Have you ever gazed up at the night sky and wondered about the twinkling stars that dot the darkness? What if you could decipher these celestial patterns and identify the constellations that they form? Learning to locate constellations in the night sky can be a fascinating and rewarding experience. By understanding the basics of constellations, preparing for sky observation, and using the right tools and techniques, you can unlock the mysteries of the universe and navigate the vast expanse above. In this comprehensive guide, we will take you step-by-step through the process of locating constellations, from familiarizing yourself with the night sky to identifying key constellations and using stargazing tools. So, grab your binoculars or telescope, get ready to uncover the wonders of the cosmos, and embark on an awe-inspiring journey through the starry realm.
Contents
- Understanding Constellations
- Preparing for Sky Observation
- Identifying Key Constellations
- Using Stargazing Tools
- Tips for Locating Constellations
- Understand Constellation Seasons
- Troubleshooting and Common Issues
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. Can anyone locate constellations in the night sky?
- 2. Do constellations look the same from different parts of the world?
- 3. Can I see constellations during the day?
- 4. Are all constellations made up of stars?
- 5. Are constellations only visible during specific seasons?
- 6. Why do constellations have different names?
- 7. Can I create my own constellations?
- 8. Are all constellations the same size?
- 9. Can constellations change over time?
- 10. Are there any benefits to learning about constellations?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How do constellations form in the night sky?
- 2. Can I see different constellations from different parts of the world?
- 3. How do I know which constellations are visible tonight?
- 4. Is it necessary to have a telescope or binoculars to locate constellations?
- 5. How do I find the North Star?
- 6. Are there any specific star patterns I should look for when identifying constellations?
- 7. How does light pollution affect stargazing and locating constellations?
- 8. Can I observe different constellations during different seasons?
- 9. Are there any stargazing events or groups that can help me locate constellations?
- 10. What should I do if the weather conditions are not ideal for stargazing?
- References
- Read More
Understanding Constellations

In simple terms, constellations are groupings of stars that form recognizable patterns or shapes in the night sky. These patterns have been passed down through generations and are often associated with myths, legends, and cultural significance. From the awe-inspiring Orion’s Belt, consisting of three bright stars, to the iconic Big Dipper, many constellations have captivated human imagination for centuries.
Constellations serve as a celestial roadmap, guiding astronomers and stargazers alike. They help navigate the night sky, locate stars, and understand the movements of celestial bodies. Additionally, constellations provide a deeper connection to our cultural heritage and inspire a sense of wonder and curiosity about the vastness of the universe. Exploring constellations allows us to appreciate the beauty of the night sky and gain a greater understanding of our place in the cosmos.
1. What are Constellations?
Constellations are arrangements of stars that form identifiable patterns in the night sky. These patterns have been recognized and named by various cultures throughout history. There are 88 official constellations designated by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). Each constellation has its own unique shape and story, often rooted in mythology and cultural traditions. For example, the constellation Orion, depicting a hunter wielding a club and a shield, has origins in Greek mythology. Similarly, the Mayans used constellations as a part of their astronomy and astrology practices to navigate their world and mark important celestial events. Understanding constellations provides a framework for observing and studying the night sky, allowing us to appreciate the ongoing connection between humans and the cosmos.
2. Importance of Constellations
Constellations hold great significance in various aspects of human culture, history, and scientific exploration. Here are some key reasons why constellations are important:
- Navigational Aid: Throughout history, constellations have been used as navigational tools, helping sailors and explorers find their way across oceans and land. They provided a sense of direction and served as a reliable reference point for celestial navigation.
- Cultural and Mythical Significance: Constellations have deep cultural and mythical roots, reflecting the beliefs, stories, and legends of different civilizations. For example, the constellation Orion is linked to Greek mythology, representing the legendary hunter. These stories provide insights into ancient cultures and their perception of the cosmos.
- Astronomical Research: Constellations play a crucial role in astronomy, serving as the building blocks for mapping and studying the night sky. Astronomers use constellations to organize and locate stars, galaxies, and other celestial objects. This classification system helps in identifying and studying specific areas of the universe.
- Education and Inspiration: Studying constellations fosters scientific curiosity and inspires individuals to explore the wonders of the universe. Learning about constellations can ignite a passion for astronomy and encourage further exploration of topics such as planetary alignments, Mayan astronomy, or the mythical origins of Greek gods and goddesses. (Insert internal link here for mythical origins of Greek gods and goddesses.)
By understanding the importance of constellations, we can appreciate their historical and cultural significance, as well as unlock the vast knowledge they offer in terms of celestial navigation and scientific exploration.
