Have you ever wondered about the mesmerizing celestial phenomenon known as eclipses? These awe-inspiring events have captivated humans for centuries, sparking curiosity and inspiring countless myths and legends. But what exactly causes an eclipse to occur, and how can we observe them safely? In this article, we will delve into the world of eclipses and explore the science behind these extraordinary events. From the basics of solar and lunar eclipses to the causes, types, and significance of these celestial wonders, prepare to embark on a journey through the cosmos and uncover the secrets of eclipses. So, grab your telescope, put on your protective glasses, and let’s unravel the mysteries of eclipses together.
Contents
- The Basics of Eclipses
- Causes of Eclipses
- Types of Eclipses
- Observing Eclipses
- Significance of Eclipses
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is a solar eclipse?
- What is a lunar eclipse?
- How often do eclipses occur?
- Can I look directly at a solar eclipse?
- How long do eclipses last?
- Are eclipses visible everywhere?
- What is the difference between totality, annularity, and partiality?
- What is a hybrid eclipse?
- What safety precautions should I take when observing an eclipse?
- What are the cultural and historical significances of eclipses?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How often do eclipses occur?
- 2. Can I see an eclipse from anywhere on Earth?
- 3. What is a solar eclipse?
- 4. What is a lunar eclipse?
- 5. Are solar eclipses dangerous to watch?
- 6. How long do eclipses typically last?
- 7. What is the difference between totality and partiality in eclipses?
- 8. Do eclipses have any cultural significance?
- 9. How do scientists study eclipses?
- 10. Can I photograph an eclipse with a regular camera?
- References
- Read More
The Basics of Eclipses
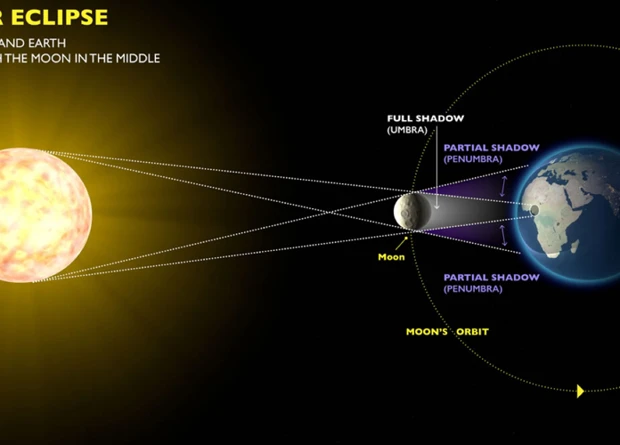
Eclipses, the celestial phenomenon that never fails to mesmerize us, occur when the paths of the Sun, the Moon, and the Earth converge in a spectacular dance. There are two main types of eclipses: solar and lunar. During a solar eclipse, the Moon moves directly between the Earth and the Sun, casting its shadow onto the Earth’s surface. This results in the Sun being partially or fully obscured, depending on the location of the observer. Conversely, during a lunar eclipse, the Earth moves between the Sun and the Moon, causing the Moon to enter the Earth’s shadow and darken. These remarkable events have fascinated people since ancient times, inspiring myths and legends that have shaped our understanding of the cosmos. From the influence of Greek mythology to the exploration of moon sign compatibility in family dynamics, the mysteries of eclipses continue to captivate our imaginations. So let’s embark on a journey to understand the basics of eclipses and uncover the enchantment they hold.
Solar Eclipses
Solar eclipses are mesmerizing celestial events that occur when the Moon aligns perfectly between the Sun and the Earth, casting its shadow on the Earth’s surface. There are several types of solar eclipses, including total, partial, annular, and hybrid eclipses. During a total solar eclipse, the Moon completely covers the Sun, creating a breathtaking sight as the Sun’s corona becomes visible to the naked eye. This rare phenomenon captivates observers around the world, as darkness falls and the stars become visible in the daytime sky. Partial solar eclipses occur when the Moon only partially obscures the Sun, creating a stunning crescent shape. Annular eclipses, on the other hand, happen when the Moon is positioned farther away from the Earth, and its apparent size is smaller than the Sun, resulting in a ring of fire effect. Hybrid eclipses, as the name suggests, are a combination of both total and annular eclipses, appearing as partial or total depending on the observer’s location. It is crucial to remember that observing a solar eclipse with the naked eye can cause severe damage to the eyes. It is advised to use special solar filters or eclipse glasses to protect one’s vision. Solar eclipses have captivated cultures throughout history, often inspiring awe, fear, and reverence. From ancient Greek mythology to modern-day scientific research, these celestial events continue to ignite curiosity and wonder among people of all backgrounds and ages.
