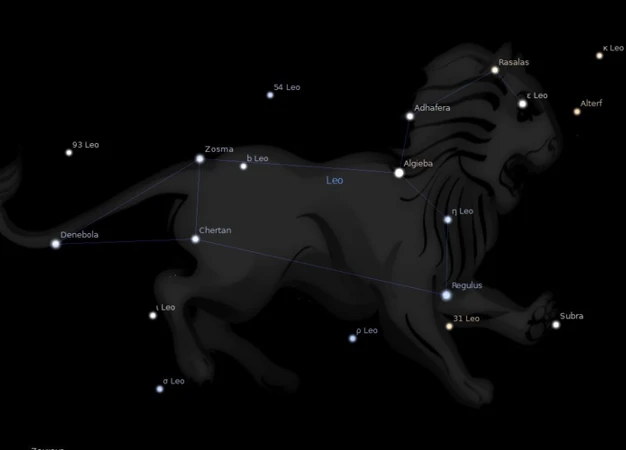
Throughout history, the constellation Leo has captivated the human imagination, serving as a celestial enigma with diverse interpretations across various civilizations. From the ancient lands of Mesopotamia to the mysterious cultures of Mesoamerica, the majestic lion has held a prominent place in the mythology and beliefs of different societies. Exploring the multifaceted symbolism associated with Leo reveals intriguing stories of gods, guardians, and powerful beings that reflect the human fascination with this celestial entity. Join us on a captivating journey as we delve into the rich tapestry of interpretations surrounding the constellation Leo in different civilizations across the globe.
Contents
- Ancient Mesopotamia
- Ancient Egypt
- Ancient Greece
- Ancient China
- Mesoamerican Cultures
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the significance of the Lion of Ishtar in Mesopotamian mythology?
- Why was the lion considered the Guardian of the Gods in Ancient Mesopotamia?
- Who was Sekhmet, the lion-headed goddess in Ancient Egypt?
- What did the lion symbolize in Ancient Egyptian culture?
- What is the story of the Nemean Lion in Ancient Greek mythology?
- How did the lion become a symbol of the zodiac in Ancient Greece?
- What role did the White Tiger play in Ancient Chinese mythology?
- Why was Tezcatlipoca associated with the constellation Leo in Mesoamerican cultures?
- What was the cultural importance of the Pleiades star cluster in ancient civilizations?
- What can we learn from studying the deities and gods in Japanese mythology?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How did the constellation Leo originate in ancient Mesopotamia?
- 2. What role did the constellation Leo play in ancient Egypt?
- 3. What was the significance of the Nemean Lion in ancient Greece?
- 4. How did the constellation Leo become a zodiac symbol in ancient Greece?
- 5. What is the White Tiger in relation to the constellation Leo in ancient China?
- 6. Which Mesoamerican god is connected to the constellation Leo?
- 7. Are there any other interpretations of Leo in different civilizations?
- 8. Can the constellation Leo be seen from all parts of the world?
- 9. Have there been any cultural references to Leo in modern times?
- 10. Are there any notable myths or legends associated with the constellation Leo?
- References
- Read More
Ancient Mesopotamia
Ancient Mesopotamia, the cradle of civilization, held a unique fascination with the constellation Leo, attributing various symbolic meanings to this celestial formation. In Mesopotamian mythology, the lion played a significant role as both a Lion of Ishtar and a Guardian of the Gods. Ishtar, the goddess of fertility and love, was often depicted accompanied by lions, signifying her power and authority. The lion also represented the great gods themselves, serving as protectors and gatekeepers. These interpretations exemplify the ancient Mesopotamians’ reverence for the majestic creature and their belief in its connection to divine forces. Such intricate symbolism offers a glimpse into the spiritual and cultural significance that the constellation Leo held for the people of Mesopotamia.
Lion of Ishtar
In ancient Mesopotamia, the concept of the “Lion of Ishtar” held great significance in their mythology and belief systems. Ishtar, the goddess of fertility, love, and war, was often depicted alongside lions, symbolizing her power and authority. The lion, as the sacred animal of Ishtar, represented her divine strength and ferocity. Ishtar was seen as a fierce protector, both nurturing and destructive, similar to the qualities associated with lions – strength, courage, and unpredictability. The imagery of Ishtar accompanied by lions emphasized her role as a formidable force in the pantheon of Mesopotamian gods. The Lion of Ishtar exemplified the intricate relationship between deities and animals, showcasing the Mesopotamians’ understanding of the natural world and its connection to the divine. It is fascinating to see how ancient civilizations attributed specific animals to their gods, weaving them into their religious narratives and cultural identity. This parallel between the divine and the animal world can be observed in various mythologies across different cultures, such as the Japanese mythology that explores the diverse pantheon of gods and their animal counterparts. This interplay between deities and animals provides valuable insights into the spiritual beliefs and customs of ancient civilizations, forming a tapestry of cultural significance intertwined with cosmic wonders like the Pleiades star cluster.