Preparing for Sky Observation

Choose the Right Time and Location
When preparing for sky observation, it is crucial to choose the right time and location to maximize your chances of spotting constellations. Find a location away from city lights and light pollution, as this can hinder visibility. Ideally, a dark and open area such as a park, field, or countryside would be ideal for a clear view of the night sky.
As for the timing, check for moonrise and moonset times as a bright moon can wash out the stars and make it difficult to see constellations. Aim for nights with minimal or no moonlight. Consult a moon phase calendar or use a sky-viewing app to plan your observation on nights with a new moon or crescent moon.
Check Weather Conditions
Weather conditions play a significant role in the visibility of constellations. Cloudy or hazy skies can obstruct the view, making it challenging to locate and identify constellations. Before heading out for sky observation, check the weather forecast to ensure clear skies. Optimal conditions include a clear and cloudless night with minimal atmospheric interference such as fog or smog.
It is also important to dress appropriately for the weather. Nights can get chilly, even during warmer months, so wear layers to stay comfortable while sky gazing. Consider bringing blankets, chairs, or a reclining lawn chair for a more relaxed and enjoyable experience.
3. Choose the Right Time and Location
In order to have a successful sky observation and locate constellations, it is crucial to choose the right time and location. First, consider the time of year and the season. Different constellations are visible at different times throughout the year due to the Earth’s orbit around the Sun. For example, during the winter months, you may have the opportunity to spot Orion, with its distinctive belt of three stars. If you’re interested in observing a specific constellation, do some research to determine the best time of year for visibility.
In addition to timing, the location of your observation site is important. Ideally, find a spot away from light pollution, such as city lights, which can hinder visibility. Consider heading to a nearby park, a remote countryside area, or even a designated stargazing location. This will allow you to have a clearer view of the night sky and make it easier to identify constellations. Remember to dress warmly and bring along comfortable seating or blankets, as sky observation can take a while.
4. Check Weather Conditions
Before heading out for a sky observation, it’s crucial to check the weather conditions to ensure optimal visibility. The clarity of the night sky plays a significant role in locating constellations. Here are a few factors to consider when checking weather conditions:
Clear Skies: Look for forecasts indicating clear skies with minimal cloud cover. Cloudy conditions can obstruct your view of the stars, making it challenging to locate constellations. If the forecast predicts cloudy skies, consider rescheduling your observation for another night when conditions are more favorable.
Light Pollution: Light pollution from city lights can significantly impact your ability to see faint stars and constellations. If you live in an area with high light pollution, consider traveling to a darker location away from city lights. This will significantly enhance your visibility and make it easier to identify constellations.
Atmospheric Conditions: Factors like humidity, air pollution, and atmospheric stability can affect the clarity of the night sky. Look for nights with low humidity and minimal air pollution for the best observation experience. Stable atmospheric conditions can provide clearer views of stars and constellations.
Planetary Alignments: Sometimes, specific astronomical events such as planetary alignments or meteor showers can make for fascinating sky observation opportunities. If there are any upcoming astronomical events, it’s worth checking how the weather conditions will align with these events to optimize your chances of witnessing unique celestial phenomena. For instance, you can refer to our guide on exploring planetary alignments and their significance.
By taking into account these weather factors, you can ensure the best possible conditions for locating constellations and enjoying a memorable stargazing experience.
Identifying Key Constellations
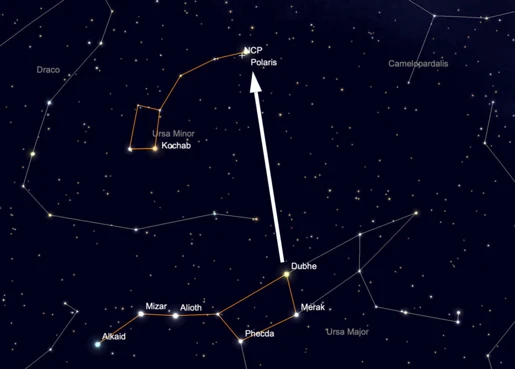
Before you can identify key constellations, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the night sky. Find a location away from bright city lights, ideally on a clear night with minimal light pollution. Look up and take in the vastness of the stars above. Observe the different brightness levels of stars and notice any distinct patterns or groupings. One helpful technique is to create a mental map of the sky by dividing it into sections and observing the stars within each section. This will assist you in recognizing constellations and their positions as you progress.
The North Star, also known as Polaris, is a key reference point for locating constellations in the night sky. It remains almost stationary throughout the night, making it a reliable guide for navigation. To find the North Star, locate the Big Dipper constellation. The two outer stars in the spoon-shaped part of the Big Dipper point directly towards the North Star. The North Star is part of the constellation Ursa Minor, and its position can help you determine directions and identify other constellations.
