Meteors and comets have long captured the curiosity and awe of scientists and sky-watchers alike. These celestial phenomena, though distinct in their nature, share a fascinating connection that extends beyond their captivating displays in the night sky. By exploring the origins, composition, impact events, and influence on planetary evolution, we can uncover the intricate relationship between meteors and comets. Join us on a journey through the cosmos as we unravel the mysteries of these cosmic entities.
Contents
- Understanding Meteors and Comets
- Meteor Showers and Cometary Orbits
- Composition Similarities and Differences
- Impacts and Spectacular Events
- Influence on Planetary Evolution
- The Ongoing Mystery
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What causes the bright streaks we see during a meteor shower?
- 2. How often do meteor showers occur?
- 3. Do all comets produce meteor showers?
- 4. Can meteors and comets pose a threat to Earth?
- 5. How are meteors and meteorites different?
- 6. Can comets hold clues about the formation of the solar system?
- 7. Have any significant impact events been caused by comets?
- 8. Could meteors and comets have played a role in the development of life on Earth?
- 9. Are there ongoing missions and studies aimed at exploring meteors and comets?
- 10. What unanswered questions remain about the connection between meteors and comets?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How often do meteor showers occur?
- 2. Are all comets visible to the naked eye?
- 3. Can a meteor shower be predicted in advance?
- 4. How fast do meteors travel through space?
- 5. What is the difference between a meteor, a meteoroid, and a meteorite?
- 6. How do comets form their characteristic tails?
- 7. Have any known comets impacted Earth?
- 8. Are meteorites valuable?
- 9. Can meteors or comets pose a threat to life on Earth?
- 10. Are there any ongoing missions specifically studying meteors and comets?
- References
- Read More
Understanding Meteors and Comets

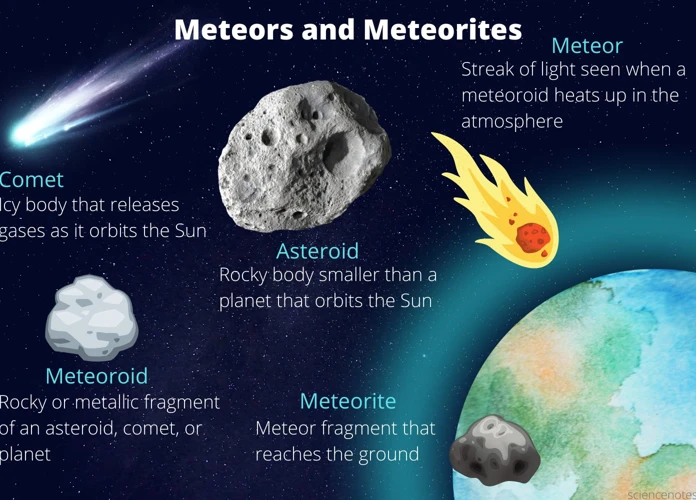
requires delving into the unique characteristics and origins of these celestial objects. Meteors, often referred to as shooting stars, are fleeting streaks of light that occur when small particles enter the Earth’s atmosphere and burn up due to friction. These cosmic fireworks are most commonly associated with meteor showers, which occur when Earth passes through the debris left behind by comets. Comets, on the other hand, are celestial snowballs composed of dust, ice, and organic compounds. They originate in the outer regions of the solar system and, when their orbits bring them closer to the Sun, they develop a glowing coma and tail. These celestial snowballs hold the key to understanding the connection between meteors and comets, as they are the source of the majority of meteors that grace our skies.
1. Meteors: Cosmic Fireworks
Meteors, often referred to as shooting stars, provide a mesmerizing display of cosmic fireworks in the night sky. These fleeting streaks of light occur when small particles, known as meteoroids, enter the Earth’s atmosphere. As they hurtle through the air, the intense heat generated by friction with the atmosphere causes them to burn up, creating a brilliant streak of light. The dazzling trails they leave behind captivate our attention and spark our imagination.
Meteors are commonly associated with meteor showers, which occur when the Earth passes through the debris left behind by comets. Each year, as our planet intersects the orbit of a comet, a shower of meteors occurs. The Perseid meteor shower, for example, is associated with the debris left by Comet Swift-Tuttle. These meteor showers create an awe-inspiring spectacle, with dozens or even hundreds of meteors visible per hour.