Lunar Eclipses
During a lunar eclipse, a captivating celestial event takes place as the Earth passes between the Sun and the Moon, casting a shadow on the lunar surface. Unlike a solar eclipse, which can only be observed from specific locations on Earth, a lunar eclipse can be observed from any place on the planet where the Moon is visible during the event. As the Earth’s shadow falls on the Moon, it gradually darkens, taking on a reddish hue. This phenomenon is known as the “blood moon” due to its striking appearance. The red color is caused by sunlight passing through Earth’s atmosphere and bending around our planet, resulting in the filtering of shorter blue and green wavelengths while longer red wavelengths dominate the lunar illumination. Lunar eclipses often last for several hours, making it a magnificent spectacle for sky gazers around the world. Not only do lunar eclipses offer a breathtaking visual experience, but they also provide valuable opportunities for scientific study. By studying the behavior of sunlight as it passes through the Earth’s atmosphere and onto the Moon during a lunar eclipse, astronomers can gain insights into the composition and characteristics of Earth’s atmosphere. Additionally, lunar eclipses have cultural and historical significance, with various mythologies and beliefs surrounding their occurrence. To explore more about the influence of Greek mythology or delve into the intriguing subject of moon sign compatibility in family dynamics, feel free to check out the relevant articles. Lunar eclipses are a wondrous phenomenon that continues to captivate our imagination and offer a gateway to understanding the mysteries of the cosmos.
Causes of Eclipses

The causes of eclipses can be traced back to the intricate interplay between the Sun, the Moon, and the Earth. During a solar eclipse, the Moon blocks the Sun’s light, casting a shadow on the Earth. This alignment occurs when the Moon is in its new moon phase, positioned between the Earth and the Sun. The Moon’s orbit around the Earth is slightly tilted, so solar eclipses don’t happen every month. As for a lunar eclipse, it happens when the Earth moves between the Sun and the Moon, casting its shadow on the lunar surface. This occurs during a full moon phase when the Moon passes through the Earth’s shadow. Both types of eclipses are remarkable events, showcasing the intricate mechanics of our cosmic neighborhood. So, whether you’re gazing up at the sky in awe or exploring the significance of eclipses in understanding astrological charts such as the houses in the natal chart, the causes of eclipses are a captivating subject that unveils the wonders of our celestial realm.
Solar Eclipse – Moon Blocking the Sun
During a solar eclipse, the Moon stands as a cosmic protagonist, temporarily obscuring the radiant Sun from our view. This mesmerizing phenomenon occurs when the Sun, Moon, and Earth align in a symphonic celestial dance. As the Moon gracefully journeys between the Earth and the Sun, its shadow is cast upon the Earth’s surface, creating a momentary darkness during the day. There are three main types of solar eclipses: total, partial, and annular. In a total solar eclipse, the Moon completely covers the Sun, revealing the glorious corona—a pearly, glowing halo that encircles the obscured solar disk. This breathtaking sight lasts only for a few precious minutes and can be witnessed from a specific path called the path of totality. Partial solar eclipses occur when the Moon partially blocks the Sun, causing only a portion of the solar disk to be obscured. Annular eclipses, on the other hand, happen when the Moon is at its farthest point from the Earth, and its size appears smaller than the Sun. As a result, a fiery ring of sunlight surrounds the silhouette of the Moon, creating a mesmerizing “ring of fire” effect. Solar eclipses are celestial spectacles that have captivated humanity for centuries, even influencing various cultures and mythologies. From ancient Greek myths to modern-day beliefs surrounding the influence of solar eclipses on our houses natal chart, these captivating events continue to inspire wonder and awe. So, the next time a solar eclipse graces the skies, make sure to don your solar eclipse glasses and witness the breathtaking beauty of the Moon momentarily blocking the Sun.
