the Inca is shrouded in mystery and awe, captivating the imaginations of historians and researchers alike. Within the vast expanse of their empire, the Inca people developed an intricate system of medicine and healing practices that played a crucial role in their society. The Inca’s deep understanding of natural remedies, shamanic healing, surgical techniques, and spiritual rituals allowed them to provide healthcare and relief to their people. In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of Inca medicine, uncovering the secrets of their healing practices, the influence of religion, and the enduring legacy they have left on modern medicine. Journey back in time to discover the ancient wisdom and ingenuity of the Inca civilization.
Contents
- Overview of the Inca Civilization
- The Importance of Medicine in the Inca Society
- Inca Healing Practices and Beliefs
- Medical Education in the Inca Civilization
- Role of Religion in Inca Medicine
- Ancient Inca Remedies and Treatments
- The Legacy of Inca Medicine
- Comparison with Modern Medicine
- The Influence of the Inca Medical System Today
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What was the political structure of the Inca civilization?
- 2. How did the Inca Empire manage to control such a vast territory?
- 3. What were the main agricultural practices of the Inca people?
- 4. What role did the Inti, the sun god, play in Inca society?
- 5. How did the Inca civilization view sickness and disease?
- 6. What plants were commonly used in Inca herbal medicine?
- 7. Did the Inca civilization have any surgical techniques?
- 8. Were there specific rituals associated with Inca healing practices?
- 9. How were aspiring healers trained in the Inca civilization?
- 10. What is the lasting legacy of Inca medicine in modern times?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- What were the common ailments and diseases in the Inca civilization?
- Did the Incas have a formal system for medical education?
- What role did religion play in Inca medicine?
- What were the main components of Inca herbal medicine?
- What types of surgical techniques were used by the Incas?
- How did the Inca civilization treat mental illnesses?
- What legacy did Inca medicine leave behind?
- How does Inca medicine compare to modern medicine?
- What impact did the Inca medical system have on the development of modern medicine?
- How can we see the influence of Inca medicine in the present day?
- References
- Read More
Overview of the Inca Civilization
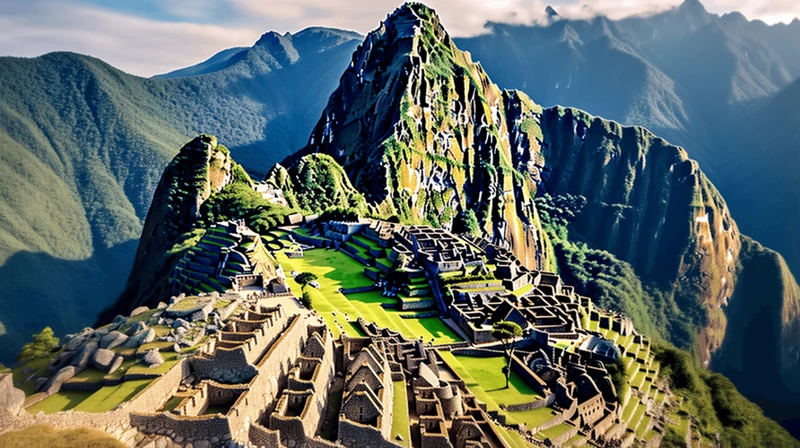

The Inca civilization, which thrived in the Andes Mountains of South America between the 13th and 16th centuries, was a remarkable and highly organized society. Stretching across an expansive territory that covered parts of modern-day Peru, Ecuador, Bolivia, and Chile, the Inca Empire was characterized by its sophisticated administrative systems and engineering marvels. At its height, it was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America, encompassing diverse landscapes ranging from the coastal deserts to the high mountains of the Andes. The Inca people, known as the “Children of the Sun,” worshipped Inti, the sun god, whom they believed to be their direct ancestor. Their social structure was hierarchical, with the Inca ruler, or Sapa Inca, at the pinnacle of power. They cultivated the land, developed advanced agricultural techniques like terrace farming, and built intricate irrigation systems to ensure a stable food supply for their population. The Inca excelled in stonemasonry, constructing impressive structures such as Machu Picchu and the mountain fortress of Sacsayhuaman. Their road network, known as the Inca Trail, facilitated communication and trade across the empire’s vast expanse. The Inca civilization’s ability to adapt and thrive in such diverse environments is a testament to their ingenuity and resourcefulness, making them one of the most remarkable ancient civilizations in history.
