How did ancient civilizations navigate and make sense of the night sky? What led to the development of the modern constellation system that we use today? These questions and more will be answered as we delve into the fascinating history and importance of constellations. From the ancient Greeks and Romans to the International Astronomical Union (IAU), the evolution of constellations has had a profound impact on astronomy, culture, and navigation. Join us as we explore the origins of constellations, their significance in studying celestial events, and their role in mythology and storytelling. Get ready to embark on a celestial journey like no other.
Contents
- The Origins of Constellations
- The Birth of the Modern Constellation System
- The Importance of Constellations in Astronomy
- Constellations in Culture and Navigation
- The Modern Constellation System: IAU and Its Significance
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. Why did ancient civilizations create constellations?
- 2. How did ancient astronomers identify constellations?
- 3. Did all civilizations have the same constellations?
- 4. Were all ancient constellations based on mythology?
- 5. How accurate were ancient constellation maps?
- 6. How did the ancient Greeks contribute to the development of constellations?
- 7. What is the difference between the zodiac constellations and other constellations?
- 8. How have constellations been used for navigation throughout history?
- 9. How do modern astronomers use constellations?
- 10. Can anyone create a new constellation?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are constellations?
- How were the first constellations created?
- Why were constellations important to ancient civilizations?
- Who were the influential astronomers in the development of modern constellations?
- What is the role of constellations in astronomy?
- How do constellations aid in studying stellar evolution and galactic structures?
- What role do constellations play in mythology and storytelling?
- How were constellations used for celestial navigation?
- What is the International Astronomical Union (IAU) and its role in the modern constellation system?
- Have there been controversies or revisions in the modern constellation system?
- References
- Read More
The Origins of Constellations
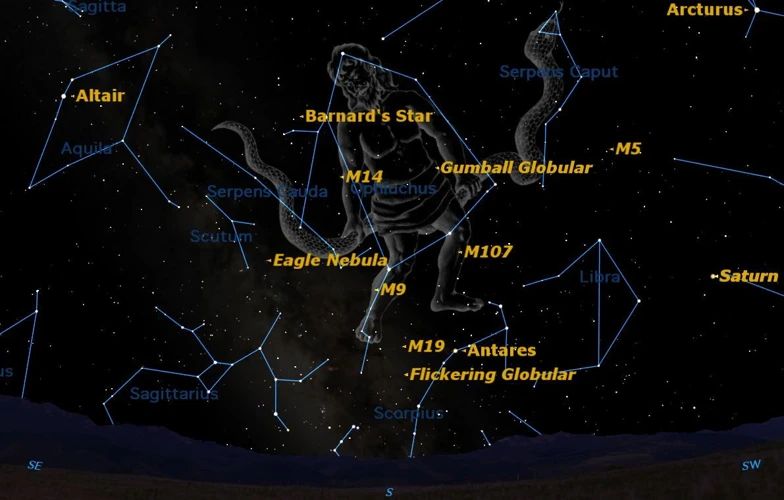
The concept of constellations dates back to ancient times when early civilizations began observing the night sky and making connections between the stars. These early astronomers saw patterns in the stars and began to associate them with mythological figures, animals, and objects. Ancient Astronomy and Early Constellations can be traced back to as early as 3000 BCE when the Mesopotamians started mapping the sky. They divided the sky into constellations, primarily for astrological purposes. Similarly, the ancient Egyptians developed a constellation system to align with their religious beliefs and funeral rites. The Egyptians associated constellations with their gods and used them for spiritual guidance. Moving forward, the ancient Greeks and Romans played a significant role in shaping the modern constellation system, as we will explore in the next section.
