The vastness of space has long captivated our imaginations, and now it presents a new frontier for resource extraction. Asteroid mining, once the stuff of science fiction, is becoming more and more feasible with advancements in space technology. The idea of extracting valuable resources from asteroids has the potential to revolutionize our approach to resource acquisition and exploration. However, diving into this uncharted territory is no small feat. From navigating spacecraft to legal and ethical considerations, there are numerous challenges to overcome. In this article, we will delve into the world of asteroid mining, exploring its potential, techniques, and the current and future projects that aim to make this ambitious endeavor a reality.
Contents
- Asteroids: Nature’s Treasure Trove
- Asteroid Mining Techniques
- Challenges and Considerations
- Current and Future Asteroid Mining Projects
- Potential Applications and Benefits
- Environmental Impact and Sustainability
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the main motivation behind asteroid mining?
- How are asteroids classified based on their composition?
- How are asteroids identified and selected for mining?
- What are the key techniques used for asteroid mining?
- What are the legal and ethical implications of asteroid mining?
- Which companies or organizations are currently involved in asteroid mining projects?
- What potential applications and benefits could asteroid mining offer?
- What is the environmental impact of asteroid mining?
- How does asteroid mining contribute to space exploration and colonization?
- What are the challenges in the field of asteroid mining?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How do asteroids form and where are they located?
- 2. What are the main resources that can be extracted from asteroids?
- 3. How are asteroids classified?
- 4. What techniques are used to prospect and identify suitable asteroids for mining?
- 5. How is extraction and processing of resources carried out on asteroids?
- 6. What is In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU) and why is it important for asteroid mining?
- 7. What are the major challenges in asteroid mining?
- 8. What are some current asteroid mining projects?
- 9. How can asteroid mining benefit space exploration and colonization?
- 10. How does asteroid mining contribute to environmental sustainability?
- References
- Read More
Asteroids: Nature’s Treasure Trove

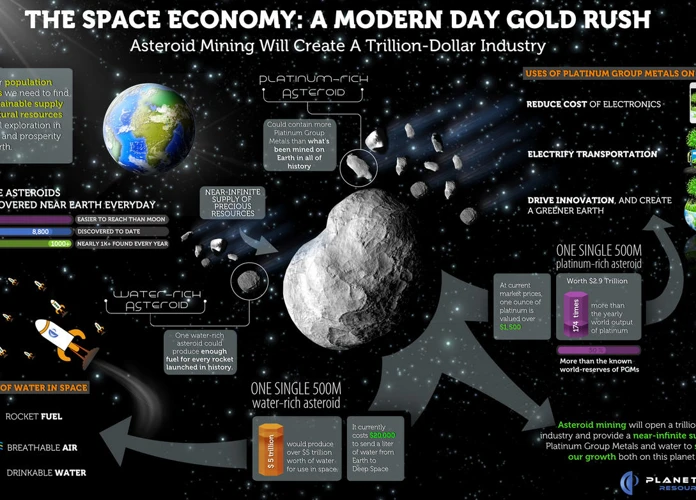
Asteroids, small rocky objects that orbit the sun, hold a wealth of resources that could be invaluable for future space exploration and resource extraction. These celestial bodies are often referred to as “nature’s treasure trove” due to their composition and potential resource abundance. Unlike planets, asteroids have not experienced the same geological processes that can alter or deplete their resources over time. This means that asteroids retain a pristine record of the early solar system, making them rich in minerals, metals, and even volatile compounds such as water ice. Some of the most sought-after resources found in asteroids include precious metals like platinum, valuable rare earth elements, and potentially even energy-rich helium-3 for future fusion power generation. Additionally, the water present in certain asteroids can be extracted and used to sustain human life in space, or broken down into its constituent hydrogen and oxygen for use as rocket propellant. The variety and abundance of resources found in asteroids make them an enticing target for mining operations, opening up a new realm of possibilities for space exploration and resource utilization.