Guardian of the Gods
In the realm of ancient Mesopotamian mythology, the constellation Leo held the distinguished title of the . The people of Mesopotamia believed that the lion, with its imposing presence and regal demeanor, possessed the power to protect and watch over the deities. This celestial guardian symbolized strength, authority, and courage, embodying the divine forces that governed the universe. In the pantheon of Mesopotamian gods, the lion had a significant role in safeguarding the heavens, ensuring the order and harmony of the cosmos. As the gods embarked on their celestial journeys and interacted with the mortal realm, the lion stood watch, defending against any threats or disruptions that might arise. This divine connection between Leo and the guardian role is a testament to the profound spiritual beliefs and reverence that ancient Mesopotamians had for the constellation and its association with their gods.
| Ancient Egypt | /mythology-pyramids-egypt/ |
| Ancient Greece | /cultural-importance-pleiades-star-cluster/ |
Ancient Egypt

In the realm of Ancient Egypt, the constellation Leo held a prominent position in their mythology and symbolism, embodying both power and royalty. The lion-headed goddess Sekhmet represented fierce protection and was believed to possess the ability to ward off evil. Sekhmet was revered as a warrior goddess and associated with the sun, reflecting the strength and ferocity of the lion. Additionally, the lion was viewed as a symbol of royalty, representing the pharaoh’s authority and divine lineage. Egyptian pharaohs often depicted themselves wearing the Nemes headdress adorned with the image of a lion, further emphasizing their connection to the constellation Leo and their claim to the throne. This intertwining of Sekhmet and the lion in Ancient Egypt showcases the people’s belief in the celestial connection between the heavens and earthly power.
The Lion-headed Goddess Sekhmet
In ancient Egypt, the constellation Leo held a profound significance, closely associated with the Lion-headed Goddess Sekhmet. Sekhmet was a fierce and powerful deity, often depicted with the head of a lioness. She embodied the potent forces of war, destruction, and healing. As the daughter of the sun god Ra, Sekhmet represented the scorching heat of the sun and its destructive potential. Egyptian mythology portrayed her as a force to be feared but also revered for her ability to ward off evil and maintain balance. Egyptians believed that Sekhmet had the power to cure illness and protect against malevolent forces. This duality of destructive power and heaIing attributes showcased her role as a fierce protector and a benevolent healer. The symbolism of Sekhmet and her association with the lion exemplified strength, ferocity, and guardianship, embodying the qualities that the ancient Egyptians admired and sought to emulate.
Note: There is no relevant anchor text to link within this specific section.
Symbol of Power and Royalty
In ancient Egypt, the constellation Leo was seen as a powerful . The Egyptians believed that the lion embodied qualities of strength, courage, and leadership, characteristics that were highly valued in their society. The association between lions and royalty can be traced back to the earliest periods of Egyptian history. The pharaohs, who were considered divine rulers, were often depicted wearing the nemes headdress adorned with the uraeus (a stylized representation of a cobra) and a lion’s mane. This imagery symbolized their connection to the gods and their authority over the land. Lions were also featured prominently in Egyptian architecture, seen in the statues and sphinxes that guarded temples and royal tombs. These majestic creatures represented the power and might of the pharaoh, reinforcing their divine right to rule over the kingdom. The concept of the lion as a symbol of royalty permeated various aspects of Egyptian culture, from art and amulets to religious rituals. It served as a reminder of the pharaoh’s strength and ability to protect the kingdom, just as the lion protected its pride. This deep-rooted belief in the lion as a symbol of power and royalty reflects the Egyptians’ profound reverence for their rulers and their fascination with the celestial representation of Leo.