- Ancient Mesopotamia
- Ancient Egypt
- Ancient Greece and Rome
Ancient Astronomy and Early Constellations
In ancient Mesopotamia, the earliest known civilization to document their astronomical observations, the night sky held great significance. Mesopotamian astronomers developed a system of Early Constellations as early as 3000 BCE. These constellations were primarily used for astrological purposes, where they believed that the positions of celestial bodies influenced human affairs and events on Earth. They divided the sky into specific constellations that corresponded to different zodiac signs. Similarly, in ancient Egypt, the Nile River played a crucial role in their civilization, and they associated constellations with their religious beliefs and agricultural practices. The Egyptians aligned their constellation system with their gods and the annual flooding of the Nile River. As a result, the movements of specific constellations became vital markers for determining the timing of various agricultural activities. The ancient Greeks and Romans built upon the knowledge and observations of their predecessors, which would eventually lay the foundation for the modern constellation system. From the early constellations of ancient civilizations, the understanding of the night sky continued to evolve, shaping the way we perceive and study constellations today.
Ancient Civilizations and their Constellation Systems
Ancient civilizations all across the world developed their own unique constellation systems based on their cultural beliefs and celestial observations. In Ancient Mesopotamia, the Babylonians were renowned astronomers who created one of the earliest known constellation systems. They divided the sky into twelve equal parts, each representing a different month of the year. Similarly, the ancient Egyptians associated constellations with their gods and religious rituals. They believed that the constellation Orion represented Osiris, the god of the afterlife. Moving on to Ancient Greece and Rome, these civilizations made significant contributions to the development of constellations. The Greek astronomer Ptolemy compiled a comprehensive catalog known as the Almagest, which included over a thousand stars and their locations. The Roman poet Aratus wrote a popular poem called the Phaenomena, which beautifully described the constellations and their mythological origins. The influence of these ancient civilizations laid the foundation for the modern constellation system we use today.
The Birth of the Modern Constellation System
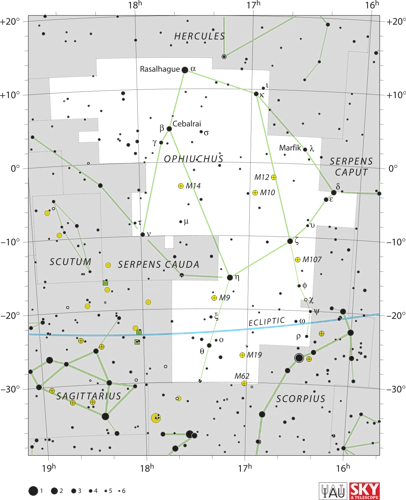
The birth of the modern constellation system can be attributed to the contributions of Greek and Roman astronomers. The Influence of Greek and Roman Astronomers During the Hellenistic period, Greek astronomers like Hipparchus and Ptolemy made significant advancements in understanding the celestial sphere. They developed a coordinate system that divided the sky into regions and assigned names to specific groups of stars. These names were often based on mythological characters and creatures, perpetuating the connection between constellations and storytelling. The work of Greek astronomers was later adopted and expanded upon by Roman astronomers, such as Claudius Ptolemy, in his influential work “Almagest.” Their efforts laid the foundation for the development of the modern constellation system. Development of Star Catalogs and Nomenclature As astronomers continued to study the stars, various star catalogues were created to document and classify the positions of celestial objects. One such notable catalogue was the “Uranometria” compiled by German astronomer Johann Bayer in 1603, which assigned Greek letters to stars within each constellation. Another significant development was the introduction of the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in 1919, which standardized the constellation boundaries and names based on the work of several astronomers. This harmonization has allowed for global consistency in the identification and study of constellations. Though the birth of the modern constellation system may have been influenced by ancient cultures, its evolution and refinement have been ongoing for centuries, ensuring a cohesive framework for astronomers around the world.
The Influence of Greek and Roman Astronomers
Greek and Roman astronomers made substantial contributions to the development and understanding of constellations. They built upon the knowledge of earlier civilizations and applied their unique perspectives and methodologies. Greek and Roman Astronomers believed that the stars were divine and had a direct influence on human affairs. One of the most influential Greek astronomers was Claudius Ptolemy, who compiled a comprehensive star catalog known as the “Almagest.” This catalog contained the positions and magnitudes of over a thousand stars and served as a foundation for later astronomers. Greek and Roman astronomers also named many constellations that we still recognize today, such as Orion, Ursa Major, and Cassiopeia. These astronomers emphasized the concept of celestial spheres, envisioning the stars as being fixed on rotating celestial spheres centered around the Earth. Their contributions laid the groundwork for the development of modern constellation systems and have had a lasting impact on our understanding of the cosmos. To learn more about the role of constellations in mythology and storytelling, you can refer to our article on major characters in Celtic mythology.