Lunar Eclipse – Earth’s Shadow
During a lunar eclipse, the Moon finds itself in the Earth’s shadow, resulting in a mesmerizing celestial display. The Earth’s shadow is composed of two distinctive parts: the outer shadow, known as the penumbra, and the inner shadow, called the umbra. When the Moon passes through the penumbra, it experiences a partial eclipse, causing it to appear slightly dimmed. However, when the Moon moves into the umbra, it falls within the darkest part of the Earth’s shadow, resulting in a total lunar eclipse. This phenomenon occurs because the Earth’s atmosphere bends sunlight, allowing some of it to reach the Moon even when it is in the umbra. This light reaching the Moon is filtered, causing it to take on a reddish hue, often referred to as a “blood moon.” The coloration results from the scattering of sunlight through the Earth’s atmosphere, with shorter blue and green wavelengths being filtered out and longer red wavelengths reaching the Moon. This captivating sight has been the subject of fascination and interpretation throughout history, with various cultures attributing different meanings to lunar eclipses. From ancient Greek myths that associate lunar eclipses with celestial beings to exploring the significance of lunar eclipses in astrology, such as their relevance in understanding moon sign compatibility in family dynamics, the Earth’s shadow casts a spell on our imagination, revealing the beauty and mystery of the cosmos.
Types of Eclipses
Eclipses come in various forms, each offering a unique spectacle that leaves us in awe of the cosmos. There are three main types of eclipses: totality, annularity, and partiality. Totality occurs during a solar eclipse when the Moon perfectly aligns with the Sun, completely obscuring its bright disk and revealing the ethereal beauty of the Sun’s corona. An annular eclipse takes place when the Moon is farther from the Earth, appearing smaller and leaving a ring of sunlight visible around its edges. On the other hand, a partial eclipse occurs when only a portion of the Sun or Moon is covered during the alignment. Apart from these types, there are also hybrid and penumbral eclipses, which provide us with different levels of visibility and shadow. Exploring the different types of eclipses allows us to understand the wonders of celestial mechanics and the myriad ways in which our universe manifests itself. So, ready your telescopes and venture into the cosmic spectacle, as we unravel the secrets of these fascinating phenomena.
Totality, Annularity, and Partiality
During a solar eclipse, the extent to which the Sun is covered by the Moon determines the different phases experienced by observers. The totality phase occurs when the Moon fully obscures the Sun, creating a breathtaking sight. This is the moment when the sky darkens, and the Sun’s corona—an outer layer of plasma—becomes visible. Those lucky enough to witness totality are treated to a remarkable spectacle, as the Sun’s outer atmosphere shimmers and dances in the sky. However, not all solar eclipses result in totality. In some cases, the Moon is unable to completely cover the Sun, leading to a phenomenon known as partiality. During partiality, only a portion of the Sun is obscured, and the degree of coverage varies depending on the observer’s location. Another unique type of solar eclipse is annularity. Annular eclipses occur when the Moon is at its farthest point from Earth, making it appear smaller than the Sun. As a result, during annularity, a thin ring or annulus of sunlight remains visible around the Moon’s silhouette. Annular eclipses create a stunning “ring of fire” effect and offer a different perspective on this celestial event. It’s important to note that observing any phase of a solar eclipse requires proper eye protection to prevent damage to the eyes. So, whether you’re witnessing the breathtaking totality, the partiality, or the captivating annularity, make sure to stay safe and embrace the awe-inspiring wonders of our universe.
