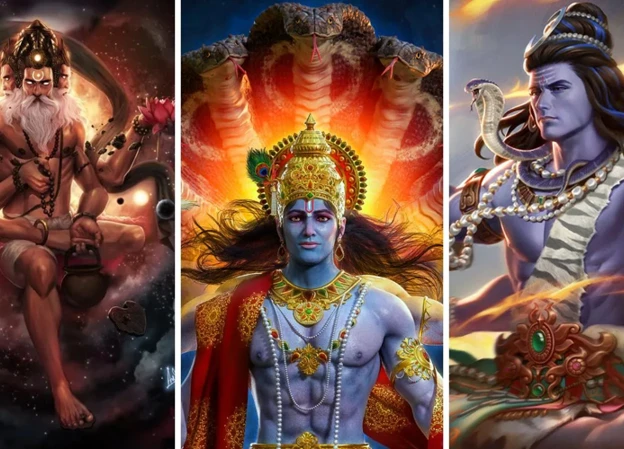
Reincarnation is a captivating concept that has fascinated humans for centuries. It offers a profound perspective on life, death, and the cyclical nature of existence. In Hindu mythology, the belief in reincarnation is deeply ingrained, shaping the way people perceive their purpose and actions in this world. Embarking on a spiritual journey through the realms of karma, samsara, and dharma, Hinduism explores the intricate interconnectedness of life and death. This article delves into the concept of reincarnation in Hindu mythology, unraveling the mysteries surrounding the journey of the soul, the significance of rebirth, and the quest for liberation. Join us as we venture into the profound depths of Hindu mythology to explore the enigmatic concept of reincarnation.
Contents
- The Belief of Reincarnation
- The Journey of the Soul
- Rebirth and Liberation
- Significance and Impact
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What is the role of karma in the belief of reincarnation?
- 2. Can someone remember their past lives?
- 3. How does dharma influence the cycle of reincarnation?
- 4. Are all living beings subject to reincarnation?
- 5. How does the concept of reincarnation differ from other religious beliefs?
- 6. Is reincarnation a form of punishment or reward?
- 7. Can one break free from the cycle of reincarnation?
- 8. Are there any rituals or practices associated with reincarnation?
- 9. Does everyone experience the same number of reincarnations?
- 10. Can one regress to a lower form of existence in reincarnation?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How does the concept of reincarnation differ from other religious beliefs about the afterlife?
- 2. Do all Hindus believe in reincarnation?
- 3. What is the role of karma in the belief of reincarnation?
- 4. Can a person be reborn as a different species in Hindu mythology?
- 5. How does the belief in reincarnation influence Hindu rituals and ceremonies?
- 6. Is there a purpose or goal to the cycle of birth and rebirth in Hindu mythology?
- 7. Can memories from past lives be accessed in Hindu mythology?
- 8. How does the concept of reincarnation impact ethical and moral behavior in Hindu society?
- 9. Are there any stories or myths in Hindu mythology that illustrate the concept of reincarnation?
- 10. How does the belief in reincarnation help individuals cope with grief and loss in Hindu culture?
- References
- Read More
The Belief of Reincarnation

The belief in reincarnation is deeply rooted in Hindu mythology, presenting a perplexing perspective on the cycle of life and death. At the core of this belief system lies the principles of karma and samsara. Karma refers to the accumulated actions and choices made by an individual, believed to shape their future lives and experiences. On the other hand, samsara alludes to the continuous cycle of birth, death, and rebirth. Hindus believe that the soul, known as the Atman, is eternal and transcends physical existence. It is through multiple lifetimes and rebirths that the Atman evolves and seeks liberation from the cycle of samsara. Dharma, another crucial aspect, guides individuals in leading righteous lives and fulfilling their moral duties. The intricacies of these beliefs intertwine to create a unique understanding of the concept of reincarnation in Hindu mythology.
1. Karma and Samsara
The concept of karma and samsara lies at the heart of Hindu mythology’s belief in reincarnation. Karma is the accumulation of an individual’s actions and choices throughout their life. It is believed that these actions have consequences that will shape future lives and experiences. Positive actions result in good karma, while negative actions lead to bad karma. The law of karma is seen as a dynamic force that governs the cycle of samsara. Samsara refers to the continuous cycle of birth, death, and rebirth. Hindus believe that the soul, known as the Atman, is eternal and goes through this cycle repeatedly. Each life presents an opportunity for the Atman to learn, grow, and attain liberation from the cycle of samsara. The quality of one’s current life is believed to be influenced by past lives’ karma, determining one’s caste, social status, and life circumstances. It is through the understanding and acceptance of karma and samsara that Hindus strive to lead righteous lives, accumulate positive karma, and seek spiritual growth and eventual liberation from the cycle of reincarnation.
