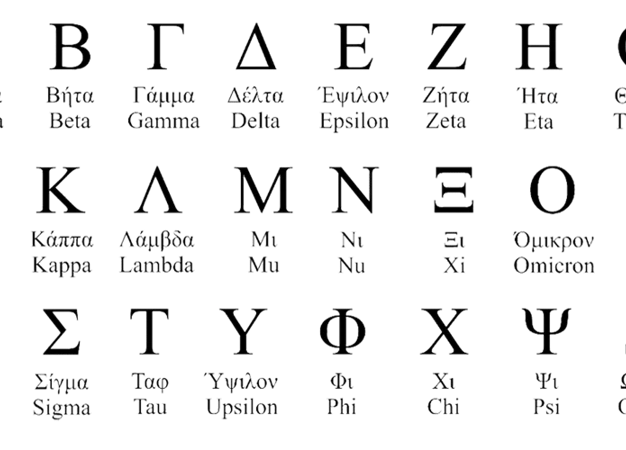The Greek Alphabet is a fascinating system of writing that has been used for centuries and has had a significant impact on language, culture, and society. Its origins can be traced back to the influence of the Phoenician alphabet, but the Greeks developed it into a unique and intricate system that played a crucial role in communication, philosophy, science, art, and architecture. The Greek alphabet has also influenced and been compared to other alphabets, such as the Latin and Cyrillic alphabets. In modern times, it continues to be used in various fields, particularly in mathematics, science, and even in the symbolism of secret societies and Freemasonry. Understanding the Greek Alphabet and its significance is key to appreciating its rich history and its enduring legacy today.
Contents
- Origins of the Greek Alphabet
- Significance of the Greek Alphabet in Ancient Greece
- Comparison with Other Alphabets
- Modern Usage and Adaptation
- The Greek Alphabet Today
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What is the significance of the Greek alphabet in ancient Greece?
- 2. How did the Greek alphabet influence Greek philosophy and science?
- 3. How did the Greek alphabet impact art and architecture?
- 4. How does the Greek alphabet compare to the Latin alphabet?
- 5. How does the Greek alphabet compare to the Cyrillic alphabet?
- 6. How is the Greek alphabet used in mathematics and science today?
- 7. Is the Greek alphabet associated with any secret societies or Freemasonry?
- 8. Is the Greek alphabet still widely used today?
- 9. Can anyone learn to read and write the Greek alphabet?
- 10. Are there any similarities between the Greek alphabet and other alphabets?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How many letters are there in the Greek alphabet?
- 2. What is the significance of the order of the Greek alphabet?
- 3. How did the Greek alphabet influence other alphabets?
- 4. How is the pronunciation of Greek letters different from English letters?
- 5. What are some common Greek words used in the English language?
- 6. Can I learn to write and pronounce the Greek alphabet?
- 7. Are there any variations or regional differences in the Greek alphabet?
- 8. How did the Greek alphabet contribute to the development of literature in Ancient Greece?
- 9. What are some Greek symbols commonly used in mathematics and science?
- 10. Are there any superstitions or beliefs associated with the Greek alphabet?
- References
- Read More
Origins of the Greek Alphabet
The origins of the Greek Alphabet can be traced back to the influence of the Phoenician alphabet. The Phoenicians, a seafaring civilization, developed their own writing system which eventually made its way to Greece. This system consisted of consonant sounds only, with no vowels. The Greeks recognized the need for vowel sounds in their language and adapted the Phoenician alphabet to suit their needs. They introduced several modifications, including the addition of vowel letters and the development of a distinct Greek style of writing. It is important to note that the Greek alphabet was not created all at once, but rather evolved over time. This evolution occurred during the 9th and 8th centuries BCE, as the Greeks interacted with other cultures and civilizations in the Mediterranean region. The Greek alphabet quickly gained popularity and became widely used in Greece and beyond. Its simplicity and adaptability contributed to its widespread adoption and played a significant role in the development of writing and communication in ancient Greece.
