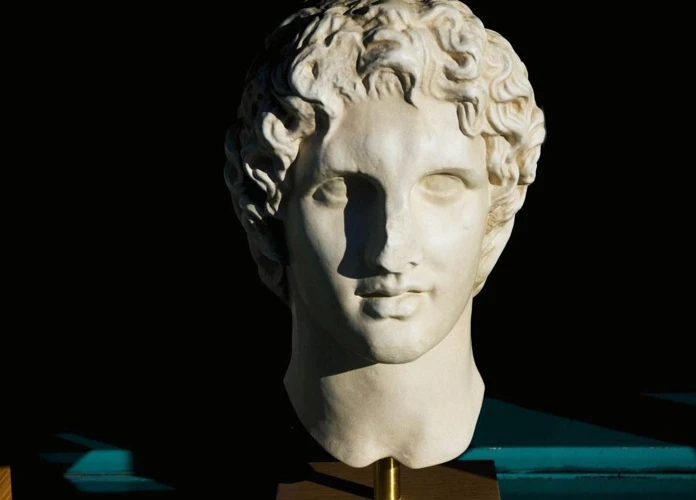
The legacy of Alexander the Great has sparked centuries of debate, leaving scholars and historians perplexed as they try to determine whether he was a visionary or simply a conqueror. With his military genius and ambitious campaigns, Alexander became one of the most successful military leaders in history, conquering vast territories and establishing a vast empire. However, his impact goes beyond his military achievements. Alexander’s conquests brought about significant cultural, societal, and intellectual changes that shaped the course of history. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating legacy of Alexander the Great, examining both his conquests and his visionary approach to ruling and influencing the world.
Contents
- A Brief Background
- Conquest of the Persian Empire
- Expansion of the Hellenistic Culture
- Foundation of Alexandria and Other Cities
- Policies and Institutions
- Legacy in the Arts and Sciences
- Controversies and Criticisms
- A Visionary or Conqueror?
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. Was Alexander the Great truly a great military strategist?
- 2. How did Alexander’s conquests impact the region?
- 3. What was the significance of the Hellenistic culture?
- 4. Why is the foundation of Alexandria important?
- 5. How did Alexander administer his vast empire?
- 6. Did Alexander’s patronage of arts and sciences have a lasting impact?
- 7. What controversies surround Alexander’s treatment of the conquered peoples?
- 8. How did Alexander’s conquests impact Greek society?
- 9. Was Alexander more of a visionary or a conqueror?
- 10. What is the overall legacy of Alexander the Great?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How did Alexander the Great become such a successful conqueror?
- 2. What impact did Alexander’s conquests have on the Persian Empire?
- 3. How did the Hellenistic culture spread under Alexander’s rule?
- 4. What architectural marvels were created during Alexander’s reign?
- 5. How did Alexander’s policies and institutions impact the administration of the empire?
- 6. What was Alexander’s patronage of artists and scholars?
- 7. Were there any controversies surrounding Alexander’s treatment of conquered peoples?
- 8. How did Alexander’s conquests impact Greek society?
- 9. Was Alexander the Great more of a visionary or a conqueror?
- 10. What is Alexander the Great’s lasting legacy?
- References
- Read More
A Brief Background
Alexander the Great was born in 356 BCE in Pella, the capital of the ancient kingdom of Macedonia. He was the son of King Philip II of Macedonia and Queen Olympias. From a young age, Alexander showed great potential and was mentored by the philosopher Aristotle. In 336 BCE, at the age of 20, he ascended to the throne after the assassination of his father. Determined to fulfill his father’s dream of conquering the Persian Empire, Alexander embarked on a military campaign to expand his empire and become the ruler of the known world. His ambition, strategic brilliance, and exceptional leadership skills led him to conquer vast territories, from Greece to Egypt and all the way to the borders of India. Through his conquests, Alexander not only expanded his empire but also spread Greek culture, language, and ideas to the lands he conquered, forever shaping the course of history.
