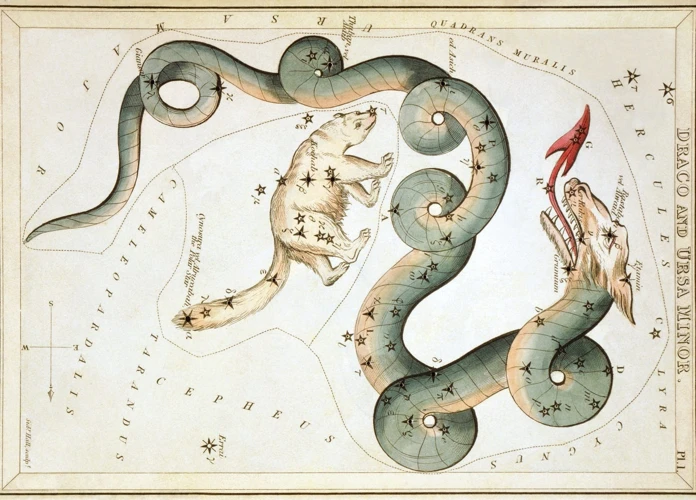
Welcome to the fascinating realm of the Draco constellation! Prepare to embark on a captivating journey as we unravel the secrets and unveil the wonders held within this celestial spectacle. Enigmatic and mythical, Draco has been an object of fascination for stargazers, astronomers, and astrologers throughout history. From its compelling mythology to its notable features and deep-sky objects, Draco offers a wealth of intrigue and discovery. Join us as we delve into the rich tapestry of this enigmatic constellation, exploring its historical significance, its celestial treasures, and its enduring influence on modern astrology. Are you ready to uncover the mysteries of Draco? Let’s begin our cosmic adventure!
Contents
- The History of Draco
- Notable Features of the Draco Constellation
- Mythology and Cultural Significance
- Exploring Draco’s Deep-Sky Objects
- Draco in Modern Astrology
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. Is Draco visible all year round?
- 2. How do I locate Draco in the sky?
- 3. Can I see the North Star within Draco?
- 4. Are there any notable stars in Draco?
- 5. What is the mythology behind Draco?
- 6. Are there any deep-sky objects within Draco?
- 7. Can I see any meteor showers associated with Draco?
- 8. How far away is Draco from Earth?
- 9. Is Draco part of the zodiac?
- 10. What is the significance of Draco in astrology?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. Can I see the Draco Constellation with the naked eye?
- 2. What is the brightest star in Draco?
- 3. Does Draco have any interesting deep-sky objects?
- 4. What is the mythology behind the Draco Constellation?
- 5. Can I see the Quadrantids Meteor Shower from Draco?
- 6. Is Draco mentioned in astrology?
- 7. How far away is the Cat’s Eye Nebula?
- 8. Can I observe the Draco Dwarf Galaxy with a telescope?
- 9. Is Draco visible from the Southern Hemisphere?
- 10. Are there any notable star clusters in Draco?