The Importance of Medicine in the Inca Society

Medicine held immense significance in the Inca society, as it played a vital role in the well-being and overall functioning of the civilization. The Inca people believed that physical health was closely intertwined with spiritual and cosmic harmony. Inca medicine was not just focused on treating illnesses but also on prevention and promoting balance within the body and the community. The importance of medicine was evident in the social structure, as the Inca ruler acted as the chief physician, responsible for the health and welfare of his people. The knowledge and practice of medicine were highly respected, and medical practitioners, known as amautas, held esteemed positions in society. These healers possessed a deep understanding of herbal remedies, spiritual healing, surgical techniques, and the power of ritualistic ceremonies. The Inca recognized the intricate connection between the physical and spiritual realms and understood that healing required a holistic approach. Medicine was integral to maintaining the well-being of the empire, ensuring not just the health of individuals but also the harmony of the entire society. The Inca’s emphasis on medicine highlights their advanced understanding of the human body and their remarkable ability to integrate science, spirituality, and cosmic wisdom to promote overall wellness and prosperity within their civilization.
Inca Healing Practices and Beliefs

Inca healing practices and beliefs were deeply rooted in the spiritual and natural world. The Inca believed that illness was caused by an imbalance within the body or a disruption in the connection between the physical and spiritual realms. To restore harmony, they utilized a combination of herbal medicine, shamanic healing practices, surgical techniques, and healing temples and rituals. Herbal medicine played a significant role in Inca healing, with various plants and herbs used for their medicinal properties. Shamans, known as “paqos,” were respected spiritual healers who communicated with the spirit world through rituals and ceremonies to diagnose and treat ailments. Surgical techniques, although limited, were practiced for procedures such as trephination. Healing temples, like the renowned Coricancha in Cusco, were sacred spaces used for rituals and offerings to the gods. The Inca believed that their gods, including Inti the sun god and Pachamama the earth goddess, played a vital role in healing and healthcare. These beliefs and practices formed the foundation of Inca medicine, intertwining the physical, spiritual, and natural realms to promote holistic well-being and restoration of health.
Herbal Medicine
Herbal medicine was a fundamental component of the Inca healing practices. The Inca civilization had an extensive knowledge of the medicinal properties of various plants and herbs found in their diverse territories. They believed that plants possessed powerful spirits that could be harnessed for the purpose of healing. The Inca used a wide range of herbs to treat ailments and diseases, including the coca plant, quinoa, and maize. Coca leaves were particularly significant in their medicinal practices, as they were believed to possess both physical and spiritual healing properties. Coca leaves were often chewed or brewed into tea to relieve pain, increase energy, and combat altitude sickness. The leaves were also used as a natural anesthetic during surgical procedures. The Inca pharmacopeia encompassed a vast array of plants with different therapeutic properties. They used herbs to treat common ailments such as digestive issues, respiratory problems, and skin diseases. The Inca’s deep understanding of the healing properties of plants laid the foundation for their effective use of herbal medicine in promoting health and well-being. Today, modern medicine continues to explore the potential of plant-based remedies, recognizing the wisdom and efficacy of the Inca’s herbal healing practices.
Shamanic Healing Practices
Shamanic healing practices played a crucial role in the Inca civilization’s medical system, combining spiritual beliefs with practical healing techniques. The Inca people believed that illnesses and ailments were often caused by spiritual imbalances or disturbances in the energy flow within the body. To restore harmony, shamanic healers, known as “paqos,” utilized various methods. The paqos would enter altered states of consciousness through the use of hallucinogenic plants like ayahuasca or coca leaves to connect with the spiritual realm. They would communicate with the spirits and the gods, seeking guidance and healing energies. It was believed that the paqos had the ability to extract negative energy or entities from the patient’s body through a process known as “soul retrieval.” They would then perform rituals and ceremonies, such as the “despacho,” which involved offering prayers and symbolic objects to appease the spirits and restore balance. In addition to spiritual healing, the shamans also possessed extensive knowledge of medicinal plants and herbs, using them in their remedies and treatments. Their deep understanding of the natural world’s healing properties allowed them to create personalized healing plans for their patients. The shamanic healing practices of the Inca civilization embraced the interconnectedness of the physical, spiritual, and energetic aspects of health, making them an integral part of the Inca’s holistic approach to medicine.