The origins of the Greek Alphabet can be traced back to the influence of the Phoenician alphabet. The Phoenicians, a seafaring civilization, developed their own writing system which eventually made its way to Greece.
1. Phoenician Influence
The Phoenician influence on the Greek Alphabet was significant. The Phoenicians, an ancient civilization living in what is now modern-day Lebanon, had developed their own writing system known as the Phoenician alphabet. This alphabet consisted only of consonant sounds and did not include vowel letters. When the Greeks encountered the Phoenician alphabet, they recognized the need for a system that included vowel sounds. As a result, they adapted the Phoenician alphabet to suit their own language by modifying the existing characters and adding additional ones to represent vowel sounds. This adaptation allowed for a more comprehensive representation of the Greek language and enabled more accurate communication. The influence of the Phoenician alphabet on the development of the Greek Alphabet cannot be overstated, as it laid the foundation for the creation of one of the most important writing systems in history.
The Phoenician influence on the Greek Alphabet was significant. The Phoenicians, an ancient civilization living in what is now modern-day Lebanon, had developed their own writing system known as the Phoenician alphabet.
2. Development of the Greek Alphabet
The development of the Greek Alphabet involved several key stages that transformed it into the robust system of writing we know today. The earliest form of the Greek alphabet, known as the “Old Greek” or “Argive” alphabet, consisted of only 22 letters and closely resembled the Phoenician alphabet. However, as the Greeks encountered new sounds in their language, they needed additional letters to represent these sounds accurately. This led to the development of the “Classical Greek” or “Ionian” alphabet, which included additional letters such as eta (Η), xi (Ξ), and omega (Ω).
Another significant development occurred during the Hellenistic period when Greek became the lingua franca of the Eastern Mediterranean. This led to the expansion and standardization of the alphabet, resulting in the inclusion of the letters phi (Φ), chi (Χ), and psi (Ψ), among others. The Greek alphabet continued to evolve, with different regions and dialects having their own variations and additions. Notably, the lowercase letters, or minuscules, were introduced during the Byzantine era. These changes and modifications ensured that the Greek alphabet remained a versatile and adaptable writing system.
It is worth mentioning that the Greek alphabet also played a crucial role in the development of other writing systems, including the Cyrillic alphabet used by many Slavic languages. The Cyrillic alphabet was created by the Greek scholars Cyril and Methodius and was heavily influenced by the Greek alphabet. This highlights the far-reaching impact and significance of the Greek alphabet beyond just the Greek language and culture.
The development of the Greek Alphabet involved several key stages that transformed it into the robust system of writing we know today.
Significance of the Greek Alphabet in Ancient Greece

The Greek Alphabet held immense significance in ancient Greece, playing a pivotal role in communication, writing, and the overall development of society.
1. Role in Communication and Writing:
The Greek Alphabet revolutionized communication in ancient Greece. Prior to its development, writing systems were limited, making it challenging to record and convey information accurately. The introduction of the Greek Alphabet enabled a more efficient and standardized method of writing. It allowed for the preservation and dissemination of knowledge through written texts, providing a means for Greeks to record their history, documents, and literature, which continue to be studied and revered to this day. The Greek Alphabet also facilitated trade, diplomacy, and governance, as written records could be easily shared and understood by different city-states.
2. Link to Greek Philosophy and Science:
The Greek Alphabet played a vital role in the advancement of philosophy and science in ancient Greece. The ability to express abstract concepts and scientific principles through writing allowed philosophers and scholars to articulate their ideas more precisely. Prominent philosophers like Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle used the Greek Alphabet to document their philosophical theories, which became the foundation of Western philosophy. The alphabet also enabled scientific advancements, with Greek scholars making significant contributions in fields such as mathematics, astronomy, and medicine. This intellectual progress was further supported by the establishment of academies, where the Greek Alphabet was utilized to teach and disseminate knowledge.
