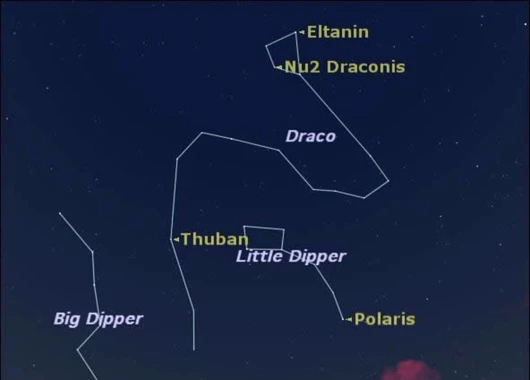
Welcome to the captivating world of the Draco constellation, an enigmatic cosmic wonder that has intrigued astronomers and mythologists for centuries. Nestled among the twinkling stars of the northern sky, Draco holds a mysterious allure that is both mesmerizing and perplexing. In this article, we delve into the ancient mythology surrounding the origins of Draco, explore its presence in Greek mythology, unveil its astronomical features and notable neighbors, uncover its significance in celestial navigation, and examine its modern interpretations and cultural significance. So, fasten your seatbelts and prepare to embark on a celestial journey like no other as we unravel the secrets of the elusive Draco constellation.
Contents
- Draco in Ancient Mythology
- Draco in Astronomy
- Draco’s Stellar Neighbors
- Draco and the Celestial Pole
- Modern Interpretations and Cultural Significance
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What is the origin of the name “Draco”?
- 2. How does Draco appear in different cultures’ mythologies?
- 3. Can Draco constellation be easily seen with the naked eye?
- 4. Are there any notable stars in the Draco constellation?
- 5. What are the neighboring constellations of Draco?
- 6. Is Draco circumpolar?
- 7. How did ancient navigators use Draco for celestial navigation?
- 8. Is Draco featured in modern popular culture?
- 9. What are some symbolic interpretations of Draco?
- 10. Are there any famous structures or monuments named after Draco?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- How did the constellation Draco get its name?
- What is the origin of the mythical dragon associated with Draco?
- Are there any famous myths or legends involving Draco?
- How was Draco depicted in Greek mythology?
- When was Draco first discovered as a constellation in astronomy?
- What are some notable features of the Draco constellation?
- Which constellations are neighbors to Draco?
- How does Draco’s position in relation to the celestial pole contribute to its importance in celestial navigation?
- Is Draco referenced in popular culture?
- What are some symbolic meanings associated with Draco?
- References
- Read More
Draco in Ancient Mythology

Legend has it that Draco, the celestial dragon, has its roots in ancient Babylonian mythology. In Babylonian astronomy, this constellation was associated with the great serpent god Tiamat, representing chaos and primordial darkness. According to the myth, Tiamat, in her battle against the gods, was slain by the hero Marduk. As a tribute to this epic victory, Marduk placed Tiamat’s body in the heavens, giving birth to the celestial dragon we now know as Draco.
In Greek mythology, Draco takes on a different role and is closely linked to two famous legends. The first story connects Draco to the hero Hercules. During one of his twelve labors, Hercules faced the daunting task of slaying the Lernaean Hydra, a many-headed serpent-like creature. As Hercules decapitated each of the serpent’s heads, they would regenerate. Realizing the futility of attacking the creature head-on, Hercules sought the aid of his charioteer, Iolaus, who came up with a cunning plan. As Hercules wielded his sword, Iolaus cauterized each decapitated head with a torch, preventing regeneration. As a reward for their victorious battle, Zeus placed the Hydra as Draco in the heavens.
The second myth linked to Draco involves Ladon, a hundred-headed dragon that guarded the golden apples of the Hesperides. In the quest for these sacred apples, Hercules slew Ladon and claimed the coveted prize. This feat of bravery earned Hercules a place among the stars, immortalizing his victory over Ladon in the form of Draco.
The captivating stories surrounding Draco in ancient mythology emphasize the ancient fascination with serpents and dragons, highlighting the enduring symbolism and celestial significance attributed to this awe-inspiring constellation. To explore more celestial connections in Greek mythology, you can read about the eternal punishment of Tantalus in the myth of Aquarius.