While most meteors burn up completely in the Earth’s atmosphere, some larger ones manage to survive the fiery descent and make it all the way to the ground. These surviving fragments are called meteorites and can provide valuable insights into the composition and nature of the objects from which they originated. Studying meteorites helps scientists unravel the mysteries of our solar system’s formation and evolution.
Intriguingly, meteor showers occur in predictable patterns, with specific times of the year associated with different showers. This predictability allows astronomers to forecast meteor shower activity, providing sky-watchers with the opportunity to witness these cosmic fireworks firsthand. Understanding the nature and origins of meteors not only adds to our appreciation of their dazzling displays but also deepens our knowledge of the vast universe in which we reside.
2. Comets: Celestial Snowballs
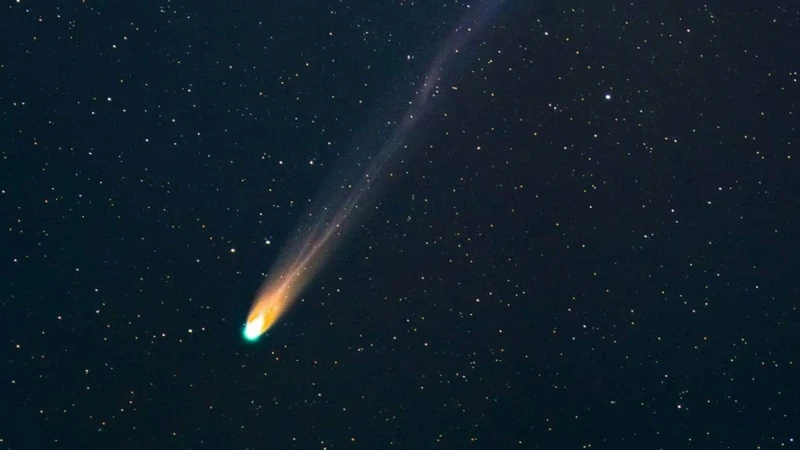
Comets, often referred to as celestial snowballs, are captivating objects that have fascinated both scientists and stargazers for centuries. These icy bodies originate from the outer regions of the solar system, where they reside in a region known as the Oort cloud or the Kuiper Belt. Comets are composed of a combination of dust, rock, organic compounds, and frozen gases, such as water, carbon dioxide, methane, and ammonia. As a comet approaches the inner solar system, the heat from the Sun causes the ices to vaporize, creating a glowing coma or a fuzzy atmosphere around the solid nucleus. The intense solar radiation and the solar wind also push against the coma, creating a tail that can extend for millions of kilometers into space. This celestial spectacle, with its distinct coma and tail, makes comets highly visible and captivating objects in the night sky.
Comets follow elliptical orbits around the Sun, with the length of their orbits varying from a few years to thousands of years. When a comet’s orbit brings it closer to the Sun, it undergoes a process called perihelion, where the intense heat causes the volatile ices to sublimate and release gas and dust into space. This outgassing forms a glowing coma and the characteristic tail that points away from the Sun. The tail always faces away from the Sun due to the pressure of the solar wind. Comets are often categorized into two types: short-period comets, which have orbital periods of less than 200 years, and long-period comets, which have orbital periods greater than 200 years. While short-period comets are believed to originate from the Kuiper Belt, long-period comets are thought to originate from the Oort cloud, a vast shell of icy bodies surrounding the solar system.
The study of comets provides valuable insights into the early solar system and the processes that contributed to the formation of planets. The organic compounds and water ice found in comets suggest that these celestial snowballs could have delivered the necessary ingredients for life on Earth. Researchers hypothesize that cometary impacts during the early stages of Earth’s formation may have provided the building blocks for life and contributed to the development of Earth’s atmosphere and oceans. Understanding comets and their composition is crucial for unraveling the mysteries of our cosmic origins.
As scientists continue to study comets and gather data from comet missions like Rosetta and Stardust, our understanding of these celestial snowballs deepens. The exploration and investigation of comets provide valuable insights into the dynamics of the solar system, the origins of life, and the evolution of celestial bodies. By unraveling the secrets of comets, scientists are unraveling the mysteries of our own cosmic story.
Related Link: Eclipse Predictions: How Astronomers Forecast Them?