Conquest of the Persian Empire
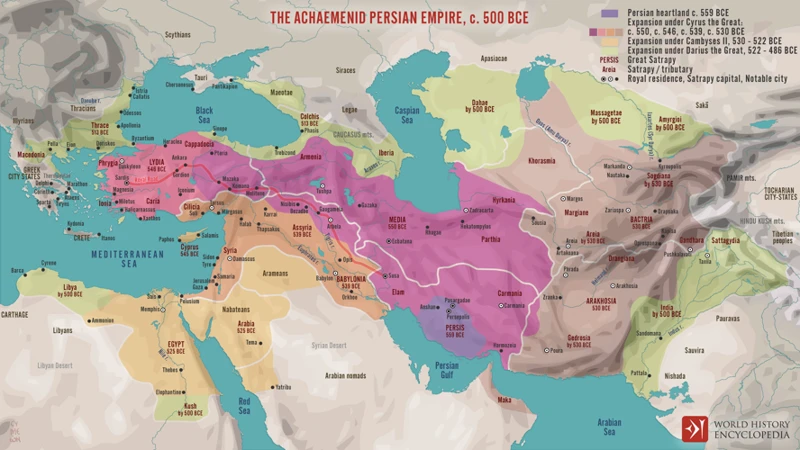
The conquest of the Persian Empire was one of Alexander the Great’s most significant military achievements. With his well-trained army and tactical brilliance, Alexander embarked on a series of battles and campaigns that ultimately led to the downfall of the powerful Persian Empire. The Battle of Issus in 333 BCE marked a turning point in the war, where Alexander’s forces emerged victorious against the Persian army led by King Darius III. Determined to secure his dominance in the region, Alexander continued his relentless march, capturing key cities such as Babylon, Susa, and Persepolis. These victories not only showcased Alexander’s military prowess but also demonstrated his ability to adapt different strategies and utilize the local resources to his advantage. Alexander’s conquest of the Persian Empire not only expanded his own empire but also forever altered the political and cultural landscape of the region, laying the foundation for the rise of Hellenistic civilization.
Battles and Strategies
Battles and strategies played a crucial role in Alexander the Great’s quest for conquest. Known for his tactical brilliance, Alexander employed various innovative strategies that helped him secure victories on the battlefield. One of his most famous battles was the Battle of Gaugamela in 331 BCE, where he faced the Persian king Darius III. Alexander’s carefully planned tactics, including the use of the phalanx formation and a cavalry charge, helped him overcome a much larger Persian army. Another notable strategic move was the Siege of Tyre in 332 BCE, where Alexander utilized a causeway to connect the mainland to the island city, ultimately leading to its capture. Additionally, he employed a swift and aggressive approach known as the “hammer and anvil” strategy, which involved the infantry acting as the anvil, pinning down the enemy, while the cavalry served as the hammer, delivering decisive blows. These strategic innovations enabled Alexander to conquer vast territories and defeat powerful opponents, paving the way for the expansion of his empire.
Impact on the Region
Alexander the Great’s conquests had a profound impact on the regions he conquered. His military campaigns brought about significant political and cultural changes throughout the ancient world. One of the key impacts was the spread of Greek influence and the Hellenization of conquered regions. As Alexander established his empire, he encouraged the adoption of Greek language, customs, and institutions by the local populations. This led to the fusion of Greek and indigenous cultures, giving rise to a new Hellenistic civilization. The conquered lands also experienced a period of relative stability and prosperity under Greek control. Alexander’s empire brought about an increase in interregional trade, as well as the exchange of ideas and knowledge. The blending of different cultures and the introduction of Greek ideas and philosophies had a lasting impact on the art, literature, and architecture of the region. The spread of Greek culture and the establishment of Greek cities in the conquered territories laid the foundation for a new era of cultural exchange and intellectual development in the Hellenistic period.