The Origin of Draco
The origin of the Draco constellation can be traced back to ancient civilizations that believed in the power of the stars and their influence on human existence. They observed the patterns formed by the stars and connected them to various myths and legends. One theory suggests that Draco was named after the mythical dragon, Ladon, from Greek mythology, who guarded the golden apples of the Hesperides. This association with dragons and serpents can be found in many ancient cultures, portraying these creatures as powerful and mysterious beings. In Babylonian astronomy, the origins of Draco can be linked to the serpent god Tiamat, representing chaos and darkness. These different interpretations of Draco’s origin highlight the universal fascination with dragons and serpents as symbols of power, wisdom, and the unknown. For more intriguing mythological tales, you can explore the eternal punishment of Tantalus in the myth of Aquarius
Draco in Greek Mythology
In Greek mythology, Draco holds a prominent place, intertwining with various tales and legends. One popular Greek myth involving Draco is the story of Cadmus, the founder of the city of Thebes. According to the myth, Cadmus was sent on a quest by his father to find his sister Europa, who had been abducted by Zeus in the form of a bull. As Cadmus searched for his sister, he consulted the Oracle of Delphi, who instructed him to follow a cow and build a city where it would lay down. Cadmus successfully completed the task and, as a reward, the goddess Athena gifted him with a set of teeth from the slain serpent of Ares. He planted these teeth in the ground, and from them, a group of fully armored warriors, known as the Spartoi, sprang forth. The Spartoi engaged in a fierce battle until only five remained. These warriors became the noble founders of Thebes and were immortalized as stars in the constellation Draco.
Another intriguing tale involving Draco is the story of Jason and the Argonauts. Jason, accompanied by his band of heroes, embarked on a perilous journey aboard the ship Argo to retrieve the fabled Golden Fleece. During their quest, they encountered many challenges, one of which involved guarding the fleece from the fiery breath of a dragon. With the guidance of the sorceress Medea, Jason successfully outsmarted the dragon and obtained the Golden Fleece. As a tribute to their triumph over the dragon, the constellation Draco was placed in the night sky as a symbol of their heroic exploits.
The association of Draco with such heroic and adventurous tales in Greek mythology signifies its significance in the ancient Greek culture. Its presence in the stars immortalizes the bravery, cunning, and triumph over seemingly insurmountable obstacles. To further explore the interplay of mythology and astrology, you can read about the eternal punishment of Tantalus in the myth of Aquarius.
Draco in Astronomy
In the realm of astronomy, Draco offers a fascinating celestial spectacle that has captivated stargazers throughout history. This magnificent constellation, located in the northern sky, is best observed during the summer months in the northern hemisphere. Let’s explore the intriguing aspects of Draco in the realm of astronomy.
Discovery and Observation: Draco was first cataloged by the Greek astronomer Ptolemy in the 2nd century AD, but its existence predates ancient Greece as it was also known to the Babylonians. Draco is one of the 88 modern constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union.
Notable Features of Draco: One of the prominent features of Draco is its resemblance to a winding dragon, with its serpentine body gracefully weaving through the sky. The constellation’s head is marked by the star Thuban, which played a significant role in ancient civilization as it was once the North Star around 4,000 BCE due to the Earth’s axial precession. Another notable feature of Draco is its exceptional length, extending for over 100 degrees across the sky, making it the eighth largest constellation.
Within Draco lies the iconic binary star system known as Gamma Draconis, or Eltanin. This system consists of two stars that orbit each other and is visible to the naked eye. Eltanin is situated near the dragon’s head, adding a touch of celestial allure to the constellation.
Another intriguing phenomenon within Draco is the Cat’s Eye Nebula, or NGC 6543. This planetary nebula, situated approximately 3,000 light-years away, reflects a mesmerizing display of hues, making it a fascinating subject for astronomers and astrophotographers alike.
Draco’s celestial presence offers a wealth of wonders for both amateur and professional astronomers. Its distinct shape, notable stars, and captivating nebula provide a celestial canvas to explore and marvel at. To learn more about the eternal punishment of Tantalus in the myth of Aquarius, check out our article here.
Discovery and Observation
The discovery and observation of the Draco constellation have fascinated astronomers throughout history. The exact origin of when Draco was first identified as a distinct constellation remains uncertain, as it has likely been recognized for thousands of years. However, it was the ancient astronomer Ptolemy who formally cataloged Draco as one of the 48 constellations in his influential work, the Almagest, during the 2nd century.