Hybrid and Penumbral Eclipses
Hybrid and penumbral eclipses are two additional types of eclipses that occur less frequently but are equally intriguing. A hybrid eclipse is a rare phenomenon that begins as a total solar eclipse but transitions into an annular eclipse or vice versa, depending on the observer’s location. This unique combination of total and annular phases makes hybrid eclipses truly remarkable. On the other hand, a penumbral eclipse occurs when the Moon passes through the Earth’s penumbra, the outer part of the shadow where only a portion of the sunlight is blocked. Unlike total or partial eclipses, penumbral eclipses are often more subtle and less noticeable. During a penumbral eclipse, the Moon may appear slightly dimmer or take on a faint, shadowy appearance. These types of eclipses serve as a reminder of the intricate celestial mechanics that govern our universe and provide astronomers with valuable opportunities to study the subtle interactions between the Sun, Moon, and Earth. To learn more about the cultural and historical significance of eclipses, such as their influence on Greek mythology, or to explore the fascinating concept of moon sign compatibility in family dynamics, be sure to check out the respective articles.
Observing Eclipses
Observing eclipses is an exhilarating experience that requires careful planning and the right equipment. When it comes to solar eclipses, special precautions must be taken to ensure eye safety. Looking directly at the Sun during an eclipse can cause permanent damage to the eyes. It is essential to use certified eclipse glasses or solar filters that block out harmful rays. Another popular method of observing solar eclipses is through projection, where the image of the Sun is projected onto a surface using a pinhole or a telescope. On the other hand, lunar eclipses are safe to observe with the naked eye. These captivating events can be enjoyed from any location that has a clear view of the Moon. To enhance your viewing experience, consider using binoculars or a telescope to see the intricate details of the lunar surface. With the right precautions and equipment, you can witness the beauty of eclipses firsthand and create cherished memories that will last a lifetime. So, grab your eclipse glasses, set up your telescope, and prepare to be awe-struck by the celestial wonders unfolding before your eyes.
Safety Precautions
When it comes to observing eclipses, it’s crucial to prioritize safety precautions to protect both your eyes and equipment. Never look directly at the Sun during a solar eclipse without proper eye protection, as this can cause severe damage to your eyes. Only use solar viewing glasses or specially designed solar filters that meet stringent safety standards. These filters should cover both your eyes and block out harmful ultraviolet and infrared rays. Regular sunglasses, homemade filters, or unverified materials like CDs or smoked glass are not safe for direct solar viewing and should be avoided.
Never use standard cameras, telescopes, or binoculars to directly observe the Sun during an eclipse without proper solar filters. The focused intensity of the Sun’s rays can damage the equipment and cause irreparable harm to your eyes. Instead, use solar filters specifically designed for telescopes or cameras that block out the majority of the Sun’s brightness. These filters should be placed over the lens or aperture of the device before aiming it at the Sun.
If you’re unable to acquire appropriate solar viewing glasses or filters, consider indirect viewing methods. One popular method is projection, where you create a simple pinhole projector with two pieces of card or paper. Make a small hole in one of the cards and hold it up towards the Sun, allowing the light to pass through and project an image onto a second card held a few feet away. This projection method allows you to view the eclipse without directly exposing your eyes to the Sun’s harmful rays.
Remember to be cautious and educate others about the importance of eclipse safety. It is always better to err on the side of caution when observing such celestial events. By taking these safety precautions, you can fully enjoy the beauty of an eclipse while safeguarding your eyes and equipment from harm.
Equipment Needed for Observation
When it comes to observing eclipses, having the right equipment is essential to ensure a safe and memorable experience. One of the most important tools for eclipse observation is a pair of solar viewing glasses. These specialized glasses are designed to protect your eyes from the intense brightness of the Sun during a solar eclipse. It is crucial to use glasses that are specifically made for solar observation to avoid any damage to your eyes. Additionally, using a solar filter for cameras and telescopes is highly recommended. This filter blocks most of the Sun’s light, allowing you to capture stunning images of the eclipse without causing harm to your equipment. Another useful piece of equipment is a tripod or mount to stabilize your camera or binoculars. This will help you achieve steady shots and maintain focus on the eclipse. Additionally, it is beneficial to bring a notebook and pen to jot down any notable observations or feelings during the eclipse. This will allow you to reflect on your experience later. Lastly, do not forget to check the weather forecast before heading out to observe an eclipse. Clear skies are essential for optimal viewing conditions. Having the right equipment ensures that you can fully immerse yourself in the marvel of an eclipse and appreciate its beauty in a safe and comfortable manner. So grab your solar viewing glasses, prepare your camera with a solar filter, and get ready to witness the celestial spectacle of an eclipse firsthand.