Asteroid Composition and Resources
Asteroids possess a diverse composition and are composed of a variety of materials that make them enticing targets for resource extraction. These rocky bodies can contain valuable metals, such as platinum, gold, and nickel, which are highly sought after for their industrial and technological applications. They can also contain rare earth elements, which are crucial for electronic devices and renewable energy technologies. Additionally, certain types of asteroids known as carbonaceous asteroids contain organic compounds, including water ice and amino acids, which are essential for sustaining life. Water extraction from these asteroids could provide a vital resource for future space missions, enabling human exploration and colonization. The composition of asteroids can vary significantly depending on their classification, with some containing a higher abundance of metals while others are predominantly composed of carbonaceous materials. Understanding the composition of asteroids is essential for determining their resource potential and developing effective mining strategies in the future.
Types of Asteroids
Types of asteroids can vary in composition, size, and location in the solar system. The classification of asteroids is primarily based on their composition, which can influence their resource potential and suitability for mining. C-type asteroids, also known as carbonaceous asteroids, are the most common type and are rich in water, organic compounds, and volatiles. These asteroids are particularly intriguing as they may contain valuable resources such as water ice that could be used for sustaining life and fuel production. S-type asteroids, or silicate asteroids, are composed mainly of silicate minerals and contain a higher concentration of valuable metals like nickel, iron, and platinum. These metals have industrial and commercial applications on Earth and could become important resources in the future. Lastly, M-type asteroids, or metallic asteroids, are primarily composed of metal alloys such as iron and nickel. These asteroids are believed to be remnants of the metallic cores of differentiated protoplanets and may contain a significant amount of precious metals like gold, silver, and platinum group elements. Understanding the composition and characteristics of different types of asteroids is essential for targeting specific resources and planning mining missions. With advancements in asteroid prospecting and identification technologies, scientists and researchers are gaining valuable insights into the types of asteroids that exist in our solar system, fueling the excitement surrounding potential mining ventures.
Asteroid Mining Techniques
Asteroid mining techniques encompass a range of sophisticated processes designed to extract valuable resources from these celestial bodies. One of the initial steps in asteroid mining is prospecting and identification, where telescopes and remote sensing instruments are employed to identify suitable asteroids that contain high concentrations of valuable resources. Once a target asteroid is identified, the next step is extraction and processing. Various methods can be used, including robotic mining, where autonomous machines are deployed to physically extract and collect resources from the asteroid’s surface. Another technique is the use of drills and excavators, which can penetrate the asteroid’s crust and extract valuable materials from within. In-situ resource utilization (ISRU) is also a key component of asteroid mining, where extracted resources are processed on-site to produce usable materials, such as metals or propellant. This reduces the need for transporting large amounts of raw materials back to Earth, making the mining process more efficient and cost-effective. As technology advances, innovative techniques such as laser ablation and electrostatic beneficiation are being explored to further enhance the mining process. Each of these techniques plays a crucial role in unlocking the potential of asteroid mining and paving the way for future resource extraction in space.
Prospecting and Identification
Prospecting and identification are crucial steps in the process of asteroid mining. The first challenge is to locate and characterize asteroids that have the desired composition and resource potential. Scientists and engineers rely on a range of techniques to prospect for suitable candidates. One method involves using ground-based telescopes to survey the night sky, searching for faint points of light that indicate the presence of asteroids. Another technique is space-based observation, which provides a clearer view of asteroids and their characteristics. To identify potential mining targets, scientists analyze the data collected from these observations, looking for asteroids that contain high concentrations of valuable resources. Spectroscopy is commonly used to determine the chemical composition of asteroids, as it provides information about the presence of different elements and compounds. By studying the reflected light from asteroids, scientists can gain insights into their mineralogy, presence of water, and even potential for organic compounds. The information obtained from prospecting and identification is crucial in selecting the most promising asteroids for further exploration and eventual mining operations.
Extraction and Processing
Extraction and processing are the key steps in asteroid mining that enable the retrieval and utilization of valuable resources from these celestial bodies. The process begins with identifying and selecting suitable asteroids for mining operations through prospecting techniques. Once a target asteroid has been chosen, the next step is to approach and land a spacecraft on its surface. This requires precise navigation and docking capabilities, as asteroids have low gravity and irregular shapes, making it challenging to establish a stable connection.