Draco’s prominent position within the northern celestial hemisphere makes it visible to observers in both the northern and southern hemispheres. Its close proximity to the north celestial pole allows it to be circumpolar, meaning it never sets below the horizon. This characteristic makes Draco observable year-round for locations in the northern latitudes.
Over the centuries, astronomers have used various techniques to observe and study Draco. Early astronomers relied on naked-eye observations to map out the constellation’s shape and locate its stars. With the advancement of telescopes and advanced imaging technologies, scientists can now delve deeper into the mysteries of Draco. They have discovered that Draco is home to several remarkable celestial objects, including double stars, globular clusters, and beautiful nebulae.
To further explore the intriguing connections between celestial objects and the potential for extraterrestrial life, you can read about the significance of asteroids in the search for potential extraterrestrial life.
Notable Features of Draco
Draco, the dragon constellation, boasts several notable features that make it a fascinating celestial sight. One standout feature is Thuban, also known as Alpha Draconis, which served as the North Star around 4,000 years ago. This historical importance is intriguing, as it predates Polaris’s designation as the current North Star. Thuban’s position as the pole star during that time period is a testament to the precision and meticulous observations made by ancient astronomers.
The constellation also contains the Cat’s Eye Nebula, a planetary nebula named for its resemblance to a cat’s eye. This nebula, located in the eastern part of Draco, exhibits stunning colors and intricate structures when observed through powerful telescopes. Its vivid hues and intricate formations make it a captivating subject of study for astronomers.
Additionally, Draco is home to a remarkable binary star system called Nu Draconis. This system consists of two stars, Nu1 Draconis and Nu2 Draconis, orbiting around a common center of mass. The two stars are similar in size and brightness, and their interaction provides a fascinating opportunity for researchers to study the dynamics of binary star systems.
Lastly, Draco is known for its abundance of meteor showers, including the Draconids and the Giacobinids. The Draconids, which peak in early October, are caused by the dust debris left behind by comet 21P/Giacobini-Zinner. The Giacobinids, on the other hand, are associated with debris from the comet Swift-Tuttle and typically occur in mid-October.
The notable features of Draco, such as Thuban, the Cat’s Eye Nebula, the Nu Draconis binary system, and its dazzling meteor showers, contribute to its allure and scientific significance. Exploring the wonders of Draco expands our understanding of the vast and diverse celestial tapestry. To delve deeper into the search for potential extraterrestrial life, you can explore the connection between asteroids and the possibility of life beyond Earth.
Draco’s Stellar Neighbors
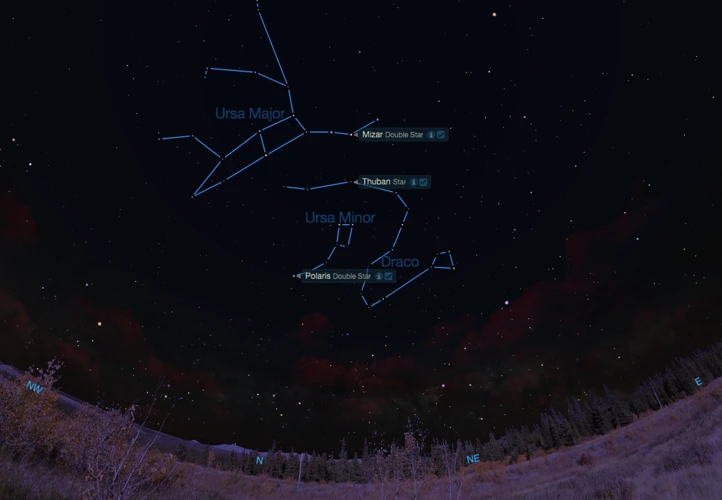
Draco, the majestic celestial dragon, resides in the northern skies, surrounded by fascinating stellar neighbors. One such neighbor is the Ursa Minor, also known as the Little Bear. Ursa Minor contains the North Star, Polaris, which is famous for its role in celestial navigation. Polaris marks the position of the North Celestial Pole and, interestingly, lies at the end of the dragon’s tail, forming a celestial connection between Draco and Ursa Minor. These neighboring constellations share a cosmic bond, shining brightly in the night sky and captivating stargazers with their timeless allure.