Once you have familiarized yourself with the night sky and located the North Star, it’s time to identify some major constellations. Start with constellations that are easily recognizable and prominent. The Big Dipper, mentioned earlier, is a popular starting point as it stands out in the northern hemisphere. The Big Dipper is part of the larger constellation Ursa Major. Another easily identifiable constellation is Orion, with its distinctive three bright stars forming Orion’s Belt. As you become more experienced, you can progress to identifying other constellations and exploring their fascinating stories and mythological connections.
Remember, becoming proficient at identifying constellations takes time and practice. It’s worth investing in a star chart or using a mobile app to assist you in your journey. By utilizing these tools and gaining familiarity with the night sky, you will soon be able to confidently identify key constellations and unlock the wonders of the universe above.
5. Familiarize Yourself with the Night Sky
Before you can start locating constellations in the night sky, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with the celestial landscape. Start by finding a location with minimal light pollution, such as a dark rural area or a designated stargazing site. On a clear night, spend some time simply looking up at the sky and observing the various stars and their brightness. Take note of any patterns or groupings that catch your eye. One helpful technique is to divide the night sky into sections using imaginary lines or using a sky map. This can help you navigate different regions and recognize the constellations within each section. You can also invest in a basic star chart or a star app for your smartphone, which can provide valuable information and identify constellations for you. By becoming familiar with the night sky and its different components, you’ll be better equipped to locate and appreciate the wonders of the celestial world.Decoding Mayan Astronomy
6. Locate the North Star
Locating the North Star is an essential step in identifying constellations and navigating the night sky. The North Star, also known as Polaris, is a bright star located close to the North Celestial Pole. It serves as a reliable reference point because it appears almost stationary in the night sky while other stars and constellations appear to rotate around it.
To find the North Star, start by locating the Big Dipper, which is part of the Ursa Major constellation. The Big Dipper is a prominent group of stars that resembles a ladle or a saucepan. Trace an imaginary line from the two stars at the end of the Big Dipper’s bowl, and extend it about five times its length. This line will lead you directly to the North Star.
Once you have located the North Star, keep in mind that it always remains in the same position relative to the horizon. In the northern hemisphere, it appears above the horizon at all times, making it a helpful guide for navigation, especially during nighttime outdoor activities. For those in the southern hemisphere, unfortunately, the North Star is not visible due to its position in relation to the Earth’s axis.
Understanding how to find the North Star is essential because it provides a starting point for locating other constellations. By using the North Star as a reference, you can begin to orient yourself and explore the surrounding constellations with greater ease and accuracy.
7. Identify Major Constellations
Identifying major constellations is an essential step in locating constellations in the night sky. These well-known constellations are easily recognizable and serve as important reference points for sky observation. Here are some tips to help you identify major constellations:
1. Learn the prominent star patterns: Major constellations often have distinct star patterns that make them stand out. For example, the Big Dipper, part of the Ursa Major constellation, forms a recognizable ladle shape. Familiarize yourself with these prominent star patterns to easily identify the corresponding constellations.
2. Use reference guides: There are plenty of books, online resources, and smartphone apps available that provide detailed information and visual aids to help you identify major constellations in the night sky. These guides highlight the key stars and patterns to look out for, making it easier for beginners to navigate the celestial landscape.
3. Follow connecting lines: Some constellations are formed by connecting imaginary lines between stars. For example, the constellation Cygnus, also known as the Northern Cross, is formed by drawing lines between a series of stars that resemble the shape of a cross. Following these connecting lines can help you identify and trace out the major constellations.
4. Look for bright stars: Major constellations usually contain one or more bright stars that act as anchor points. These stars are often referred to as “guide stars” and can help you locate and identify the surrounding constellation. Once you’ve found a bright star, look for neighboring stars and patterns to determine the constellation it belongs to.
Remember, identifying major constellations takes practice and patience. As you spend more time stargazing and familiarize yourself with the night sky, you’ll become more adept at recognizing and identifying these celestial wonders.
Using Stargazing Tools

When it comes to locating constellations in the night sky, having the right tools can significantly enhance your stargazing experience. Here are two essential stargazing tools that can help you in your celestial exploration:
- Binoculars or Telescope: Binoculars or a telescope can provide a closer and more detailed look at the stars and constellations. They enable you to see celestial objects that may be too faint to observe with the naked eye. Look for binoculars or a telescope with a magnification power suitable for stargazing. Familiarize yourself with the basic features and controls of your chosen instrument to make the most out of your stargazing sessions.