3. Influence on Art and Architecture:
The Greek Alphabet left an indelible mark on art and architecture in ancient Greece. Its letters became integral components of architectural ornamentation, as seen in the intricate inscriptions found on temples, statues, and monuments. The elegant and symmetrical shapes of the Greek letters were stylized and employed as decorative motifs, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of various structures. The ability to record and communicate artistic ideas through writing enabled the Greeks to document their artistic techniques and theories, contributing to the development of art as a discipline.
The significance of the Greek Alphabet in ancient Greece cannot be overstated. Its impact on communication, philosophy, science, and art shaped the culture and intellectual achievements of the ancient Greek civilization.
The Greek Alphabet held immense significance in ancient Greece, playing a pivotal role in communication, writing, and the overall development of society.
1. Role in Communication and Writing
The Greek Alphabet played a vital role in communication and writing in ancient Greece. It provided a standardized and efficient system for recording information, ideas, and stories. The introduction of vowels in the Greek alphabet allowed for more precise representation of sounds and improved clarity in writing. This, in turn, enhanced the overall effectiveness of communication. The Greeks used the alphabet to write a variety of texts ranging from literature and philosophy to historical accounts and scientific observations.
One significant aspect of the Greek Alphabet’s role in communication was its influence on the spread of knowledge. Writing became a means of preserving and transmitting information across generations. Important works of philosophy, such as those by Plato and Aristotle, were transcribed and shared widely, contributing to the intellectual development of society.
The Greek Alphabet fostered a sense of cultural identity and unity among the ancient Greeks. It provided a shared medium of communication, allowing people from different city-states and regions to connect and understand one another. This facilitated trade, diplomacy, and the exchange of ideas, ultimately contributing to the flourishing of Greek civilization.
To illustrate the importance of the Greek Alphabet in communication and writing, we can consider some notable examples. The epic poems of Homer, including the Iliad and the Odyssey, were written in the Greek Alphabet and achieved widespread fame throughout the ancient world. These works not only entertained audiences but also served as a vehicle for preserving and propagating Greek cultural values and mythology.
In addition to literature, the Greek Alphabet was also used for recording historical events and accounts. The works of Herodotus, often referred to as the “Father of History,” were written in Greek and laid the foundations for the study of history as a discipline.
The Greek Alphabet’s impact on communication and writing extended beyond the ancient world. It served as a foundation for the development of the Latin alphabet, which is widely used today in various languages. The Greek Alphabet’s legacy is evident in the modern world, where it continues to be recognized and appreciated for its influence on the written word.
2. Link to Greek Philosophy and Science
Greek philosophy and science were closely intertwined with the Greek Alphabet. The alphabet played a crucial role in the development and preservation of Greek philosophical and scientific texts, which have had a profound influence on the Western intellectual tradition. Philosophers such as Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle used the Greek Alphabet to record their ideas and teachings, laying the foundation for various branches of philosophy. These texts explored topics such as ethics, metaphysics, and epistemology, shaping the way we understand the world and ourselves. The Greek Alphabet also facilitated the growth of scientific knowledge in ancient Greece. Important scientific works, including those by renowned mathematicians like Pythagoras and Euclid, were written using the Greek Alphabet. Mathematics, astronomy, and natural sciences greatly benefited from the Greek Alphabet’s precision and ability to convey complex ideas. Through the alphabet, Greek philosophers and scientists were able to document and disseminate their discoveries, contributing to the advancement of knowledge in ancient Greece and beyond. The Greek Alphabet’s link to Greek philosophy and science is a testament to its significance as a tool for intellectual exploration and the pursuit of wisdom.