Meteor Showers and Cometary Orbits
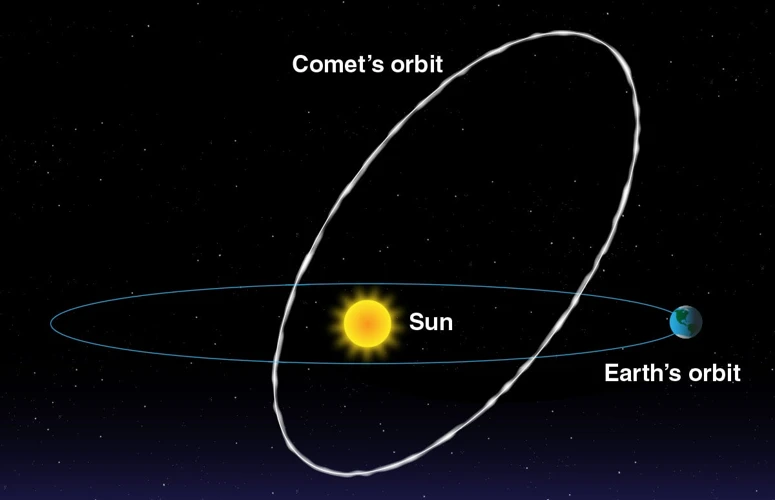
Meteor showers are captivating celestial events that occur when Earth passes through the debris left behind by comets. The source of this cosmic spectacle lies in the cometary orbits of these celestial objects. As comets journey through the solar system, they leave behind a trail of dust and small particles in their wake. When Earth’s orbit intersects with this debris trail, the particles enter our atmosphere and create the mesmerizing display of meteors streaking across the night sky. While meteor showers are typically associated with a specific time of year, such as the Perseids in August or the Orionids in October, their occurrence depends on the orbital path of the parent comet. By understanding the cometary orbits and the gravitational influences that shape them, scientists can predict the timing and intensity of meteor showers, allowing sky-watchers to marvel at these celestial phenomena on predetermined dates.
1. The Source of Meteor Showers
The source of meteor showers lies in the leftover debris from comets. As comets orbit the Sun, they leave behind trails of dust, rocks, and ice in their wake. When Earth’s orbit intersects with these debris trails, the particles enter our planet’s atmosphere at high speeds, causing them to heat up and create the mesmerizing streaks of light we observe as meteors. Each year, Earth encounters several meteor showers, named after the constellation from which they appear to originate. For example, the famous Perseids meteor shower occurs when Earth passes through the debris left behind by the comet Swift-Tuttle. During the peak of a meteor shower, observers can witness dozens or even hundreds of meteors per hour, creating a celestial spectacle that delights astronomers and stargazers alike. Understanding the connection between meteors and comets allows us to appreciate the beauty and transient nature of these cosmic events. If you want to learn more about celestial events, you can explore the importance of sextiles in astrology.
2. The Role of Comets
Comets play a crucial role in the connection between meteors and comets. As they journey through the vastness of space, comets leave behind a trail of debris composed of dust, rocks, and ice. These debris trails are known as cometary orbits and serve as the source of many meteor showers that occur on Earth. When our planet intersects one of these cometary orbits, the debris left by the comet enters our atmosphere and creates the spectacular phenomenon of a meteor shower. Throughout history, scientists have carefully studied the timing and frequency of meteor showers to trace them back to the comets that spawned them. This has allowed astronomers to identify specific comets as the source of famous meteor showers such as the Perseids and the Leonids. The role of comets in producing meteor showers sheds light on their dynamic nature and their impact on Earth’s celestial events.
Composition Similarities and Differences

Meteors and comets may share a connection, but their compositions differ in significant ways. Meteors, also known as shooting stars, are primarily composed of stardust – tiny particles that originated from asteroids or comets. These particles are made up of various minerals and elements, such as iron, nickel, and silicates, giving meteors their characteristic glow as they burn up in the atmosphere. On the other hand, comets are like frozen time capsules, consisting of a mix of ice, dust, and organic compounds that date back to the early stages of the solar system’s formation. This unique composition makes comets valuable resources for studying the building blocks of planets and the possibility of extraterrestrial life. Tracing the connection between meteors and comets provides valuable insights into the origins and evolution of our cosmic neighborhood.