Once the spacecraft is successfully landed, extraction of resources can begin. Various techniques can be employed depending on the type of resources being targeted. For metallic resources, such as platinum or gold, the mining process may involve drilling, blasting, and excavation to break apart the asteroid and collect the valuable materials. For volatile resources like water ice, a method known as thermal mining can be utilized. This involves heating the asteroid’s surface using solar concentrators or microwaves to cause the icy material to vaporize. The resulting vapor can then be captured and condensed into a usable form.
After the extraction phase, the collected resources need to be processed and refined to separate the desired elements or compounds from the asteroid’s regolith or waste material. This can involve various techniques such as crushing, grinding, and chemical separation processes. Once the desired resources have been isolated, they can be stored on-site or transported back to Earth or other destinations for further use or commercial purposes.
It is important to note that extraction and processing operations in asteroid mining are still largely theoretical, with ongoing research and development aiming to validate and refine these techniques. The successful implementation of these processes would pave the way for a new era of resource utilization beyond Earth, providing valuable materials for space exploration, colonization efforts, and potentially addressing resource scarcity and sustainability challenges on our home planet.
In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU)
In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU) is a key concept in asteroid mining that involves utilizing local resources found on asteroids to sustain and support mining operations. This approach eliminates the need to transport large quantities of materials from Earth, reducing costs and increasing efficiency. One of the primary resources targeted for ISRU is water ice, which can be found in abundance in certain asteroids. Water ice is a versatile resource that can be used for a variety of purposes in space exploration. Firstly, it can be broken down into its constituent hydrogen and oxygen through electrolysis, providing a sustainable source of breathable air and propulsion fuel. Secondly, water can serve as a vital resource for sustaining human life on long-duration space missions or future colonization efforts. Additionally, water can be used for radiation shielding and as a coolant for equipment. Another resource of interest for ISRU is regolith, the loose surface material found on asteroids. Regolith can be processed to extract valuable metals and minerals, such as platinum group metals, iron, nickel, and rare earth elements. These metals and minerals can be used for various purposes, including construction, manufacturing, and energy generation. Implementing ISRU techniques in asteroid mining is essential for achieving sustainability and self-sufficiency in space exploration, paving the way for long-term space missions and facilitating the establishment of human presence beyond Earth.
Challenges and Considerations
Challenges and considerations arise when it comes to venturing into the world of asteroid mining. One of the primary challenges is spacecraft navigation and retrieval. Navigating through space to reach specific asteroids requires precise calculations and trajectory adjustments to account for gravitational forces and orbital dynamics. Additionally, the retrieval of mined resources poses logistical challenges, as the mass and volume of extracted materials need to be safely transported back to Earth or utilized in space. A key consideration in asteroid mining is the legal and ethical implications surrounding resource extraction. The Outer Space Treaty, signed by various nations, prohibits any nation from claiming celestial bodies, including asteroids, as national territory. This raises questions regarding ownership and the distribution of mined resources. Addressing these legal and ethical concerns is crucial to ensure responsible and fair practices in asteroid mining. The sustainability of asteroid mining is also a concern. While asteroids offer abundant resources, their finite nature necessitates careful management and extraction techniques to avoid depleting them too quickly. Implementing sustainable mining practices and considering the long-term impact on the asteroid’s composition and stability are essential. Addressing these challenges and considerations will pave the way for the successful and responsible development of asteroid mining projects in the future.
Spacecraft navigation and retrieval pose significant challenges in the field of asteroid mining. Due to the vast distances and complex orbital dynamics involved, precise navigation is crucial to ensure successful missions. Autonomous navigation systems equipped with sensors and imaging technologies are employed to enable spacecraft to navigate through the vastness of space and identify suitable asteroid targets. Once a target is identified, the retrieval process becomes a delicate operation. The spacecraft must approach the asteroid carefully, often using thrusters to maintain a stable position. Specialized robotic tools and drills are then employed to extract the desired resources from the asteroid’s surface or interior. The retrieval process must be carefully planned and executed to prevent damage to the spacecraft and ensure the safe retrieval of the extracted resources. These technological challenges are critical to overcome in order to unlock the vast resource potential of asteroids and pave the way for future space exploration and sustainable resource utilization.