Expansion of the Hellenistic Culture

As Alexander the Great expanded his empire through his military campaigns, he also played a significant role in the spread of Hellenistic culture. The Greek influence on the eastern lands under his control was immense. One way this was achieved was through the establishment of Greek cities and institutions, which served as centers for the dissemination of Greek language, architecture, art, and philosophy. The foundation of cities such as Alexandria in Egypt, Antioch in Syria, and Seleucia in Persia became vibrant hubs of cultural exchange. Greek settlers, artists, and intellectuals flocked to these cities, bringing with them their traditions, customs, and ideas, which fused with the local cultures to create a unique blend. This cultural fusion resulted in an era known as the Hellenistic period, which saw the synthesis of Greek, Persian, Egyptian, and other cultures, giving rise to a rich and diverse civilization that has left a lasting legacy.
Greek Influence on the Eastern Lands
Greek Influence on the Eastern Lands:
1. Hellenistic Culture: Alexander’s conquests brought about a significant cultural shift in the eastern lands. The spread of Hellenistic culture, characterized by the adoption of Greek language, customs, and traditions, had a profound impact on the indigenous populations. Greek became the lingua franca of the territories, facilitating communication and trade among diverse ethnic groups. Greek cultural practices, such as the Olympic Games, theater, and philosophy, gained popularity and became integrated into the societal fabric of the conquered lands.
2. Art and Architecture: The Greek influence on art and architecture was particularly prominent during this period. The Eastern lands witnessed the construction of grand cities adorned with magnificent structures, echoing the architectural styles of classical Greece. One notable example is the city of Alexandria, founded by Alexander, which became a hub of cultural exchange and learning. The Library of Alexandria, known for its vast collection of ancient texts, attracted scholars from far and wide, fostering intellectual growth and the dissemination of knowledge.
3. Religious Syncretism: Greek influence also extended to the religious practices of the Eastern lands. In some cases, Greek gods and goddesses were assimilated into existing local belief systems, resulting in a fusion of Greek and indigenous religious traditions. This syncretism gave rise to new religious cults and artistic representations, exemplified by the Greco-Buddhist art in ancient Gandhara (present-day Pakistan and Afghanistan). The blending of Greek and Eastern religious elements contributed to the rich cultural tapestry of the conquered territories.
4. Education and Philosophy: The establishment of Greek-style educational institutions, known as gymnasiums, played a crucial role in disseminating Greek philosophy and intellectual ideas. These institutions became centers of learning, where students studied under Greek philosophers and scholars. Greek philosophical schools, such as the Stoics and Epicureans, gained popularity in the eastern regions, shaping the intellectual discourse and encouraging critical thinking among the local elites.
The Greek influence on the Eastern lands, fostered by Alexander’s conquests, resulted in a rich cultural exchange, merging Greek ideals with indigenous traditions. This cultural hybridity formed the foundation of Hellenistic civilization, leaving a lasting impact on art, language, religion, and intellectual pursuits in the conquered territories.
Spread of Knowledge and Ideas
The conquests of Alexander the Great not only brought about political and territorial changes but also facilitated the spread of knowledge and ideas across different cultures. As Alexander and his armies traveled through conquered territories, they encountered various societies with diverse traditions, languages, and belief systems. Alexander recognized the value of shared knowledge and actively encouraged the exchange of ideas among his subjects. He established libraries and encouraged the translation of texts into Greek, making them accessible to a wider audience. This led to a significant cross-pollination of intellectual traditions, merging the wisdom of the East with the philosophical and scientific advancements of the Greeks. The Hellenistic period that followed Alexander’s conquests witnessed the flourishing of art, science, philosophy, and literature as diverse cultures interacted and exchanged ideas with one another. This cultural fusion, spearheaded by Alexander’s empire, laid the foundation for the development of future civilizations and intellectual movements.
Reference: perfect-match-ophiuchus-zodiac-compatibility.