- References
- Read More
The History of Draco
Draco, the dragon, has a rich and storied history that spans across various civilizations and cultures. In ancient Greece, Draco was believed to be a dragon that guarded the Golden Apples of the Hesperides, a task assigned to him by the goddess Hera. In Chinese mythology, Draco represented a dragon that controlled the weather and brought rains to the crops. It was also associated with the Emperor and symbolized imperial power. The constellation’s name itself originates from the Latin word for dragon. The earliest known record of Draco dates back to the second century AD, with the Greek astronomer Ptolemy including it in his influential work, the Almagest. Draco’s position in the northern sky, near the celestial pole, made it highly visible and easily identifiable. Its prominence also led to its inclusion in the zodiac by the Babylonians. Despite eventually being excluded from the zodiac by astronomer Hipparchus due to the introduction of the constellation Ophiuchus, Draco remained an essential part of the celestial sphere. Today, the history of Draco serves as a testament to humanity’s enduring fascination with the stars and the mythical narratives we weave to make sense of the cosmos. (/astronomical-perspective-ophiuchus-constellation/)
Notable Features of the Draco Constellation

Draco, the dragon constellation, boasts several notable features that captivate the imagination of astronomers and stargazers alike. First and foremost, the most famous star in Draco is Thuban, also known as Alpha Draconis, which served as the North Star around 4,500 years ago during the time of the ancient Egyptians. This celestial landmark held immense navigational significance during that period. Another remarkable feature is the distinctive shape of the Draco constellation itself, resembling a winding dragon. Its head, formed by four stars, and its long, serpentine body add to its allure. Additionally, the Quadrantids meteor shower, an annual meteoric phenomenon that occurs in early January, has its radiant point located within Draco. This meteor shower is known for its intense and brief outbursts, making it a spectacle for skywatchers. The Draco constellation’s unique characteristics and celestial phenomena make it a captivating sight in the night sky, inspiring wonder and awe for centuries. (/saturn-influence-discipline-responsibility/)
1. The North Star: Thuban
Thuban, also known as Alpha Draconis, holds the prestigious title of the North Star, marking the celestial north pole. This bright star has played a significant role in navigation throughout history. Located at a distance of approximately 305 light-years from Earth, Thuban emits a luminosity over 120 times greater than our Sun. During ancient times, Thuban held even greater importance as the pole star around 3000 BCE. Its position near the celestial pole made it a crucial reference point for early navigators and explorers. The ancient Egyptians, in particular, revered Thuban and aligned their pyramids to its position. However, due to the precession of the Earth’s axis, Thuban gradually lost its status as the North Star around 1900 BCE and was replaced by Polaris, the current North Star. Today, Thuban remains a fascinating celestial object, showcasing the ever-changing nature of our universe. (/phenomenon-gravitational-waves-black-holes/)
2. Dragon’s Head and Tail
In the Draco constellation, two prominent features stand out: the Dragon’s Head and the Dragon’s Tail. These distinctive parts of the constellation are key markers that help astronomers locate and identify Draco in the night sky. The Dragon’s Head is marked by the bright star known as Thuban, also referred to as Alpha Draconis. Thuban, once the North Star, served as a reliable navigational guide for ancient civilizations. While it no longer holds this title due to the precession of Earth’s axis, Thuban’s historical significance is indelible. The Dragon’s Tail, on the other hand, is a curving line of faint stars that stretches across the night sky. These stars depict the long and sinuous trail left behind by the mythical dragon as it slithers through the heavens. Together, the Dragon’s Head and Tail create a celestial spectacle, capturing the imagination and inspiring countless tales throughout history. So, next time you gaze up at the night sky, look for the distinctive Dragon’s Head and Tail of the Draco constellation, and be transported to a realm of myth and wonder.
3. Quadrantids Meteor Shower
The Quadrantids meteor shower is one of the most remarkable celestial phenomena associated with the Draco constellation. Known for its intense and vibrant display, the Quadrantids occur every year during the first week of January. Its name is derived from the now-defunct Quadrans Muralis constellation, which was situated near Draco. Although Quadrans Muralis is no longer officially recognized, the meteor shower retains its original name. The source of the Quadrantids is believed to be the remnants of an asteroid called 2003 EH1. Interestingly, this meteor shower is known for its brief but spectacular peak activity, often producing up to 100 meteors per hour in optimal conditions. Despite its beauty, the Quadrantids can be challenging to observe due to several factors. First, its peak lasts for only a few hours, making precise timing crucial. Second, the cold weather in January can deter stargazers from venturing outside for prolonged periods. Nevertheless, for those dedicated enough to brave the elements and time their observations accurately, the Quadrantids meteor shower offers a celestial spectacle like no other. Be sure to mark your calendars and keep an eye on the skies for this captivating display of cosmic fireworks!
Mythology and Cultural Significance
Mythology and cultural significance surround the Draco constellation, adding layers of intrigue and meaning to its celestial presence. In Greek mythology, Draco is often associated with the dragon Ladon, who guarded the golden apples in the Garden of the Hesperides. It is believed that the hero Hercules slew Ladon as one of his Twelve Labors. In Chinese mythology, Draco is known as the Azure Dragon and is considered one of the four celestial guardians. The Azure Dragon represents the east and symbolizes spring and the element of wood. In Hindu mythology, Draco is associated with the Naga, serpent-like deities known as protectors of the waters and sources of life. The Naga are often depicted with multiple heads or as half-human, half-serpent beings. Draco’s influence is not limited to mythology. Its position near the North Celestial Pole has made it an important navigational marker throughout history. Sailors and explorers from various cultures used the constellation to guide their journeys and find their way home. Today, Draco continues to hold cultural significance, appearing in popular culture, including books, movies, and games, where its mythical and legendary nature is often portrayed. The varied mythologies and cultural interpretations of Draco only add to its allure and make it a captivating constellation to explore and ponder.