1. Stardust in Meteors
The topic of “1. Stardust in Meteors” delves into the composition of meteors and the presence of stardust within them. Meteors are not just fleeting streaks of light in the sky; they are also a glimpse into the vast universe and the material it contains. When meteors enter Earth’s atmosphere, they heat up rapidly due to friction, causing the outer layers to melt and vaporize. This process releases tiny particles of dust and minerals that were once part of larger asteroids or comets. These particles, known as stardust, can provide valuable insights into the formation and evolution of our solar system.
Stardust found in meteors is composed of a variety of minerals and elements, such as silicates, carbonates, and metals. Analyzing this stardust can reveal important information about the age of the solar system and the processes that shaped it. Scientists use specialized techniques to study the composition of stardust, including electron microscopy and mass spectrometry.
One of the most remarkable aspects of stardust in meteors is its origin. Some stardust grains are older than the Sun itself, dating back to before the formation of our solar system. These ancient particles offer a unique opportunity to study the conditions present in the interstellar medium before the birth of our solar system. By examining the isotopic composition and chemical signatures of stardust, scientists can gain insights into stellar evolution and the processes that led to the formation of our planetary system.
Stardust in meteors serves as a testament to the interconnectedness of celestial bodies and their role in shaping the cosmos. It provides a tangible link between Earth and the vastness of space, allowing us to unravel the mysteries of our origins. The study of stardust in meteors continues to contribute valuable knowledge to our understanding of the universe and its fascinating history.
2. Comets: Frozen Time Capsules
Comets, often referred to as frozen time capsules, harbor invaluable information about the early solar system. These celestial snowballs are composed of a mixture of ice, dust, and organic compounds, providing us with a glimpse into the conditions that prevailed during the formation of our solar system. The nucleus of a comet is essentially a solid ball of ice and rock, often several kilometers in diameter. As a comet approaches the Sun, the heat causes the ice to vaporize, creating a glowing coma, or atmosphere, around the nucleus. This coma can stretch for thousands of kilometers and is often accompanied by a magnificent tail that points away from the Sun. By studying the composition of comets, scientists can gain insights into the chemical and physical processes that occurred billions of years ago. The volatile materials contained within comets, such as water, carbon dioxide, methane, and ammonia, can help us understand the origins of Earth’s oceans, atmosphere, and even the building blocks of life itself. Comets are like time capsules, preserving remnants of the past and offering us a window into the early history of our solar system. It is through the study of these celestial wanderers that we can unlock the secrets of our cosmic origins.
3. Tracing the Connection
Tracing the connection between meteors and comets sheds light on the fascinating interplay between these celestial phenomena. Scientists have found compelling evidence linking meteorites found on Earth to specific comets through chemical analysis. Meteorites, which are fragments of meteors that survive their journey through the atmosphere and land on Earth’s surface, contain unique compositions that can be traced back to specific parent bodies. By studying the isotopic compositions of meteorites, scientists can determine their origin in the solar system and match them to the compositions of comets. This suggests that comets, with their icy nuclei and organic compounds, serve as the source material for many of the meteorites that fall to Earth. This connection further strengthens the relationship between meteors and comets, offering valuable insights into the origins and dynamics of these cosmic entities.
Impacts and Spectacular Events
Meteorite impacts on Earth and comet impacts are both rare but powerful events that have left a lasting impact on our planet’s history. Meteorite impacts occur when meteors make it through Earth’s atmosphere and collide with the surface. These impacts have the potential to create large craters, alter landscapes, and even cause mass extinctions. One of the most well-known impact events in history is the Chicxulub impact, which is believed to have caused the extinction of the dinosaurs. Comet impacts, although less common, can be even more catastrophic due to the large size and composition of comets. The Shoemaker-Levy 9 comet, for example, collided with Jupiter in 1994, resulting in a series of spectacular and massive explosions that were visible from Earth. These impact events, whether they occur on Earth or other celestial bodies, are reminders of the dynamic and ever-changing nature of our universe.
1. Meteorite Impacts on Earth
Meteorite Impacts on Earth
1. Meteorite impacts on Earth have played a significant role in shaping the planet’s geology and history. These extraterrestrial objects, ranging in size from tiny fragments to massive rocks, have collided with Earth throughout its existence, leaving behind evidence of their powerful impact.
2. One of the most notable impact events in Earth’s history is the Chicxulub impact, which occurred about 66 million years ago. It is believed to be the cause of the mass extinction event that wiped out the dinosaurs and many other species. The impact crater, located in present-day Mexico, is a stark reminder of the immense forces at play when a meteorite strikes the planet.