Foundation of Alexandria and Other Cities

One of the most significant contributions of Alexander the Great was the foundation of Alexandria and other cities throughout his empire. Alexandria, located in Egypt, became a thriving center of culture, trade, and learning. The city was strategically positioned near the Mediterranean Sea, making it an important hub for maritime trade. Alexander’s vision for Alexandria included architectural marvels such as the famous lighthouse, known as the Pharos, and the Great Library which housed countless volumes of knowledge and attracted scholars from all over the world. The city became a melting pot of different cultures, with Greek, Egyptian, and Persian influences converging. Other cities founded by Alexander, such as Antioch and Seleucia, became cultural and commercial centers in their own right. These cities served not only as symbols of Alexander’s imperial power but also as hubs of intellectual exchange and innovation, fostering a legacy that lasted long after his death.
Architectural Marvels
The architectural marvels created during the reign of Alexander the Great still stand as testament to his vision and influence. One of the most notable examples is the city he founded, Alexandria, in Egypt. Known for its grandeur and sophistication, Alexandria was home to iconic structures such as the Great Library of Alexandria, which housed thousands of scrolls and served as a center of knowledge and scholarship. Another remarkable architectural achievement was the Pharos Lighthouse, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. This towering structure rose over 350 feet and served as a navigational beacon for ships entering the harbor. In addition to Alexandria, Alexander’s conquests also led to the establishment of other cities with impressive architectural feats. For instance, the Hellenistic city of Pergamon in Anatolia boasted the magnificent Altar of Zeus, adorned with intricate sculptures and reliefs. These architectural marvels not only showcased the wealth and power of the empire but also became symbols of Greek influence and culture across the conquered lands. Their enduring legacy continues to captivate historians and architects alike, serving as reminders of the grandeur and ambition of Alexander the Great’s empire.
Societal Impact
The societal impact of Alexander the Great’s conquests cannot be overstated. As he expanded his empire, he established numerous cities and encouraged the blending of Greek and local cultures. These new cities, known as “Alexandrias,” served as hubs of Greek influence and became centers for trade, education, and intellectual pursuits. The spread of Greek language and customs brought about a cultural fusion that influenced art, architecture, literature, and even religious practices. The Hellenistic period, characterized by this blending of cultures, had a lasting impact on the Eastern lands that Alexander conquered. The establishment of these cities also created opportunities for social mobility, as people from diverse backgrounds had opportunities to rise in society. The construction of monumental architectural structures, such as the Library of Alexandria and the Lighthouse of Alexandria, showcased the wealth and grandeur of the empire, leaving a lasting impression on future generations. The societal impact of Alexander’s conquests laid the foundation for the Hellenistic world, shaping the societies and cultures of the conquered lands for centuries to come.
Policies and Institutions

Alexander the Great was not only a conqueror but also a visionary in terms of his policies and institutions. In order to effectively govern his vast empire, he implemented various administrative reforms that left a lasting impact. One of his notable policies was the fusion of Macedonian and Persian customs and traditions, which aimed to create a sense of unity among his diverse subjects. He appointed local administrators, known as satraps, to oversee different regions, allowing for a more decentralized form of governance. Additionally, Alexander encouraged intermarriage between his soldiers and the local populations, further promoting cultural integration. His policies also focused on promoting trade and commerce, leading to economic prosperity in his empire. He established cities and colonies, including the renowned city of Alexandria in Egypt, which became centers of learning and cultural exchange. These policies and institutions laid the groundwork for the Hellenistic period, influencing future rulers for centuries to come.
Administration of the Empire
The administration of Alexander the Great’s vast empire was a complex and innovative endeavor. To efficiently govern and maintain control over his conquered territories, Alexander established a system of satrapies. Satraps, or governors, were appointed to oversee different regions, ensuring the collection of taxes, maintaining law and order, and upholding the authority of the empire. These satraps were often native rulers who were aligned with Alexander’s vision of cultural integration and cooperation. Additionally, Alexander encouraged intermarriage between Greeks and non-Greeks, further promoting unity and fostering loyalty among his subjects. He also implemented a system of coinage, which standardized currency and facilitated trade throughout the empire. Alexander’s policy of adopting local customs and traditions helped to maintain stability and acceptance among the diverse populations under his rule. His administrative strategies were visionary for their time, emphasizing a balance between centralized control and local autonomy. These innovative administrative practices laid the foundation for future empires and influenced the governance systems of subsequent rulers.
