From the enchanting tales of ancient mythology to the awe-inspiring discoveries of modern science, the evolution of constellations is a captivating journey that spans centuries. In this article, we delve into the origins of constellations, exploring the mythical stories that inspired their creation and the cultural influences that shaped their identities. We then shift our focus to the birth of scientific constellations, paying homage to the ancient astronomers whose groundbreaking contributions paved the way for our understanding of the celestial realm. As we delve deeper, we uncover the development of celestial coordinate systems and the role of the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in officially naming and recognizing constellations. With the advent of technological advancements, we also explore the world of constellation mapping and visualization techniques, from traditional stellar cartography to cutting-edge 3D visualization and virtual reality applications. Finally, we turn our gaze towards the future, contemplating the possibilities that lie ahead in constellation research, including the integration of artificial intelligence and the ethical considerations surrounding modern naming conventions. Join us as we embark on a fascinating expedition through time and space, unraveling the mysteries of the cosmos.
Contents
- Ancient Mythology and Constellations
- The Birth of Scientific Constellations
- Modern Constellations: A Scientific Approach
- Constellation Mapping and Visualization Techniques
- The Future of Constellations
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What is the significance of constellations in ancient mythology?
- 2. How did different cultures influence the creation of constellations?
- 3. How did ancient astronomers contribute to the study of constellations?
- 4. What was Ptolemy’s role in the evolution of modern constellations?
- 5. How were celestial coordinate systems developed?
- 6. Who has the authority to name and recognize constellations?
- 7. What are the techniques used in stellar cartography?
- 8. How has digital mapping revolutionized constellation visualization?
- 9. What are the applications of 3D visualization and virtual reality in understanding constellations?
- 10. What are the future possibilities for constellation research?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How did ancient civilizations use constellations for navigation?
- 2. How were constellations named in ancient mythology?
- 3. What contributions did ancient astronomers make to the development of modern constellations?
- 4. How does the International Astronomical Union (IAU) play a role in modern constellations?
- 5. What are celestial atlases, and how are they used in constellation mapping?
- 6. How has digital mapping and software tools revolutionized constellation research?
- 7. What are the benefits of using 3D visualization and virtual reality in studying constellations?
- 8. How do advanced telescopes contribute to the future of constellation exploration?
- 9. How can artificial intelligence support constellation research?
- 10. What factors should be considered when naming new constellations?
- References
- Read More
Ancient Mythology and Constellations
Ancient mythology weaves a rich tapestry of stories and legends that ignited the imagination of civilizations past, giving rise to the creation of constellations. These celestial formations were not mere patterns in the night sky; they were an embodiment of the gods, heroes, and creatures of mythological lore. From the Greek myth of Perseus and his encounter with Medusa to the Egyptian tale of Osiris and Set, these ancient narratives served as the foundation for the mythological origins of constellations. Cultural influences further shaped the constellations, as different civilizations embraced their own interpretations and assigned unique names to the formations above. A fascinating example of this cultural diversity is the constellation Orion, known as “The Hunter” in Greek mythology but endowed with different significance in other cultures. The stories of ancient mythology intertwined with the celestial realm, forging a bond that transcended time and connected humanity to the cosmos. To explore lesser-known constellations and their hidden stories, click here.
1.1 Mythological Origins of Constellations
The mythological origins of constellations offer a captivating glimpse into the rich tapestry of ancient stories and beliefs that laid the groundwork for our understanding of the celestial realm. These stories varied across different cultures, each weaving their own narratives into the constellations that adorned the night sky. One such example is the Greek mythology that bestowed constellations with legendary tales of gods, heroes, and mythical creatures. The story of Perseus and his encounter with the monstrous Medusa, resulting in the creation of the constellation bearing his name, highlights the intertwining of myth and the celestial realm. Similarly, the constellation of Orion, known for its depiction of a mighty hunter, has roots in Greek mythology as well. These mythological origins provided ancient civilizations with a way to interpret and navigate the night sky, as they drew connections between the stories passed down through generations and the formations of stars above. To delve deeper into the cultural significance of constellations like the Big Dipper across different cultures, click here. The mythological origins of constellations reflect the imaginative prowess of ancient civilizations, who sought to understand and make meaning of the vast expanse of the universe.