Surgical Techniques
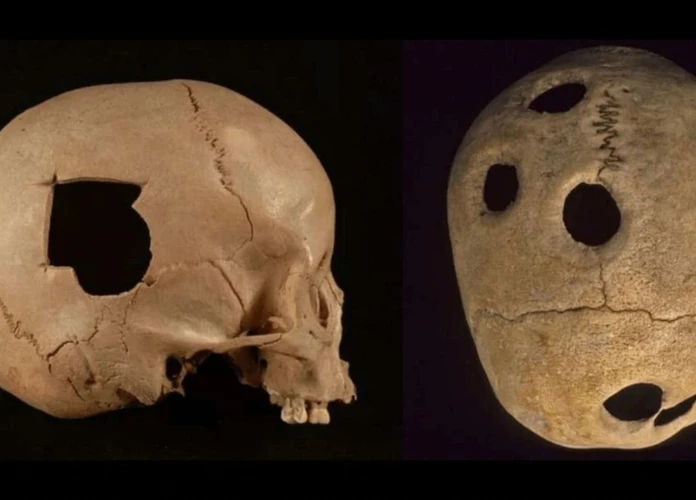
Surgical techniques in the Inca civilization were surprisingly advanced and displayed a deep understanding of human anatomy. Inca surgeons, known as “Yanachacas,” performed various procedures using rudimentary but effective tools made from stone, bronze, and obsidian. They possessed a wealth of knowledge regarding bone setting, wound stitching, and even trepanation, a surgical procedure involving drilling or cutting holes into the skull. One of the most remarkable aspects of Inca surgical techniques was their ability to successfully perform cranial surgeries, evidenced by the discovery of skulls with evidence of healing following trepanation. These procedures were likely carried out to treat head injuries, alleviate pressure on the brain, and possibly address spiritual imbalances. Surprisingly, the Inca did not rely on anesthesia during surgeries. Pain management techniques, such as the application of herbal remedies and the consumption of coca leaves, were utilized instead. The Inca’s success in surgical procedures, without the aid of anesthetics, is a testament to their exceptional skill and understanding of the human body. These ancient surgical techniques provide a glimpse into the sophisticated medical practices of the Inca civilization and their commitment to the well-being of their people.
Healing Temples and Rituals
Healing temples played a significant role in the Inca civilization’s medical practices and were central to their healing rituals. These temples, known as “wakas,” were sacred spaces where individuals sought spiritual guidance and physical healing. Located in strategic spots across the empire, these temples were constructed in alignment with celestial bodies, emphasizing the Inca’s deep connection with the cosmos and the belief that planetary alignments influenced human health and well-being. The Inca placed great importance on rituals and ceremonies to restore balance and harmony within the body and the community as a whole. Priests and healers performed intricate ceremonies involving offerings, incantations, and special rituals to invoke the gods and spirits for healing purposes. These rituals often included the burning of sacred herbs, the offering of food and drink, and the chanting of prayers. The Inca believed that through these practices, they could appease the spirits and receive their blessings for physical and spiritual healing. These healing temples and rituals were not only places of physical restoration but also served as centers of community and spiritual rejuvenation, reinforcing the interconnectedness of the Inca people with nature and the divine. Today, the influence of these ancient healing practices can still be seen in modern Peruvian culture, where traditional healers and shamans continue to uphold and honor the Inca’s sacred traditions.