Legal and Ethical Implications
Legal and ethical implications surrounding asteroid mining are crucial considerations as we navigate this new domain of resource extraction. From a legal perspective, the ownership and rights to mine asteroids have been a subject of international debate. The Outer Space Treaty of 1967, ratified by most spacefaring nations, states that celestial bodies and their resources cannot be claimed by any nation. However, there is ongoing discussion about whether this applies to private entities or if a more comprehensive legal framework is needed to regulate asteroid mining operations. Another legal aspect is the liability associated with mining activities in space. If a mining operation unintentionally causes damage to another asteroid or satellite, who bears the responsibility and potential consequences? These are questions that need to be addressed to ensure a fair and equitable framework for all parties involved.
Ethically, the potential impact of asteroid mining on celestial bodies and its implications for scientific research needs to be taken into account. Some argue that mining asteroids could disrupt the natural balance and potentially hinder our understanding of the solar system’s history. Additionally, the extraction and utilization of extraterrestrial resources raise questions about environmental sustainability and the preservation of celestial bodies as unique scientific and cultural heritage sites. As we venture into asteroid mining, it is crucial to establish ethical guidelines and protocols that prioritize scientific exploration, respect for indigenous cultures, and sustainable resource management.
The legal and ethical implications surrounding asteroid mining are multifaceted and require careful consideration. It is essential for international agreements and regulations to be established to ensure responsible and sustainable practices in this emerging industry. By addressing these concerns, we can navigate this new frontier while preserving the integrity of celestial bodies and upholding the values of scientific exploration and resource stewardship.
Current and Future Asteroid Mining Projects

Current and future asteroid mining projects are paving the way for the exploration and extraction of resources from these celestial bodies. One notable company involved in this endeavor is Deep Space Industries (DSI). DSI aims to develop innovative technologies for prospecting, mining, and utilizing asteroid resources. Their plans include identifying suitable asteroids for mining, extracting valuable materials, and using in-situ resource utilization (ISRU) techniques. Another key player in the field is Planetary Resources, which envisions a future where asteroid mining becomes a sustainable industry. They have developed spacecraft and robotic technology to enable the identification, characterization, and extraction of resources from asteroids. Additionally, NASA’s Asteroid Redirect Mission (ARM) aims to demonstrate the feasibility of capturing and redirecting an asteroid to a stable orbit around the Moon for subsequent exploration and potential resource utilization. These projects, along with other emerging initiatives, hold great promise for unlocking the vast potential of asteroid mining and propelling humanity into a new era of space exploration and resource acquisition.
Deep Space Industries (DSI)
Deep Space Industries (DSI) is a private space exploration company that is at the forefront of asteroid mining efforts. Founded in 2012, DSI aims to develop the necessary technologies and infrastructure to identify, extract, and process resources from asteroids. One of their key projects is the Prospector-1 mission, which is set to be the world’s first commercial interplanetary mining mission. The Prospector-1 spacecraft, equipped with advanced imaging and spectrometry instruments, will be sent to a near-Earth asteroid to prospect for valuable resources. DSI envisions a future where space resources are utilized to fuel human expansion and exploration in space, while also benefiting our planet by reducing the environmental impact of terrestrial resource mining. Through their innovative approach and commitment to advancing asteroid mining technologies, DSI is playing a crucial role in unlocking the potential of asteroids as abundant sources of precious resources.