- Sky-Viewing Apps and Maps: In this digital age, sky-viewing apps and maps have become invaluable tools for locating constellations. There are numerous apps available for smartphones and tablets that can help you identify constellations in real-time. These apps use GPS technology to pinpoint your location and provide an interactive map of the night sky. They can overlay constellation lines, labels, and even provide additional information about stars and planets. Additionally, you can also make use of printable star charts or planispheres, which are circular star maps that can be adjusted to match the date and time of your stargazing session.
By utilizing binoculars or a telescope, along with sky-viewing apps or maps, you can delve deeper into the captivating world of constellations and unravel the celestial wonders that adorn the night sky.
8. Binoculars or Telescope
When it comes to locating constellations in the night sky, having the right tools can greatly enhance your sky-gazing experience, and that’s where binoculars or telescopes come into play. Binoculars are a portable and affordable option for beginners or casual stargazers. These handheld optical devices offer a wider field of view, making it easier to scan the night sky and locate constellations. Binoculars also amplify the brightness and clarity of stars, enabling you to see more detail. On the other hand, telescopes are ideal for those looking to delve deeper into the universe. They provide a higher magnification and allow you to observe celestial bodies, such as planets and galaxies, with greater detail. Telescopes come in various designs and sizes, and more advanced models often have features like computer-controlled tracking to help you stay locked onto specific constellations. Whether you opt for binoculars or a telescope, investing in a pair of these sky-gazing tools will undoubtedly enhance your ability to observe and appreciate the wonders of the night sky.
9. Sky-Viewing Apps and Maps
Thanks to modern technology, we now have the convenience of using sky-viewing apps and maps to enhance our stargazing experiences. These apps and maps are designed to help both beginners and seasoned stargazers identify constellations, planets, and other celestial objects.
One popular option is to use mobile applications specifically developed for sky-viewing. These apps utilize your device’s GPS and gyroscopes to provide an interactive map of the night sky in real-time. They can pinpoint your location and display an overlay of constellations, stars, and planets directly on your screen. Notable sky-viewing apps include Star Walk, SkyView, and Stellarium Mobile.
Another handy tool is a sky map or planisphere. These printed or digital maps are designed to be easily portable and provide a visual representation of the night sky throughout the year. They typically rotate to match the visible constellations based on the date and time. By aligning the map with the current time and date, you can easily identify constellations and their positions in the sky.
Whether you prefer the convenience of a mobile app or the charm of a physical map, using sky-viewing apps and maps can greatly enhance your ability to locate constellations. They can help you identify specific stars, find patterns, and navigate the night sky with ease. So, make sure to download a sky-viewing app or acquire a sky map before your next stargazing adventure!
Tips for Locating Constellations
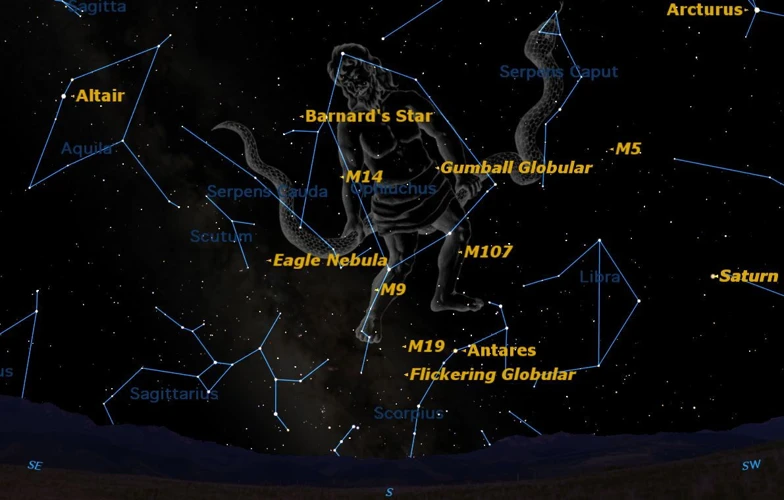
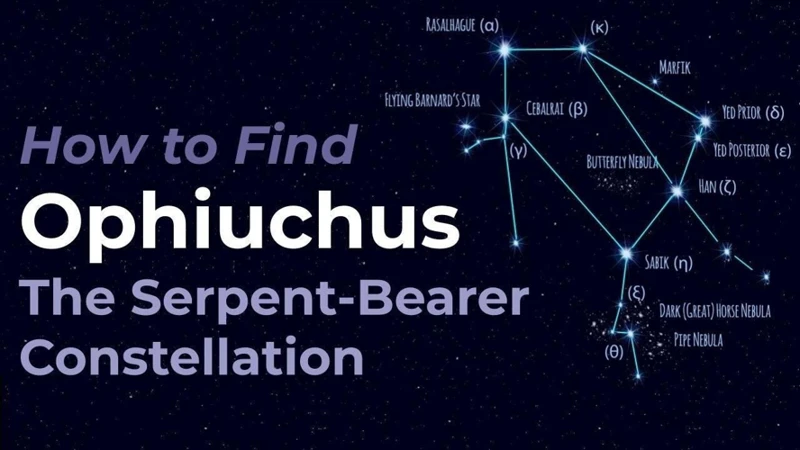
When you first begin your journey of locating constellations in the night sky, it’s best to start with bright stars that are easily visible. Scan the sky and look for stars that shine with a noticeable intensity. These bright stars act as guideposts, leading you to the constellations they belong to. Once you’ve identified a bright star, use it as a reference point to find other stars and patterns in the vicinity.