1.2 Cultural Influences on Constellation Creation
Cultural influences played a significant role in the creation and interpretation of constellations, shaping the way different civilizations saw the celestial realm. Each culture imbued the night sky with their unique beliefs, stories, and values, resulting in diverse interpretations of the constellations. For example, in ancient Greece, constellations were often associated with the gods and heroes of their mythology. The story of Perseus, who slayed the Gorgon Medusa, gave rise to the constellation that bears his name. Similarly, the constellation Aquarius, representing the water-bearer, has ties to the myth of Ganymede, a mortal youth who became a cupbearer to the gods. In contrast, ancient Egyptian constellations were linked to their deities and pharaohs. The constellation of Orion was seen as the representation of the god Osiris, while the constellation of Ursa Major held a connection with the pharaohs and their role as rulers. Other cultures, such as the Chinese and Polynesian civilizations, also had their own unique constellations and celestial stories. These cultural influences not only brought a sense of identity to the constellations but also provided a way for people to connect with their heritage and understand their place in the world. To explore the compatibility between Libra and Aquarius and how their zodiac signs align, click here.
The Birth of Scientific Constellations
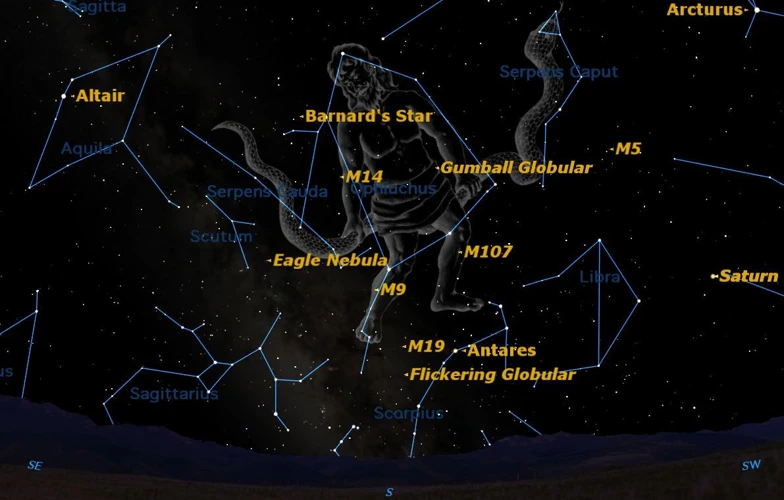
The birth of scientific constellations marked a significant shift in our understanding of the night sky, as ancient astronomers made groundbreaking contributions that laid the foundation for modern celestial knowledge. These early stargazers, such as Hipparchus and Claudius Ptolemy, observed and documented the motion of celestial bodies, developing mathematical models to explain their movements. Ptolemy’s influential work, “Almagest,” compiled the astronomical knowledge of the time, including a catalog of over 1,000 stars and a systematic framework for defining constellations. This manuscript became the cornerstone of astronomy for centuries, shaping the study of the stars. The scientific approach to constellations marked a departure from mythological interpretations, focusing instead on the precise measurement and categorization of celestial objects. It laid the groundwork for future advancements and opened the doors to further discoveries in the field of astronomy.
- Hipparchus and early astronomers observed and documented celestial motion.
- Ptolemy’s “Almagest” compiled astronomical knowledge and defined constellations.
- Scientific constellations shifted focus from mythology to precise measurement.
2.1 Contributions of Ancient Astronomers
Ancient astronomers made substantial contributions to our understanding of the night sky, laying the groundwork for the development of scientific constellations. Among these trailblazers was the Greek philosopher and mathematician Thales of Miletus, who is considered one of the first known astronomers. Thales predicted solar eclipses and studied the motion of celestial bodies, challenging prevailing beliefs that celestial events were the result of divine intervention. Another notable figure, Anaximander, proposed the concept of an Earth-centered universe with celestial bodies arranged in concentric circles. His work set the stage for the later development of the geocentric model.
Astronomer and mathematician Hipparchus made remarkable contributions to the field by introducing the concept of stellar magnitude and creating the first comprehensive catalog of stars. Hipparchus also noted the phenomenon of precession, the gradual shift in the Earth’s axis that impacts the position of stars over time. This groundbreaking discovery laid the foundation for understanding the long-term changes in the night sky.