Ancient Greece
In the realm of Ancient Greece, the constellation Leo held a prominent place in both mythological tales and astrological beliefs. The lion’s legendary status was epitomized in the mythical Nemean Lion, a fearsome creature that was said to be invulnerable to mortal weapons. The hero Heracles, as part of his Twelve Labors, was tasked with slaying this formidable beast. The Nemean Lion became a symbol of strength and triumph over adversity, representing the indomitable spirit of the Greek heroes. In the realm of astrology, Leo became one of the twelve zodiac symbols, associated with individuals born during the summer months. The constellation represented qualities such as leadership, confidence, and creativity, reflecting the Greek admiration for these characteristics. From the mythical tales of Heracles to its inclusion in the zodiac, the diverse interpretations of Leo showcased the cultural significance that this constellation held for the ancient Greeks.
The Nemean Lion
In Ancient Greece, the constellation Leo found its place in one of the most famous mythological tales – the story of . According to Greek mythology, this fearsome lion possessed impenetrable golden fur and terrorized the region of Nemea, causing havoc and destruction. The Nemean Lion was believed to be the offspring of the monstrous Typhon and Echidna, making it a formidable and mythical creature. In Heracles’ Twelve Labors, one of his arduous tasks was to slay the Nemean Lion. The lion’s impenetrable hide made it invulnerable to weapons, bringing a new level of challenge to the hero. With his incredible strength and resourcefulness, Heracles defeated the lion by choking it and eventually killed it with its own claws. The legend of the Nemean Lion became a symbol of valor, strength, and triumph over adversity in Greek culture. This mythical creature embodied the courage and heroism of Heracles, showcasing the importance of bravery and resilience in the face of formidable challenges. The story of the Nemean Lion serves as a testament to the enduring power and influence of the constellation Leo in Ancient Greek mythology.
The Zodiac Symbol
In ancient Greece, the constellation Leo held a special place as a Zodiac Symbol. The Greeks, known for their fascination with astrology and divination, incorporated Leo into their zodiac system. Represented by a regal lion, Leo was believed to exert significant influence over those born under its celestial influence. Individuals born between July 23 and August 22 were said to possess the traits associated with the mighty lion – courage, leadership, and a charismatic presence. The ancient Greeks believed that each zodiac sign had a unique impact on a person’s destiny, and those born under the sign of Leo were destined to be leaders and rulers. This symbolic association between Leo and leadership can be seen in the Greek myth of the Nemean Lion, a legendary creature Hercules had to overcome as part of his Twelve Labors. The lion’s strength and bravery became synonymous with the sign, further reinforcing its powerful symbolism. Even today, astrology enthusiasts explore the traits and characteristics linked to the zodiac sign Leo, drawing inspiration from its representation as the king of the celestial realm. To delve deeper into the intricacies of mythological deities and gods, you can explore the fascinating world of Japanese mythology and their diverse pantheon.
Ancient China

In Ancient China, the constellation Leo held a special place in the hearts and minds of the people, represented by the White Tiger. This celestial being was associated with strength, power, and protection. The White Tiger was believed to be the Guardian of the West and played a crucial role in Chinese mythology and astrology. It was often depicted as a divine creature with a ferocious appearance, symbolizing bravery and awe-inspiring might. The reverence for the White Tiger in Ancient Chinese culture showcases the deep connection between the celestial realm and the values held by the people, emphasizing the significance of this awe-inspiring constellation in their beliefs and traditions.
The White Tiger
The White Tiger holds a significant place in ancient Chinese mythology and is closely associated with the constellation Leo. Considered one of the Four Symbols of the Chinese constellations, the White Tiger represents the west direction. According to Chinese folklore, the White Tiger is a powerful creature that possesses divine attributes and guards against evil influences. It is often depicted as a fierce and majestic beast with white fur and is believed to possess the ability to repel demons and protect the land. In Chinese astrology, the White Tiger is also associated with the season of autumn and the element of metal, further emphasizing its symbolism of strength and authority. Its celestial counterpart in the constellation Leo serves as a reminder of the White Tiger’s esteemed role as a guardian and protector in Chinese culture.
Guardian of the West
In ancient China, the constellation Leo was regarded as the . This belief stemmed from the Chinese astrological system, where the sky was divided into four cardinal directions, with Leo representing the west. Known as the White Tiger, the constellation was associated with power, strength, and protection. The White Tiger was believed to be a fierce creature that guarded the western gate of heaven, preventing evil spirits from entering. This guardian role was considered crucial, as the west was seen as the direction of the setting sun and the realm of the afterlife. The White Tiger’s presence in the western skies instilled a sense of security and protection in the Chinese people, with its celestial position signifying the ongoing battle between light and darkness. The concept of the Guardian of the West exemplifies the profound connection between celestial bodies and Chinese cultural beliefs, showcasing how different civilizations interpreted the constellation Leo in unique and fascinating ways.