One effective way to locate constellations is by finding distinctive star patterns within them. Constellations often have unique shapes or arrangements of stars that can be easier to identify compared to individual stars. Look for patterns that resemble animals, mythological figures, or everyday objects. These recognizable star patterns make it simpler to navigate the night sky and locate specific constellations.
A helpful technique for locating constellations is to use celestial landmarks as reference points. Celestial landmarks are prominent stars, planets, or other celestial objects that can guide you in finding constellations. For example, the North Star, also known as Polaris, is a reliable landmark in the northern hemisphere. By determining the direction of the North Star, you can identify constellations that lie in its vicinity.
Understanding the astrology of ancient civilizations and their interpretation of celestial landmarks can provide additional insights into the history and cultural significance behind constellation identification.
10. Start with Bright Stars
When it comes to locating constellations in the night sky, a good starting point is to focus on bright stars. These stars act as guideposts and can help orient you in the vastness of space. One way to identify bright stars is by researching the brightest stars in the sky, such as Sirius, Canopus, or Vega. Once you have identified these stars, use them as reference points to find the nearby constellations. For example, if you locate Sirius, you can easily spot the constellation Orion, which features the distinctive Orion’s Belt. By starting with the brightest stars, you can gradually build your knowledge and confidence in identifying constellations.
11. Find Star Patterns
One of the key techniques for locating constellations is to find star patterns. Star patterns are distinct arrangements of stars that form recognizable shapes in the night sky. These patterns can help you identify and navigate constellations. Here are a few steps to help you find star patterns:
- Research common star patterns: Before heading out for sky observation, familiarize yourself with common star patterns. There are various resources available such as books, online guides, and mobile apps that provide information on popular star patterns.
- Learn about asterisms: Asterisms are smaller star patterns within a larger constellation. For example, the Big Dipper is an asterism within the Ursa Major constellation. Knowing about these smaller patterns can help you locate constellations more easily.
- Use constellations as reference points: Once you have identified a recognizable star pattern, use it as a reference point to locate neighboring constellations. Look for other stars and patterns nearby to help guide you in your exploration.
- Find connecting lines: Look for imaginary lines that connect stars within a pattern. These lines can help you visualize the shape of the constellation more clearly. For example, in the constellation Orion, the three stars of Orion’s Belt are connected by an invisible line.
- Practice, observe, and compare: Spend time observing the night sky and identifying different star patterns. Compare what you see to star charts or mobile apps to verify your observations and deepen your understanding.
By honing your ability to find star patterns, you’ll become more adept at locating and identifying constellations. Remember, patience and practice are key in developing this skill. So, grab a stargazing companion and embark on a celestial treasure hunt to discover the mesmerizing star patterns that adorn our night sky.
12. Use Celestial Landmarks
Celestial landmarks are invaluable tools for locating constellations in the night sky. These are prominent stars or easily identifiable objects that can serve as reference points. By using these landmarks, you can navigate your way through the sky and find the desired constellations. Here are a few celestial landmarks that can help you in your stargazing journey:
The North Star (Polaris): One of the most famous celestial landmarks is the North Star, also known as Polaris. This star lies almost directly above the North Pole and remains almost stationary throughout the night. Finding the North Star can provide you with a sense of direction and help orient yourself in the night sky.
Orion’s Belt: Orion’s Belt is a distinct line of three bright stars located in the constellation Orion. This trio of stars is easily recognizable due to its straight alignment. Once you locate Orion’s Belt, you can use it as a starting point to find other constellations and objects.