2. The Atman and the Eternal Soul
In Hindu mythology, the concept of the Atman and the eternal soul is a fundamental aspect that contributes to the belief in reincarnation. The Atman refers to the individual soul, which is believed to be immortal and divine. It is viewed as a fragment of the universal consciousness, often referred to as Brahman. The Atman is considered to be distinct from the physical body and the mind, representing the essence of an individual’s being. This concept implies that the true nature of individuals transcends their temporary earthly existence. Hinduism teaches that the Atman goes through a series of births and deaths, experiencing different earthly lives in order to learn and evolve. Each life presents an opportunity for the Atman to fulfill its karmic responsibilities and progress on the path to liberation from the cycle of samsara. This understanding of the Atman and the eternal soul underscores the profound nature of reincarnation in Hindu mythology, highlighting the eternal nature of the individual and the continuous journey of self-realization. (Reference: ophiuchus-art-literature)
3. The Role of Dharma
Dharma plays a pivotal role in the concept of reincarnation in Hindu mythology. It refers to one’s moral duties, responsibilities, and righteous actions that guide individuals in leading purposeful lives. According to Hindu beliefs, each person has a unique dharma based on their caste, age, gender, and occupation. By adhering to their dharma, individuals contribute to the greater cosmic order and maintain harmony in the universe. Dharma also serves as a compass, directing individuals towards righteous actions and away from negative karma. It encourages individuals to perform their duties selflessly, without attachment to the results, focusing on the intention and integrity behind their actions. Embracing one’s dharma plays a crucial role in shaping future lives and determining the quality of reincarnations. It is believed that by fulfilling one’s dharma in each lifetime, individuals accumulate positive karma, paving the way for spiritual growth and eventual liberation. The significance of dharma in Hindu mythology lies in its ability to guide individuals towards a fulfilling and purposeful existence, bringing them closer to the ultimate goal of transcending the cycle of samsara. Explore more about the impact of planetary alignments on global economic trends in the fascinating world of astrology and economics.
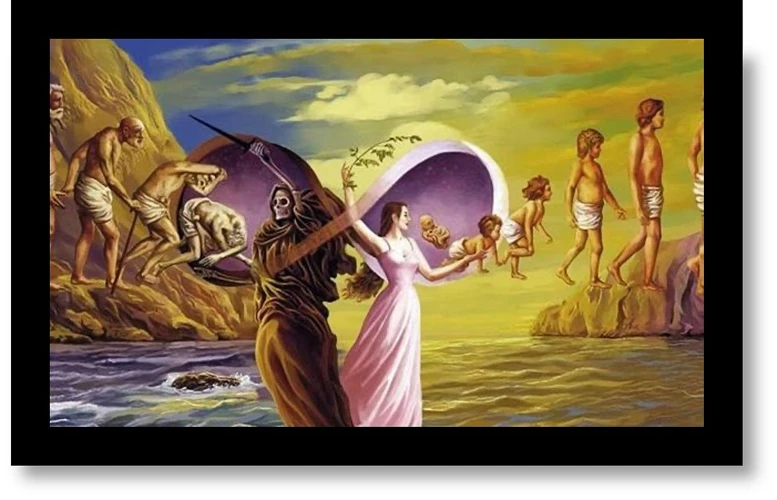
The Journey of the Soul
The journey of the soul in Hindu mythology encompasses various stages, each laden with its own mysteries and revelations. Death and Transition mark the initial stage as the soul departs from the physical body and embarks on its next phase of existence. According to Hindu beliefs, the soul may venture into different realms during this transitional period, including higher planes of existence or lower realms based on its accumulated karma. These realms, known as the afterlife realms, offer distinct experiences and opportunities for spiritual growth. Additionally, there exists an in-between state where the soul awaits its next rebirth, known as the antarabhava. This liminal phase carries its own significance, providing a time for reflection, purification, and preparation for the soul’s upcoming incarnation. The journey of the soul is a profound exploration of the intricacies of life, death, and the eternal cycle of rebirth in Hindu mythology.