Ancient astronomers in various civilizations also made significant advancements. For instance, the Indian astronomer Aryabhata accurately calculated the Earth’s circumference and proposed a heliocentric model in the 5th century. Chinese astronomers meticulously recorded celestial phenomena and developed elaborate calendars based on astronomical observations. These contributions collectively enriched our understanding of celestial objects and their movements.
The remarkable achievements of these ancient astronomers paved the way for future scientific discoveries and laid the foundation for the modern understanding of constellations. Their meticulous observations and mathematical calculations formed the basis for the development of precise celestial coordinate systems and the construction of comprehensive star catalogs. With their relentless pursuit of knowledge, these ancient scholars unlocked the secrets of the cosmos, forever transforming our understanding of the universe we inhabit.
2.2 Ptolemy’s Almagest and the Beginnings of Modern Constellations
Ptolemy’s Almagest played a pivotal role in the evolution of constellations, marking the beginnings of the transition from mythological to scientific interpretations. Ptolemy, a Greek astronomer and mathematician, compiled his extensive work in the 2nd century AD, serving as a comprehensive guide to the celestial sphere. In Almagest, Ptolemy cataloged and described 48 constellations, many of which are still recognized today. He introduced a coordinate system that divided the celestial sphere into degrees and minutes of arc, allowing for precise measurements and calculations. Ptolemy’s influential work laid the foundation for the modern understanding of constellations, establishing a scientific approach based on observation and mathematical principles. His contributions facilitated the study of stars and their positions, supporting advancements in navigation and astronomy. The legacy of Ptolemy’s Almagest endures to this day, serving as a cornerstone in the development of modern constellations and shaping our understanding of the vast cosmos.
Modern Constellations: A Scientific Approach
The scientific approach to constellations emerged with the contributions of ancient astronomers who meticulously observed and recorded celestial phenomena. These early astronomers, such as Claudius Ptolemy and Hipparchus, laid the groundwork for modern constellation studies. Ptolemy’s influential work, the Almagest, documented the positions and movements of stars, introducing the concept of celestial coordinate systems. This allowed astronomers to precisely locate and identify stars within the night sky. As scientific advancements continued, the International Astronomical Union (IAU) was established as the official body responsible for naming and recognizing constellations. Their efforts ensured a standardized approach to constellation designations and led to the creation of new constellations based on contemporary scientific discoveries. Today, constellations are not only a means to navigate the vastness of the night sky but also a testament to the ongoing evolution of our understanding of the universe. To explore the contemporary discoveries and revisions in the world of constellations, click here.
3.1 Development of Celestial Coordinate Systems
The development of celestial coordinate systems marked a significant milestone in the study of constellations and the celestial sphere. Early astronomers recognized the need for a standardized way to locate and identify celestial objects, leading to the creation of these coordinate systems. One of the oldest and most widely used systems is the equatorial coordinate system. It utilizes two coordinates: right ascension (RA) and declination (Dec) to precisely specify the position of an object in the sky. Right ascension is measured in hours, minutes, and seconds, representing the celestial equivalent of longitude, while declination is measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds, akin to latitude on Earth. Another commonly used system is the ecliptic coordinate system, which is based on the apparent path of the Sun against the backdrop of stars throughout the year. It utilizes celestial longitude (celestial equivalent of the Sun’s longitude along the ecliptic) and celestial latitude (measured perpendicular to the ecliptic), allowing astronomers to locate objects along the ecliptic plane. These coordinate systems served as crucial tools for astronomers, enabling them to record observations accurately and facilitating communication and collaboration across the scientific community. With these standardized systems in place, astronomers were able to map and chart the positions of stars and other celestial objects with greater precision, further advancing our understanding of the cosmos.
3.2 IAU: The Official Body for Naming and Recognizing Constellations
The recognition and naming of constellations are not simply left to individual interpretation or cultural tradition. The International Astronomical Union (IAU) serves as the official body responsible for overseeing the process of naming and recognizing constellations. Established in 1919, the IAU plays a crucial role in promoting international cooperation and standardization in astronomical research. The IAU’s role in constellation naming is guided by specific guidelines and criteria that ensure consistency and accuracy. They work closely with various astronomical societies, experts, and professional astronomers from around the world to review and determine the names and boundaries of constellations. With advancements in technology and the discovery of new celestial objects, the IAU also revises and updates constellation boundaries to reflect our expanding knowledge of the universe. These updates are made through a rigorous scientific process, ensuring that any changes to constellation boundaries are well-supported and based on sound astronomical principles. The IAU’s efforts in naming and recognizing constellations contribute to a unified understanding of the night sky across different cultures and allow astronomers and stargazers alike to communicate and share their observations effectively.
