Contents
- Welcome to the Kepler Mission: Revolutionizing Exoplanet Research
- The Kepler Mission: Pioneering Exoplanet Exploration
- Revolutionizing Exoplanet Research
- Implications and Future Prospects
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What is the Kepler Mission?
- 2. How did the Kepler Space Telescope detect exoplanets?
- 3. What did Kepler discover about exoplanets?
- 4. What is the habitable zone and why is it significant?
- 5. Did Kepler discover any Earth-like exoplanets?
- 6. What other information did Kepler provide about exoplanets?
- 7. How has the Kepler Mission influenced future exploration?
- 8. What is the significance of detecting exoplanet atmospheres?
- 9. How long did the Kepler Mission last?
- 10. Can we still access data from the Kepler Mission?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How does the Kepler mission detect exoplanets?
- 2. What is the significance of the Kepler mission’s exoplanet census?
- 3. How does the Kepler mission define the habitable zone?
- 4. What types of exoplanets has the Kepler mission discovered?
- 5. How does the Kepler mission study the characteristics of exoplanets?
- 6. What advancements has the Kepler mission made in exoplanet detection techniques?
- 7. How does the Kepler mission study exoplanet atmospheres?
- 8. What is the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) and its role in exoplanet research?
- 9. What is the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and its significance for exoplanet research?
- 10. How does the Kepler mission contribute to future prospects of exoplanet research?
- References
- Read More
Welcome to the Kepler Mission: Revolutionizing Exoplanet Research

Embark on a journey to the stars as we delve into the groundbreaking Kepler Mission, which has redefined our understanding of the universe. By venturing beyond the boundaries of our own solar system, scientists have developed unprecedented ways to detect and study exoplanets, planets that orbit stars outside our own cosmic neighborhood. Join us as we explore the incredible advancements made during the Kepler Mission, from uncovering the secrets of the habitable zone to identifying exoplanet candidates for further exploration. Discover how this mission has paved the way for future missions, building on the legacy of Kepler and propelling us even closer to unraveling the mysteries of our universe.
The Kepler Mission: Pioneering Exoplanet Exploration
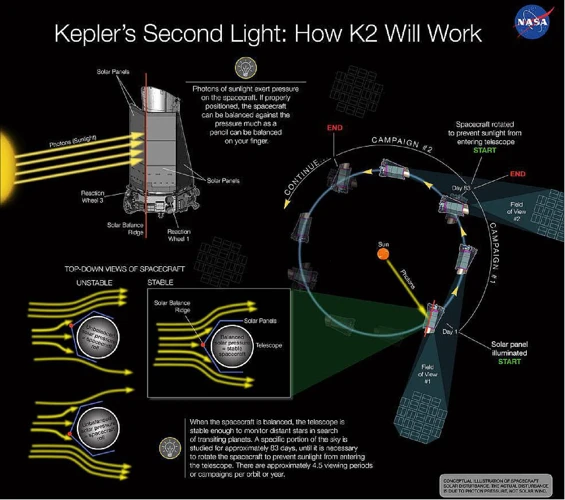
The Kepler Mission, launched by NASA in March 2009, has been at the forefront of exoplanet exploration, revolutionizing our understanding of the cosmos. The mission aimed to determine the frequency of Earth-sized planets within the habitable zone of other stars in our Milky Way galaxy. To accomplish this, the mission utilized the Kepler Space Telescope, a spacecraft equipped with a photometer capable of measuring the brightness of over 150,000 stars simultaneously.
1. Launching the Kepler Space Telescope: The Kepler Space Telescope was specifically designed to search for exoplanets by measuring variations in the brightness of stars. By monitoring these fluctuations in light, astronomers could identify the telltale signs of planets passing in front of their host stars, known as transit events. This groundbreaking technique allowed scientists to detect exoplanets with remarkable precision and accuracy.
2. Unveiling the Exoplanet Census: During its mission, Kepler discovered thousands of exoplanets, revealing for the first time the incredible abundance and diversity of other worlds in our galaxy. These findings debunked the long-held notion that our solar system was unique, leading to a paradigm shift in our understanding of planetary systems and the potential for life beyond Earth. The Kepler mission provided a detailed census of exoplanets, giving valuable insights into their distribution, size, and orbital characteristics.
3. Discovering the Habitable Zone: One of the standout achievements of the Kepler mission was the identification of exoplanets within the habitable zone of their host stars. The habitable zone, also known as the “Goldilocks zone,” refers to the region around a star where conditions are just right for liquid water to exist on a planet’s surface. This discovery has been instrumental in the search for potentially habitable exoplanets and has provided valuable data for future missions seeking signs of extraterrestrial life.
4. Investigating Exoplanet Characteristics: Kepler not only detected the presence of exoplanets but also provided detailed information about their characteristics. By analyzing the data collected by the telescope, scientists could determine the size, mass, and orbital period of exoplanets, providing insights into their composition and formation. Kepler also played a significant role in identifying and characterizing planetary systems with multiple exoplanets, unlocking the secrets of planetary architecture and dynamics.