Mesoamerican Cultures

Mesoamerican cultures, including the Aztecs and Mayans, incorporated the constellation Leo into their rich tapestry of beliefs and mythology. Within these civilizations, the constellation held a connection to the powerful god Tezcatlipoca, who was often associated with strength and leadership. Tezcatlipoca, known as the Smoking Mirror, was one of the most significant deities in Mesoamerican pantheons, embodying both the light and dark aspects of life. The lion symbolism associated with Leo reflected Tezcatlipoca’s fierce and authoritative nature, mirroring his role as a god of war and rulership. These intricate interpretations highlight the significance of the constellation Leo in the cosmology of Mesoamerican cultures, emphasizing its connection to ideas of strength, leadership, and divine power.
The Aztec God Tezcatlipoca
The Aztec God Tezcatlipoca was a central figure in the religious beliefs of the Aztec civilization. Known as the god of the night sky, Tezcatlipoca was often associated with the constellation Leo due to its prominent presence during the nighttime. Tezcatlipoca was depicted as a powerful and enigmatic god, often portrayed with a jaguar form, symbolizing his connection to the animal kingdom and the celestial realm. As a patron of rulers, warriors, and sorcerers, Tezcatlipoca was revered for his ability to bestow strength, leadership, and power upon those who worshipped him. In Aztec mythology, he was believed to have played a vital role in the creation and destruction of the world. With his contrasting characteristics of benevolence and malevolence, Tezcatlipoca represented the dual nature of existence and served as a reminder of the transient and unpredictable nature of life. The worship of Tezcatlipoca by the Aztecs exemplifies their deep spiritual beliefs and the revered status of the constellation Leo in their cosmology.
Associated with Strength and Leadership
In Mesoamerican cultures, the constellation Leo was associated with strength and leadership. One fascinating example of this symbolism can be found in the Aztec civilization, where the celestial depiction of a lion corresponded to the god Tezcatlipoca. Tezcatlipoca, known as the “Smoking Mirror,” was revered as a powerful deity associated with the night sky and various aspects of leadership. As the embodiment of strength and valor, Tezcatlipoca was believed to grant strength and courage to warriors in battle. His association with leadership extended beyond warfare, as he was also considered the patron deity of rulers and governors. The Aztecs revered Tezcatlipoca as a divinity who possessed the qualities necessary to govern and lead their society. The constellation Leo, known as the lion in their celestial lexicon, thus served as a constant reminder of the strength and leadership attributes embodied by their revered god Tezcatlipoca.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the investigation into the diverse interpretations of the constellation Leo across different civilizations reveals a shared fascination with the symbolic power and regal nature of the lion. From Mesopotamia to Egypt, Greece to China, and Mesoamerica, the lion has been venerated as a deity, guardian, and embodiment of strength and royalty. These interpretations illustrate the universality of human imagination and our attempts to make sense of the night sky. Whether representing the ferocity and protection of gods or symbolizing leadership and bravery, the constellation Leo has left an indelible mark on various cultures throughout history. By exploring these diverse interpretations, we gain a deeper understanding of the human connection to the stars and the enduring significance they hold in shaping our beliefs and cultures. The constellation Leo continues to inspire awe and curiosity, reminding us of the vastness of the universe and the timeless stories woven within its celestial tapestry.
Frequently Asked Questions

What is the significance of the Lion of Ishtar in Mesopotamian mythology?
The Lion of Ishtar held great symbolic value in Mesopotamian mythology, representing strength, power, and divine protection. It was associated with the goddess Ishtar, the embodiment of love and fertility. The lion symbolized Ishtar’s authority and her role as a divine guardian.
Why was the lion considered the Guardian of the Gods in Ancient Mesopotamia?
In Ancient Mesopotamia, the lion was revered as the Guardian of the Gods due to its fierce and protective nature. Mesopotamians believed that lions possessed supernatural strength and were capable of warding off evil spirits. As guardians, lions were seen as protectors of the divine realm.
Who was Sekhmet, the lion-headed goddess in Ancient Egypt?
Sekhmet was an ancient Egyptian goddess depicted with a lioness head. She was associated with war, destruction, and healing. In Egyptian mythology, Sekhmet represented the destructive power of the sun and also had a role as a protective deity.
What did the lion symbolize in Ancient Egyptian culture?