3.3 Contemporary Discoveries and Revisions
The field of astronomy is continuously advancing, and with it comes a wealth of contemporary discoveries and revisions in the realm of constellations. As technology and observational instruments become more sophisticated, astronomers are able to uncover new celestial objects and refine our understanding of existing ones. These recent discoveries have led to the identification of previously unknown stars, galaxies, and exoplanets, expanding the boundaries of our known universe. Advancements in telescopes and imaging techniques have allowed for more detailed observations of distant celestial bodies, enabling scientists to suggest revisions to the boundaries and shapes of existing constellations. For example, the identification of stars with slight positional shifts or the discovery of new star clusters can prompt reevaluation and adjustments to constellation maps. In recent years, there have also been efforts to incorporate previously overlooked cultural perspectives into the naming and recognition of constellations, highlighting a more inclusive approach. This evolving nature of constellation research ensures that our knowledge of the cosmos remains dynamic and ever-growing. By staying abreast of contemporary discoveries and revisions, astronomers and enthusiasts alike can engage in a deeper exploration of the celestial wonders that surround us.
Constellation Mapping and Visualization Techniques
Constellation mapping and visualization techniques have undergone a remarkable transformation over time, enabling us to explore and understand the vastness of the night sky in increasingly immersive ways. Stellar cartography, the ancient art of mapping the stars, laid the foundation for our early understanding of constellations. Astronomers meticulously recorded the positions and magnitudes of stars, creating celestial atlases that served as visual guides for navigating the heavens. With the advent of digital technologies, software tools have become invaluable in the creation and manipulation of virtual star maps. These tools allow astronomers to plot precise coordinates, overlay additional data such as spectral information, and even simulate the movement of the stars over time. Advancements in 3D visualization and virtual reality have taken constellation mapping to new heights, allowing users to immerse themselves in a virtual cosmos, explore constellations from different perspectives, and even embark on virtual journeys through the universe. The combination of these powerful techniques has revolutionized our understanding and appreciation of the celestial realm, enhancing the accessibility and beauty of the stars above.
4.1 Stellar Cartography and Celestial Atlases
Stellar cartography and celestial atlases form the backbone of our understanding and representation of the night sky. Through meticulous observations and measurements, astronomers have produced detailed maps and atlases that showcase the location and characteristics of stars, galaxies, nebulae, and other celestial objects. Stellar cartography involves the process of mapping and charting the positions and motions of stars, creating comprehensive catalogs that serve as references for astronomers and stargazers alike. These catalogs often provide valuable information such as the magnitude, spectral type, and distance of each star. Celestial atlases, on the other hand, are visual representations of the night sky, presenting the constellations and their associated stars in an easily navigable format. They are filled with intricate illustrations and annotations, helping astronomers identify and locate celestial objects with precision. Notable examples of celestial atlases include Johann Bayer’s “Uranometria,” John Flamsteed’s “Atlas Coelestis,” and the modern digital atlas known as the “Digital Sky Survey.” These tools have been invaluable in advancing our knowledge of the cosmos, enabling us to explore the wonders of the universe and unravel its mysteries.
4.2 Digital Mapping and Software Tools
Digital mapping and software tools have revolutionized the way we explore and understand constellations. With advancements in technology, astronomers now have access to a myriad of powerful tools that aid in mapping and analyzing the vastness of the cosmos. One such tool is planetarium software, which creates immersive and interactive virtual environments where users can navigate the night sky in real-time. These software applications simulate the position and movement of stars, planets, and other celestial objects, allowing astronomers and enthusiasts alike to observe constellations from any location on Earth and at any point in time. By inputting specific coordinates or selecting a date and time, users can witness the beauty of constellations and their intricate connections unfold before their very eyes.
Sophisticated digital mapping techniques enable astronomers to create detailed sky charts that accurately represent the positions and relationships of stars and constellations. Using data gathered from telescopes and observatories around the world, these maps provide a comprehensive view of the celestial sphere. High-resolution imagery, combined with advanced algorithms, creates visually stunning representations of constellations, enhancing our understanding of their complex structures and configurations. These maps not only serve as valuable references for astronomers but also offer a visual feast for stargazers and enthusiasts.