Another notable neighbor of Draco is Boötes, the Herdsman. Boötes is associated with Arcas, the son of Zeus and Callisto. According to Greek mythology, Callisto was transformed into a bear by Zeus’ wife, Hera, out of jealousy. However, Arcas, unaware of his mother’s true identity, almost killed her while hunting. To prevent tragedy, Zeus transformed Arcas into a bear and placed them both in the sky as Ursa Major and Ursa Minor, placing them near Draco. This celestial configuration further highlights the interconnectedness among these constellations, weaving a celestial tapestry of mythical tales and cosmic wonder.
Lyra, the Lyre, is yet another neighbor of Draco. Lyra is associated with the mythical musician Orpheus, who possessed unmatched musical talent. In Greek mythology, Orpheus’ music was so enchanting that it could calm wild animals and even move rocks and trees. When Orpheus met his tragic end at the hands of the frenzied Maenads, Zeus placed his lyre in the heavens as a constellation. As Draco overlooks this harmonious symbol of music and creativity, the celestial dragon adds an air of mystique and grandeur to the cosmic tales woven by its stellar neighbors.
The celestial dance of Draco and its neighboring constellations serves as a reminder of the interconnectedness and vastness of the universe. As you gaze at the night sky, marvel at the celestial symphony performed by Draco, Ursa Minor, Boötes, and Lyra, and let your imagination soar among the stars. To explore further the potential for extraterrestrial life, you can read about the fascinating connection between asteroids and the search for life beyond Earth.
Ursa Minor: The Little Bear
Ursa Minor, also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation that neighbors Draco in the celestial sphere. One of the most prominent features of Ursa Minor is its brightest star, Polaris, also called the North Star. This star has been revered for its role in celestial navigation, serving as a reliable guide for travelers and explorers throughout history. The Little Bear is known for its distinct shape, resembling a small ladle or a celestial wagon. It is often linked to the legend of Callisto, a beautiful nymph who caught the eye of Zeus. Infuriated by Callisto’s betrayal, Zeus transformed her into a bear, casting her into the night sky as Ursa Major, or the Great Bear, along with her son Arcas, who became Ursa Minor. Ursa Minor’s proximity to the North Celestial Pole makes it a valuable reference point for stargazers and astronomers. Interestingly, due to Earth’s axial precession, which causes a slow change in the orientation of the planet’s axis, Polaris was not always the North Star. Thousands of years ago, the star Thuban in the Draco constellation held that distinction. The connection between Draco and Ursa Minor adds to the celestial beauty of the northern sky, where these two constellations share a fascinating celestial relationship. For more insights into the potential existence of extraterrestrial life, you can read about asteroids and their role in the search for extraterrestrial life.
Boötes: The Herdsman
Boötes, the Herdsman, is a neighboring constellation of Draco that adds to the celestial tapestry of the northern sky. In Greek mythology, Boötes is associated with various legends and characters. One popular narrative connects Boötes with Arcas, the son of Zeus and Callisto. Callisto was a nymph who caught the attention of Zeus, much to the dismay of his jealous wife, Hera. To protect Callisto, Zeus transformed her into a bear. Years later, when Arcas was on the verge of unknowingly killing his mother in bear form while hunting, Zeus intervened and placed both Callisto and Arcas in the night sky. Callisto became the Ursa Major constellation, and Arcas became Boötes, forever destined to chase his mother across the celestial sphere.
Boötes is often depicted as a herdsman or a plowman due to his association with agriculture and rural life. His prominent star, Arcturus, one of the brightest stars in the night sky, serves as one of the key markers in navigating the heavens. Arcturus, derived from the Greek word meaning “guardian of the bear,” guides astronomers in locating the Big Dipper and the North Star, aiding celestial navigation.
In astrology, Boötes holds significance as well, representing qualities of diligence, hard work, and practicality. Those born under the sign of Boötes are believed to possess a strong sense of responsibility and a relentless pursuit of goals.
As we delve deeper into the mysteries of the cosmos, it becomes evident that each constellation intertwines with others, forming a complex celestial network. To further explore the cosmic mysteries and the potential for extraterrestrial life among asteroids, you can dive into the fascinating world of asteroids and their link to the possibility of life beyond Earth.