3. Influence on Art and Architecture
The Greek Alphabet had a profound influence on art and architecture in ancient Greece. It provided a means of communication and expression that allowed artists and architects to convey their ideas and concepts more effectively. In art, the Greek Alphabet was often used to inscribe dedicatory or descriptive texts on sculptures, vases, and other artistic objects. This practice not only provided information about the piece itself but also added an aesthetic element to the artwork. The alphabet’s letters were carefully etched or painted onto the surface, enhancing the overall visual appeal. In architecture, the Greek Alphabet played a significant role in the design and ornamentation of buildings. Greek architects used inscriptions and epigraphs to add decorative elements to their structures, such as on friezes, pediments, and columns. These inscriptions sometimes featured names of deities, rulers, or significant events, adding a symbolic and cultural dimension to the architecture. The Greek Alphabet’s influence on art and architecture extended beyond ancient Greece and continued to inspire artists and architects throughout the centuries. Even today, we can find traces of Greek lettering and design elements in various forms of art and architecture, showcasing the enduring impact of the Greek Alphabet on artistic expression.
Comparison with Other Alphabets
When comparing the Greek Alphabet with other alphabets, two notable examples are the Latin Alphabet and the Cyrillic Alphabet.
1. Latin Alphabet: The Latin Alphabet, also known as the Roman Alphabet, is derived from the Greek Alphabet. It shares many similarities with the Greek Alphabet, including the use of alphabetic letters for both consonant and vowel sounds. However, the Latin Alphabet has a different set of letter shapes and order. It consists of 26 letters, whereas the Greek Alphabet has 24 letters. Additionally, the Latin Alphabet does not include certain letters found in the Greek Alphabet, such as theta (Θ) and phi (Φ). The Latin Alphabet is widely used in various languages, including English, Spanish, French, Italian, and many others.
2. Cyrillic Alphabet: The Cyrillic Alphabet is predominantly used in Slavic languages such as Russian, Ukrainian, and Serbian. It was developed in the 9th century by Greek missionaries, who adapted the Greek Alphabet to represent the sounds of Slavic languages. While the Cyrillic Alphabet shares some similarities with the Greek Alphabet, such as a similar letter order, many letters have different shapes and pronunciations. The Cyrillic Alphabet includes additional letters that are not found in the Greek Alphabet. This alphabet has had a significant impact on the cultural and linguistic development of Slavic countries.
By comparing the Greek Alphabet with these other alphabets, we can appreciate the unique characteristics and influence that the Greek Alphabet has had on the development of written languages throughout history.
/unveiling-secrets-pleiades-star-cluster-taurus-constellation/.
1. Latin Alphabet
The Latin Alphabet, also known as the Roman Alphabet, is a writing system that evolved from the Greek Alphabet. Although the Latin Alphabet shares some similarities with its Greek counterpart, it also has distinct characteristics and differences. One significant difference is the number of letters in each alphabet. The Greek Alphabet consists of 24 letters, while the Latin Alphabet has 26 letters. This difference is due to the inclusion of two letters in the Latin Alphabet that are not present in the Greek Alphabet: “J” and “U.” Additionally, the Latin Alphabet is predominantly used in the Western world and is the standard writing system for many languages, including English, Spanish, French, and Italian. It is widely recognized and used in various fields, such as literature, academia, and international communication. The Latin Alphabet’s widespread usage and influence can be attributed to the expansion of the Roman Empire and the subsequent spread of the Latin language. This expansion led to the adoption of the Latin Alphabet by many cultures and languages, ultimately solidifying its significance and prominence in the modern world.
The Latin Alphabet, also known as the Roman Alphabet, is a writing system that evolved from the Greek Alphabet.
2. Cyrillic Alphabet
The Cyrillic Alphabet is another significant alphabet that is closely related to the Greek Alphabet. It is primarily used in countries that have historical and cultural ties to the Eastern Orthodox Church, such as Russia, Ukraine, and Bulgaria. The Cyrillic Alphabet was developed in the 9th century CE by the brothers Cyril and Methodius, who were Byzantine Greek missionaries. They created the alphabet specifically to translate religious texts into the Slavic languages spoken by the people of the region. The Cyrillic Alphabet is based on the Greek Alphabet, with some modifications and additions to accommodate the specific sounds of the Slavic languages. While there are similarities between the Greek and Cyrillic alphabets, there are also notable differences. For example, some letters in the Cyrillic Alphabet are pronounced differently or have additional sounds compared to their Greek counterparts. Additionally, the Cyrillic Alphabet contains letters that have no equivalent in Greek. Some examples of shared characters include ‘A’ (Alpha), ‘B’ (Beta), ‘N’ (Nu), ‘O’ (Omicron), and ‘P’ (Pi). The Cyrillic Alphabet represents an important variation of the Greek Alphabet and has been instrumental in preserving and shaping the written traditions of Eastern Europe and parts of Asia.