Planetary Resources
Planetary Resources is a prominent company at the forefront of asteroid mining efforts. Founded in 2009, their mission is to harness the vast resources of asteroids to enable the expansion of humanity into space. With a focus on technological advancements and innovation, Planetary Resources aims to develop cost-effective and sustainable methods for prospecting, extracting, and refining resources from asteroids. Their approach involves the use of small spacecraft equipped with advanced sensors and robotic systems to survey asteroids and identify potential mining targets. The company also places emphasis on the utilization of in-situ resource utilization (ISRU) techniques, meaning they aim to process and use the resources directly in space rather than bringing them back to Earth. Planetary Resources has attracted significant investment and partnerships from individuals and organizations in both the private and public sectors, including billionaires such as Larry Page and Richard Branson. Their ambitious vision and commitment to unlocking the potential of asteroids make them a key player in the realization of asteroid mining as a viable industry. [Anchor: /big-dipper-in-different-cultures/]
NASA’s Asteroid Redirect Mission (ARM)
NASA’s Asteroid Redirect Mission (ARM) is an ambitious project aimed at advancing our understanding of asteroids and developing techniques for future asteroid mining endeavors. The primary objective of ARM is to identify, capture, and redirect a small asteroid to a stable orbit around the moon. This mission serves as a crucial stepping stone towards mining asteroids by providing valuable data on asteroid composition, structure, and behavior. ARM consists of two major components: the Asteroid Redirect Robotic Mission (ARRM) and the Asteroid Redirect Crewed Mission (ARCM). The ARRM involves the use of a robotic spacecraft to rendezvous with a target asteroid, perform detailed investigations, and collect a multi-ton boulder from its surface. This boulder will then be redirected to a lunar orbit using solar electric propulsion. The ARCM, on the other hand, will involve astronauts visiting the captured asteroid in the lunar orbit to further study and gather samples for analysis. The knowledge gained from ARM will not only inform future resource extraction techniques but also contribute to our understanding of the threat asteroids pose to Earth and potential methods for planetary defense. Through such missions, NASA aims to pave the way for future asteroid mining endeavors and expand our capabilities in space exploration.
Potential Applications and Benefits

The potential applications and benefits of asteroid mining are vast and far-reaching. Here are some of the key areas where asteroid mining can have a significant impact:
1. Space Exploration and Colonization: The availability of resources from asteroids can greatly support human space exploration and colonization efforts. By extracting water from certain asteroids, it becomes possible to produce life-sustaining resources such as oxygen for breathing and hydrogen for fuel. This would reduce the need for resupply missions from Earth, making long-term missions and establishing bases on the Moon, Mars, or beyond more sustainable.
2. Strategic Resource Availability: Earth’s limited resources can be supplemented and augmented through asteroid mining. Precious metals like platinum, gold, and rare earth elements that are critical for many industries can be extracted from asteroids. This would ensure a continuous supply of these resources without depleting the finite amounts available on our planet.
3. Scientific Research: The study of asteroids provides invaluable insights into the early history of the solar system. By mining and analyzing their composition, scientists can deepen their understanding of planetary formation, the origin of life, and the potential for habitable environments elsewhere in the universe.
4. Technological Advancements: The pursuit of asteroid mining necessitates advancements in various fields including robotics, spacecraft design, and resource extraction techniques. These developments can have spin-off benefits for other industries on Earth and push the boundaries of technology, fueling innovation and creating new opportunities.
5. Economic Opportunities: The successful establishment of asteroid mining operations could potentially lead to a new industry with significant economic benefits. Job creation, technological innovation, and the availability of valuable resources in space could stimulate economic growth and the development of new markets.
6. Environmental Conservation: By mining resources from asteroids, we can reduce the need for extensive terrestrial mining operations, which often have significant environmental impacts. Asteroid mining has the potential to lessen our dependence on Earth’s limited resources, preserving and protecting our planet’s natural ecosystems.
Harnessing the potential applications and benefits of asteroid mining requires overcoming various challenges, but the prospects of unlocking the vast resources available in space are tantalizing. By venturing into this new frontier, we can not only expand our understanding of the cosmos but also pave the way for a more sustainable and prosperous future.
Space Exploration and Colonization
Space exploration and colonization are two significant areas that could greatly benefit from asteroid mining. The resources extracted from asteroids can fuel future deep space missions, allowing for further exploration of our solar system and beyond. The availability of water ice in certain asteroids is of particular interest, as it can be used to produce breathable air and drinking water for astronauts, reducing the need for costly resupply missions from Earth. The extraction of metals and minerals from asteroids can provide the necessary materials for constructing habitats, spacecraft, and infrastructure needed for human colonization of other celestial bodies, such as the Moon or Mars. By utilizing the resources already present in space, we can significantly reduce the cost and logistical challenges associated with long-duration space missions and pave the way for a sustainable and self-sufficient future in outer space. The potential synergy between asteroid mining and space exploration is an exciting prospect that may shape the future of interplanetary travel and the realization of ambitious colonization efforts.