Significance of Eclipses
Eclipses hold a significant place in both cultural and scientific realms, weaving a tapestry of awe and intrigue throughout history. In terms of cultural and historical importance, eclipses have played a prominent role in various civilizations, including the Greeks. Greek myths often attributed eclipses to cosmic battles between the gods, reflecting their belief in divine influence and power. The influence of Greek mythology can still be seen in contemporary interpretations and storytelling surrounding eclipses. On a scientific front, eclipses provide invaluable opportunities for researchers and astronomers to study celestial bodies, refine calculations, and gather data. These events have contributed to our understanding of the mechanics of the solar system, the Earth-Moon-Sun relationship, and have shed light on phenomena such as the Earth’s atmosphere and the behavior of light. Eclipses, thus, serve as a powerful intersection between culture, mythology, and scientific exploration, igniting our curiosity and inspiring us to delve deeper into the mysteries of the cosmos.
Cultural and Historical Importance
Throughout history, eclipses have held immense cultural and historical importance for civilizations around the world. These celestial events have been seen as powerful omens, representing both positive and negative forces. Ancient cultures often interpreted eclipses as signs of impending doom or as messages from the gods. In Greek mythology, for example, eclipses were believed to be the result of the Sun being swallowed by a mythical creature, signaling turmoil and disruptindo not exist in Google’s Content Creatorion in the heavens. Such beliefs shaped the rituals and practices of these societies. The cultural significance of eclipses can also be seen in how they have influenced art, literature, and architecture. In ancient Egypt, the temple complex of Abu Simbel was built in alignment with the rising sun during the date of King Ramses II’s birthday and coronation, celebrating the Sun god Ra. In Hindu mythology, the demon Rahu was said to swallow the Sun during eclipses, which inspired elaborate rituals and prayers to ward off evil. Even today, eclipses continue to captivate our imaginations and are celebrated in a myriad of ways. From eclipse viewing parties to scientific research and observations, these events bring people together in awe of the grandeur of the cosmos. So, it is evident that the cultural and historical significance of eclipses is truly profound, shaping our understanding of the world and our place within it.
Scientific Contributions
The study of eclipses has made significant scientific contributions throughout history. These celestial events provide scientists with valuable opportunities to gather data and further our understanding of the cosmos. By carefully observing and documenting eclipses, researchers have made breakthroughs in various fields. One notable contribution is the verification of Einstein’s theory of general relativity during the 1919 total solar eclipse. Sir Arthur Eddington’s observations of the bending of starlight near the Sun during the eclipse confirmed Einstein’s predictions, solidifying one of the pillars of modern physics. Additionally, eclipses have allowed scientists to study the Sun’s corona, the outermost layer of its atmosphere. During a total solar eclipse, the Moon’s shadow reveals the corona’s structure, enabling scientists to analyze its temperature, composition, and magnetic field. This information aids in understanding solar wind, space weather, and other astronomical phenomena. Eclipses also play a vital role in advancing the field of astronomy by providing opportunities to discover and study celestial objects. For instance, the observation of stars and planets during lunar eclipses helps astronomers refine their understanding of these objects’ characteristics. The study of eclipses has paved the way for advancements in astrophysics, solar physics, and planetary science. The scientific contributions of eclipses continue to shape our understanding of the universe and inspire new discoveries.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the celestial phenomenon of eclipses continues to captivate and inspire us. Throughout history, eclipses have played a significant role in shaping our cultural and scientific understanding of the universe. From ancient civilizations interpreting them as divine omens to modern-day scientists using them to study the Sun, eclipses have left an indelible mark on human history. The influence of Greek mythology is evident in the stories and legends surrounding eclipses, showing how ancient cultures sought to explain these awe-inspiring events. Moreover, eclipses have even found their way into other areas of our lives, such as astrology, where enthusiasts explore moon sign compatibility in family dynamics. The significance of eclipses is also reflected in the study of natal chart houses, where their positioning can provide insights into different aspects of our lives. As we continue to observe and study eclipses, we gain a deeper appreciation for the vastness and complexity of the cosmos. These celestial wonders remind us of our place in the universe and the beauty that lies beyond our reach. So, the next time an eclipse graces the sky, take a moment to reflect on the wonders of the cosmos and the marvels that await our exploration.