Medical Education in the Inca Civilization
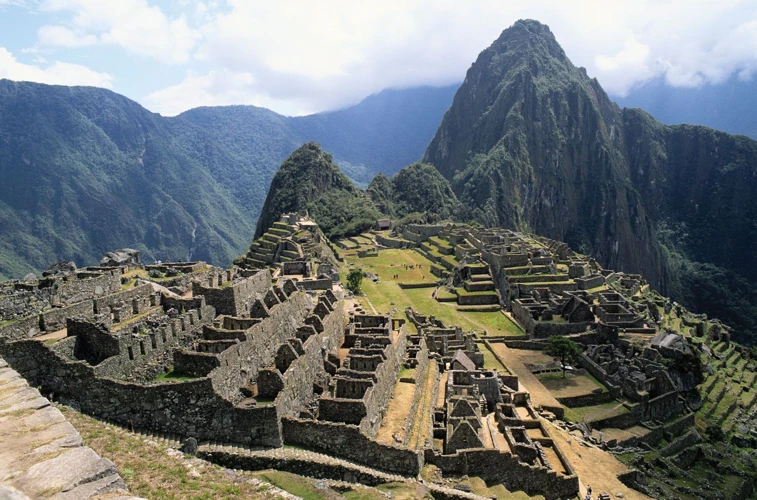

Medical education in the Inca civilization was highly specialized and reserved for a select few individuals who demonstrated exceptional aptitude and dedication to the healing arts. The Inca believed that the ability to heal was a divine gift, and therefore, medical knowledge was passed down through generations within specific families or lineages. These individuals, known as amautas, were revered for their wisdom and were responsible for training the next generation of healers. The education of amautas was a rigorous process that included both theoretical and practical components. They were taught about various plants and herbs used for medicinal purposes, the principles of diagnosing and treating illnesses, and the spiritual aspects of healing. The amautas also learned about the body’s energy systems and how to manipulate them for healing purposes. Practical training involved observing and assisting experienced healers in a variety of medical procedures, such as herbal preparations, surgical techniques, and diagnostic methods. The training of an amauta was a lifelong commitment, emphasizing the importance of continuous learning and honing one’s skills. Medical education in the Inca civilization was based on a deep respect for ancestral knowledge and a strong connection to the spiritual realm, resulting in a highly skilled and revered class of healers who played a vital role in the well-being of the Inca society.
Role of Religion in Inca Medicine
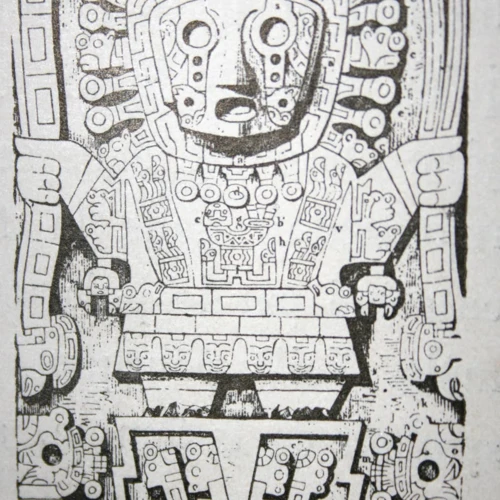
The role of religion in Inca medicine was deeply intertwined with their belief systems and spiritual practices. The Inca people believed that health and illness were closely connected to the spiritual realm, and therefore, healing involved not only addressing physical symptoms but also restoring spiritual balance. The religious leaders, known as the Amautas, played a crucial role in guiding the healing process. They possessed extensive knowledge of herbal medicine, rituals, and prayers, which were used to invoke the assistance of divine forces. Pachamama, the Earth Mother, was central to their religious beliefs, representing fertility, sustenance, and the cycles of life. The Inca also revered Inti, the sun god, who was believed to have the power to heal and provide protection. Temples, such as Coricancha in Cusco, served as sacred spaces for ceremonies and offerings, and priests performed rituals to appease the gods and ensure physical and spiritual well-being. The Inca calendar, which was based on the movement of celestial bodies, also played a significant role in medical practices, as it guided the timing of treatments and rituals. The harmonious relationship between religion and medicine in Inca society underscored their holistic approach to healing, recognizing the interplay between the physical, spiritual, and cosmic realms.