The Kepler Mission marked a milestone in exoplanet research, forever changing the way we perceive the vastness of the universe. Through its innovative technologies and groundbreaking discoveries, Kepler paved the way for future missions, igniting our curiosity and propelling us closer to unraveling the mysteries of the cosmos.
Revolutionizing Exoplanet Research
1. Advancing Exoplanet Detection Techniques: The Kepler Mission revolutionized exoplanet research by introducing new and innovative techniques for detecting these distant worlds. The transit method employed by Kepler allowed scientists to detect minute variations in a star’s brightness as a planet passes in front of it. This method provided a wealth of information about the size, orbit, and composition of exoplanets. Additionally, the mission pioneered the use of the transit timing variation (TTV) method, which involves studying the irregularities in a planet’s transit times caused by the gravitational influence of other nearby planets in the system.
2. Unveiling the Diversity of Exoplanets: Kepler’s observations unveiled the extraordinary diversity of exoplanets that exist throughout the galaxy. Prior to the mission, our knowledge of exoplanets was limited to a few gas giants. However, Kepler’s data showed that exoplanets come in various sizes, ranging from smaller rocky planets, similar to Earth, to massive gas giants and even weird and exotic worlds that challenge our understanding of planetary formation and dynamics. This newfound knowledge expanded the boundaries of our understanding and shed light on the incredible tapestry of planetary systems that exist beyond our own.
3. Studying Exoplanet Atmospheres: Another groundbreaking aspect of the Kepler Mission was the study of exoplanet atmospheres. By analyzing the light passing through a planet’s atmosphere during a transit event, scientists could identify the presence of certain gases and molecules. This technique, known as transit spectroscopy, provided valuable insights into the composition and potential habitability of exoplanets. Kepler’s observations allowed us to study the atmospheres of exoplanets in unprecedented detail, opening up new avenues for understanding the conditions necessary for life as we know it.
4. Identifying Exoplanet Candidates for Further Exploration: Kepler’s observations provided a vast catalog of exoplanet candidates that warrant further exploration. By identifying potential targets, the mission paved the way for future telescopes and spacecraft to study these exoplanets in more detail. The discoveries made by Kepler allowed scientists to prioritize exoplanets based on their potential for habitability or other scientific significance, guiding the development of future missions and telescopes such as TESS and the James Webb Space Telescope.
The Kepler Mission truly revolutionized exoplanet research, transforming our understanding of the universe and inspiring future generations of astronomers and scientists. With its incredible discoveries and advancements, Kepler laid the foundation for a new era of exploration and pushed the boundaries of our knowledge, bringing us closer than ever to answering the fundamental question: Are we alone in the universe?
Implications and Future Prospects
- Building on Kepler’s Legacy: The wealth of data gathered by the Kepler mission has opened up exciting avenues for further research and exploration. Scientists are continuing to analyze and study the vast amount of information collected, leading to new insights into exoplanet formation, evolution, and habitability. The legacy of Kepler serves as a foundation for future missions, pushing the boundaries of our knowledge even further.
- The Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS): NASA’s next-generation exoplanet hunter, TESS, was launched in 2018 and has since taken over the mantle from Kepler. TESS is designed to survey the entire sky, focusing on nearby stars and searching for exoplanets using the transit method. With its wide field of view, TESS is expected to discover thousands of new exoplanets, including potentially habitable ones, providing a wealth of information for future studies.
- The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST): The upcoming launch of the James Webb Space Telescope, scheduled for 2021, holds immense promise for exoplanet research. JWST will be equipped with powerful instruments capable of analyzing exoplanet atmospheres, searching for signs of habitability and even potential biosignatures. By studying the composition and chemistry of exoplanet atmospheres, JWST will offer a deeper understanding of these distant worlds, paving the way for future missions and the search for life beyond Earth.
The implications of the Kepler Mission are far-reaching and have ignited a renewed interest in exoplanet research. With new missions on the horizon and advancing technologies, we are on the brink of uncovering even more fascinating discoveries about the universe and our place within it.
Conclusion

Conclusion:
The Kepler Mission has undoubtedly revolutionized exoplanet research, providing us with unprecedented insights into the vastness and diversity of the universe. Through its pioneering efforts, Kepler has advanced our understanding of exoplanets and their potential for supporting life beyond Earth. Here are some key takeaways from the Kepler Mission:
- Building on Kepler’s Legacy: The legacy of the Kepler Mission lives on, as its findings and techniques continue to shape the field of exoplanet research. Scientists now have a wealth of data to analyze and further understand exoplanetary systems, and this knowledge will undoubtedly be instrumental in future missions.
- The Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS): TESS, launched in 2018, is the successor to the Kepler Mission and is tasked with continuing Kepler’s work of detecting and characterizing exoplanets. TESS is expected to expand on Kepler’s discoveries and potentially provide insights into habitable exoplanets even closer to our solar system through its all-sky survey.
- The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST): Set to launch in the near future, the James Webb Space Telescope is anticipated to play a crucial role in exoplanet research. With its advanced instrumentation, JWST will study the atmospheres of exoplanets, searching for biomarkers and potentially revealing signs of habitability.