The Summer Triangle: The Summer Triangle is a prominent asterism consisting of three bright stars from different constellations: Vega in the Lyra constellation, Altair in the Aquila constellation, and Deneb in the Cygnus constellation. This large and noticeable triangle is visible during the summer months in the northern hemisphere and can help you find other nearby constellations.
Planets: Occasionally, planets become visible in the night sky and can serve as temporary celestial landmarks. These bright objects, such as Venus, Mars, or Jupiter, stand out against the backdrop of stars and can help guide your efforts in locating specific constellations.
By utilizing these celestial landmarks, you can effectively navigate the night sky and locate your desired constellations with ease.
Understand Constellation Seasons
Understanding Constellation Seasons
The night sky is constantly changing, and so are the constellations visible from Earth. The concept of constellation seasons refers to the period of time when specific constellations are most prominent in the sky. Each season brings forth a unique set of constellations that rise and set at different times.
To understand constellation seasons, it’s important to grasp the concept of the celestial sphere. The celestial sphere is an imaginary dome surrounding Earth, and all the stars and constellations are projected onto this sphere. As Earth orbits the Sun, different parts of the celestial sphere become visible, leading to changes in the constellations we can observe.
One of the primary factors influencing constellation seasons is the tilt of Earth’s axis. As the Earth orbits the Sun, the tilt causes the Sun’s apparent position in the sky to change. This shifting position of the Sun directly affects the visibility of constellations during different times of the year.
The night sky can be divided into four main seasons: spring, summer, autumn, and winter. Each season has its own distinct set of constellations that are more prominent during that time. For example, in the northern hemisphere, during winter, constellations such as Orion, Taurus, and Gemini dominate the night sky, while in the summer, we see constellations like Cygnus, Lyra, and Aquila.
It is important to note that the visibility of constellations also depends on the observer’s location on Earth. Constellations that are visible in the northern hemisphere may not be visible in the southern hemisphere and vice versa.
By understanding the concept of constellation seasons and keeping track of the changing night sky, you can plan your stargazing adventures to observe specific constellations during their peak times. This knowledge allows you to deepen your understanding of the night sky and appreciate the dynamic nature of our cosmic surroundings.
13. Know the Night Sky Cycle
One key aspect of understanding constellations is knowing the night sky cycle. The night sky changes throughout the year as the Earth orbits around the Sun. This movement causes different constellations to be visible during different seasons. By familiarizing yourself with the night sky cycle, you can anticipate which constellations will be prominent on any given night. For example, during winter months, you might spot the dazzling constellation of Orion, while in summer, the prominent Scorpius or Ursa Major may grace the night sky. Understanding the night sky cycle allows you to plan your stargazing adventures accordingly and ensures that you don’t miss the opportunity to witness the beauty of specific seasonal constellations.
14. Observe Seasonal Constellations
As the Earth orbits the Sun, the apparent position of constellations in the night sky changes throughout the year. This means that certain constellations are more visible during specific seasons. To enhance your stargazing experience, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the seasonal constellations.
During the winter months in the northern hemisphere, you can spot prominent constellations such as Orion, Taurus, and Gemini. Orion, the Hunter, is particularly recognizable with its distinctive belt of three bright stars. The constellation Taurus features the well-known Pleiades star cluster, also called the Seven Sisters. Gemini, the Twins, can be identified by the two bright stars, Castor and Pollux.
In the spring, Leo the Lion dominates the night sky, with its bright star Regulus marking its heart. Another notable spring constellation is Virgo, represented by a maiden holding a sheaf of wheat. Look for the bright star Spica to locate Virgo.
As summer approaches, the constellation Cygnus, also known as the Northern Cross, graces the sky. Cygnus is easily identifiable by its prominent cross-shaped formation. Additionally, Scorpius, with its distinct curved tail, and Sagittarius, resembling a teapot, are visible during the summer months.
In the autumn, the constellation Pegasus, the Winged Horse, can be spotted, marked by its square-shaped pattern known as the Great Square of Pegasus. Additionally, Andromeda, the Chained Princess, featuring the Andromeda Galaxy, is another autumn constellation worth observing.
By keeping track of the seasonal constellations, you can anticipate which constellations will be visible at specific times throughout the year. This knowledge will allow you to plan your stargazing sessions in advance and ensure that you don’t miss out on witnessing the ever-changing celestial wonders above.
Troubleshooting and Common Issues
When it comes to locating constellations in the night sky, there can be a few challenges and common issues that arise. Here are some troubleshooting tips to help you overcome these obstacles:
- Dealing with Light Pollution: Light pollution from city lights or other sources can make it difficult to see stars and constellations clearly. To minimize the impact of light pollution, choose a location away from city lights, such as a rooftop or a nearby park. Additionally, consider using a skyglow filter for your telescope or binoculars to reduce the effects of light pollution.