Exploring Draco’s Deep-Sky Objects
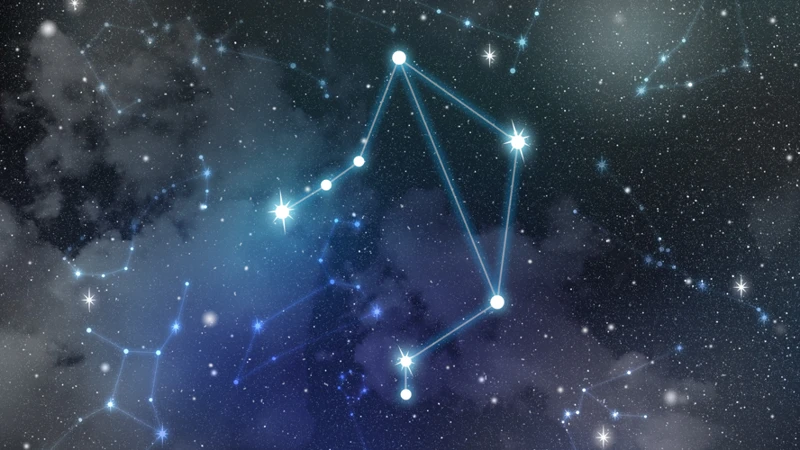

Explore the depths of Draco’s mesmerizing deep-sky objects that adorn the night sky. Within this celestial tapestry lies a treasure trove of astronomical wonders waiting to be discovered. One of the most captivating objects within Draco is the Cat’s Eye Nebula, a planetary nebula characterized by its striking blue-green hue and ethereal appearance. The nebula’s intricate structure, resembling a glowing feline eye, is a result of a dying star casting off its outer layers and illuminating the surrounding gas. Another celestial gem in Draco is NGC 6543, famously known as the Draco Triple Ring. This planetary nebula showcases three concentric rings, which are believed to be the remnants of multiple ejections of material from the central star. Lastly, the Draco Dwarf Galaxy, a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way, captures the imagination with its faint glow among the countless stars. Located approximately 260,000 light-years away, this dwarf galaxy offers insights into the nature of galaxy formation and evolution. With each deep-sky object in Draco holding its own allure and mystery, set your sights on these celestial wonders for an unforgettable journey through the cosmos.
1. The Cat’s Eye Nebula
The Cat’s Eye Nebula, also known as NGC 6543, is a mesmerizing celestial object located within the Draco constellation. Its distinctive name comes from its remarkable appearance, which resembles a glowing cat’s eye when observed through a telescope. This planetary nebula is the remnant of a dying star, shedding its outer layers into space in a beautiful display of cosmic artistry. The central star, which once resembled our Sun, has now transformed into a white dwarf, surrounded by intricate concentric rings of gas and dust. These rings are illuminated by ultraviolet radiation emitted by the hot central star, causing the nebula to radiate vibrant colors, including shades of green and blue. The Cat’s Eye Nebula has been a subject of intense study and fascination for astronomers due to its complex structure and unique properties. The intricate details of its rings and shells provide insights into the late stages of stellar evolution and the mechanisms behind the formation of such stunning nebulae. Its distance from Earth, estimated to be around 3,000 light-years, makes it a relatively nearby and accessible object for observation and analysis. Captivating and enigmatic, the Cat’s Eye Nebula stands as a testament to the remarkable beauty and complexity that exists within our vast universe.