In Ancient Egyptian culture, the lion symbolized power, royalty, and strength. It was often associated with the pharaohs, who were considered the embodiment of kingship and divine authority. The lion was also seen as a guardian and protector in Egyptian mythology.
What is the story of the Nemean Lion in Ancient Greek mythology?
The Nemean Lion was a fearsome creature in Ancient Greek mythology. It was said to have impenetrable golden fur and was invulnerable to mortal weapons. One of the twelve labors of Hercules was to defeat this lion, which he accomplished by strangling it with his bare hands.
How did the lion become a symbol of the zodiac in Ancient Greece?
In Ancient Greece, the lion became one of the symbols of the zodiac due to its association with the constellation Leo. The zodiac was a celestial map depicting the path of the sun, and the lion was chosen to represent the sign of Leo due to its regal and dominant nature.
What role did the White Tiger play in Ancient Chinese mythology?
The White Tiger held immense significance in Ancient Chinese mythology. It was considered one of the Four Symbols, representing the cardinal direction of the West. The White Tiger was believed to be a celestial creature capable of warding off evil spirits and symbolized power and authority.
Why was Tezcatlipoca associated with the constellation Leo in Mesoamerican cultures?
In Mesoamerican cultures, Tezcatlipoca was a god associated with many aspects, including leadership and strength. His connection to the constellation Leo stemmed from his role as a powerful ruler and warrior figure, often depicted as a jaguar or a powerful predator like the lion.
What was the cultural importance of the Pleiades star cluster in ancient civilizations?
The Pleiades star cluster held cultural importance in many ancient civilizations, including Mesopotamia, Egypt, and Greece. It served as a celestial navigation point, agricultural calendar marker, and had mythological associations. The celestial cluster held different meanings across cultures, highlighting its universal significance.
What can we learn from studying the deities and gods in Japanese mythology?
The study of deities and gods in Japanese mythology offers insights into the cultural, religious, and historical practices of Japan. Exploring these myths allows us to understand the values, beliefs, and folklore that shaped ancient Japanese society. It provides a glimpse into their rich storytelling tradition and the way they perceived the world around them.
References
- Leo Constellation for Kids. Facts, Myth, and photos.
- (PDF) Comparing constellations across cultures
- Why is the constellation Leo shown differently, and …
Frequently Asked Questions

1. How did the constellation Leo originate in ancient Mesopotamia?
The constellation Leo originated in ancient Mesopotamia as a representation of the Lion of Ishtar, a symbol associated with the goddess Ishtar and her power.
2. What role did the constellation Leo play in ancient Egypt?
In ancient Egypt, the constellation Leo was connected to the lion-headed goddess Sekhmet, who was believed to possess immense power and was associated with protection and warfare.
3. What was the significance of the Nemean Lion in ancient Greece?
The Nemean Lion was a legendary creature in ancient Greece that Hercules had to defeat as one of his twelve labors. The constellation Leo represents Hercules’ triumph over this formidable lion.
4. How did the constellation Leo become a zodiac symbol in ancient Greece?
In ancient Greece, the constellation Leo represented one of the twelve zodiac signs. It was believed to have influence over those born between July 23 and August 22, symbolizing qualities such as leadership and confidence.
5. What is the White Tiger in relation to the constellation Leo in ancient China?
In ancient China, the White Tiger was associated with the constellation Leo. It represented courage, power, and protection, and was considered the guardian of the West.
6. Which Mesoamerican god is connected to the constellation Leo?
In Mesoamerican cultures, the constellation Leo is associated with the god Tezcatlipoca. This revered deity was seen as a symbol of strength, leadership, and divine intervention.
7. Are there any other interpretations of Leo in different civilizations?
Yes, there are various other interpretations of the constellation Leo in different civilizations. For example, in Hindu astrology, Leo is associated with the fire element and is believed to be ruled by the Sun.
8. Can the constellation Leo be seen from all parts of the world?
Yes, the constellation Leo can be seen from almost all parts of the world, although its visibility may vary depending on the time of year and the observer’s location.
9. Have there been any cultural references to Leo in modern times?
Absolutely! The symbolism of Leo is still widely recognized and referenced in popular culture, astrology, and even in the names of astrological signs and constellations.
10. Are there any notable myths or legends associated with the constellation Leo?
Yes, besides the Greek myth of Hercules and the Nemean Lion, there are other myths and legends across different civilizations that feature lions or lion-like creatures, often with connections to power, bravery, and divine beings.
References
- On the origin of the 12 zodiac constellation system in ancient …
- Why is the constellation Leo shown differently, and …