3. Meteorite impacts also leave behind unique geological features called impact craters. These craters can vary in size, with some measuring just a few meters in diameter while others span tens or even hundreds of kilometers. They are formed when a meteorite collides with the Earth’s surface, causing an explosion that creates a bowl-shaped depression. The resulting impact crater can preserve important geological and biological information, providing valuable insights into Earth’s history.
4. In addition to their geological significance, meteorite impacts can also have a profound impact on the planet’s climate. Large impacts can release enormous amounts of energy and eject debris into the atmosphere, leading to temporary global cooling. This phenomenon, known as an impact winter, can disrupt ecosystems and have long-lasting effects on life on Earth.
5. By studying meteorite impacts and their effects, scientists can gain insight into the dynamics of Earth’s past, as well as the potential risks posed by future impact events. Ongoing research and monitoring of near-Earth objects help provide early warning systems and inform strategies for planetary defense. Meteorite impacts continue to shape our understanding of the Earth’s history and hold valuable clues about the origins of life on our planet.
2. Comet Impacts: Rare but Powerful
Comet impacts on celestial bodies can be rare occurrences, but they can have a powerful and transformative effect. When a comet collides with a planet or moon, the impact can release an incredible amount of energy. This energy is equivalent to that of multiple nuclear bombs exploding simultaneously. The impact of a comet can create enormous craters, trigger seismic activity, and even cause widespread devastation. One example of a powerful comet impact is the one that occurred on Jupiter in 1994. Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 broke apart and impacted Jupiter, leaving a series of dark impact scars on its surface. These scars were visible for several months and were estimated to be as large as the Earth itself. The impact of comets on Earth has also shaped our planet’s geological history. It is believed that a comet impact approximately 65 million years ago led to the extinction of the dinosaurs and other species. The impact caused dust and debris to fill the atmosphere, blocking sunlight and causing a significant drop in temperature. This catastrophic event altered the course of life on Earth. While comet impacts are rare, they have the potential to leave a lasting impact on celestial bodies, shaping their landscapes and influencing the evolution of life.
3. Historical Impact Events
- Crater Lake: One notable historical impact event is believed to have formed Crater Lake in Oregon, USA. The lake is situated within the caldera of Mount Mazama, a volcano that collapsed approximately 7,700 years ago after a massive eruption. The collapse created a large depression which later filled with water, forming the stunning Crater Lake.
- Chicxulub Impact: Approximately 66 million years ago, a massive asteroid or comet collided with Earth near what is now the Yucatan Peninsula in Mexico. This impact event, known as the Chicxulub impact, triggered a chain of events that ultimately led to the extinction of the dinosaurs and many other species. The impact left behind a crater over 180 kilometers (112 miles) in diameter and caused widespread devastation.
- Tunguska Event: In 1908, a powerful explosion occurred near the Tunguska River in Siberia, Russia. The cause of this event is still debated, but most scientists believe it was caused by the airburst of a meteoroid or comet fragment. The explosion flattened trees over a vast area of about 2,000 square kilometers (770 square miles), but fortunately, due to the remote location, there were no reported human casualties.
Influence on Planetary Evolution
The influence of meteors and comets extends beyond their captivating displays in the night sky. These celestial objects have played a vital role in shaping the evolution of planets. Meteors, with their fiery descent through the atmosphere, have been responsible for delivering essential building blocks to planets. These stardust particles contain valuable elements and compounds that contribute to the formation of planetary bodies and the development of life. Comets, with their icy composition, have also played a significant role in the evolution of planets. As they approach the Sun, comets release gases and dust, contributing to the formation of planetary atmospheres. This process has been crucial in creating the diverse and complex atmospheres that exist in our solar system. The impact events caused by meteors and comets have the potential to stir up biological possibilities by providing energy and creating favorable conditions for life to thrive. The ongoing study of meteors and comets continues to shed light on the intriguing connection between these cosmic objects and the evolution of planets.
1. Delivering Essential Building Blocks
Meteors and comets play a crucial role in delivering essential building blocks for the formation of planets and life itself. Both meteors and comets contain a variety of organic and inorganic compounds that serve as the raw materials necessary for the development of complex molecules. These compounds include amino acids, nucleotides, and other organic molecules that are the building blocks of proteins and nucleic acids, the fundamental components of life. When meteors and comets collide with planets, they deposit these compounds onto their surfaces, enriching the planetary environment with the necessary ingredients for life to emerge.