2. NGC 6543: The Draco Triple Ring
NGC 6543, famously known as the Draco Triple Ring, is a remarkable planetary nebula situated within the boundaries of the Draco constellation. This celestial gem, located approximately 3,000 light-years away from Earth, captivates astronomers and stargazers alike with its stunning appearance. The Draco Triple Ring is formed by a dying star, shedding its outer layers and illuminating the surrounding gases. What makes this nebula particularly intriguing is its three distinct rings, giving it its name. The innermost ring showcases a glowing blue hue, while the middle ring radiates a vibrant red color. The outer ring, with a fainter glow, completes the mesmerizing trio. Astronomical observations have revealed that the central star of NGC 6543 is a binary system, consisting of two stars orbiting one another. This unique characteristic adds to the enigma and beauty of the Draco Triple Ring. It is believed that the intricate structures seen in the nebula result from the complex interactions between the central binary system and the surrounding material. NGC 6543 serves as a reminder of the stunning and diverse celestial wonders that grace our universe, urging us to continue exploring and marveling at the mysteries that lie beyond our reach.
3. Draco Dwarf Galaxy
The Draco Dwarf Galaxy is a small and faint galaxy that is part of the Local Group, a collection of galaxies that includes the Milky Way. Named after the Draco constellation in which it is located, this dwarf galaxy captivates astronomers with its intriguing features. Spanning only about 3,000 light-years in diameter, the Draco Dwarf Galaxy is considered one of the smallest galaxies in the Local Group. It is located approximately 260,000 light-years away from Earth. The galaxy is characterized by its relatively low abundance of heavy elements, such as oxygen and iron. Astronomers believe that the Draco Dwarf Galaxy may have experienced multiple episodes of star formation throughout its history. The presence of young stars, as well as stellar populations dating back billions of years, provides valuable insights into the galaxy’s evolution. With its proximity to the Milky Way, the Draco Dwarf Galaxy has been subject to tidal interactions, which have influenced its structure and star formation activity. These interactions between galaxies can cause distortions and trigger the formation of new stars. Studying the Draco Dwarf Galaxy and other dwarf galaxies can provide valuable information about the processes of galaxy formation and the evolution of the universe as a whole. Astronomers continue to explore this diminutive galactic neighbor, unraveling its secrets and expanding our understanding of the cosmos.
Draco in Modern Astrology
Draco, though not traditionally a part of the zodiac, has found its place in modern astrology. Astrologers have attributed various meanings and interpretations to the constellation, drawing inspiration from its mythical symbolism. In modern astrology, Draco represents power, transformation, and spiritual growth. It is seen as a constellation that brings intensity and depth to the astrological chart. Individuals with strong Draco placements in their birth chart are believed to possess a potent force within them, capable of overcoming challenges and achieving great personal transformation. Draco is often associated with the energy of the dragon, symbolizing inner strength, intuition, and the ability to rise above adversity. Its influence can bring a sense of mystery and depth to a person’s personality, encouraging them to embrace their hidden potential and navigate life’s twists and turns with resilience. While not as widely recognized as the traditional zodiac signs, Draco holds a unique and compelling place in modern astrological interpretations, offering a different perspective on personality traits and life experiences. For astrology enthusiasts seeking a deeper understanding of their own journey, exploring the influence of Draco can provide valuable insights and guidance.
Conclusion

In conclusion, delving into the secrets of the Draco constellation has been a captivating journey. From its mythical origins and historical significance to its notable features and deep-sky objects, Draco has left an indelible mark on human imagination. Its association with dragons in various cultures has fascinated people for centuries, adding a touch of mystique to our understanding of the celestial world. The North Star Thuban, the Dragon’s Head and Tail, and the Quadrantids Meteor Shower are just a few of the remarkable features that make Draco a constellation worth exploring. Additionally, the deep-sky objects within Draco, such as the Cat’s Eye Nebula, NGC 6543: The Draco Triple Ring, and the Draco Dwarf Galaxy, offer celestial wonders that continue to astound astronomers and stargazers alike. Moreover, the influence of Draco extends beyond mythology and astronomy into modern astrology, where it plays a significant role in shaping interpretations and horoscopes. Overall, the Draco constellation invites us to gaze at the stars with wonder and curiosity, reminding us of the vastness and complexity of the universe we inhabit. As we continue to explore the secrets of our cosmos, Draco will remain a guide, captivating our imagination and inspiring us to reach for the stars.