- Recognizing Cloudy Skies: Cloudy skies can hinder your view of the night sky and make it challenging to locate constellations. If you encounter cloudy conditions, try to wait it out or plan your stargazing session for a clear night. Alternatively, you can explore stargazing apps or websites that provide virtual sky maps to learn about constellations even when the sky is not visible.
By being prepared for these common issues, you can navigate through the challenges and make the most of your stargazing experience. Remember, persisting through obstacles will only enhance your ability to locate constellations and deepen your understanding of the night sky.
15. Dealing with Light Pollution
Dealing with light pollution is essential for a successful stargazing experience. Light pollution refers to the excessive artificial light that brightens the night sky and hinders our ability to see stars and constellations clearly. To combat light pollution, there are several steps you can take. Firstly, consider finding a location away from cities and urban areas, where the night sky is less affected by artificial lighting. Additionally, use shielding techniques, such as placing a hood on your flashlight or using red filters, to minimize the amount of light emitted. It can also be helpful to familiarize yourself with areas on a star map that have low light pollution levels, allowing for better visibility of constellations. By taking these measures, you can enhance your stargazing experience and have the opportunity to fully appreciate the beauty of the night sky.
16. Recognizing Cloudy Skies
Recognizing cloudy skies is crucial when it comes to observing constellations at night. Cloud cover can obstruct the view and make it difficult to see the stars. To determine if the sky is cloudy or not, you can follow a few simple steps.
First, look up at the sky and assess the overall visibility. If you notice a thick blanket of clouds or haze, it is a clear indication of cloudy skies. However, sometimes clouds may be thin or scattered, making it trickier to determine the extent of cloud cover.
Another indication of a cloudy sky is to observe the brightness of celestial objects. If stars appear dimmer or have a hazy glow, it is likely that the sky is covered by clouds. Stars that are normally visible may be completely obscured, leading to reduced visibility of constellations.
Furthermore, you can utilize technology to assist in assessing cloud cover. Many weather apps and websites provide real-time satellite imagery, allowing you to check the cloud cover in your area. These resources can be particularly helpful for planning stargazing sessions in advance, as they offer hourly or daily cloud forecasts.
It’s important to note that even if the sky appears cloudy, it doesn’t necessarily mean you have to abandon your stargazing plans completely. Sometimes, there may be breaks in the clouds or areas where the sky is relatively clear. It is worth waiting for these windows of opportunity to catch a glimpse of the constellations.
In conclusion, recognizing and navigating cloudy skies is an essential skill for any stargazer. By observing the visual cues, utilizing technology, and keeping an eye out for breaks in the clouds, you can maximize your chances of enjoying a clear view of the mesmerizing night sky and the captivating constellations it holds.
Conclusion

Locating constellations in the night sky can be an enchanting and fulfilling experience. By understanding the basics of constellations, preparing for sky observation, and utilizing the right tools and techniques, you can embark on a journey through the stars.
Throughout this guide, we have explored the significance of constellations and their role as celestial roadmaps. We have discussed the importance of choosing the right time and location for sky observation, as well as the need to check weather conditions to ensure optimal viewing conditions.
We have delved into the process of identifying key constellations, including familiarizing ourselves with the night sky, locating the North Star as a navigational guide, and recognizing major constellations using star patterns and celestial landmarks.
We have also explored the use of stargazing tools such as binoculars or telescopes, as well as sky-viewing apps and maps to enhance our celestial exploration.
Furthermore, we have provided tips for locating constellations, such as starting with bright stars, finding star patterns, and using celestial landmarks to navigate the night sky.
Understanding constellation seasons and the night sky cycle is crucial for observing seasonal constellations and planning stargazing activities accordingly.
We have also addressed common issues faced by stargazers, such as light pollution and cloudy skies, and provided strategies to overcome these challenges.
In conclusion, the wonder of the night sky awaits you. Whether you are exploring the mystical constellations of ancient civilizations, tracking planetary alignments, or simply marveling at the beauty of the stars above, this guide has equipped you with the knowledge and resources to unlock the secrets of the cosmos. So, grab your binoculars, download a sky-viewing app, and immerse yourself in the awe-inspiring world of constellations.
Frequently Asked Questions

1. Can anyone locate constellations in the night sky?
Absolutely! Locating constellations in the night sky is accessible to everyone, regardless of age or experience. All you need is a clear view of the sky and some basic knowledge about the stars and their patterns.