One notable example is the Murchison meteorite, which fell in Australia in 1969. Analysis of this meteorite revealed the presence of over 100 different amino acids, including some that are essential for life as we know it. This discovery suggests that meteors and comets could have played a significant role in seeding Earth with the necessary organic compounds for life to originate.
The delivery of water, another essential ingredient for life, is also attributed to comets. Comets are composed mainly of ice, and when they approach the Sun, the heat causes the ice to vaporize, creating a glowing coma and tail. This process releases vast amounts of water vapor, which can later condense and fall onto planets. It is believed that comets played a vital role in bringing water to Earth during its early stages of formation.
Meteors and comets act as cosmic delivery systems, transporting essential building blocks and water to planets like Earth. These celestial objects are intricately connected to the origins and development of life in the universe, making them of great interest to scientists studying the complexities of our existence.
2. Contributing to Atmospheres
Comets play a significant role in the development and evolution of planetary atmospheres. When a comet approaches the Sun, the heat causes the frozen gases within it to vaporize, creating a glowing coma and a tail. As the comet moves closer to a planet, some of these released gases, such as water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane, can interact with the planet’s atmosphere. This interaction can have several effects.
Atmospheric Composition: The gases released by comets can introduce new elements and compounds to a planet’s atmosphere, altering its composition. For example, the impact of cometary particles can deposit organic molecules that are essential for the development of life. The delivery of these building blocks can potentially fuel the emergence of life forms on planets.
Chemical Reactions: The interaction between cometary gas and atmospheric molecules can initiate chemical reactions, leading to the formation of new compounds. These reactions can contribute to the diversity of atmospheric chemistry, shaping the characteristics and properties of the atmosphere.
Physical Processes: Cometary impacts can also trigger physical processes within a planet’s atmosphere. The release of large amounts of energy during impact events can generate shockwaves that propagate through the atmosphere, affecting its dynamics and circulation patterns.
The influence of comets on atmospheres is not limited to their direct interactions. The influx of cometary material over time can have long-term effects on the composition and evolution of planetary atmospheres, contributing to the overall habitability and environmental conditions of a planet.
Comets, through their interactions with planetary atmospheres, bring about changes in composition, initiate chemical reactions, and influence physical processes. These contributions play a vital role in shaping the atmospheric conditions of planets and potentially facilitating the emergence of life.
3. Stirring Up Biological Possibilities
Stirring Up Biological Possibilities: The connection between meteors and comets goes beyond their visual spectacle and impact events. These cosmic wanderers may have played a significant role in the origin and evolution of life on Earth. When meteors and comets enter the atmosphere, they bring with them a plethora of organic compounds, including amino acids, the building blocks of life. These compounds have been found in meteorites that have landed on Earth, providing evidence for the delivery of important ingredients for the development of life. The impacts of large meteors and comets can lead to significant environmental changes, such as altering climate patterns and triggering mass extinctions. While these events may cause devastation, they also offer an opportunity for new life forms to flourish in the aftermath. Additionally, the water vapor released by comets could contribute to the formation of oceans on early Earth, providing a suitable environment for life to thrive. Understanding the role of meteors and comets in stirring up biological possibilities not only sheds light on our own origins but also invites us to ponder the potential for life elsewhere in the universe.
The Ongoing Mystery

The connection between meteors and comets continues to intrigue scientists, leaving many unanswered questions. One of the ongoing mysteries is the origin of comets. While it is believed that most comets originate from the outer regions of the solar system, known as the Oort Cloud and Kuiper Belt, the exact mechanisms that trigger their migration towards the Sun are not fully understood. Additionally, the role of comets in delivering water and organic compounds to Earth, potentially contributing to the development of life, remains a topic of ongoing research and debate. Future missions and discoveries, such as the Europa Clipper mission to Jupiter’s moon Europa and the Comet Interceptor mission, provide hope for shedding more light on these enigmatic celestial bodies. By unlocking the secrets of meteors and comets, we can gain deeper insights into the origins and evolution of our solar system and beyond, unraveling the ongoing mystery that captivates astronomers and stargazers worldwide.