Development of Star Catalogs and Nomenclature
During the Hellenistic period, Greek and Roman astronomers made significant contributions to the development of star catalogs and nomenclature. involved creating systematic records of stars and assigning names or designations to them. One of the notable astronomers of this period was Hipparchus, who compiled the first comprehensive star catalog known as the “Hipparchus Catalog.” This catalog contained information about the positions, magnitudes, and spectral classes of over 850 stars. Another influential figure was Claudius Ptolemy, whose work “Almagest” included an expanded star catalog, incorporating stars from earlier Greek astronomers. Ptolemy’s catalog listed around 1,022 stars and introduced a magnitude system to describe the brightness of stars. This system classified stars into six magnitudes, with magnitude 1 being the brightest and magnitude 6 being the faintest visible to the naked eye. The development of star catalogs and nomenclature laid the foundation for future astronomers to organize and identify stars accurately. These catalogs became crucial references for later astronomers, including those in the modern era. To this day, astronomers continue to refine and update star catalogs, incorporating advancements in technology and observations to deepen our understanding of the celestial realm.
The Importance of Constellations in Astronomy
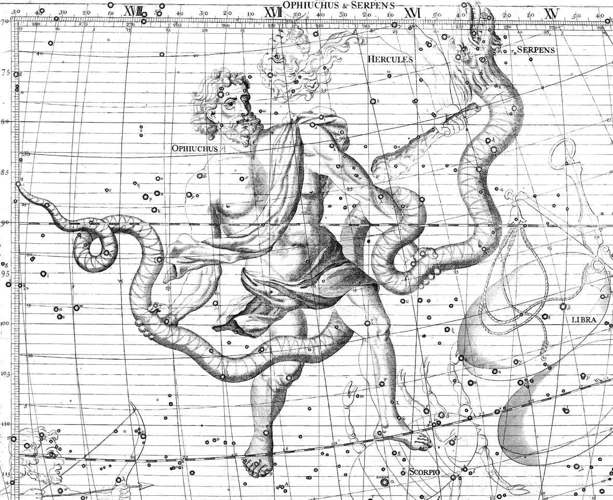
Constellations play a crucial role in the field of astronomy, offering valuable tools for astronomers to observe, study, and understand the vast expanse of the universe. The Importance of Constellations in Astronomy cannot be overstated. One key aspect is their role in guiding astronomical observations. By dividing the sky into recognizable patterns, constellations provide a celestial map, allowing astronomers to locate specific stars, galaxies, and other celestial objects more easily. This aids in the identification and tracking of various astronomical events such as meteor showers, eclipses, and planetary alignments. Constellations are instrumental in studying stellar evolution and galactic structures. Astronomers analyze the distribution and movement of stars within constellations to gain insights into the life cycles of stars, including their birth, evolution, and eventual demise. Additionally, the study of constellations helps unravel the vast structures of galaxies, clusters, and even the cosmic web itself. By observing the relative positions and movements of stars within constellations, astronomers can map out the three-dimensional layout of these cosmic structures and gain a deeper understanding of the universe’s organization and evolution. The importance of constellations in astronomy extends beyond scientific research, as they also serve practical purposes in navigation and cultural contexts.
Guiding Astronomical Observations
:
Constellations have played a crucial role in guiding astronomical observations throughout history. By identifying and mapping constellations, astronomers have been able to navigate the night sky, locate specific celestial objects, and track their movements. In ancient times, constellations served as navigational aids for seafarers and explorers, helping them determine their position and direction. Today, astronomers continue to rely on constellations to locate and study celestial bodies. By using star charts and telescopes, astronomers can pinpoint specific constellations and study the stars and other objects within them. These observations provide valuable insights into various astronomical phenomena, such as stellar evolution, galaxy formations, and even the discovery of new celestial bodies. Understanding the constellations is essential for both amateur stargazers and professional astronomers, as they provide a framework for exploring and comprehending the vastness of the universe.