Cyrillic Alphabet Comparison with the Greek Alphabet
| Greek Alphabet | Cyrillic Alphabet |
|---|---|
| Α | А |
| Β | В |
| Ν | Н |
| Ο | О |
| Π | Р |
The Cyrillic Alphabet is another significant alphabet that is closely related to the Greek Alphabet. It is primarily used in countries that have historical and cultural ties to the Eastern Orthodox Church, such as Russia, Ukraine, and Bulgaria.
Modern Usage and Adaptation

Modern Usage and Adaptation of the Greek Alphabet can be seen in various fields and aspects of society today. One significant area where the Greek alphabet continues to play a crucial role is in mathematics and science. Many Greek letters are used as symbols in mathematical equations and scientific formulas. For example, the Greek letter “Π” (Pi) represents the mathematical constant that represents the ratio of a circle’s circumference to its diameter. Similarly, the Greek letter “Σ” (Sigma) is used to denote summation in mathematical equations. The Greek alphabet’s use in these disciplines highlights its enduring significance and the continued relevance of its symbols in academic and scientific contexts.
The Greek Alphabet’s symbolic nature is also evident in secret societies and Freemasonry. Many secret societies and fraternities have adopted the use of Greek letters as symbols of their organization. For example, the letter “Α” (Alpha) is often associated with leadership or the beginning, while the letter “Ω” (Omega) represents completion or the end. These letters can be found on logos, flags, and other insignia of these secret societies, adding an air of mystery and exclusivity to their practices.
In addition to its specific usage in mathematics, science, and secret societies, the Greek Alphabet has also influenced the broader cultural landscape. Greek letters can be found in popular culture, fashion, and even brand names. Greek letter tattoos and apparel featuring Greek letters have become trendy, reflecting the enduring appeal and recognition of these symbols in modern society.
The adaptability of the Greek alphabet is evident in its continued usage in everyday life. It is worth noting that the modern Greek alphabet has undergone some changes and modifications from its ancient form. However, the core letters and their symbolic meanings have remained intact. Whether it is in academic disciplines, secret societies, or popular culture, the Greek Alphabet continues to hold significance and captivate the imagination of people around the world.
1. Greek Alphabet in Mathematics and Science
The Greek Alphabet has had a significant impact on mathematics and science throughout history. Each letter of the Greek alphabet is assigned a numerical value, which allows for the use of Greek letters as mathematical symbols. This has proven especially valuable in fields such as geometry, where Greek letters are commonly used to represent angles, lines, and shapes. For example, the letter “alpha” (α) is often used to represent an angle, while the letter “pi” (π) is used to represent the mathematical constant pi.
In addition to their use as mathematical symbols, Greek letters are also used in scientific terminology and nomenclature. Many scientific terms and concepts are named after Greek letters, such as “alpha particles” and “beta decay” in physics, “delta cells” in biology, and “gamma rays” in astronomy. These Greek-lettered terms help scientists to communicate and describe complex phenomena in a concise and standardized manner.
The Greek Alphabet has been used to represent variables and unknown quantities in equations and formulas. This allows mathematicians and scientists to express mathematical relationships and scientific principles in a concise and symbolic way. The use of Greek letters adds a level of precision and clarity to mathematical and scientific communication.
The Greek Alphabet plays a crucial role in mathematics and science, serving as a versatile tool for representing mathematical concepts, labeling scientific terms, and expressing equations and formulas.