1. Death and Transition
The concept of death and transition in Hindu mythology is deeply intertwined with the belief in reincarnation. When an individual’s physical body ceases to exist, it is believed that the soul undergoes a journey to the afterlife realms. This transition is guided by the accumulated karmic impressions and the actions performed in the previous life. According to Hindu scriptures, there are multiple paths that the soul may take after death. One such path is known as the Pitru Loka, where the soul reunites with ancestral spirits and receives blessings. Another path is the Deva Loka, where the soul experiences heavenly realms and indulges in celestial pleasures. However, for those who have accumulated negative karma, the path may lead to lower realms such as the Naraka or hellish realms, where they undergo purification and penance for their past actions. It is important to note that these realms are not permanent destinations but rather temporary stages in the cycle of reincarnation. The exact transition and destination of the soul are determined by their karma and the balance of virtues and vices in their life. The complexities of death and transition offer a profound understanding of the continuous cycle of life and the consequences of one’s actions in Hindu mythology.
2. The Afterlife Realms
In Hindu mythology, the concept of the afterlife is multifaceted, encompassing various realms that souls may traverse after death. According to Hindu scriptures, these realms are categorized into two main paths: the path of light and the path of darkness.
The Path of Light: Souls who have lived virtuous lives, performed good deeds, and accumulated positive karma may find themselves on the path of light. This path leads to realms of higher existence, such as Svarga (heaven), where individuals experience bliss, happiness, and the rewards of their righteous actions. In Svarga, celestial beings and divine entities reside, enjoying the fruits of their past virtues and engaging in spiritual activities.
The Path of Darkness: Souls who have led lives filled with negative actions, harmful deeds, and accumulated negative karma may find themselves on the path of darkness. This path leads to realms of lower existence, such as Naraka (hell) or Patala (underworld). In these realms, individuals may undergo various forms of suffering and purification, allowing them to eventually balance their negative karma and progress towards a higher state of existence.
It is important to note that these realms are not considered permanent abodes but rather temporary destinations where souls undergo their karmic consequences. The duration of stay in these realms is determined by an individual’s actions and karma. Ultimately, the goal for souls is to transcend these realms and attain moksha, liberation from the cycle of samsara and union with the divine.
In Hindu mythology, the concept of the afterlife realms serves as a moral compass, emphasizing the importance of leading a righteous life and accumulating positive karma. It offers individuals an opportunity for spiritual growth, redemption, and the potential for ascending towards higher planes of existence. The exploration of these afterlife realms further deepens the understanding of the intricate cycle of reincarnation in Hindu mythology.
For more information on the impact of planetary alignments on global economic trends, check out this fascinating article.
3. The In-Between State
The in-between state, also known as the antarabhava in Hindu mythology, refers to the transitional period between death and rebirth. According to Hindu beliefs, after the physical body dies, the soul enters this intermediate state, where it undergoes purification and reflection before embarking on its next incarnation. The duration of this state can vary depending on various factors, such as the individual’s karma and spiritual progress. During the antarabhava, the soul may experience a range of emotions and sensations as it reflects on its past life while preparing for the next. This period serves as an opportunity for the soul to learn from its past actions, resolve any unresolved karmic debts, and purify itself. The antarabhava is considered a crucial phase in the journey of the soul, as it helps shape the circumstances and experiences of the soul’s subsequent rebirth. It is a time of introspection, growth, and renewal as the soul prepares itself for its next chapter in the cycle of reincarnation. The significance of the in-between state highlights the intricate nature of the soul’s journey and underscores the importance of self-reflection and spiritual development. Through this introspective period, the soul is prepared for its next adventure in the grand tapestry of existence.
Rebirth and Liberation

Rebirth and liberation serve as the ultimate goals in the concept of reincarnation within Hindu mythology. Hindus believe that the process of rebirth is influenced by the karmic imprints accumulated in past lives. Inherited traits and past lives play a significant role in shaping an individual’s current existence, as they carry the consequences of their previous actions. Liberation, known as moksha, represents the ultimate liberation from the cycle of birth and death. Attaining moksha allows the individual’s soul to break free from the bondage of samsara and merge with the divine. This pursuit of liberation inspires individuals to lead virtuous lives, seek spiritual growth, and ultimately transcend the cycle of rebirth. The path to liberation may vary, with different schools of thought advocating for various practices such as meditation, devotion, or selfless service. Regardless of the approach, the ultimate aim remains the same – to achieve liberation from the perpetual cycle of reincarnation and find eternal unity with the divine.