Frequently Asked Questions

1. Is Draco visible all year round?
Yes, Draco is visible in the northern hemisphere throughout the year. However, its visibility may vary depending on the time of year and your location.
2. How do I locate Draco in the sky?
To locate Draco, look for the Big Dipper constellation. Follow the last two stars of the Big Dipper’s bowl, and they will lead you to the head of Draco.
3. Can I see the North Star within Draco?
No, the North Star or Polaris is not a part of the Draco constellation. However, it is located very close to the tip of the Little Dipper’s handle, which is in the same region of the sky.
4. Are there any notable stars in Draco?
While Draco does not contain any particularly bright stars, Thuban, also known as Alpha Draconis, used to serve as the North Star around 4,000 years ago.
5. What is the mythology behind Draco?
According to Greek mythology, Draco represents the dragon that guarded the Golden Apples of the Hesperides. It was slain by the hero Hercules during his twelve labors.
6. Are there any deep-sky objects within Draco?
Yes, Draco boasts several fascinating deep-sky objects, including the Cat’s Eye Nebula, NGC 6543, and the Draco Dwarf Galaxy.
7. Can I see any meteor showers associated with Draco?
Yes, Draco is associated with the Quadrantids meteor shower, which peaks in early January each year. Keep an eye out for shooting stars radiating from the northern sky.
8. How far away is Draco from Earth?
The distance between Earth and Draco varies depending on the specific object within the constellation. However, on average, Draco is located approximately 260 light-years away from us.
9. Is Draco part of the zodiac?
Draco was once part of the zodiac but was later removed by astronomer Hipparchus. It was replaced by the constellation Ophiuchus.
10. What is the significance of Draco in astrology?
In astrology, Draco is not as widely recognized as other zodiac constellations. However, it is associated with strength, wisdom, and protection due to its dragon symbolism.
References
- The Mystery of the Dragon: Mythology and Astronomical …
- Exploring the Constellation of Draco: A Guide to Viewing from …
- The Draco Constellation – The Secret of Skinwalker Ranch Wiki
Frequently Asked Questions

1. Can I see the Draco Constellation with the naked eye?
Yes, the Draco Constellation is easily visible in the northern hemisphere with the naked eye. It can be seen all year round from latitudes between 90 degrees and -15 degrees.
2. What is the brightest star in Draco?
The brightest star in Draco is called Thuban. It was once the North Star around 4,500 years ago, and it has a visual magnitude of 3.6.
3. Does Draco have any interesting deep-sky objects?
Yes, Draco is home to several fascinating deep-sky objects, including the Cat’s Eye Nebula, NGC 6543: The Draco Triple Ring, and the Draco Dwarf Galaxy. These objects are a treat for astronomers and stargazers alike.
4. What is the mythology behind the Draco Constellation?
In Greek mythology, Draco is associated with the dragon Typhon, who fought against the gods. This dragon was eventually defeated and thrown into the sky, forming the constellation we know today.
5. Can I see the Quadrantids Meteor Shower from Draco?
No, you cannot see the Quadrantids Meteor Shower from Draco. This meteor shower is actually associated with the defunct constellation Quadrans Muralis, which is located near Draco.
6. Is Draco mentioned in astrology?
Yes, Draco is mentioned in modern astrology. It is believed to represent power, wisdom, and protection. People born under the sign of Draco are said to possess strong leadership qualities.
7. How far away is the Cat’s Eye Nebula?
The Cat’s Eye Nebula, located in Draco, is approximately 3,300 light-years away from Earth. It is a planetary nebula formed from the outer layers of a dying star.
8. Can I observe the Draco Dwarf Galaxy with a telescope?
Yes, the Draco Dwarf Galaxy can be observed with a telescope. It is a faint galaxy located in Draco and is part of the Local Group, which includes the Milky Way, Andromeda, and other small galaxies.
9. Is Draco visible from the Southern Hemisphere?
No, Draco is not visible from the Southern Hemisphere. It is a circumpolar constellation, meaning it never sets below the horizon for observers in the northern hemisphere.
10. Are there any notable star clusters in Draco?
While Draco is not known for its star clusters, it does have a few notable ones. One example is the open cluster NGC 6633, which contains dozens of stars and is located within the boundaries of the Draco constellation.