In conclusion, the Kepler Mission has been a remarkable scientific endeavor that has reshaped our understanding of the cosmos. It has laid the foundation for further exploration and expanded our view of the universe, fueling our curiosity to delve deeper into the mysteries of exoplanet research.
Frequently Asked Questions

1. What is the Kepler Mission?
The Kepler Mission was a NASA space exploration program launched in 2009 to search for exoplanets and determine their frequency within the habitable zone of other stars.
2. How did the Kepler Space Telescope detect exoplanets?
The Kepler Space Telescope detected exoplanets by observing the brightness of stars and looking for periodic dips in brightness caused by planets passing in front of their host stars (transits).
3. What did Kepler discover about exoplanets?
Kepler discovered thousands of exoplanets, revealing the abundance and diversity of other worlds in our galaxy. It provided insights into their distribution, size, orbital characteristics, and even identified multiple exoplanet systems.
4. What is the habitable zone and why is it significant?
The habitable zone is the region around a star where conditions are suitable for liquid water to exist on a planet’s surface. Kepler’s discovery of exoplanets within this zone has been crucial in the search for potentially habitable worlds and the presence of extraterrestrial life.
5. Did Kepler discover any Earth-like exoplanets?
Yes, Kepler discovered several Earth-sized exoplanets within the habitable zone, some of which are considered to have the potential for hosting liquid water and therefore, life as we know it.
6. What other information did Kepler provide about exoplanets?
Kepler provided information about the size, mass, and orbital periods of exoplanets, which helped scientists gather insights into their composition, formation, and even their architectural dynamics in planetary systems.
7. How has the Kepler Mission influenced future exploration?
The Kepler Mission has laid the foundation for future exoplanet research and exploration. Its discoveries have sparked further interest and advancements in technology and paved the way for missions like the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) and the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST).
8. What is the significance of detecting exoplanet atmospheres?
Detecting exoplanet atmospheres is essential because they can provide clues about the planet’s potential habitability and the presence of key molecules such as water vapor, oxygen, or methane, which could hint at the existence of life.
9. How long did the Kepler Mission last?
The Kepler Mission originally had a planned mission duration of 3.5 years but was extended to 9 years before officially concluding its mission in 2018.
10. Can we still access data from the Kepler Mission?
Yes, data from the Kepler Mission is publicly available and continues to be a valuable resource for scientific research and the exploration of exoplanets.
References
Frequently Asked Questions

1. How does the Kepler mission detect exoplanets?
The Kepler mission detects exoplanets through the transit method. It measures the slight decrease in brightness when a planet passes in front of its host star, causing a temporary dip in light intensity.
2. What is the significance of the Kepler mission’s exoplanet census?
The Kepler mission’s exoplanet census is significant because it provides us with a better understanding of the prevalence of exoplanets in our galaxy. It helps us estimate the frequency of Earth-like planets and informs us about the potential for life beyond our solar system.
3. How does the Kepler mission define the habitable zone?
The Kepler mission defines the habitable zone as the region around a star where conditions might be right for liquid water to exist on the surface of an orbiting planet. This is considered a key factor in determining the potential for life as we know it.
4. What types of exoplanets has the Kepler mission discovered?
The Kepler mission has discovered various types of exoplanets, including gas giants, rocky planets, and potentially habitable Earth-sized planets. The mission has also identified many multi-planet systems and even some exoplanets with multiple suns.
5. How does the Kepler mission study the characteristics of exoplanets?
The Kepler mission studies the characteristics of exoplanets by measuring their size, mass, and orbit. It also examines their composition, atmosphere, and potential for hosting life. This data helps scientists understand the diversity and nature of exoplanets.
6. What advancements has the Kepler mission made in exoplanet detection techniques?
The Kepler mission has made significant advancements in exoplanet detection techniques by improving the precision and sensitivity of its measurements. It has also developed new algorithms and data analysis methods to identify exoplanet candidates more accurately.
7. How does the Kepler mission study exoplanet atmospheres?
The Kepler mission studies exoplanet atmospheres by analyzing the light that passes through or reflects off these atmospheres. This can provide information about the chemical composition and physical properties of the gases present, offering insights into the potential habitability of these exoplanets.
8. What is the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) and its role in exoplanet research?
The Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) is a follow-up mission to Kepler and aims to survey the entire sky to discover new exoplanets, especially those closer to our solar system. TESS will provide valuable data about exoplanet sizes, masses, and orbital characteristics.
9. What is the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and its significance for exoplanet research?
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is the upcoming flagship space observatory that will be launched to study the universe. It will play a significant role in exoplanet research by providing detailed observations of exoplanet atmospheres, helping us understand their composition, temperature, and potential habitability.
10. How does the Kepler mission contribute to future prospects of exoplanet research?
The Kepler mission’s contributions lay the foundation for future exoplanet research. Its discoveries and insights have inspired new missions like TESS and JWST, which will build upon Kepler’s legacy and further expand our knowledge of exoplanets, their diversity, and their potential for harboring life.
References
- Chasing Shadows in the Nigh: How NASA’s Kepler and …
- Planet-Hunting Kepler Mission’s Legacy Assured
- History of Kepler’s Major Exoplanet “Firsts”