Lyra: The Lyre
Lyra, also known as The Lyre, is a neighboring constellation of Draco that adds another layer of enchantment to the celestial tapestry. In Greek mythology, Lyra holds a special place as it is associated with the mythical musician Orpheus, known for his extraordinary musical talents. According to the legend, Orpheus was gifted a lyre by the god Apollo, the patron of music, and he became renowned for the beauty of his melodies. The music produced by Orpheus’s lyre was said to have the power to charm even the fiercest beasts and move the stones and trees with its enchanting sound.
Orpheus’s music played a pivotal role in his quest to retrieve his beloved wife, Eurydice, from the Underworld. He traveled to Hades and captivated the gods of the Underworld with the haunting melodies of his lyre. His music moved the god of the Underworld, Pluto, and his wife Persephone, who granted him permission to bring Eurydice back to the realm of the living. However, there was one condition: Orpheus must not look back until they reached the surface. Tragically, overcome with doubt and longing, Orpheus glanced back, causing him to lose Eurydice forever.
To honor the legendary musician, Zeus placed the lyre in the heavens as the constellation Lyra. Within the Lyra constellation lies the bright star Vega, which represents the instrument’s main body. This brilliant star, seen as one of the brightest in the summer sky, adds to the allure of Lyra and serves as a prominent guide for stargazers and navigators alike.
By exploring the neighboring constellation of Lyra, its connection to the legendary musician Orpheus, and the mesmerizing star Vega, we gain a deeper appreciation of the intricate interplay between mythology and astronomy. To learn more about the potential for extraterrestrial life, you can read about asteroids and their significance in the search for life beyond Earth.
Draco and the Celestial Pole
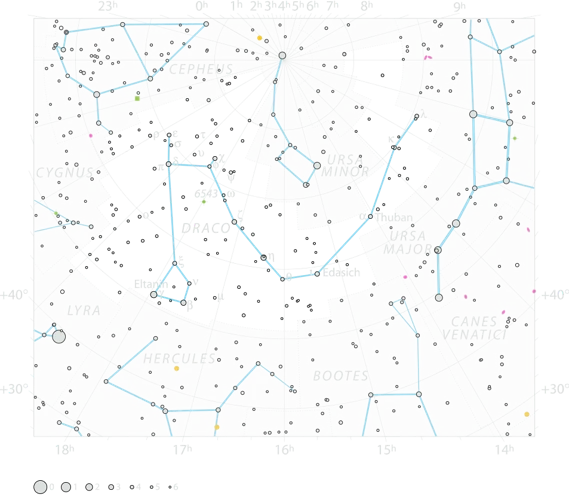
Draco, the celestial dragon, plays a significant role in the realm of celestial navigation due to its proximity to the celestial pole. At present, the North Celestial Pole aligns closely with the star Polaris, also known as the North Star. However, this was not always the case.
Draco, with its distinctive shape and position, served as the closest approximation to the pole in ancient times. Due to the Earth’s axial precession, the slow wobbling of its axis, the North Celestial Pole has shifted over thousands of years. In around 3000 BCE, the star Thuban, located in the tail of Draco, was the closest star to the pole and served as the guiding star for navigators. Ancient civilizations such as the Egyptians and the Greeks utilized Thuban’s position to navigate their way across vast seas and uncharted territories.
Draco’s status as a circumpolar constellation, meaning it remains visible all year round in the northern hemisphere, made it invaluable for navigating during the night. By establishing the location of Draco and its neighboring constellations, mariners and explorers could determine their latitude in relation to the celestial pole. This knowledge was crucial for determining their position and planning their journeys.
In modern times, while Draco may no longer serve as the primary guide for celestial navigation, it remains a testament to the historical importance of understanding and utilizing the stars. The intricate dance of the celestial pole and the stars of Draco reminds us of the ever-changing nature of our planet and the cosmic wonders that guide us. To explore more about the potential for extraterrestrial life in our universe, you can read about asteroids and their significance in the search for life beyond Earth.
Draco as a Circumpolar Constellation
Draco holds a unique position in the night sky as a circumpolar constellation. This means that it never sets below the horizon from certain latitudes in the northern hemisphere. Due to its proximity to the North Celestial Pole, Draco can be observed all year round in these regions. Its prominent position around the celestial pole makes it an easily recognizable and constant fixture in the night sky.