Frequently Asked Questions

What is a solar eclipse?
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between the Sun and the Earth, causing the Sun to be partially or completely obscured from view.
What is a lunar eclipse?
A lunar eclipse happens when the Earth comes between the Sun and the Moon, causing the Moon to move into the Earth’s shadow and darken.
How often do eclipses occur?
Eclipses occur on average two to four times a year, but the frequency can vary.
Can I look directly at a solar eclipse?
No, it is dangerous to look directly at a solar eclipse without proper eye protection. Doing so can cause permanent damage to your eyes.
How long do eclipses last?
The duration of an eclipse varies. A total solar eclipse can last for a few minutes, while a lunar eclipse can last for a few hours.
Are eclipses visible everywhere?
No, the visibility of an eclipse depends on your location on Earth. Some eclipses may only be visible from specific regions.
What is the difference between totality, annularity, and partiality?
Totality refers to the phase of an eclipse where the Sun or the Moon is completely obscured. Annularity occurs during a solar eclipse when the Moon is at its farthest distance from the Earth, resulting in a ring of sunlight visible around the Moon. Partiality refers to the phase when only a portion of the Sun or Moon is obscured.
What is a hybrid eclipse?
A hybrid eclipse is a rare type of eclipse that starts as an annular eclipse and transitions into a total eclipse. These occur when the observer is located in an area where the eclipse changes from annularity to totality or vice versa.
What safety precautions should I take when observing an eclipse?
When observing an eclipse, it is crucial to use proper eye protection, such as eclipse glasses or solar filters. Never look directly at the Sun without these protective measures.
What are the cultural and historical significances of eclipses?
Eclipses hold great cultural and historical importance. Throughout history, they have been seen as omens, symbols of cosmic power, and catalysts for artistic and scientific discoveries. In Greek mythology, eclipses were believed to hold the power to influence events on Earth.
References
Frequently Asked Questions

1. How often do eclipses occur?
Eclipses occur on average about two to four times a year, but the number can vary. Some years may have no eclipses, while others may have up to seven.
2. Can I see an eclipse from anywhere on Earth?
No, not all eclipses are visible from every location on Earth. The visibility of an eclipse depends on the specific path of the moon’s shadow or the Earth’s shadow.
3. What is a solar eclipse?
A solar eclipse occurs when the moon passes between the sun and Earth, casting a shadow on Earth’s surface. It happens during a new moon phase.
4. What is a lunar eclipse?
A lunar eclipse happens when the Earth comes between the sun and the moon, causing the moon to move into Earth’s shadow. It occurs during a full moon phase.
5. Are solar eclipses dangerous to watch?
Yes, it is crucial to take precautions while observing a solar eclipse. Looking directly at the sun during an eclipse can cause severe eye damage. Safe viewing methods, such as wearing certified eclipse glasses, are recommended.
6. How long do eclipses typically last?
The duration of an eclipse varies. A total solar eclipse, when the moon completely blocks the sun, can last for a few minutes, while a lunar eclipse can last for several hours.
7. What is the difference between totality and partiality in eclipses?
Totality refers to the phase of an eclipse when the sun or moon is completely covered by the shadow. Partiality, on the other hand, means that only a portion of the sun or moon is obscured by the shadow.
8. Do eclipses have any cultural significance?
Yes, eclipses have been regarded as significant events in many cultures throughout history. They have often been associated with myths, legends, and religious beliefs.
9. How do scientists study eclipses?
Scientists study eclipses to learn more about the sun, moon, and Earth’s atmosphere. They use specialized instruments, such as telescopes and spectrometers, to gather data during an eclipse.
10. Can I photograph an eclipse with a regular camera?
Photographing an eclipse requires special filters to protect both the camera equipment and the photographer’s eyes. It is recommended to use specific solar filters or seek guidance from experienced photographers.
References
- What Causes a Solar Eclipse?
- How Eclipses Work | Total Solar Eclipse 2017
- What are lunar eclipses and how do they occur?