Studying Stellar Evolution and Galactic Structures
Studying stellar evolution and galactic structures is one of the primary reasons why constellations hold great importance in astronomy. By observing the position, brightness, and movement of stars within a constellation, astronomers can gather valuable data about the life cycle of stars and the structure of our galaxy. Stellar Evolution refers to the processes that stars undergo from their formation to their eventual demise. By studying the characteristics of stars within constellations, astronomers can determine their age, size, and composition, providing insights into the different stages of stellar evolution, including the formation of protostars, main sequence stars, red giants, and even supernovae. Constellations also offer a way to study Galactic Structures, such as spiral arms, globular clusters, and interstellar clouds. By examining the distribution of stars and other celestial objects within constellations, astronomers can map out the structure and dynamics of our Milky Way galaxy and gain a better understanding of its formation and evolution. This knowledge contributes to our overall understanding of the universe and our place within it.

Throughout history, constellations have played a significant role in shaping cultural beliefs and aiding in navigation. The Role of Constellations in Mythology and Storytelling is evident in various ancient civilizations. Greek mythology, for example, is filled with tales connected to constellations. The story of Orion, a mighty hunter, who was placed among the stars after his death, is just one example. Similarly, the twelve zodiac constellations of the astrological calendar hold great significance in interpreting personality traits and making predictions about the future. In addition to mythology and astrology, constellations have been crucial for Constellations for Celestial Navigation and exploration. Sailors and navigators have relied on prominent constellations, such as the Big Dipper and the North Star, to guide their journeys across vast oceans. By using these stellar landmarks, ancient seafarers could determine their position and plot their course. Even today, celestial navigation techniques are taught to ensure safe travel on the open sea. The intricate relationship between constellations and culture, as well as their practical application in navigation, highlights their enduring importance in human history.
The Role of Constellations in Mythology and Storytelling
Constellations have long played a vital role in mythology and storytelling, captivating the imaginations of different cultures throughout history. Many ancient civilizations believed that the arrangement of stars in the night sky held great significance and told intricate stories about their gods, heroes, and legendary creatures. In Greek mythology, for example, the constellation Orion is associated with the mythical hunter Orion, who was considered one of the greatest hunters in the world. The constellation Ursa Major, or the Great Bear, is linked to the story of Callisto, a nymph who was transformed into a bear by the jealous goddess Hera. These celestial stories served as a way of passing down cultural myths and teachings from one generation to another.
Constellations in storytelling weren’t limited to just Greek mythology. In Celtic mythology, the constellation Draco represents a dragon, while the constellation Cassiopeia symbolizes the legendary queen of Ethiopia. These mythological stories not only entertained ancient cultures but also helped them make sense of the world around them, providing explanations for natural phenomena and offering moral lessons.
Even today, constellations continue to inspire our storytelling and creative expressions. They serve as a source of inspiration for authors, artists, and filmmakers who weave captivating tales involving the stars and the mythical beings associated with them.
+internal reference /major-characters-celtic-mythology/
have been an essential tool for sailors and explorers throughout history. By observing and charting the positions of specific constellations, navigators were able to determine their location and navigate their vessels accurately. One of the most famous navigation constellations is the North Star, also known as Polaris. Positioned very close to the North Celestial Pole, Polaris remains relatively stationary while other stars appear to rotate around it throughout the night. This fixed reference point provided navigators with a reliable marker to determine their northward direction. Sailors in the northern hemisphere would use the Big Dipper, which is part of the Ursa Major constellation, to find Polaris. In the southern hemisphere, the constellation Crux, also known as the Southern Cross, served as a guiding star for navigation. These constellations, along with others like Orion, Cassiopeia, and Leo, have played a crucial role in helping sailors navigate the vast oceans for centuries.