1. Unanswered Questions
Unanswered Questions:
- What causes the variability in meteor showers? While we have a general understanding that meteor showers occur when Earth passes through the debris left by comets, the specific factors that contribute to the variability in meteor shower activity remain unclear. Scientists continue to investigate the influence of factors such as the size and composition of the particles within the debris field, as well as the gravitational interactions between comets and other celestial bodies.
- Are there undiscovered comets influencing meteor activity? The known periodic comets are responsible for several meteor showers, but scientists suspect that there may be undiscovered comets that also contribute to meteor activity. Identifying these comets and understanding their characteristics could provide valuable insights into the relationship between comets and meteors.
- What is the exact composition of comets and meteors? While we have made significant progress in analyzing the composition of cometary and meteoritic material, there are still many unanswered questions. Scientists are particularly interested in understanding the organic compounds present in these celestial objects, as they could provide crucial insights into the origins of life on Earth.
- How do comets and meteors impact planetary evolution? While we know that comets and meteors have played a role in delivering essential building blocks and contributing to planetary atmospheres, the exact extent of their influence on planetary evolution remains a topic of ongoing research. Scientists are working to uncover the specific mechanisms through which these celestial bodies shape the evolution of worlds throughout the universe.
- What other mysteries lie within the realm of meteors and comets? The study of meteors and comets has always been filled with unanswered questions. From the origin of the first stars to the potential for extraterrestrial life, there are countless mysteries waiting to be unraveled. Further exploration and advancements in technology will undoubtedly lead to new discoveries and fuel our curiosity for generations to come.
2. Future Missions and Discoveries
As our understanding of meteors and comets continues to evolve, future missions and discoveries hold the promise of uncovering even more intriguing insights. Scientists and space agencies are actively planning and executing missions to explore these enigmatic cosmic phenomena. One such mission is the European Space Agency’s (ESA) Comet Interceptor, which aims to be the first spacecraft to visit a pristine comet or interstellar object that has never before entered the inner solar system. The mission, expected to launch in the early 2030s, will provide invaluable data and observations about comets and their composition, shedding light on their connection to meteors and the early solar system. Another significant upcoming mission is NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART), set to launch in 2022. DART will test the effectiveness of an asteroid deflection technique by colliding with the moonlet of the Didymos asteroid. This mission will not only help us understand the possibility of deflecting hazardous asteroids but also provide insights into the composition and structure of these objects, potentially revealing more about their connection to meteors and comets. The ongoing advancements in technology and our continued exploration of space hold immense potential for unraveling the mysteries surrounding meteors, comets, and their interplay in the cosmic tapestry. These future missions and discoveries are poised to take us closer to understanding the profound connection between these celestial entities.
Conclusion

The fascinating connection between meteors and comets has been unveiled through our exploration of their origins, composition, impact events, influence on planetary evolution, and existing mysteries. While meteors provide us with captivating cosmic fireworks and meteor showers, comets act as celestial snowballs, leaving behind a trail of debris that produces these mesmerizing displays. By studying the stardust found in meteors and the frozen time capsules of comets, scientists gain insight into the building blocks of our universe. Meteorite impacts on Earth and rare but powerful comet impacts have shaped the history of our planet, leaving behind intriguing historical impact events. Furthermore, meteors and comets have played a significant role in delivering essential building blocks, contributing to planetary atmospheres, and stirring up the possibilities of life. Yet, the connection between meteors and comets remains an ongoing mystery, spurring scientists to seek answers to unanswered questions. The future holds promise for further missions and discoveries that will deepen our understanding of this cosmic relationship. As we continue to gaze at the night sky, the intertwining story of meteors and comets invites us to marvel at the beauty and complexity of the universe.
Frequently Asked Questions

1. What causes the bright streaks we see during a meteor shower?
During a meteor shower, the bright streaks, known as meteors, are caused by small particles, often no larger than a grain of sand, entering Earth’s atmosphere and burning up due to friction.
2. How often do meteor showers occur?
Meteor showers occur throughout the year, but certain showers are more prominent and predictable. The frequency of meteor showers varies, with some occurring annually, while others may be more sporadic.
3. Do all comets produce meteor showers?
No, not all comets produce meteor showers. Only comets that leave behind a debris trail in their orbit around the Sun result in meteor showers when the Earth passes through that trail.
4. Can meteors and comets pose a threat to Earth?
While meteors and comets can potentially collide with Earth, the chances of a large impact are extremely rare. Earth’s atmosphere typically burns up smaller meteors, and comets tend to disintegrate or veer off course due to gravitational forces.