2. Symbolism in Secret Societies and Freemasonry
Symbolism in Secret Societies and Freemasonry is a subject that has long captivated the curiosity of many. The Greek Alphabet plays a significant role in these esoteric practices, where each letter is assigned a specific meaning or attribute. In Freemasonry, for example, the Greek letters are used to represent various concepts and principles. The letter Alpha represents the beginning or origin, while Omega represents the end or completion. Other letters are assigned to different virtues and qualities, such as Epsilon for industry, Gamma for wisdom, and Delta for change. The Greek Alphabet is also found in the symbolism of other secret societies, such as the Illuminati. In these organizations, the letters are believed to hold hidden meanings and messages that can only be deciphered by the initiated. For those who study or practice these mystical arts, the Greek Alphabet becomes a language of symbols and secrets, adding to the allure and mystique of these secret societies.
- Alpha: Represents the beginning or origin.
Omega: Represents the end or completion. - Epsilon: Symbolizes industry.
- Gamma: Symbolizes wisdom.
- Delta: Symbolizes change.
The Greek Alphabet Today
Today, the Greek Alphabet continues to hold significance and has found its place in various aspects of modern life. One area where the Greek Alphabet is heavily used is in mathematics and science. Many mathematical equations, formulas, and symbols are represented using Greek letters. For example, the symbol π (pi) is used to represent the mathematical constant that represents the ratio of a circle’s circumference to its diameter. Other Greek letters such as α (alpha), β (beta), γ (gamma), and θ (theta) are commonly used in equations, physics, and other scientific disciplines.
Additionally, the Greek Alphabet has also found its way into popular culture and symbolism. In secret societies and organizations like Freemasonry, the Greek Alphabet is often associated with mystical meanings and teachings. Different Greek letters symbolize various concepts and principles within these organizations. The influence of the Greek Alphabet can also be seen in fraternity and sorority systems, where Greek letters are used as representations for different organizations.
The Greek Alphabet is still utilized in the naming of stars, constellations, and celestial objects. Many of these objects have Greek names based on the Greek Alphabet, such as the Pleiades star cluster in the Taurus constellation. These names have been passed down through generations and continue to be used by astronomers and space enthusiasts.
The Greek Alphabet holds a significant place in modern society. Its use in mathematics, science, secret societies, and even astronomy showcases its versatility and lasting impact. Understanding the Greek Alphabet today helps us appreciate its ongoing legacy and its connection to both the ancient and contemporary world.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Greek Alphabet holds great significance in both ancient and modern times. Its origins in the Phoenician alphabet, as well as its development and evolution in ancient Greece, have paved the way for a rich history and legacy. The Greek Alphabet played a vital role in communication, writing, and the spread of knowledge in ancient Greece. It became a fundamental tool for philosophers, scientists, and artists to express their ideas and discoveries. Today, the Greek Alphabet continues to be used and adapted in various fields, particularly in mathematics and science, where it serves as a universal language for equations, formulas, and symbols. Its symbolism has also extended into secret societies and Freemasonry, adding an air of mystery and esotericism. The Greek Alphabet remains a timeless and influential system of writing, reflecting the ingenuity and intellectual prowess of ancient Greece. Understanding its significance allows us to appreciate the profound impact it has had on language, culture, and society throughout history.
Frequently Asked Questions

1. What is the significance of the Greek alphabet in ancient Greece?
The Greek alphabet played a crucial role in communication and writing in ancient Greece. It provided a standardized system for recording and transmitting information, allowing for the development of literature, historical accounts, and scientific texts.
2. How did the Greek alphabet influence Greek philosophy and science?
The Greek alphabet enabled philosophers and scientists to express their ideas and theories in writing. This facilitated the exchange of knowledge and the development of fields such as mathematics, astronomy, and medicine, laying the foundation for Western scientific thought.