Ancient Inca Remedies and Treatments
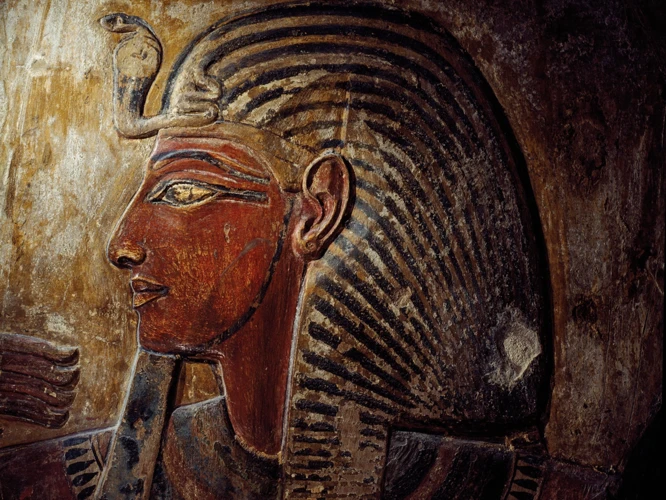

The Inca civilization possessed a rich repository of ancient remedies and treatments that were integral to their healthcare practices. One prominent aspect of Inca medicine was their extensive use of herbal remedies. The Inca relied on the knowledge of medicinal plants, harnessing their healing properties to treat various ailments. Herbs such as coca leaves were used for pain relief and to combat altitude sickness, while the bark of the quina-quina tree was used to treat fevers and infections. Another intriguing facet of Inca medicine was the practice of acupuncture and moxibustion, where thin needles were inserted into specific points on the body to restore the flow of energy and promote healing. Additionally, the Inca employed the use of minerals and crystals, believing in their ability to channel spiritual and healing energies. Massage and physical manipulation were also employed to alleviate physical discomforts. These ancient remedies and treatments highlight the holistic approach the Inca took towards healing, recognizing the intricate connections between the body, mind, and spirit. Today, while modern medicine has advanced significantly, the knowledge and wisdom of the Inca’s medical practices continue to captivate and inspire.
Herb-based Remedies
Herb-based remedies formed a fundamental aspect of the Inca medical system, showcasing their deep understanding and utilization of the natural world for healing purposes. The Inca people believed that plants possessed powerful medicinal properties, and through extensive observation and experimentation, they developed a vast repertoire of herbal remedies. These remedies were derived from a wide range of plants, each with its specific healing properties. Some commonly used herbs included coca leaves, quinine bark, and cat’s claw. Coca leaves were highly regarded for their stimulant properties and were used to alleviate fatigue and altitude sickness. Quinine bark, known for its antimalarial properties, was used in the treatment of fevers and infections. Cat’s claw, a woody vine native to the Amazon rainforest, was utilized as an anti-inflammatory and immune system booster. The Inca’s knowledge of herbal medicine was passed down through generations, with specialized individuals, known as amautas, serving as the custodians of this wisdom. These amautas possessed an extensive catalogue of plant knowledge, understanding the medicinal properties of various herbs and their application in treating different ailments. It is truly remarkable to see the Inca’s in-depth understanding of the healing powers of nature and their ability to harness these properties for the well-being of their people. To learn more about the influence of celestial bodies on ancient civilizations, you can read about the role of planetary alignments in shaping their beliefs and practices.
Acupuncture and Moxibustion
Acupuncture and moxibustion were significant therapeutic practices in Inca medicine, aimed at restoring balance and promoting healing in the body. Acupuncture involved the insertion of thin, sharp needles into specific points along the body’s meridian channels. These meridians were believed to be pathways through which vital energy, or “kawsay,” flowed. By stimulating these points, the Inca healers sought to restore the proper flow of energy and alleviate various ailments. Moxibustion, on the other hand, involved the burning of dried mugwort herb, known as “moxa,” near the acupuncture points, generating heat and warmth. This heat was believed to strengthen the body’s energy and promote circulation. Inca healers had extensive knowledge of the body’s meridian system, understanding the interconnectedness of different points and their corresponding organs. They used their expertise to target specific points for various conditions, such as headaches, digestive issues, and musculoskeletal problems. While there is no evidence of the Inca using metal needles like those used in modern acupuncture, they employed other objects, such as bird bones or cactus spines, for stimulation. The use of acupuncture and moxibustion in Inca medicine demonstrates their understanding of the body’s energy flow and their ability to manipulate it for therapeutic purposes, contributing to their comprehensive system of healing practices.