5. How are meteors and meteorites different?
Meteors are the streaks of light observed when particles enter Earth’s atmosphere, whereas meteorites are the remnants that survive the journey through the atmosphere and reach the surface of the Earth.
6. Can comets hold clues about the formation of the solar system?
Yes, comets are often referred to as “frozen time capsules” because they contain a wealth of information about the formation of the solar system. By studying the composition of comets, scientists can gain insight into the materials present during the early stages of our cosmic neighborhood.
7. Have any significant impact events been caused by comets?
While rare, comets have been associated with some of the most significant impact events in Earth’s history. One notable example is the impact of Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 with Jupiter in 1994.
8. Could meteors and comets have played a role in the development of life on Earth?
It is possible that meteors and comets brought essential building blocks, such as water and organic compounds, to Earth. These components could have contributed to the formation of the early Earth’s oceans and provided the necessary ingredients for the origin of life.
9. Are there ongoing missions and studies aimed at exploring meteors and comets?
Yes, numerous missions and studies are dedicated to exploring meteors and comets. NASA’s Stardust mission and the ongoing study of the Hayabusa2 mission are examples of endeavors aimed at deepening our understanding of these celestial objects.
10. What unanswered questions remain about the connection between meteors and comets?
Despite considerable research, there are still unanswered questions about the precise role of comets in meteor showers, the exact nature of certain impact events, and the potential biological implications of extraterrestrial materials brought by meteors and comets.
References
Frequently Asked Questions

1. How often do meteor showers occur?
Meteor showers occur on a regular basis throughout the year. Some showers, like the Perseids in August and the Geminids in December, are widely known and observed annually. However, there are numerous smaller meteor showers happening frequently that may not be as well-known.
2. Are all comets visible to the naked eye?
No, not all comets are visible to the naked eye. Comets vary in size, composition, and distance from the Earth, which determines their visibility. Some comets remain far away from us and require telescopes to see, while others come close enough to be seen without any optical aid.
3. Can a meteor shower be predicted in advance?
Yes, meteor showers can be predicted in advance based on the known orbits of comets and their debris. Astronomers use computer models to calculate when the Earth will intersect the path of a comet’s debris, resulting in a meteor shower. However, the intensity of the shower and the number of visible meteors can be unpredictable.
4. How fast do meteors travel through space?
Meteors typically travel through space at speeds ranging from 25,000 to 160,000 miles per hour (40,000 to 260,000 kilometers per hour). The exact speed depends on various factors, including the velocity of the parent comet and the Earth’s relative motion.
5. What is the difference between a meteor, a meteoroid, and a meteorite?
A meteoroid is a small rocky or metallic object that orbits the sun. When a meteoroid enters the Earth’s atmosphere and burns up, it is called a meteor. If a meteor survives the atmospheric entry and lands on Earth’s surface, it is called a meteorite.
6. How do comets form their characteristic tails?
The tails of comets are formed when the heat from the sun causes the cometary ice to vaporize. This vaporization process releases gas and dust particles, which create bright tails that can extend millions of kilometers into space. The pressure of solar radiation also contributes to the shaping of the tails.
7. Have any known comets impacted Earth?
There is no definitive record of a comet impacting Earth in recorded history. However, some researchers speculate that large comet impacts may have occurred in the past, leaving craters and causing significant changes to the planet’s climate and environment.
8. Are meteorites valuable?
Meteorites can have scientific and monetary value. Some meteorites contain rare elements or minerals that are not commonly found on Earth, making them valuable for scientific research. Additionally, collectors and enthusiasts are often willing to pay significant amounts of money for unique or highly sought-after meteorite specimens.
9. Can meteors or comets pose a threat to life on Earth?
Meteoroids and comets that burn up in the Earth’s atmosphere pose no direct threat to life on Earth. However, larger objects that survive atmospheric entry, such as asteroid impacts, can potentially cause significant damage and have long-term effects on the planet’s ecosystem.
10. Are there any ongoing missions specifically studying meteors and comets?
Yes, there are several ongoing missions dedicated to studying meteors and comets. For example, NASA’s Stardust mission collected samples from a comet’s coma and returned them to Earth for analysis, while the ESA’s Rosetta mission orbited a comet and deployed a lander to its surface to gather data.