Contents
- The Draco Constellation
- Observing Draco in the Night Sky
- Scientific Study of Draco
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What is the cultural significance of the Draco constellation?
- 2. How many stars are in the Draco constellation?
- 3. Can Draco be seen from the Southern Hemisphere?
- 4. What is the story behind Draco’s mythology?
- 5. How can I locate Draco in the night sky?
- 6. What is the best time to observe the Draco constellation?
- 7. Are there any specific tools or equipment needed for observing Draco?
- 8. What is Draco’s role in modern astronomy?
- 9. Has any significant research been conducted on the Draco constellation?
- 10. Are there any other constellations connected to Draco?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How did the Draco constellation get its name?
- 2. Is Draco the largest constellation?
- 3. Are there any famous stars in the Draco constellation?
- 4. Can Draco be seen from the Southern Hemisphere?
- 5. What is the mythology behind the Draco constellation?
- 6. How can I find Draco in the night sky?
- 7. When is the best time to observe Draco?
- 8. Can I observe Draco with the naked eye?
- 9. What role does Draco play in astronomy?
- 10. Has any space mission or telescope captured images of Draco?
- References
- Read More
The Draco Constellation
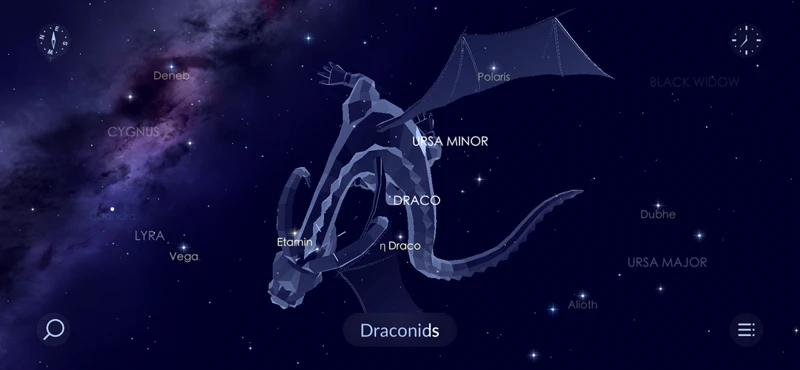
Observing Draco in the Night Sky
Scientific Study of Draco
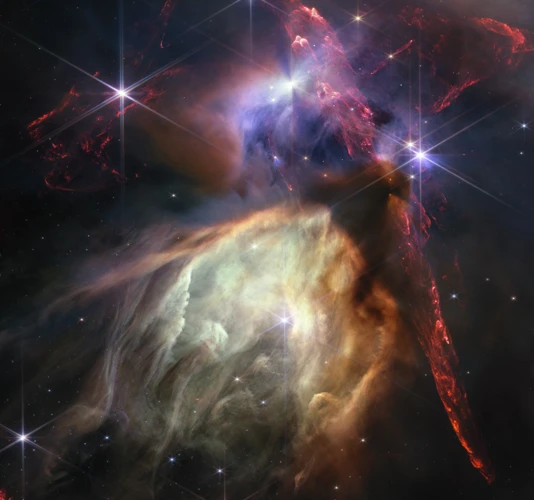