Use of Minerals and Crystals
The Inca civilization had a deep understanding of the healing properties of minerals and crystals, incorporating them into their medical practices. They believed that different stones held unique energies and could be utilized to restore balance and promote healing in the body. One such example is the use of quartz crystals, which the Inca believed possessed purifying and energizing properties. Quartz crystals were used in rituals and ceremonies to cleanse and align the chakras, the energy centers of the body. They were also ground into powder and mixed with herbal remedies to enhance their healing effects. Another mineral highly valued by the Inca was obsidian, a naturally occurring volcanic glass. Obsidian was used for its sharp edges in surgical procedures, such as the extraction of superficial tumors or the removal of foreign objects from the body. Additionally, obsidian was believed to have energetic properties that could help release negative energy and promote emotional healing. The Inca also had an appreciation for colorful gemstones like amethyst, lapis lazuli, and jade. These stones were believed to have specific healing properties and were often used in amulets or jewelry worn close to the body for their therapeutic effects. The Inca’s use of minerals and crystals in their healing practices reflects their holistic approach to medicine, recognizing the power of nature and the spiritual energies associated with these precious stones.
Massage and Physical Manipulation
Massage and physical manipulation were integral components of Inca medicine, aimed at restoring balance and promoting healing within the body. Inca healers, known as “curanderos,” employed various techniques to alleviate physical ailments and ease discomfort. One commonly used technique was the art of therapeutic massage, known as “churunga.” During churunga, the curandero would use their hands, fingers, and elbows to apply firm pressure and manipulate the muscles and soft tissues of the body. This gentle kneading and rubbing helped improve blood circulation, relieve muscle tension, and promote relaxation. The Inca believed that by manipulating the body, they could release blocked energy, known as “hucha,” and restore the flow of vital life force, or “kawsay.”
In addition to massage, physical manipulation techniques such as joint mobilization and spinal alignment were also practiced by Inca healers. These techniques were based on the understanding that the body’s well-being depended on the proper alignment and balance of its various components. Inca healers were skilled in assessing and treating misalignments or blockages that could hinder the body’s natural healing processes.
To complement their physical manipulations, Inca healers often incorporated the use of medicinal oils and herbal remedies during their treatments. These natural substances were believed to possess healing properties and enhance the effectiveness of the massage and manipulation techniques. The curanderos would carefully select and blend specific herbs and oils based on their therapeutic properties and the needs of the patient.
It is important to note that Inca medicine was deeply intertwined with spiritual beliefs and rituals. The curanderos believed that physical ailments were often manifestations of spiritual imbalances, and thus, their treatments aimed to address both the physical and spiritual aspects of the individual. This holistic approach to healing set the foundation for the Inca’s comprehensive medical system.
Despite the passage of time, some of the Inca’s massage and physical manipulation techniques have been passed down through generations and continue to be practiced by indigenous communities in the Andean regions. Today, these ancient healing techniques are gaining recognition for their therapeutic benefits and contribution to overall well-being. The reverence for the healing power of touch and manipulation in the Inca civilization reminds us of the interconnectedness of the body, mind, and spirit in the pursuit of wellness.
The Legacy of Inca Medicine

The legacy of Inca medicine continues to intrigue and inspire modern researchers and practitioners alike. Despite the absence of written records, there is evidence to suggest that their holistic approach to healthcare and their effective healing practices have had a lasting impact. One of the most notable aspects of Inca medicine was their extensive use of herbal remedies. The knowledge of medicinal plants passed down through generations of Inca healers still holds value today, as many herbal remedies used by the Inca have been found to possess therapeutic properties. Additionally, their understanding of surgical techniques, including skull trepanation, demonstrates their remarkable level of skill and knowledge in the field of medicine. Even more intriguing is the incorporation of spiritual rituals and beliefs into their healing practices. The Inca viewed illness as a result of imbalances in the spiritual realm, and their healing rituals aimed to restore harmony between the physical and metaphysical realms. This holistic approach to medicine, encompassing the body, mind, and spirit, laid the foundation for many alternative healing practices that exist today. While modern medicine has made significant advancements, the preservation and exploration of Inca healing practices provide valuable insights and alternative methods for treating various ailments. The enduring legacy of Inca medicine reminds us of the importance of a holistic approach to healthcare and the profound connection between the physical and spiritual aspects of well-being.