In addition to planetarium software and sky maps, software tools like telescopic control software allow astronomers to automate the tracking and observation of specific constellations. By connecting their telescopes to computers and utilizing specialized software, astronomers can accurately position their instruments and track celestial objects with precision. This automation not only saves time but also minimizes human error, enabling astronomers to focus on conducting research and gathering data.
The digital era has also given rise to online platforms and mobile applications specifically designed for celestial navigation and exploration. These user-friendly tools provide interactive star maps, augmented reality features, and educational resources to engage and educate users about constellations. Whether it’s identifying a particular constellation, learning about their mythological origins, or discovering interesting facts, these digital tools make astronomy accessible to a wider audience.
Digital mapping and software tools have ushered in a new era of exploration and understanding when it comes to constellations. Through planetarium software, telescopic control software, sky maps, and mobile applications, astronomers and enthusiasts can now navigate the celestial expanse with ease and precision. These tools not only enable us to unravel the complexities of constellations but also inspire curiosity and bring the wonders of the universe closer to us all.
4.3 3D Visualization and Virtual Reality Applications
Advancements in technology have revolutionized the way we visualize and explore constellations, thanks to the emergence of 3D visualization and virtual reality (VR) applications. These cutting-edge tools take us beyond traditional two-dimensional images and allow us to immerse ourselves in a three-dimensional representation of the cosmos. Through 3D visualization, we can experience the depth and intricacy of the celestial objects that make up constellations, gaining a more comprehensive understanding of their spatial relationships. VR applications take this experience to the next level by creating a simulated environment where we can interact with constellations in a lifelike manner. With VR headsets, users can navigate through virtual space, observe constellations from various angles, and even explore hypothetical scenarios such as the movement of stars and planets over time. This technology not only enhances our ability to study and comprehend constellations but also offers a unique and immersive way to engage with the wonders of the universe. As our understanding of 3D visualization and VR applications continues to evolve, the possibilities for exploring and experiencing constellations in unprecedented ways are boundless. Whether for educational purposes, scientific research, or simply the pursuit of cosmic wonder, these technological advancements enable us to venture further into the awe-inspiring realm of the stars and beyond.
The Future of Constellations
The future of constellations holds immense potential for exploration and discovery, driven by technological advancements and a deepening understanding of the cosmos. With advanced telescopes like the James Webb Space Telescope set to launch, we are poised to unravel even more mysteries of the universe, peering deeper into space and unveiling celestial wonders yet unseen. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in constellation research promises to revolutionize the way we study and analyze the vast expanse of the night sky. AI algorithms can assist in identifying patterns, detecting anomalies, and uncovering new insights in astronomical data, pushing the boundaries of our knowledge even further. However, the future of constellations also requires a careful consideration of cultural and ethical implications, particularly in the realm of naming conventions. Society will need to navigate the balance between preserving tradition and embracing inclusivity, ensuring that the names given to constellations reflect our evolving understanding of diversity and respect. As we embark on this cosmic journey, the future of constellations beckons with endless possibilities, fueling our curiosity and inspiring generations to come.
5.1 Exploration and Discovery with Advanced Telescopes
Exploration and discovery in the realm of constellations have reached unprecedented heights with the advent of advanced telescopes. These state-of-the-art instruments have revolutionized our ability to explore the cosmos, uncovering new celestial phenomena and expanding our knowledge of distant galaxies. Advanced telescopes, such as the Hubble Space Telescope and the James Webb Space Telescope (set to launch in the near future), utilize cutting-edge technology to observe the cosmos across different wavelengths, from visible light to infrared radiation. This expanded range of observations grants astronomers a deeper understanding of the universe and enables them to make groundbreaking discoveries. For example, the Hubble Space Telescope has provided breathtaking images of distant galaxies, while also capturing the birth and death of stars within our own Milky Way galaxy. The James Webb Space Telescope, with its enhanced infrared capabilities, is expected to further unravel the mysteries of deep space, probing the formation of planets and the atmospheres of exoplanets. With these advanced telescopes pushing the boundaries of exploration, the future holds the promise of even more astonishing discoveries and a deeper understanding of the wonders that exist beyond Earth’s boundaries.