1. Draco’s Role in Astronomy
Conclusion

Frequently Asked Questions

1. What is the cultural significance of the Draco constellation?
The Draco constellation holds cultural significance in various ancient civilizations, including Greek, Egyptian, and Mesopotamian cultures. It has been associated with dragons, serpents, and deities, symbolizing power, wisdom, and protection.
2. How many stars are in the Draco constellation?
The Draco constellation contains several notable stars, including Thuban, Etamin, and Rastaban. In total, there are approximately 17 stars that have been identified and named within this celestial formation.
3. Can Draco be seen from the Southern Hemisphere?
Due to its location in the northern sky, the Draco constellation is not visible from most parts of the Southern Hemisphere. It is primarily visible to observers located in the northern latitudes.
4. What is the story behind Draco’s mythology?
In Greek mythology, Draco is often associated with Ladon, the dragon that guarded the golden apples in the Garden of the Hesperides. In other cultures, Draco is linked to serpent deities and cosmic dragons that represent creation and balance.
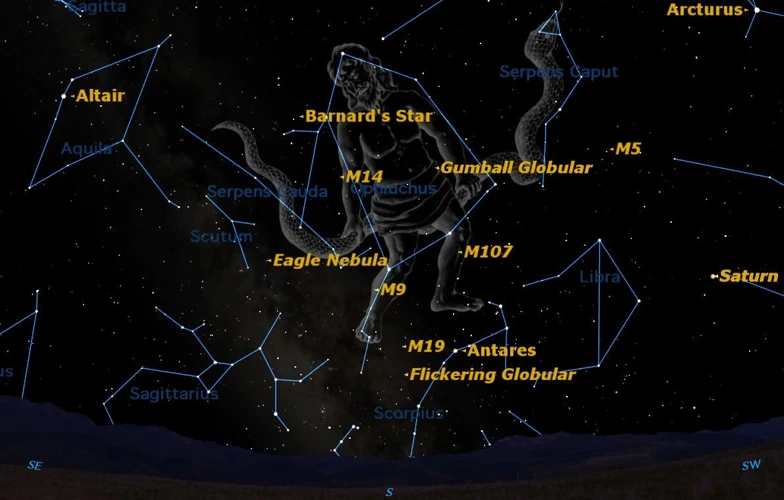
5. How can I locate Draco in the night sky?
To locate Draco, it is helpful to first find the Big Dipper, as Draco’s head lies between the Big and Little Dipper. Follow the curve of the Big Dipper’s handle to find the head of the dragon.
6. What is the best time to observe the Draco constellation?
The best time to observe Draco is during the late spring and early summer months in the Northern Hemisphere when it is at its highest point in the sky. During this time, Draco can be easily seen in the northern celestial hemisphere.
7. Are there any specific tools or equipment needed for observing Draco?
Observing Draco does not require any specific tools or equipment. However, a pair of binoculars or a small telescope can enhance your viewing experience by allowing you to see the finer details of the constellation’s stars.
8. What is Draco’s role in modern astronomy?
Draco plays a crucial role in modern astronomy as it is home to many deep-sky objects, including galaxies and stellar clusters. These objects provide astronomers with valuable insights into the formation and evolution of celestial bodies.
9. Has any significant research been conducted on the Draco constellation?
Yes, scientists have conducted extensive research on Draco. Notable studies include investigating the distribution of dark matter, studying star formation in other galaxies within the constellation, and exploring the gravitational influence of Draco on nearby celestial bodies.
10. Are there any other constellations connected to Draco?
No specific constellations are connected to Draco. However, neighboring constellations like Ursa Major, Ursa Minor, and Hercules are often found in proximity to Draco in the night sky.
References
Frequently Asked Questions

1. How did the Draco constellation get its name?
The name “Draco” is derived from the Latin word for dragon. It was named after the mythical dragon-like creature from ancient Greek mythology.
2. Is Draco the largest constellation?
No, Draco is not the largest constellation. It is actually the eighth largest constellation in the night sky, covering an area of about 1083 square degrees.
3. Are there any famous stars in the Draco constellation?
Yes, there are several notable stars in Draco. One of them is Thuban, which was the North Star around 4,000 years ago. Another notable star is Eltanin, which is one of the brightest stars in Draco.
4. Can Draco be seen from the Southern Hemisphere?
No, Draco is primarily a constellation of the Northern Hemisphere. It is best viewed from latitudes between +90° and -15°.
5. What is the mythology behind the Draco constellation?
The Draco constellation is associated with various mythological tales. One prominent myth is that it represents Ladon, the dragon who guarded the Golden Apples in the Garden of the Hesperides.
6. How can I find Draco in the night sky?
To find Draco in the night sky, locate the Big Dipper (Ursa Major) and trace an imaginary line from the two stars at the end of the Big Dipper’s bowl, leading to the dragon’s head in Draco.
7. When is the best time to observe Draco?
The best time to observe Draco is during the summer months in the Northern Hemisphere, specifically from June to September. During this time, Draco reaches its highest point in the night sky.
8. Can I observe Draco with the naked eye?
Yes, Draco can be observed with the naked eye, especially in areas with minimal light pollution. Its brightest stars are visible, and fainter stars can be spotted using binoculars or a telescope.
9. What role does Draco play in astronomy?
Draco is significant in astronomy as it contains several deep-sky objects, such as galaxies, star clusters, and nebulae. It has been a subject of scientific study and exploration to understand the formation and evolution of celestial objects.
10. Has any space mission or telescope captured images of Draco?
Various space missions and telescopes, such as the Hubble Space Telescope and the Sloan Digital Sky Survey, have captured stunning images of Draco. These images have provided scientists with valuable data and insights into the structure and composition of the constellation.