Comparison with Modern Medicine

When comparing the medicine practiced by the Inca civilization to modern medicine, it becomes evident that there are significant differences in approach, knowledge, and techniques. While the Inca relied heavily on natural remedies and spiritual rituals, modern medicine is grounded in scientific research and evidence-based practices. The Inca’s understanding of the human body and its ailments was limited compared to the vast medical knowledge available today. Modern medicine has made groundbreaking advancements in areas such as anatomy, microbiology, pharmacology, and surgery, equipped with sophisticated diagnostic tools and technology. In contrast, the Inca relied on observation, trial and error, and the wisdom passed down through generations. Modern medical practices prioritize patient safety and follow strict ethical guidelines, while the Inca’s practices lacked standardization and were influenced by cultural and spiritual beliefs. The use of sterile techniques, antibiotics, vaccines, and advanced surgical procedures are some of the stark contrasts between the two medical systems. However, it is important to recognize that the Inca’s understanding of herbal medicine and their emphasis on holistic healing align with some aspects of modern alternative medicine. As our understanding of the human body continues to evolve, modern medicine continues to push boundaries and develop new treatments, medications, and improved patient care. So, while the Inca medical practices were impressive for their time, the advancements in modern medicine have revolutionized healthcare and provided more effective and evidence-based treatments for a wide range of conditions and diseases.
The Influence of the Inca Medical System Today

The influence of the Inca medical system continues to resonate in various ways in modern times. While many of the specific practices and remedies of the Inca have evolved or been replaced by contemporary medical advancements, their emphasis on holistic healing and the interconnectedness of the mind, body, and spirit still holds relevance. This view aligns with the growing interest in alternative and complementary medicine, which emphasizes a more integrative approach to healthcare. The use of natural remedies and herbal medicine, reminiscent of Inca practices, has gained popularity as people seek out non-pharmaceutical solutions for various ailments. Additionally, the Inca belief in the healing power of nature and the importance of maintaining balance and harmony has sparked an appreciation for ecotherapy and the therapeutic benefits of spending time in natural environments. The Inca’s reverence for spiritual rituals and the connection between spirituality and health has also influenced the field of mind-body medicine, with practices such as meditation, energy healing, and mindfulness gaining recognition for their potential impact on overall well-being. While the Inca medical system may not be directly practiced today, its fundamental principles and philosophies continue to shape and inspire alternative approaches to healing and wellness.
/lyra-constellation-vega-celestial-harp/
Conclusion
In conclusion, the medicine and healing practices of the Inca civilization were a testament to their advanced understanding of the human body, nature, and spirituality. Through the use of herbal remedies, shamanic healing techniques, surgical interventions, and sacred rituals, the Inca people were able to address a variety of ailments and promote overall well-being. Their medical education system, although limited to the chosen few, enabled the passing down of knowledge from one generation to the next. Religion played a significant role in Inca medicine, with healers often invoking the gods and spirits for assistance in the healing process. The legacy of Inca medicine can still be felt today, as modern medicine continues to embrace and acknowledge the potential of natural remedies and complementary healing practices. By studying the ancient wisdom of the Inca civilization, we gain valuable insights into alternative approaches to health and well-being. To learn more about the influences that shape our personalities, you can explore the fascinating connection between zodiac signs and personality traits.
Frequently Asked Questions

1. What was the political structure of the Inca civilization?
The Inca civilization had a hierarchical political structure with the Sapa Inca, or emperor, at the top. They ruled over an extensive network of provinces, each governed by a noble local leader called an Apu.
2. How did the Inca Empire manage to control such a vast territory?
The Inca Empire maintained control through a centralized administration system. They established an elaborate system of roads and messengers that facilitated communication and allowed for efficient governance and the swift movement of armies when necessary.
3. What were the main agricultural practices of the Inca people?
The Inca people were skilled agriculturalists and employed various techniques to ensure successful crop cultivation. They practiced terrace farming, which involved carving step-like platforms into steep hillsides. They also constructed complex irrigation systems to support their crops.