The Modern Constellation System: IAU and Its Significance
The modern constellation system as we know it today is governed by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). Established in 1919, the IAU is responsible for officially recognizing and naming constellations. Their work has had profound significance in the field of astronomy, providing a standardized method for study and communication across the globe. The IAU defines 88 official constellations that cover the entire celestial sphere. These constellations serve as a universal framework that allows astronomers to precisely locate and identify celestial objects. By providing a common reference point, the IAU’s constellation system enables collaboration and facilitates the exchange of information among astronomers worldwide. It also helps in accurately cataloging and classifying stars, galaxies, and other astronomical phenomena. While the IAU’s constellation system has undergone revisions and updates over the years, its significance in promoting international cooperation and advancing our understanding of the universe remains paramount. To learn more about reading natal charts, you can check our article on Understanding the Basics of Reading Natal Charts.
The International Astronomical Union (IAU)
The International Astronomical Union (IAU) is a global organization that plays a vital role in the modern constellation system. Established in 1919, the IAU acts as the authority responsible for officially naming and defining celestial objects, including constellations. With its headquarters in Paris, France, the IAU brings together astronomers from around the world to collaborate on important astronomical decisions. One of the notable achievements of the IAU is the creation of the official list of 88 constellations, which includes both ancient and modern constellations. This standardized list ensures that astronomers and researchers worldwide can communicate effectively and avoid confusion when referring to specific regions of the night sky. The IAU also plays a crucial role in determining the boundaries and defining the shapes of constellations. Through their rigorous scientific processes and collaborations, the IAU has contributed significantly to the study and understanding of constellations in modern astronomy.
Controversies, Revisions, and Inclusivity
The modern constellation system established by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) continues to evolve, and with that evolution come controversies, revisions, and a push for inclusivity. As our understanding of the universe expands, scientists discover new celestial objects and redefine boundaries within the sky. One example of this is the controversy surrounding the inclusion of Ophiuchus as a zodiac constellation. Ophiuchus, also known as the Serpent Bearer, was omitted from the traditional zodiac system due to its location on the ecliptic. However, its rediscovery has sparked debates about the need to revise and update the constellation boundaries. Inclusivity is another significant aspect of the modern constellation system. Efforts are being made to represent different cultures and traditions by incorporating their mythological characters and stories into the constellation system. This ensures that the sky is inclusive and reflects the diversity of human cultures. While controversies may arise, the goal remains to create a comprehensive and accurate constellation system that represents the vastness and wonder of the universe.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the history and importance of the modern constellation system are rich and diverse. Constellations have deep roots in ancient cultures, where they served as astronomical guides, religious symbols, and storytelling tools. Throughout the centuries, the influence of Greek and Roman astronomers paved the way for the development of star catalogs and standardized nomenclature. Today, constellations continue to play a crucial role in astronomy, facilitating astronomical observations, studying stellar evolution, and understanding galactic structures. Additionally, constellations have maintained their cultural significance, appearing in mythology, literature, and even celestial navigation. The International Astronomical Union (IAU) plays a crucial role in ensuring consistency and inclusivity within the modern constellation system, despite occasional controversies and revisions. As we look to the night sky and observe the familiar patterns of stars, we are reminded of the timeless beauty and fascination that constellations hold. Whether guiding our way through the night or igniting our imaginations, constellations continue to captivate humanity and inspire us to explore the vast wonders of the cosmos.
Frequently Asked Questions

1. Why did ancient civilizations create constellations?
Ancient civilizations created constellations as a way to navigate and make sense of the night sky. They believed that the positions and movements of the stars held significant meaning, both in terms of spiritual guidance and practical purposes.
2. How did ancient astronomers identify constellations?
Ancient astronomers identified constellations by tracing and connecting the patterns formed by the stars. They assigned names and meanings to these patterns based on their cultural or mythological beliefs.