The circumpolar nature of Draco is a result of Earth’s rotation on its axis, causing the stars to appear to revolve around the celestial poles. From latitudes above approximately 40 degrees North, Draco can be observed continuously, completing its celestial circle without ever dipping below the horizon. This perpetual presence makes Draco an essential navigational tool for ancient and modern astronomers alike.
Draco’s circumpolar designation makes it particularly useful for navigation purposes. For centuries, sailors and explorers relied on the position of this constellation to determine their latitude and direction. By aligning Draco’s position with the North Star, navigators were able to establish their bearings, ensuring accurate travel across vast expanses of land or sea. Even today, despite advances in modern navigation technology, understanding the circumpolar constellations remains crucial for certain outdoor activities and astronomical observations.
The significance of Draco as a circumpolar constellation goes beyond its navigational importance. Its unceasing presence in the night sky symbolizes endurance, determination, and resilience. In astrology, individuals born under the sign of Draco are believed to possess these qualities, exhibiting great fortitude and an unwavering spirit. To explore more about the role of astrology in understanding personality traits, you can delve into the world of zodiac signs.
Navigating through the vast expanse of the open seas or the desolate landscapes of uncharted territories has always posed a great challenge to explorers and mariners throughout history. However, the presence of the Draco constellation in the night sky has played a crucial role in celestial navigation. Due to its position in the northern sky, Draco is classified as a circumpolar constellation, meaning it never sets below the horizon. This unique characteristic allows sailors and explorers to use Draco as a reliable reference point for finding their way.
One of the key stars in Draco is Thuban, which, in ancient times, was the North Star. Before Polaris took on this role around 3000 BCE, Thuban held the distinction of guiding navigators and travelers as they ventured across unknown lands. With the aid of simple instruments like the astrolabe, sailors would align Thuban with the horizon to determine their latitude and ensure they stayed on the correct course.
Draco’s importance in celestial navigation extended beyond its role as a reference point. Its association with the celestial pole made it a crucial component in determining the Earth’s axial precession – the gradual shift in the direction of the Earth’s rotation axis. By observing the subtle movement of Draco relative to other stars, astronomers were able to measure the rate of precession, providing vital information for accurately plotting positions on Earth.
While technology and advances in navigation have rendered celestial navigation less prevalent in modern times, the cultural and historical significance of Draco in guiding explorers and mariners remains. Today, we can appreciate the role Draco played in celestial navigation as we marvel at its rich history and symbolism. To explore more about the potential for extraterrestrial life in asteroids, check out our article on the intriguing possibilities of asteroids hosting life beyond Earth.
Modern Interpretations and Cultural Significance

In modern times, Draco continues to captivate the imagination of people around the world, finding its way into various aspects of popular culture. In literature and fantasy, dragons often embody power, wisdom, and mystery, drawing inspiration from the majestic symbolism of Draco. These mythical creatures serve as central figures in countless novels, such as J.R.R. Tolkien’s “The Hobbit” and George R.R. Martin’s “A Song of Ice and Fire” series.
Draco’s cultural significance extends beyond literature and permeates other forms of media as well. In movies and television shows, dragons are often portrayed as majestic beings, capable of both destruction and wisdom. The character of Drogon in the popular TV series “Game of Thrones” exemplifies this duality, with his fiery breath and strong connection to the character Daenerys Targaryen.
In astrology, the influence of Draco is seen in its association with transformation, rebirth, and hidden knowledge. Although not an official zodiac sign, some astrologers recognize the influence of Draco in the interpretation of natal charts, as it represents deep and profound transformations in one’s life.
Draco’s role in celestial navigation is not diminished in modern times. While its importance may have waned with the advent of advanced navigation technology, the symbolism of Draco as a fixed point in the sky remains significant for both professional and recreational stargazers.
The cultural significance of Draco is evident in its enduring presence in art, literature, and popular culture. Whether as a source of inspiration for mythical creatures or as a symbol of transformation and hidden knowledge, Draco continues to capture the imagination and curiosity of people worldwide. To explore the link between celestial bodies and potential extraterrestrial life, you can read about asteroids and their potential role in the search for life beyond Earth.