5.2 Integration of Artificial Intelligence in Constellation Research
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) has opened up new frontiers in constellation research, revolutionizing the way we explore and understand the cosmos. AI algorithms and machine learning techniques have proven invaluable in analyzing vast amounts of astronomical data, allowing researchers to uncover hidden patterns and make groundbreaking discoveries. With AI, telescopes can automatically detect and track celestial objects, helping to identify new constellations or confirming the existence of previously unknown phenomena. The use of AI in constellation research has also led to advancements in the classification and categorization of stars, galaxies, and other celestial entities. By training AI models on massive datasets, scientists can now accurately identify stellar properties and predict their behavior, providing crucial insights into the evolution of constellations over time. AI-powered algorithms also play a significant role in data processing and analysis, speeding up the discovery process and enabling more efficient and accurate observations. These innovations in AI integration pave the way for future breakthroughs in constellation research, offering exciting possibilities for unraveling the mysteries of the universe.
5.3 Cultural and Ethical Considerations in Modern Naming Conventions
As we contemplate the future of constellations, it is crucial to consider the cultural and ethical considerations that arise in modern naming conventions. The naming of constellations has traditionally been tied to the mythologies and cultural significances of various civilizations. However, the discoveries of new celestial objects have raised important questions about representation and inclusivity. The cultural and ethnic diversity of our world begs the question: should constellations continue to be named based solely on Western mythological figures? There has been a growing movement to recognize the cultural significance of indigenous stories and celestial knowledge. Efforts are underway to incorporate indigenous constellations into the official records, highlighting their rich cosmological traditions. This shift towards inclusivity not only brings diverse narratives to the forefront but also encourages a deeper understanding and appreciation of different cultural perspectives. Ethical considerations arise when it comes to commercial ventures that seek to trademark or commodify constellation names. The commercialization of celestial bodies invokes concerns about cultural appropriation and the exploitation of indigenous knowledge. Striking a balance between authenticity, respect, and scientific accuracy is vital in the modern naming conventions of constellations. It requires collaboration and consultation with diverse communities and experts to ensure a fair and equitable representation of cultures and their celestial stories. The ongoing discussions surrounding cultural and ethical considerations in constellation naming have the potential to shape the future of how we view and understand the cosmos.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the evolution of modern constellations from their mythological origins to the scientific discoveries of today is a testament to humankind’s ongoing quest for understanding and connection with the cosmos. From the ancient stories that inspired the creation of constellations to the contributions of ancient astronomers who laid the groundwork for scientific understanding, we have witnessed a transformation in our perception of the night sky. The development of celestial coordinate systems and the establishment of the International Astronomical Union as the official body for naming and recognizing constellations brought a standardized approach to studying and mapping the stars. With the advent of technology, we have seen advancements in constellation mapping and visualization techniques, from traditional stellar cartography to the use of digital tools and 3D visualization. Looking forward, the future of constellations holds promises of exploration and discovery through advanced telescopes and the integration of artificial intelligence in research. However, as we continue to uncover the mysteries of the universe, it is important to consider cultural and ethical aspects in the modern naming conventions of constellations. The evolution of constellations reflects our ever-evolving understanding of the universe and the profound impact it has on our collective human experience.
Frequently Asked Questions

1. What is the significance of constellations in ancient mythology?
Constellations held great symbolism in ancient mythology, representing gods, heroes, and mythical creatures. They served as a way to immortalize these characters and their mythical stories, connecting the heavens to the human realm.
2. How did different cultures influence the creation of constellations?
Each culture had its own unique interpretations of the constellations. They assigned names and meanings based on their own mythologies and beliefs, resulting in a rich tapestry of cultural influences that shaped the constellations we recognize today.
3. How did ancient astronomers contribute to the study of constellations?
Ancient astronomers observed the night sky meticulously, identifying and cataloging constellations. They developed methods to track celestial movements, laying the foundation for our understanding of the stars and their patterns.
4. What was Ptolemy’s role in the evolution of modern constellations?
Ptolemy, an influential ancient Greek astronomer, compiled the Almagest, a comprehensive treatise on astronomy. This work described a system of celestial coordinates and provided a basis for categorizing and naming constellations, acting as a precursor to modern constellations.