Influence on Future Rulers
Alexander the Great’s influence on future rulers cannot be overstated. His military strategies and political tactics served as a model for countless leaders throughout history. One of the most notable examples is Julius Caesar, who admired Alexander and saw him as a role model. Caesar emulated Alexander’s style of governance and military conquest, leading him to become one of the most powerful rulers of Rome. Another leader who was greatly influenced by Alexander was Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. Napoleon studied Alexander’s tactics and often quoted him, using his strategies as a foundation for his own military campaigns. Even in modern times, leaders like General George S. Patton have studied Alexander’s campaigns to gain insights into military tactics and leadership. Alexander’s legacy continues to inspire and shape the actions of leaders around the world, showcasing his enduring influence on the art of ruling and warfare.
Legacy in the Arts and Sciences

Alexander the Great’s legacy extends far beyond his military conquests. He played a pivotal role in the advancement of arts and sciences during his reign. As a passionate lover of Greek culture and philosophy, Alexander actively patronized artists and scholars, fostering a vibrant intellectual climate within his empire. He established the famous Library of Alexandria, which became a center of knowledge and attracted scholars from all corners of the world. This library housed a vast collection of books, manuscripts, and scrolls, preserving and disseminating knowledge in various disciplines. Not only did Alexander support the arts, but he also encouraged scientific exploration, particularly in fields such as astronomy, mathematics, and medicine. The Hellenistic period following Alexander’s reign witnessed remarkable advancements in these areas, laying the groundwork for future scientific breakthroughs. The impact of Alexander’s patronage and support for the arts and sciences can still be seen in the rich cultural heritage of the Hellenistic world today.
Patronage of Artists and Scholars
Alexander the Great’s patronage of artists and scholars played a crucial role in the advancement of arts and sciences during his reign. As a lover of Greek culture and knowledge, Alexander cultivated a rich intellectual environment in his empire. He surrounded himself with philosophers, scientists, and poets, providing them with generous funding and support to pursue their research and creative endeavors. The city of Alexandria, founded by Alexander, became a thriving center for intellectual pursuits. The Library of Alexandria, built under his patronage, housed countless scrolls and manuscripts, attracting scholars from all over the world. Alexander’s patronage not only encouraged the production of great works of art and literature but also facilitated the exchange of ideas and the cross-pollination of various scientific disciplines. This intellectual environment nurtured the development of advancements in fields such as mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and philosophy, leaving a lasting legacy that influenced subsequent generations of scholars and scientists.
Advancements in Science
The reign of Alexander the Great not only marked a significant period of military conquests but also witnessed remarkable advancements in the field of science. During his expeditions, Alexander brought scholars, scientists, and philosophers from various parts of his empire together in a quest for knowledge and discovery. These intellectual exchanges led to groundbreaking advancements across multiple scientific disciplines. One notable area of progress was in the field of astronomy. Under the influence of Greek astronomers, such as Aristarchus and Eratosthenes, who accompanied him on his campaigns, Alexander sponsored the mapping of the stars and the measurement of the Earth’s circumference. These studies laid the foundation for future astronomical advancements and increased our understanding of the cosmos. Additionally, Alexander’s expansion into Egypt provided an opportunity for Greek scholars to interact with Egyptian scholars, leading to the fusion of Greek and Egyptian knowledge in fields like medicine, mathematics, and engineering. This cross-pollination of ideas resulted in advancements such as the development of new surgical techniques, the calculation of pi, and the construction of majestic architectural structures like the Lighthouse of Alexandria. The intellectual vibrancy and scientific progress that flourished under Alexander’s rule left an indelible mark on the history of science.