3. How did the Greek alphabet impact art and architecture?
The Greek alphabet influenced the inscription of names and dedicatory phrases on buildings and sculptures in ancient Greece. It also contributed to the development of calligraphy and ornamental lettering styles, lending a distinct aesthetic quality to Greek art and architecture.
4. How does the Greek alphabet compare to the Latin alphabet?
While both alphabets have similar origins, the Greek alphabet predates the Latin alphabet. The Greek alphabet has 24 letters, whereas the Latin alphabet has 26. Additionally, certain letter shapes and sounds differ between the two alphabets.
5. How does the Greek alphabet compare to the Cyrillic alphabet?
The Cyrillic alphabet was derived from the Greek alphabet, incorporating some of its letters and sounds. However, the Cyrillic alphabet has additional letters to represent specific Slavic sounds, making it distinct from the Greek alphabet.
6. How is the Greek alphabet used in mathematics and science today?
The Greek alphabet continues to be used as a symbol system in various scientific fields. Greek letters are commonly used to represent variables, constants, and mathematical functions in equations, formulas, and scientific notation.
7. Is the Greek alphabet associated with any secret societies or Freemasonry?
Yes, certain symbols and letters from the Greek alphabet are used in the symbolism of secret societies and Freemasonry. They carry specific meanings and represent philosophical concepts and principles embraced by these organizations.
8. Is the Greek alphabet still widely used today?
While the Greek alphabet is no longer the primary writing system of any language today, it continues to be used in various contexts. It is taught in schools and universities for the study of ancient Greek language and culture, and it remains prevalent in scientific and mathematical disciplines.
9. Can anyone learn to read and write the Greek alphabet?
Yes, anyone can learn to read and write the Greek alphabet. Numerous resources, including books, online tutorials, and language courses, are available to help individuals learn the alphabet and its pronunciation.
10. Are there any similarities between the Greek alphabet and other alphabets?
Yes, there are similarities between the Greek alphabet and other alphabets, such as the Phoenician, Latin, and Cyrillic alphabets. These similarities can be attributed to the historical connections and influences between different cultures throughout ancient history.
References
Frequently Asked Questions

1. How many letters are there in the Greek alphabet?
The Greek alphabet consists of 24 letters.
2. What is the significance of the order of the Greek alphabet?
The order of the Greek alphabet has no specific meaning or significance.
3. How did the Greek alphabet influence other alphabets?
The Greek alphabet served as the basis for the development of other alphabets, including the Latin and Cyrillic alphabets.
4. How is the pronunciation of Greek letters different from English letters?
The pronunciation of Greek letters can differ from English letters. For example, the letter “alpha” is pronounced as “AL-fuh” in Greek, whereas in English it is pronounced as “AL-fuh” or “AL-fay”.
5. What are some common Greek words used in the English language?
Many English words have Greek origins, such as “philosophy,” “democracy,” and “theater”.
6. Can I learn to write and pronounce the Greek alphabet?
Yes, learning to write and pronounce the Greek alphabet is achievable with practice and resources such as language courses or online tutorials.
7. Are there any variations or regional differences in the Greek alphabet?
Generally, the Greek alphabet is consistent across regions and variations, with minor differences in pronunciation.
8. How did the Greek alphabet contribute to the development of literature in Ancient Greece?
The Greek alphabet provided a standardized writing system, enabling the preservation and transmission of literary works in Ancient Greece.
9. What are some Greek symbols commonly used in mathematics and science?
Greek symbols commonly used in mathematics and science include alpha (α), beta (β), gamma (γ), delta (δ), and sigma (σ).
10. Are there any superstitions or beliefs associated with the Greek alphabet?
In some secret societies and Freemasonry, certain Greek letters are believed to hold symbolic meanings representing various concepts and principles.
References
- The 24 Greek Alphabet Letters and What They Mean
- Alpha, Beta, What’s Next? The Greek Alphabet Explained
- Decoding Hidden Meanings of Ancient Greek Alphabet …