Strategic Resource Availability
The availability of strategic resources is a crucial aspect of asteroid mining that holds significant implications for various industries and technologies. Asteroids contain a wide range of resources that are considered strategically important due to their scarcity or limited accessibility on Earth. For instance, rare earth elements, which are essential for manufacturing electronics and advanced technologies, are found in abundance within certain asteroids. By extracting these resources from asteroids, we can reduce our dependence on terrestrial reserves, which are subject to geopolitical tensions and potential supply disruptions. The utilization of asteroid resources can spur innovation and development in industries such as renewable energy, aerospace, and telecommunications. For example, the availability of platinum group metals from asteroids could enable the production of more efficient fuel cells and catalytic converters. Additionally, the accessibility of water ice on asteroids has the potential to revolutionize space exploration by providing a sustainable supply of water, oxygen, and hydrogen for long-duration missions. The strategic resource availability offered by asteroid mining opens up new possibilities for technological advancement and resilience, ensuring a more sustainable and prosperous future for humankind.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
As we venture into asteroid mining, it becomes essential to consider the potential environmental impact and strive for sustainable practices. One significant advantage of asteroid mining is the potential to reduce terrestrial resource extraction, which often involves harmful practices and contributes to land degradation, water pollution, and deforestation. By harnessing the resources readily available in space, we can alleviate some of the pressures on our planet’s ecosystems. Additionally, asteroid mining can contribute to space debris mitigation. Satellites, rocket parts, and other space junk pose a growing problem in Earth’s orbit. By extracting resources from asteroids, we can potentially repurpose and recycle existing space debris, reducing the clutter and minimizing the risk of collisions. Sustainability is at the forefront of many space agencies’ plans, and efforts are being made to develop innovative solutions for sustainable asteroid mining. For instance, in-situ resource utilization techniques can minimize the need to transport resources from Earth and rely on locally available materials instead. This approach reduces the energy consumption and associated carbon footprint of mining operations. By establishing sustainable mining practices from the beginning, we can ensure that the benefits of asteroid mining outweigh any potential environmental drawbacks. It is crucial to approach asteroid mining with a long-term perspective, considering the potential consequences and striving for sustainable practices that promote the well-being of both Earth and space.
Reducing Terrestrial Resource Extraction
Reducing terrestrial resource extraction is one of the key benefits of asteroid mining. By tapping into the vast resources available in asteroids, we can alleviate the strain on our planet’s limited resources. Traditional mining practices on Earth often result in environmental degradation, habitat destruction, and the release of harmful pollutants. However, by shifting resource extraction operations to asteroids, we can minimize these negative impacts. Extracting resources from asteroids means less mining on Earth, leading to reduced deforestation, lower carbon emissions, and the preservation of natural habitats. Asteroid mining can provide a sustainable and renewable source of raw materials for industries here on Earth, reducing the need for continuous extraction from our planet’s fragile ecosystems. By embracing the potential of asteroid mining, we can take a step towards a more environmentally conscious and sustainable future.
Space Debris Mitigation
Space debris mitigation is a critical aspect of asteroid mining endeavors that cannot be overlooked. As humans continue to explore and exploit space resources, the accumulation of space debris poses a significant threat to both operational spacecraft and existing satellites. Space debris refers to defunct satellites, spent rocket stages, and fragments from previous space missions that orbit the Earth. These objects move at incredibly high speeds, making even the smallest debris a potential hazard capable of causing catastrophic damage to operational spacecraft. By engaging in asteroid mining activities, we can indirectly contribute to space debris mitigation. By extracting resources from asteroids, we can reduce the need for terrestrial mining and manufacturing processes, which in turn reduces the number of rockets and satellites launched into space. This reduces the risk of collision and subsequent space debris generation. Additionally, by utilizing in-situ resource utilization techniques, such as extracting water from asteroids, we can minimize the need to transport resources from Earth, further reducing the number of launches and potential space debris. As we navigate the burgeoning field of asteroid mining, it is crucial to prioritize space debris mitigation to ensure the long-term sustainability of space exploration and safeguard the vastness of the cosmos.