Controversies and Criticisms

Controversies and criticisms have surrounded the legacy of Alexander the Great, challenging the perception of him as a benevolent visionary. One of the main points of contention is his treatment of the conquered peoples. While Alexander introduced policies aimed at assimilating cultures and promoting intermarriage, his conquests and rule also led to the destruction of cities, loss of lives, and the enslavement of many. Additionally, some critics have argued that his actions had a detrimental impact on Greek society itself, as the constant military campaigns drained resources, leading to economic decline and social upheaval. Despite his accomplishments, these controversies highlight the complexities of Alexander’s character and the consequences of his conquests.
Treatment of Conquered Peoples
The treatment of conquered peoples by Alexander the Great has been a subject of controversy and criticism. While he implemented policies to integrate conquered territories into his empire, his methods were not always benevolent. Despite his admiration for Greek culture, Alexander recognized the need to respect local customs and traditions. He allowed conquered peoples to maintain their own systems of governance as long as they paid tribute and acknowledged his authority. However, there were instances where Alexander’s treatment was harsher. In cities that resisted his rule, he often employed force and brutality, executing or enslaving those who opposed him. This approach aimed to instill fear and discourage further uprisings. One notable example is the city of Tyre, where Alexander laid siege for months before eventually sacking and destroying the city as a warning to others. It is important to note that while Alexander sought to spread Greek culture, he also incorporated elements from the cultures of the conquered peoples into his empire, promoting a fusion of cultures that would later shape the Hellenistic era. Nonetheless, the treatment of conquered peoples under Alexander’s rule remains a controversial aspect of his legacy. (/exploring-sixth-house-health-daily-routine/)
Impact on Greek Society
The impact of Alexander the Great’s conquests on Greek society cannot be overstated. As he expanded his empire into Persia and beyond, Greek culture, language, and ideas experienced a significant influence. The conquests brought a wave of Hellenization, as Greek customs, traditions, and practices permeated the conquered lands. Greek became the lingua franca of the eastern Mediterranean and the official language of administration. Many Greeks migrated to the new cities, bringing with them their art, literature, and philosophy. The blending of Greek and local traditions resulted in a vibrant fusion of cultures, known as Hellenistic culture. Greek theater, sports, and philosophical schools thrived in the newly founded cities. The spread of Greek influence also led to the rise of new dynasties that adopted Greek customs and employed Greek scholars and artists. However, it is important to note that not all Greeks welcomed Alexander’s conquests and saw them as an expansion of their own culture. Some believed that it diluted the purity of Greek society and undermined the traditional city-states. Regardless of the criticisms, the impact of Alexander’s conquests on Greek society was profound, forever changing the cultural landscape of the region.
A Visionary or Conqueror?

The question of whether Alexander the Great was a visionary or simply a conqueror is a matter of debate among historians and scholars. On one hand, Alexander’s military conquests and ambition to build a vast empire cannot be denied. He led his armies through grueling campaigns, defeating powerful adversaries such as the Persian Empire. His military strategies and tactics were innovative and effective, showcasing his brilliance as a military leader. However, Alexander’s vision extended beyond mere conquest. He had a deep admiration for Greek culture and sought to spread it throughout the lands he conquered. He encouraged the fusion of Greek and local customs, promoting the exchange of ideas, knowledge, and culture. This led to the establishment of Hellenistic cities, such as Alexandria, which became centers of learning and intellectual growth. Alexander’s patronage of scholars, artists, and philosophers resulted in significant advancements in various fields, including science, literature, and art. His vision to create a united and cosmopolitan empire, where Greek culture flourished alongside local traditions, sets him apart from being solely categorized as a conqueror. While his methods may have been ruthless at times, Alexander’s impact on the world went beyond military conquest, making him a visionary in his own right. [Check out the difference between solar and lunar eclipses] (/solar-lunar-eclipses-difference/)
Conclusion
In conclusion, the legacy of Alexander the Great is a complex and multifaceted one. While he is undoubtedly remembered as a conqueror who expanded his empire through military might, his impact goes far beyond his military achievements. Alexander’s visionary approach to ruling and his influence on culture, society, and knowledge shaped the world in profound ways. Through his conquests, he spread Hellenistic culture, leading to the fusion of Greek and Eastern traditions. The foundation of cities like Alexandria became centers of learning and artistic innovation. His policies and institutions laid the foundation for future empires, and his patronage of the arts and sciences fostered advancements in various fields. However, Alexander’s legacy is not without controversy and criticism, particularly in terms of his treatment of conquered peoples and the impact on Greek society. Ultimately, whether he is seen as a conqueror or a visionary depends on one’s perspective, but there is no denying the lasting impact Alexander the Great had on the ancient world and beyond.