4. What role did the Inti, the sun god, play in Inca society?
Inti, the sun god, held immense significance in Inca society. The Inca believed he was their ancestor, and they worshipped him for his role in providing light, warmth, and life. The ruler, the Sapa Inca, was believed to be the son of Inti.
5. How did the Inca civilization view sickness and disease?
The Inca believed that sickness and disease were caused by imbalances in spiritual or supernatural forces. They viewed illness as a consequence of violating moral and social norms. Healing practices aimed to restore harmony and balance in these realms.
6. What plants were commonly used in Inca herbal medicine?
The Inca had an extensive knowledge of medicinal plants and used them to treat various ailments. Some commonly used plants included coca leaves for pain relief and stamina, quinoa for digestive disorders, and muña leaves for respiratory issues.
7. Did the Inca civilization have any surgical techniques?
Yes, the Inca people practiced basic surgical techniques such as trepanation, which involved drilling or cutting holes in the skull. They also performed surgeries for the removal of tumors, fractures, and other injuries.
8. Were there specific rituals associated with Inca healing practices?
Yes, healing rituals were an essential part of Inca medicine. These rituals often involved offerings to the gods, chanting, and the use of sacred objects. Shamans played a vital role in conducting these rituals and invoking spiritual forces for healing.
9. How were aspiring healers trained in the Inca civilization?
Training to become a healer in the Inca civilization was rigorous and involved a combination of formal education and apprenticeship. Aspiring healers learned from experienced shamans and received knowledge passed down through generations.
10. What is the lasting legacy of Inca medicine in modern times?
The legacy of Inca medicine can be seen in various traditional healing practices still followed by indigenous communities in the Andean regions today. Additionally, the Inca’s sustainable agricultural practices and knowledge of herbal medicine continue to influence modern approaches to natural medicine and botanical research.
References
Frequently Asked Questions

What were the common ailments and diseases in the Inca civilization?
Common ailments and diseases in the Inca civilization included respiratory infections, digestive problems, parasites, fevers, and wounds from battles or accidents.
Did the Incas have a formal system for medical education?
Yes, the Incas had a formal system for medical education. Young men and women were selected to be trained as healers, and they underwent years of rigorous training to become skilled in the art of healing.
What role did religion play in Inca medicine?
Religion played a significant role in Inca medicine. Healing practices and rituals were often intertwined with religious beliefs, and the shamans or healers would invoke the assistance of deities and spirits to aid in the healing process.
What were the main components of Inca herbal medicine?
The main components of Inca herbal medicine were plants and herbs, many of which were native to the Andes region. These plants were used to make potions, poultices, and teas that were believed to have medicinal properties.
What types of surgical techniques were used by the Incas?
The Incas were skilled in performing various surgical techniques. These included bone setting, trepanation (drilling holes in the skull), and the removal of tumors or growths.
How did the Inca civilization treat mental illnesses?
The Inca civilization believed that mental illnesses were caused by spiritual imbalances. Shamanic healers would perform rituals, ceremonies, and spiritual cleansings to restore harmony and balance to the individual’s spirit.
What legacy did Inca medicine leave behind?
The legacy of Inca medicine includes a deep understanding and use of herbal remedies, surgical techniques, and the belief in the connection between spirituality and healing. These practices continue to influence traditional healing methods in the Andean region today.
How does Inca medicine compare to modern medicine?
Inca medicine and modern medicine differ in many ways. While modern medicine relies heavily on scientific research and technological advancements, Inca medicine focused on herbal remedies, spiritual healing, and a holistic approach to wellness.
What impact did the Inca medical system have on the development of modern medicine?
The Inca medical system, with its emphasis on herbal medicine and surgical techniques, laid the foundation for the development of modern medicine. Many of the plants and herbs used by the Incas have been scientifically proven to have medicinal properties and are still used in modern medicine today.
How can we see the influence of Inca medicine in the present day?
The influence of Inca medicine can be seen in the continued use of herbal remedies, the incorporation of spiritual healing practices in some alternative medicine approaches, and the preservation and documentation of Inca medical knowledge by modern researchers.