1. Inherited Traits and Past Lives
In the concept of reincarnation, the idea of inherited traits and past lives is a fascinating aspect. According to Hindu mythology, when a soul is reborn, it carries with it the imprints of its past lives. These imprints can manifest as inherited traits, talents, or even certain unexplained preferences or phobias. This belief suggests that our current life is influenced by the actions, experiences, and learnings of our previous lives. It is believed that these inherited traits serve as a form of spiritual growth and learning. Through these traits, individuals have the opportunity to continue their evolution and work towards liberation from the cycle of birth and death. This belief in inherited traits and past lives underscores the interconnectedness of different lifetimes and the continuous journey of the soul. It invites contemplation on the richness and complexity of human existence, supporting the idea of multiple lifetimes contributing to one’s spiritual progression. Exploring the depths of our inherited traits can offer insights into our own unique spiritual journey. Whether through familiar skills, unconscious memories, or unexplained passions, these glimpses into our past lives fuel our quest for self-discovery and spiritual growth. It is a fascinating aspect of reincarnation that helps us understand the enigmatic journey of the soul and our place within it.
2. Steps Towards Liberation
Liberation, known as moksha in Hindu mythology, represents the ultimate goal of the soul’s journey through multiple lifetimes and reincarnations. While the cycle of birth and rebirth can be seen as an opportunity for spiritual growth, attaining liberation is the ultimate aim for Hindus. The path towards moksha involves three crucial steps. The first step is self-realization, where an individual becomes aware of their true divine nature and recognizes the illusion of the material world. This self-realization leads to the second step, which is detachment from worldly desires and attachments. By detaching oneself from the material realm, one can focus on spiritual growth and seek unity with the divine. The final step is union with the divine, where the individual merges their consciousness with the universal consciousness, transcending the cycle of birth and death. Achieving liberation is considered the ultimate liberation from the cycles of samsara and the attainment of eternal bliss and oneness with the divine. It is the culmination of countless lifetimes of learning, evolving, and seeking spiritual enlightenment (source).
Significance and Impact

The belief in reincarnation holds immense significance in Hindu mythology, impacting various aspects of individuals’ lives and shaping their worldview. One significant impact is the emphasis on moral responsibility and accountability. The concept of karma ensures that individuals are held accountable for their actions, as they believe that their choices in this life will have consequences in future incarnations. This understanding fosters a sense of ethical behavior and encourages individuals to strive for righteousness. Additionally, the belief in reincarnation allows for a unique way of conceptualizing life’s purpose. It suggests that life is not a singular event but rather a continuous journey of spiritual evolution. This realization prompts individuals to explore their inner selves, seek self-improvement, and pursue spiritual growth. Lastly, the idea of reincarnation inspires individuals to embark on a quest for self-realization. Through understanding their past lives and accumulated experiences, individuals can gain insights into their strengths, weaknesses, and the lessons they need to learn in order to attain liberation from the cycle of rebirth. This quest for self-realization empowers individuals to attain a deeper understanding of their true nature and their connection to the divine. The significance and impact of the belief in reincarnation permeate through every aspect of life, guiding individuals on a profound spiritual journey.
1. Moral Responsibility and Accountability
One of the significant aspects of the belief in reincarnation in Hindu mythology is the emphasis on moral responsibility and accountability. The concept of karma plays a crucial role in this, as it suggests that every action has consequences that will shape future lives. Hindus believe that individuals are responsible for their actions, and these actions have a direct impact on their future existence and experiences. Whether good or bad, the consequences of one’s actions are believed to manifest in subsequent lives. This belief instills a deep sense of personal accountability and encourages individuals to act in accordance with dharma, or righteousness, in order to accumulate positive karma. The understanding of moral responsibility and accountability in the context of reincarnation serves as a guiding principle for Hindus to lead virtuous lives and strive towards spiritual growth. It offers a framework for making conscious choices and understanding the interconnectedness of one’s actions and their long-term repercussions.