Frequently Asked Questions

1. Was Alexander the Great truly a great military strategist?
Alexander the Great is widely regarded as one of history’s greatest military strategists. He employed innovative tactics such as the oblique formation, which allowed his forces to attack the enemy’s vulnerable flank, thereby gaining a decisive advantage in battle.
2. How did Alexander’s conquests impact the region?
Alexander’s conquests brought significant political, cultural, and societal changes to the regions he conquered. They led to the decline of the Persian Empire, the spread of Greek culture, the merging of Eastern and Western influences, and the establishment of major cities that became centers of learning and trade.
3. What was the significance of the Hellenistic culture?
The Hellenistic culture that emerged after Alexander’s conquests blended Greek, Egyptian, Persian, and other Eastern cultures. It had a profound influence on art, architecture, literature, philosophy, and scientific advancements, creating a rich and vibrant cultural landscape.
4. Why is the foundation of Alexandria important?
The foundation of Alexandria was significant as it became a major center of trade, scholarship, and intellectual activity. It housed the famous Library of Alexandria, one of the largest repositories of ancient knowledge, attracting scholars from across the ancient world.
5. How did Alexander administer his vast empire?
Alexander introduced administrative reforms that decentralized power and allowed local rulers to maintain control under his overall authority. He adopted a policy of assimilation, encouraging intermarriage between Greeks and Persians and embracing local customs and traditions.
6. Did Alexander’s patronage of arts and sciences have a lasting impact?
Alexander’s patronage of the arts and sciences had a lasting impact. It fostered a flourishing cultural and intellectual environment, attracting renowned scholars and artists from various disciplines, leading to numerous advancements in literature, philosophy, mathematics, and astronomy.
7. What controversies surround Alexander’s treatment of the conquered peoples?
There are controversies surrounding Alexander’s treatment of the conquered peoples. While he did strive to integrate different cultures, he also employed harsh tactics and forced assimilation. These actions led to resistance and resentment among the conquered populations.
8. How did Alexander’s conquests impact Greek society?
Alexander’s conquests had a profound impact on Greek society. The influx of wealth and cultural exchange brought by the conquered territories revitalized Greek cities, resulting in a period known as the Hellenistic Age, characterized by an increased interest in philosophy, art, and learning.
9. Was Alexander more of a visionary or a conqueror?
Alexander the Great can be seen as both a visionary and a conqueror. His military campaigns were driven by a grand vision of spreading Greek Hellenistic culture and creating a unified world empire. However, his methods of achieving this vision involved conquest and often ruthless means.
10. What is the overall legacy of Alexander the Great?
Alexander’s legacy is far-reaching. His conquests expanded the boundaries of the known world, blending cultures, and leaving a long-lasting impact on art, architecture, language, and politics. He is remembered as one of the most influential figures in history, whose feats continue to captivate and inspire people to this day.