2. Do constellations look the same from different parts of the world?
No, constellations can appear different depending on your location on Earth. The orientation and visibility of constellations change as you move across different latitudes. However, some constellations such as the Big Dipper are visible from both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres.
3. Can I see constellations during the day?
No, constellations are not visible during the day. The brightness of the sun drowns out the stars and makes it impossible to see them. Wait until nighttime when the sky is dark for optimal stargazing.
4. Are all constellations made up of stars?
While most constellations are formed by groups of stars, some constellations do include other celestial objects. For example, the constellation Orion includes the Orion Nebula, a stunning cloud of gas and dust where new stars are being born.
5. Are constellations only visible during specific seasons?
No, constellations can be seen throughout the year. However, different constellations are more prominent during certain seasons due to the Earth’s orbit around the sun. This means that some constellations may be easier to spot during specific times of the year.
6. Why do constellations have different names?
Constellations have different names because they originate from various cultures and civilizations around the world. Different cultures developed their own legends and stories to explain the patterns they saw in the stars, therefore assigning unique names to these constellations.
7. Can I create my own constellations?
While you can certainly make your own patterns using stars, the International Astronomical Union (IAU) is responsible for officially recognizing and naming constellations. The IAU has defined 88 constellations that are universally accepted.
8. Are all constellations the same size?
No, constellations come in various sizes. Some constellations cover a large portion of the sky, while others are smaller and more compact. The size of a constellation is determined by the arrangement and spacing of the stars within it.
9. Can constellations change over time?
While the individual stars in a constellation may have slight movements over thousands of years, the overall patterns of constellations remain relatively stable for human timescales. This means that the constellations we see today have been recognized for centuries and will continue to be visible in the future.
10. Are there any benefits to learning about constellations?
Absolutely! Learning about constellations not only allows you to appreciate the beauty of the night sky but also helps increase your understanding of astronomy and celestial movements. It can be a fulfilling hobby, and knowing constellations can even assist with navigation if you ever find yourself without a compass.
References
- Simple Ways to Identify the Stars: 10 Steps (with Pictures)
- How to observe and explore the constellations in …
- Stargazing: Finding the Stars and Constellations
Frequently Asked Questions

1. How do constellations form in the night sky?
Constellations are formed by groups of stars that appear to form patterns or shapes when viewed from Earth. These patterns are a result of the way the stars are positioned in relation to our planet.
2. Can I see different constellations from different parts of the world?
Yes, the constellations visible in the night sky vary depending on your location on Earth. Different latitudes offer different views of the stars, so traveling to different parts of the world can provide you with new constellations to explore.
3. How do I know which constellations are visible tonight?
You can determine which constellations are visible on a particular night by using sky-viewing apps or websites. These tools provide real-time information about the current positions of stars and constellations in the night sky.
4. Is it necessary to have a telescope or binoculars to locate constellations?
No, you can locate many constellations with the naked eye. However, using binoculars or telescopes can enhance your stargazing experience by allowing you to see more details and fainter stars within the constellations.
5. How do I find the North Star?
The North Star, also known as Polaris, can be found by following the line formed by the two outer stars in the Big Dipper’s bowl. The North Star is located at the end of the handle of the Little Dipper.
6. Are there any specific star patterns I should look for when identifying constellations?
Yes, many constellations are associated with distinct star patterns or asterisms. For example, Orion is known for its belt of three bright stars. Learning these patterns can help you locate and identify constellations more easily.
7. How does light pollution affect stargazing and locating constellations?
Light pollution from city lights can make it more challenging to see stars and constellations. Finding a location away from bright city lights will provide a clearer view of the night sky and make it easier to locate constellations.
8. Can I observe different constellations during different seasons?
Yes, the constellations visible in the night sky change with the seasons. Certain constellations can only be seen during specific times of the year, so it’s important to be aware of the celestial cycles to maximize your stargazing opportunities.
9. Are there any stargazing events or groups that can help me locate constellations?
Yes, many communities and organizations host stargazing events or have astronomy clubs that offer assistance and guidance in locating constellations. These events can be a great way to connect with fellow stargazers and learn more about the night sky.
10. What should I do if the weather conditions are not ideal for stargazing?
If the weather conditions are unfavorable for stargazing, such as a cloudy sky or inclement weather, it’s best to wait for a clearer night. Patience is key in stargazing, and you want to ensure that you have optimal visibility to locate constellations.
References
- Learn the constellations | Astronomy.com
- Simple Ways to Identify the Stars: 10 Steps (with Pictures)
- How to observe and explore the constellations in …