Draco in Popular Culture
In popular culture, Draco has left an indelible mark, making appearances in various forms of literature, art, and entertainment. One notable example can be found in J.K. Rowling’s beloved Harry Potter series, where Draco Malfoy, a complex and conflicted character, bears the name of the constellation. Just like the celestial dragon, Draco Malfoy possesses an air of mysteriousness and cunning throughout the course of the story.
Draco also finds a place in the realm of video games, with several titles featuring references to the constellation. One such game is “The Elder Scrolls V: Skyrim,” an epic fantasy role-playing game. In this game, players encounter the College of Winterhold, a magical institution that holds the Midden Dark, a hidden underground area in the college where the entrance is shaped like the Draco constellation.
Beyond literature and video games, Draco has cemented its presence in the world of music. The progressive rock band Muse released a song titled “Guiding Light” from their album “The Resistance.” In the lyrics, they sing about finding a guiding light in the darkness, referencing the celestial dragon’s position in the night sky.
Draco’s allure extends to other forms of popular culture as well, including tattoos, artwork, and even fashion. Some individuals choose to immortalize the constellation through body art, etching the intricate pattern of Draco onto their skin. Artists and designers often draw inspiration from the mystique of Draco, incorporating its serpentine form into their creations.
It is fascinating to see how Draco, the constellation of the celestial dragon, has made its way into the realms of popular culture, captivating the imaginations of people around the world. To explore more about the influence of astrology in popular culture, you can delve into the connection between zodiac signs and various aspects of our lives.
Symbolic Meanings and Interpretations
Symbolic interpretations of Draco vary across different cultures and belief systems. In astrology, Draco is not considered one of the traditional zodiac signs, but it holds significance for some astrologers who believe in the power of fixed stars. They associate Draco with qualities such as strength, power, and resilience. Those born under the influence of Draco are believed to possess a strong sense of purpose and unwavering determination in their pursuits.
In Chinese mythology, dragons hold a revered status and are seen as powerful, benevolent beings associated with good fortune and the elements. The celestial dragon, Draco, is often associated with the element of water, symbolizing creativity, wisdom, and adaptability. Dragons in Chinese culture are believed to bring prosperity and luck.
In Western mythology, dragons are often portrayed as fierce and dangerous creatures, representing chaos and destruction. However, some interpretations see dragons as guardians and protectors of hidden treasures or gateways to hidden realms. In this context, Draco can be seen as a symbol of the unknown, mystery, and the unseen forces of the universe.
Beyond mythology, Draco’s symbolism extends to modern culture as well. In literature and fantasy, dragons are often portrayed as majestic creatures with immense power and wisdom. They represent mythical creatures that challenge the human spirit and embody both fear and awe.
The symbolic meanings and interpretations of Draco in different cultures emphasize its association with strength, mystery, wisdom, and the unpredictable forces of the cosmos. To explore more about the potential for extraterrestrial life in the far reaches of the universe, you can read about asteroids and their potential role in hosting life forms.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the Draco constellation, with its rich history in ancient mythology and significant presence in astronomy, continues to captivate the imagination of humans. From its origins as the Babylonian serpent god Tiamat to its associations with the heroic deeds of Hercules, Draco embodies the eternal struggle between chaos and order, light and darkness. Astronomically, Draco stands out with its distinctive shape and notable features, drawing the gaze of stargazers and astronomers alike. Its proximity to the celestial pole makes it a key player in celestial navigation, guiding sailors and explorers through the vastness of the night sky.
Furthermore, Draco’s cultural significance extends beyond ancient tales, as it has found its place in popular culture, inspiring numerous books, movies, and artwork. Its symbolic meanings, ranging from protection and strength to wisdom and transformation, have made it a sought-after symbol in various belief systems and spiritual practices. In astrology, Draco is not considered one of the traditional zodiac signs. However, its influence can be felt in the cosmic dance of the celestial bodies, adding layers of symbolism and interpretation to astrological readings.
As our exploration of Draco comes to an end, we are reminded of the vast wonders that the night sky holds. The mysteries of the constellations, like Draco, continue to spark our curiosity and imagination, urging us to look upwards and contemplate our place in the universe. Whether we gaze upon Draco to navigate the seas or gaze upon it in awe, this celestial dragon holds a special place in our collective consciousness, reminding us of the enduring connection between mythology, astronomy, and the human spirit. To delve further into the exploration of celestial wonders, you can learn about the potential existence of extraterrestrial life hiding in asteroids.