2. Conceptualizing Life’s Purpose
Conceptualizing life’s purpose is a fundamental aspect associated with the concept of reincarnation in Hindu mythology. The belief in multiple lifetimes offers individuals a broader perspective on the meaning and significance of their existence. According to Hindu philosophy, life is not merely a singular event but a continuous journey of the soul. Through the process of reincarnation, each individual has the opportunity to learn, evolve, and fulfill their ultimate purpose. This understanding encourages introspection and self-reflection, as individuals contemplate their actions and strive to align themselves with their higher selves. The concept of life’s purpose in Hindu mythology is not limited to personal fulfillment, but also extends to the collective well-being and the pursuit of righteousness. It emphasizes the significance of leading a Dharmic life, where one’s actions contribute positively to society and uphold moral values. This perspective promotes a sense of responsibility, accountability, and interconnectedness, as individuals recognize their role in the grand tapestry of existence. Whether through personal growth, service to others, or the pursuit of spiritual enlightenment, the belief in reincarnation provides a framework for individuals to discover and fulfill their unique life’s purpose in a way that aligns with the principles of dharma. It offers solace and motivation, inspiring individuals to make conscious choices and lead a life that is meaningful, virtuous, and in harmony with the intricacies of the cosmic order.
3. Seeking Self-Realization
In Hindu mythology, the concept of seeking self-realization plays a significant role in the belief of reincarnation. Individuals on the path of self-realization aim to break free from the cycle of birth and death, ultimately attaining moksha, or liberation. This spiritual journey involves delving deep into one’s inner self, seeking to understand the true nature of existence and their connection to the divine. Meditative practices, such as yoga and pranayama (breath control), are integral to this process, allowing individuals to quiet their minds and explore the depths of their consciousness.
Self-realization is not only about detaching oneself from worldly desires but also about cultivating self-awareness, compassion, and wisdom. It involves recognizing one’s innate divinity and realizing their interconnectedness with all beings and the universe. Through self-realization, individuals aim to transcend the limitations of the physical world and experience a sense of unity and oneness with the divine cosmic energy.
The journey towards self-realization requires dedication, discipline, and a sincere desire for spiritual growth. It involves shedding the layers of ego, attachments, and ignorance that bind the soul to the cycle of reincarnation. The teachings of enlightened gurus, scriptures such as the Bhagavad Gita and the Upanishads, and the guidance of a spiritual community can serve as invaluable resources on this transformative path.
By seeking self-realization, individuals in Hindu mythology aim to break free from the perpetual cycle of birth and death, finding ultimate liberation and merging with the eternal consciousness. This pursuit not only brings profound inner transformation but also offers a deep understanding of the nature of reality and the purpose of human existence.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the concept of reincarnation in Hindu mythology offers a profound insight into the cyclical nature of existence and the journey of the soul. Through the interconnected principles of karma, samsara, and dharma, Hindus believe in the evolution of the eternal soul, seeking liberation from the cycle of birth and death. The belief in reincarnation carries great significance, as it instills a sense of moral responsibility and accountability for one’s actions. It allows individuals to conceptualize the purpose of life beyond mere material existence, prompting them to strive for self-realization and spiritual growth. The exploration of past lives and inherited traits further deepens the understanding of oneself and others. The quest for liberation becomes a transformative journey, guiding individuals towards self-discovery and ultimately, union with the divine. Reincarnation in Hindu mythology has a profound impact on the way individuals perceive their existence and the choices they make. It compels them to seek a higher understanding of the universe and their place within it. Thus, the concept of reincarnation serves as a guiding light on the path of self-exploration and enlightenment.
Frequently Asked Questions

1. What is the role of karma in the belief of reincarnation?
Karma plays a fundamental role in the belief of reincarnation in Hindu mythology. It is the accumulated sum of an individual’s actions, thoughts, and intentions. Good karma leads to a positive future life, while negative karma results in a challenging or lower existence.
2. Can someone remember their past lives?
While some individuals claim to have memories or glimpses of their past lives, it is not a universally experienced phenomenon. According to Hindu beliefs, these memories are often obscured as a person transitions from one life to another, serving as a means of spiritual growth and liberation.
3. How does dharma influence the cycle of reincarnation?
Dharma guides individuals in fulfilling their moral and societal duties. By leading a righteous life in accordance with their dharma, individuals accumulate positive karma, which can lead to a higher existence in future lives. It helps shape the trajectory of their reincarnation journey.
4. Are all living beings subject to reincarnation?
According to Hindu belief, not only humans but all living beings, including animals and plants, are subject to the cycle of reincarnation. The form of existence in each life is determined by past actions and karma.
5. How does the concept of reincarnation differ from other religious beliefs?
While reincarnation is commonly associated with Hinduism, similar beliefs exist in other religions as well, such as Buddhism and Jainism. However, the specific mechanisms and interpretations of reincarnation may differ between these religious traditions.