3. Did all civilizations have the same constellations?
No, different civilizations had their own unique constellation systems based on their cultural and mythological beliefs. While some constellations may have been shared or influenced by neighboring cultures, each civilization often had its own distinct set of constellations.
4. Were all ancient constellations based on mythology?
No, not all ancient constellations were based solely on mythology. While many constellations had mythological associations, some were also based on practical observations of celestial events or used for agricultural purposes, such as indicating the changing seasons.
5. How accurate were ancient constellation maps?
Ancient constellation maps were relatively accurate considering the limited resources and technology available at the time. However, these maps often lacked the precision and detail that we have in modern star charts, as they were based on naked-eye observations without the aid of telescopes.
6. How did the ancient Greeks contribute to the development of constellations?
The ancient Greeks made significant contributions to the development of constellations. They introduced the concept of linking constellation patterns to mythology and created elaborate stories and narratives around the stars, which influenced the way constellations were perceived.
7. What is the difference between the zodiac constellations and other constellations?
The zodiac constellations are a specific group of constellations that lie along the ecliptic path of the Sun, Moon, and planets. These constellations are of utmost importance in astrology as they are associated with the twelve signs of the zodiac. In contrast, other constellations cover the rest of the celestial sphere.
Constellations have been used as navigational markers by sailors and travelers for centuries. By observing the positions of specific constellations relative to the horizon, sailors could determine their latitude and steer their ships in the right direction.
9. How do modern astronomers use constellations?
Modern astronomers use constellations as a convenient grouping of stars to locate and identify objects in the sky. They serve as reference points for locating galaxies, nebulae, and other celestial objects, making it easier to navigate the vastness of space.
10. Can anyone create a new constellation?
Technically, anyone can create a new constellation, but it would not hold any official recognition without approval from the International Astronomical Union (IAU). The IAU is responsible for naming and classifying celestial objects and would need to evaluate and approve any proposed new constellation.
References
Frequently Asked Questions

What are constellations?
Constellations are groups of stars that form patterns or shapes in the night sky. They have been used for centuries as a way to navigate and identify celestial objects.
How were the first constellations created?
The first constellations were created by ancient civilizations who observed the patterns of stars in the night sky and associated them with figures from their mythology and culture.
Why were constellations important to ancient civilizations?
Constellations played a vital role in ancient civilizations as they used them for agriculture, navigation, and tracking the seasons. They also believed that the stars held great significance in guiding their lives.
Who were the influential astronomers in the development of modern constellations?
Greek and Roman astronomers such as Ptolemy and Hipparchus greatly contributed to the development of the modern constellation system. They developed star catalogs and defined the nomenclature that is still used today.
What is the role of constellations in astronomy?
Constellations are essential for guiding astronomical observations. They help astronomers locate and identify specific stars, galaxies, and other celestial objects in the vastness of the night sky.
How do constellations aid in studying stellar evolution and galactic structures?
By studying the characteristics and movements of the stars within constellations, astronomers can understand the various stages of stellar evolution and gain insights into the formation and structure of galaxies.
What role do constellations play in mythology and storytelling?
Constellations have been integral to mythology and storytelling throughout history. They were used to explain natural phenomena, pass down cultural knowledge, and convey moral lessons through the rich narratives associated with each constellation.
In ancient times, sailors and explorers relied on constellations to navigate and find their way across vast oceans. By memorizing the positions of constellations relative to the Earth’s horizon, they could determine their location and chart their course.
What is the International Astronomical Union (IAU) and its role in the modern constellation system?
The International Astronomical Union (IAU) is the governing body for astronomy. It establishes and maintains the official list of constellations, their boundaries, and names. Its role is crucial in maintaining consistency and accuracy in the modern constellation system.
Have there been controversies or revisions in the modern constellation system?
Yes, there have been debates and revisions in the modern constellation system. Some controversies arise from cultural perspectives and attempts to be more inclusive. The IAU has made efforts to address these concerns and make the system more representative of diverse cultures and perspectives.
References
- What are constellations and how did they form?
- The Constellations
- Constellation | Definition, Origin, History, & Facts