Preserving Earth’s Natural Resources
Preserving Earth’s natural resources is one of the key benefits of asteroid mining. By extracting valuable resources from asteroids, we can reduce our reliance on terrestrial mining operations, which often have significant environmental impacts. Traditional mining methods on Earth can lead to habitat destruction, air and water pollution, and the release of greenhouse gases. Asteroid mining offers a more sustainable alternative, as it allows us to access resources without damaging the delicate ecosystems of our planet. By sourcing materials such as metals, minerals, and even water from asteroids, we can alleviate the strain on Earth’s resources and minimize the need for destructive mining practices. This not only helps protect our environment but also ensures the availability of vital resources for future generations. With asteroid mining, we have the opportunity to explore and utilize extraterrestrial resources while simultaneously preserving and safeguarding the resources of our own planet. It represents a step towards a more sustainable and responsible approach to resource extraction.
Conclusion

In conclusion, asteroid mining represents an exciting and promising avenue for resource extraction in the future. The vast potential of asteroids as treasure troves of valuable resources, coupled with advancements in space technology, has brought us to the brink of embarking on this new frontier. While there are numerous challenges and considerations to overcome, such as spacecraft navigation, legal and ethical implications, and environmental sustainability, the rewards are immense. Asteroid mining has the potential to revolutionize space exploration, provide strategic resource availability, and reduce our dependence on terrestrial resource extraction. It also offers opportunities for space colonization and a means to mitigate the growing issue of space debris. As we continue to push the boundaries of human ingenuity and explore the vast cosmic expanse, asteroid mining promises to unlock a wealth of resources and expand our horizons in ways we have yet to fathom. The future of mining may indeed lie in the stars.
Frequently Asked Questions

What is the main motivation behind asteroid mining?
The main motivation behind asteroid mining is the abundance of valuable resources that asteroids contain, such as precious metals, rare earth elements, and water. These resources can be used to support human missions in space, provide a sustainable source of materials for future colonization efforts, and reduce our reliance on Earth’s limited resources.
How are asteroids classified based on their composition?
Asteroids are classified into three main categories based on their composition: C-type (carbonaceous), S-type (silicate), and M-type (metallic). C-type asteroids are rich in carbon and contain volatiles like water and organic compounds. S-type asteroids are composed of silicate minerals, while M-type asteroids are predominantly metallic, consisting of iron and nickel.
How are asteroids identified and selected for mining?
Asteroids are identified and selected for mining through a process called prospecting. Scientists use telescopes and space missions to study asteroids’ size, composition, and proximity to Earth. They also look for asteroids with accessible orbits, low delta-v (change in velocity) requirements, and an abundance of valuable resources.
What are the key techniques used for asteroid mining?
The key techniques used for asteroid mining are prospecting and identification, extraction and processing, and in-situ resource utilization (ISRU). Prospecting involves studying asteroids to assess their resource potential. Extraction and processing techniques can vary but may involve drilling, crushing, and refining methods. ISRU involves utilizing resources on-site for activities such as producing fuel or construction materials.
What are the legal and ethical implications of asteroid mining?
The legal and ethical implications of asteroid mining are complex. There is currently no internationally agreed-upon framework for governing asteroid mining activities. Questions arise regarding property rights, space traffic management, environmental impacts, and the preservation of celestial bodies for scientific study. Efforts are underway to establish regulations and guidelines to address these concerns.
Which companies or organizations are currently involved in asteroid mining projects?
Several companies and organizations are actively involved in asteroid mining projects. Notable players in the industry include Deep Space Industries (DSI), Planetary Resources, and NASA with its Asteroid Redirect Mission (ARM). These entities are pioneering new technologies and strategies for the future of asteroid mining.
What potential applications and benefits could asteroid mining offer?