6. Is reincarnation a form of punishment or reward?
In Hindu mythology, reincarnation is not seen as solely a form of punishment or reward. It is a means for the soul to learn, grow, and eventually attain liberation from the cycle of birth and death. The circumstances of each life are influenced by the karmic patterns accumulated over past lives.
7. Can one break free from the cycle of reincarnation?
Yes, the ultimate goal in Hindu mythology is to achieve liberation from the cycle of reincarnation, known as moksha. By attaining self-realization, transcending attachment to worldly desires, and realizing the true nature of the Atman, one can break free from the cycle and merge with the divine.
8. Are there any rituals or practices associated with reincarnation?
Hinduism encompasses various rituals and practices that are believed to influence the journey of the soul in the cycle of reincarnation. These can include acts of charity, meditation, prayer, and performing religious ceremonies and rites.
9. Does everyone experience the same number of reincarnations?
There is no fixed number of reincarnations that everyone must go through. The number of lifetimes a soul experiences before attaining liberation can vary greatly based on individual spiritual progress, karmic patterns, and the realization of self.
10. Can one regress to a lower form of existence in reincarnation?
Yes, reincarnation in Hindu mythology includes the possibility of regressing to a lower form of existence based on the accumulation of negative karma. This regression serves as an opportunity for the soul to learn lessons and rectify past mistakes in order to progress on its spiritual journey.
References
- How does the Hindu religion support the concept of …
- The Importance of Reincarnation in Hindu Philosophy
- Reincarnation and Samsara – Heart Of Hinduism
Frequently Asked Questions

1. How does the concept of reincarnation differ from other religious beliefs about the afterlife?
The concept of reincarnation in Hindu mythology differs from other religious beliefs about the afterlife in that it revolves around the idea of the soul being reborn into new bodies, whereas other beliefs may focus on concepts such as heaven, hell, or a single afterlife destination.
2. Do all Hindus believe in reincarnation?
Reincarnation is a central belief in Hinduism, but not all Hindus necessarily believe in it. Different sects and individuals within the religion may interpret and understand the concept of reincarnation in different ways.
3. What is the role of karma in the belief of reincarnation?
Karma plays a significant role in the belief of reincarnation. Hindus believe that one’s actions in previous lives determine the nature of their current life and future lives. Good actions lead to positive karma, while negative actions result in negative karma.
4. Can a person be reborn as a different species in Hindu mythology?
According to Hindu mythology, yes, a person can be reborn as a different species. The cycle of reincarnation allows for the possibility of being reborn as animals, plants, or even celestial beings, depending on the accumulated karma and the soul’s spiritual evolution.
5. How does the belief in reincarnation influence Hindu rituals and ceremonies?
The belief in reincarnation influences Hindu rituals and ceremonies in various ways. For example, rituals may be performed to honor and provide support to the departed soul during the transition from one life to the next. Ceremonies such as ancestral worship and prayers also acknowledge the ongoing journey of the soul through multiple births.
6. Is there a purpose or goal to the cycle of birth and rebirth in Hindu mythology?
Yes, according to Hindu mythology, the ultimate goal of the cycle of birth and rebirth is to attain liberation (moksha) and break free from the cycle. This liberation allows the soul to merge with the divine and end the cycles of suffering and reincarnation.
7. Can memories from past lives be accessed in Hindu mythology?
According to Hindu mythology, it is believed that some individuals can access memories from past lives through spiritual practices and deep meditation. These memories can provide insights into one’s karmic journey and aid in personal growth and self-realization.
8. How does the concept of reincarnation impact ethical and moral behavior in Hindu society?
The concept of reincarnation in Hinduism encourages individuals to take responsibility for their actions and strive for ethical and moral behavior. The understanding that actions in the present life can have consequences in future lives promotes compassion, kindness, and the desire to accumulate positive karma.
9. Are there any stories or myths in Hindu mythology that illustrate the concept of reincarnation?
Yes, Hindu mythology is rich with stories and myths that illustrate the concept of reincarnation. One well-known example is the story of Lord Rama, who is believed to be an incarnation (avatar) of Lord Vishnu. Lord Rama’s story highlights the idea of divine beings taking birth on Earth and going through the cycle of life and death.
10. How does the belief in reincarnation help individuals cope with grief and loss in Hindu culture?
The belief in reincarnation provides comfort and solace to individuals dealing with grief and loss in Hindu culture. It offers the understanding that death is not the end but rather a transition to a new life. This belief can alleviate the fear of loss and provide hope for future reunions and continued spiritual growth.