5. How were celestial coordinate systems developed?
Celestial coordinate systems evolved to provide a standardized way of locating celestial objects. It involved the establishment of reference points, such as the celestial poles and equator, and the adoption of specific measurement units like right ascension and declination.
The International Astronomical Union (IAU) is the official body responsible for naming and recognizing constellations. They follow strict guidelines and procedures to ensure consistency and accuracy in the identification and nomenclature of celestial objects.
7. What are the techniques used in stellar cartography?
Stellar cartography involves mapping and charting the positions of stars and constellations. Traditional techniques include manual plotting on charts and celestial atlases using specialized tools like micrometers and projection devices.
8. How has digital mapping revolutionized constellation visualization?
Digital mapping tools and software have made constellation visualization more accessible and accurate. They allow astronomers to create detailed and interactive maps, enhancing the understanding and exploration of the celestial realm.
9. What are the applications of 3D visualization and virtual reality in understanding constellations?
With advancements in technology, 3D visualization and virtual reality have provided immersive experiences for studying constellations. They allow users to explore the cosmos in a simulated environment, offering new perspectives and enhancing scientific research.
10. What are the future possibilities for constellation research?
The future of constellation research is promising, with advancements in telescopes and instruments allowing for deeper exploration of the universe. The integration of artificial intelligence in data analysis and the consideration of cultural and ethical aspects in naming conventions will also shape the future of this field.
References
- Sky Tellers – Constellations
- What’s the story behind the stars?
- The Origin of the Greek Constellations
Frequently Asked Questions

Ancient civilizations used constellations as navigational aids, allowing them to navigate across land and sea. By observing the positions of specific constellations in the night sky, sailors and explorers could determine their directions and locations.
2. How were constellations named in ancient mythology?
Constellations were often named after characters from ancient mythology, such as Orion, Hercules, and Perseus. These names were based on the myths and legends associated with these figures, adding a sense of storytelling and cultural significance to the constellations.
3. What contributions did ancient astronomers make to the development of modern constellations?
Ancient astronomers such as Hipparchus and Ptolemy made significant contributions to the development of modern constellations. They created celestial coordinate systems and cataloged the positions and movements of stars – foundational knowledge that forms the basis of modern astronomical observations and mapping.
4. How does the International Astronomical Union (IAU) play a role in modern constellations?
The International Astronomical Union (IAU) is the official body responsible for naming and recognizing constellations. They establish guidelines and criteria for the naming of celestial objects and ensure consistency in the cataloging and identification of constellations.
5. What are celestial atlases, and how are they used in constellation mapping?
Celestial atlases are maps of the night sky that depict the positions and configurations of stars, constellations, and other celestial objects. Astronomers use these atlases to visually identify and locate constellations, aiding in their mapping and understanding of the night sky.
6. How has digital mapping and software tools revolutionized constellation research?
Digital mapping and software tools have transformed constellation research by enabling astronomers to create accurate and dynamic maps of the night sky. These tools allow for precise measurements, analysis, and real-time updates of celestial objects, enhancing our understanding of constellations and their characteristics.
7. What are the benefits of using 3D visualization and virtual reality in studying constellations?
3D visualization and virtual reality provide immersive experiences that allow astronomers to explore and understand constellations in a more interactive and engaging way. These technologies enable the visualization of constellations from different perspectives, aiding in the interpretation of their spatial relationships and structures.
8. How do advanced telescopes contribute to the future of constellation exploration?
Advanced telescopes, such as space-based observatories and next-generation ground-based telescopes, offer improved sensitivity, resolution, and data collection capabilities. These instruments enable astronomers to make groundbreaking discoveries, uncover hidden details within constellations, and expand our knowledge of the universe.
9. How can artificial intelligence support constellation research?
Artificial intelligence can assist in constellation research by analyzing vast amounts of data, identifying patterns, and making complex calculations more efficiently than humans. AI algorithms can aid in the classification, identification, and tracking of celestial objects, accelerating the process of discovering and understanding constellations.
10. What factors should be considered when naming new constellations?
When naming new constellations, cultural and ethical considerations should be taken into account. Respecting cultural diversity and avoiding offensive or controversial names are vital to ensure inclusivity and maintain the integrity of the scientific community.
References
- Ancient Greek Astronomy and Cosmology | Modeling the …
- How the Night Sky Constellations Got Their Names