Asteroid mining has the potential to revolutionize space exploration and colonization. The resources extracted from asteroids can sustain human missions in space, provide materials for constructing habitats and spacecraft, and offer strategic resources to support future industries. It also reduces the need for terrestrial resource extraction and helps mitigate space debris by utilizing materials from asteroids.
What is the environmental impact of asteroid mining?
Asteroid mining has the potential to reduce the environmental impact of terrestrial resource extraction. By sourcing materials from asteroids, we can minimize harmful mining practices on Earth’s delicate ecosystems. Additionally, asteroid mining can contribute to space debris mitigation by utilizing resources already present in space instead of adding more debris through traditional manufacturing methods.
How does asteroid mining contribute to space exploration and colonization?
Asteroid mining contributes to space exploration and colonization by providing essential resources for sustained human presence in space. It can provide materials for building habitats, manufacturing equipment, and maintaining life support systems. By utilizing resources from asteroids, we can establish a more self-sufficient presence in space and reduce the reliance on resupply missions from Earth.
What are the challenges in the field of asteroid mining?
The field of asteroid mining faces numerous challenges. These include spacecraft navigation and retrieval, developing efficient and cost-effective mining techniques, addressing the legal and ethical concerns surrounding property rights and environmental impacts, and ensuring the safety of mining operations in space. Overcoming these challenges requires significant technological advancements and international cooperation.
References
Frequently Asked Questions

1. How do asteroids form and where are they located?
Asteroids are rocky bodies that are believed to have formed during the early stages of the solar system’s formation. They are primarily located in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter, but can also be found in other regions, such as near Earth.
2. What are the main resources that can be extracted from asteroids?
Asteroids are rich in valuable resources such as metals like iron, nickel, and platinum group metals, as well as water, which can be extracted and used as a vital resource for future space missions.
3. How are asteroids classified?
Asteroids are classified into three main types based on their composition: C-type asteroids, which are carbon-rich and abundant in water; S-type asteroids, which are rocky and metallic; and M-type asteroids, which are metallic in nature and contain a higher percentage of nickel and iron.
4. What techniques are used to prospect and identify suitable asteroids for mining?
Scientists and engineers use a variety of techniques, including telescopic observations, remote sensing, and spectroscopy, to identify and characterize potential asteroids for mining. They analyze the composition, size, and orbit of the asteroids to determine their suitability for resource extraction.
5. How is extraction and processing of resources carried out on asteroids?
After a suitable asteroid is identified, extraction techniques such as drilling, blasting, and surface mining can be employed to obtain the desired resources. Once the resources are extracted, they can be processed using various methods such as heating or chemical reactions to refine and purify them.
6. What is In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU) and why is it important for asteroid mining?
In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU) refers to the utilization of resources available on-site or in close proximity to a specific location. ISRU is crucial for asteroid mining as it allows for the extraction and utilization of resources directly from the asteroid, reducing the need for transportation of resources from Earth and lowering costs.
7. What are the major challenges in asteroid mining?
The major challenges in asteroid mining include spacecraft navigation and retrieval, as asteroids can have irregular shapes and variable compositions. There are also legal and ethical implications related to space mining, such as ownership rights and the potential impact on the space environment.
8. What are some current asteroid mining projects?
Some current asteroid mining projects include Deep Space Industries (DSI) and Planetary Resources, which are privately funded companies aiming to develop technologies and infrastructure for asteroid mining. NASA’s Asteroid Redirect Mission (ARM) also focuses on the study and potential mining of asteroids.
9. How can asteroid mining benefit space exploration and colonization?
Asteroid mining can provide essential resources for space missions, reducing reliance on Earth’s limited resources. It can also serve as a stepping stone for further exploration and colonization of space, enabling sustained human presence in space and supporting future space habitats.
10. How does asteroid mining contribute to environmental sustainability?
Asteroid mining has the potential to reduce terrestrial resource extraction, as resources can be obtained from space instead. This can help preserve Earth’s natural resources and mitigate the environmental impact associated with traditional mining activities. Additionally, asteroid mining can contribute to space debris mitigation efforts by removing potentially hazardous asteroids from near-Earth orbits.