References
Frequently Asked Questions

1. How did Alexander the Great become such a successful conqueror?
Alexander the Great’s success as a conqueror can be attributed to his strategic military genius and his ability to inspire his troops. He meticulously planned his campaigns, implemented innovative battle tactics, and led his army from the front, leading by example. His charisma and leadership skills motivated his soldiers to fight fiercely and remain loyal to him, resulting in numerous victories.
2. What impact did Alexander’s conquests have on the Persian Empire?
Alexander’s conquests significantly weakened and transformed the Persian Empire. He overthrew the Persian king Darius III and established Greek rule throughout much of the empire. This led to the spread of Hellenistic culture, the introduction of Greek language and administration, and the integration of Persian nobility into the ruling class. This period witnessed a fusion of Greek and Persian cultures, ultimately shaping the region’s history.
3. How did the Hellenistic culture spread under Alexander’s rule?
Under Alexander’s rule, the Hellenistic culture spread beyond Greece and reached the Eastern lands he conquered. Greek settlers established new cities, bringing with them their language, customs, and artistic traditions. These cities became centers of Greek influence, where local populations adopted Greek practices in various aspects of life, including architecture, art, literature, and philosophy.
4. What architectural marvels were created during Alexander’s reign?
One of the most significant architectural marvels built under Alexander’s reign was the city of Alexandria in Egypt. This city became a center of academic and intellectual excellence, with its renowned library, the Great Library of Alexandria. Other notable architectural projects included the construction of grand palaces, temples, and monuments, showcasing the wealth and power of the empire.
5. How did Alexander’s policies and institutions impact the administration of the empire?
Alexander implemented a system of administration that blended elements of Greek and Persian governance. He appointed local officials to govern conquered territories, combining their knowledge of local customs with Greek administrative practices. This allowed for a degree of self-rule while maintaining overall control. Alexander’s policies and institutions laid the groundwork for future rulers, such as the Seleucids and the Ptolemies, to govern diverse territories effectively.
6. What was Alexander’s patronage of artists and scholars?
Alexander the Great was a great patron of the arts and sciences. He encouraged the creation of epic poems and historical accounts glorifying his conquests, commissioning famous writers like Callisthenes and Aristobulus. He also supported scholars and philosophers, including Aristotle, who became his personal tutor. This patronage helped foster a vibrant intellectual and artistic climate in the Hellenistic world.
7. Were there any controversies surrounding Alexander’s treatment of conquered peoples?
Yes, there were controversies surrounding Alexander’s treatment of conquered peoples. While he did demonstrate a degree of cultural tolerance by incorporating local customs and figures into his administration, he also imposed Greek customs and forced assimilation. Additionally, his military campaigns resulted in the loss of countless lives and caused suffering to the conquered populations. These actions led to criticism and opposition from some quarters.
8. How did Alexander’s conquests impact Greek society?
Alexander’s conquests brought immense wealth and cultural exchange to Greek society. The influx of wealth from the conquered territories fueled economic growth and the emergence of patronage for the arts and sciences. However, it also led to social and political upheaval, as returning soldiers and aristocrats vied for power and influence. The expansion of the Greek world also created a sense of pride and a growing belief in Greek exceptionalism.
9. Was Alexander the Great more of a visionary or a conqueror?
Alexander the Great can be seen as both a visionary and a conqueror. His military conquests expanded Greek influence and established an empire that promoted cultural fusion. He also had a vision for a united world based on shared language and culture, as demonstrated by his policies of blending Greek and Eastern traditions. However, his methods of achieving this vision, including military force and enforced assimilation, were often brutal and oppressive.
10. What is Alexander the Great’s lasting legacy?
Alexander the Great’s lasting legacy is multifaceted. He shaped the course of history through his conquests, which paved the way for the spread of Hellenistic culture and Greek influence in the Eastern lands. His policies and institutions laid the foundation for future empires, and his patronage of the arts and sciences fostered intellectual and artistic advancements. However, his legacy also includes controversies and criticisms regarding his treatment of conquered peoples and the impact on Greek society.