Frequently Asked Questions

1. What is the origin of the name “Draco”?
The name “Draco” comes from the Latin word for “dragon.” It is believed to have been derived from ancient Greek or Babylonian mythology, where serpents and dragons held great symbolic importance.
2. How does Draco appear in different cultures’ mythologies?
Draco is present in various ancient mythologies, including Babylonian, Greek, and Roman. In Babylonian mythology, Draco is associated with the serpent god Tiamat, representing chaos. In Greek mythology, Draco is linked to the battles of Hercules and the guarding of the golden apples by Ladon.
3. Can Draco constellation be easily seen with the naked eye?
Yes, Draco can be observed with the naked eye in the northern hemisphere. It is visible throughout the year and can be found slithering between the constellations of Ursa Major and Ursa Minor.
4. Are there any notable stars in the Draco constellation?
One of the most prominent stars in Draco is Thuban (Alpha Draconis). In ancient times, Thuban served as the North Star. Additionally, Eltanin (Gamma Draconis) is another notable star known for its distinct orange hue.
5. What are the neighboring constellations of Draco?
Draco shares its celestial neighborhood with other well-known constellations. It is bordered by Ursa Minor (the Little Bear), Boötes (the Herdsman), and Lyra (the Lyre).
6. Is Draco circumpolar?
Yes, Draco is a circumpolar constellation, meaning it never sets below the horizon. Its position near the celestial pole allows it to be visible all year round in the northern hemisphere.
Ancient navigators relied on circumpolar constellations like Draco to determine their latitude. By observing the position of Draco and its relationship to the North Star, sailors could calculate their position on the globe.
8. Is Draco featured in modern popular culture?
Yes, the mystique and symbolism surrounding Draco have made it a popular subject in modern literature, movies, and fantasy genre. It often appears in fictional works depicting dragons or mythical creatures.
9. What are some symbolic interpretations of Draco?
Draco has been associated with various symbolic meanings, including wisdom, power, protection, and transformation. Its serpentine form is often linked to the concept of eternal life or the cycle of renewal.
10. Are there any famous structures or monuments named after Draco?
While there are no famous structures specifically named after Draco, the dragon motif is often used in architecture and art around the world. Dragons can be found in ancient Chinese temples, European castles, and even modern urban sculptures.
References
- Draco | Mythology, Stars, Northern Sky
- Draco Constellation: Facts About the Dragon
- DragonHeart: Constellation Draco by Bvega41 on DeviantArt
Frequently Asked Questions

How did the constellation Draco get its name?
The constellation Draco is named after the Latin word for dragon. Its serpentine shape resembling a dragon is believed to have inspired its name.
What is the origin of the mythical dragon associated with Draco?
The ancient Mesopotamian culture believed that the dragon Tiamat represented chaos and primordial waters. This concept likely influenced the dragon mythology associated with the constellation Draco.
Are there any famous myths or legends involving Draco?
Yes, one notable myth is the story of Ladon, a hundred-headed dragon that guarded the golden apples in the mythical garden of the Hesperides.
How was Draco depicted in Greek mythology?
In Greek mythology, Draco is often associated with Ladon, a dragon-like creature with serpentine features. It is depicted as a fearsome guardian in various mythological tales.
When was Draco first discovered as a constellation in astronomy?
Draco was one of the 48 constellations listed by the ancient Greek astronomer Ptolemy in his Almagest, which dates back to the 2nd century AD.
What are some notable features of the Draco constellation?
Among the notable features in Draco is the Cat’s Eye Nebula, a planetary nebula located in the constellation’s northern region. It is known for its distinctive shape and vibrant colors.
Which constellations are neighbors to Draco?
Draco shares its borders with several prominent constellations, including Ursa Minor, Boötes, and Lyra.
As a circumpolar constellation, Draco is visible year-round in the Northern Hemisphere. Its proximity to the celestial pole makes it useful for determining the North Star and aiding in navigation.
Is Draco referenced in popular culture?
Absolutely! Draco has made appearances in various forms of popular culture, including books, movies, and video games. It often symbolizes strength, power, or the mythical world.
What are some symbolic meanings associated with Draco?
Draco is sometimes seen as a symbol of wisdom, protection, and the balance between order and chaos. In astrology, it is associated with qualities such as leadership and determination.