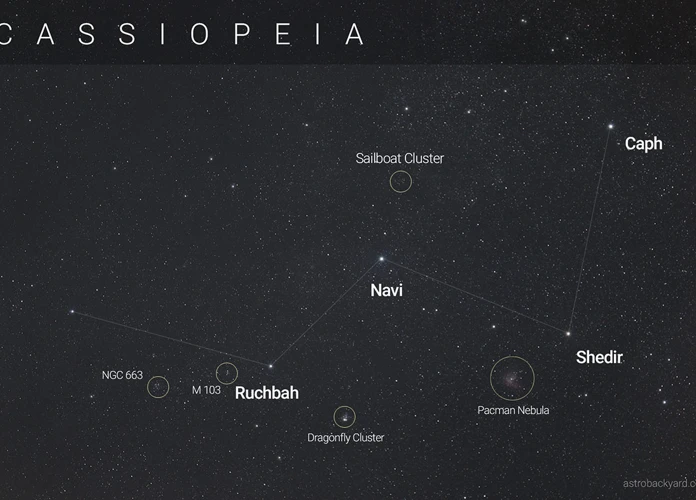
Embark on a celestial journey as we unveil the hidden wonders of the Cassiopeia Constellation. Nestled amidst the vast expanse of the night sky, Cassiopeia has captivated stargazers for centuries with its unmistakable shape, resembling a grand “W” or “M”, depending on its orientation. While the zodiac may steal the limelight, this constellation boasts a treasure trove of non-zodiac stars waiting to be discovered. From the majestic Caph, the crown jewel, to the radiant Schedar, the luminary princess, and the enigmatic Ruchbah, the celestial arch, we invite you to unravel the myths, delve into the scientific significance, and marvel at the remarkable deep-sky objects that adorn the canvas of Cassiopeia. Prepare to be dazzled by the secrets that lie within this celestial masterpiece.
Contents
- The Cassiopeia Constellation
- The Non-Zodiac Stars
- The Mythology Behind Cassiopeia
- Scientific Significance
- Notable Deep Sky Objects in Cassiopeia
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What are some other prominent stars in the Cassiopeia Constellation besides the zodiac stars?
- 2. How is the Cassiopeia Constellation significant historically?
- 3. Where is the Cassiopeia Constellation located? Can it be easily spotted?
- 4. What makes Caph an exceptional star in the Cassiopeia Constellation?
- 5. What distinguishes Schedar as a remarkable star in the Cassiopeia Constellation?
- 6. What celestial arch does Ruchbah represent in the Cassiopeia Constellation?
- 7. What is the mythological story behind the Cassiopeia Constellation?
- 8. How are the non-zodiac stars in Cassiopeia classified and what are their properties?
- 9. Has the Cassiopeia Constellation contributed to any significant astrophysical research or discoveries?
- 10. Are there any notable deep sky objects within the Cassiopeia Constellation?
- References
- Read More
The Cassiopeia Constellation
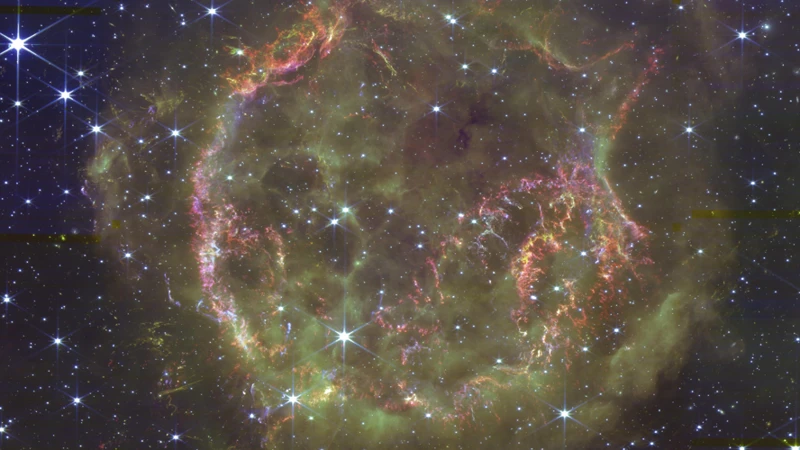

The Cassiopeia Constellation, with its enthralling celestial display, has intrigued astronomers and stargazers throughout history. This constellation holds great historical significance, featuring prominently in various mythological stories and cultural beliefs. It is located in the northern hemisphere and is highly visible from latitudes above 30 degrees. Whether you are in search of the mythical Queen Cassiopeia, looking to understand the missing zodiac sign of Ophiuchus, or exploring the intriguing world of zodiac signs, the Cassiopeia Constellation offers a captivating window into the cosmos. Its unmistakable shape and easily identifiable stars make it a perfect starting point for stargazing adventures. So, grab your telescope and prepare to lose yourself in the enchanting mysteries of the Cassiopeia Constellation.
1.1 Historical Significance
The historical significance of the Cassiopeia Constellation is deeply rooted in ancient mythology and cultural beliefs. In Greek mythology, Cassiopeia was said to be the beautiful but boastful queen of Ethiopia. She claimed to be more beautiful than the sea nymphs known as the Nereids, angering the god Poseidon. As punishment for her hubris, Cassiopeia was placed in the night sky, doomed to circle the celestial sphere upside-down for eternity. This captivating tale not only highlights the consequences of pride but also serves as a reminder of the enduring nature of celestial bodies and their influence on human beliefs and storytelling.
Additionally, the Cassiopeia Constellation plays a role in the astrology community, particularly regarding the missing zodiac sign of Ophiuchus. Ophiuchus, sometimes referred to as the serpent bearer, is positioned between the constellations of Scorpius and Sagittarius. Its positioning infringes on Cassiopeia’s region of the sky. This has led to debates and discussions about incorporating Ophiuchus as a thirteenth zodiac sign. The rich historical and mythological significance of Cassiopeia adds a layer of fascination to the ongoing exploration of zodiac signs and their interpretations, offering a glimpse into the diverse cultural beliefs and their impact on astrology.
In other cultural contexts, Cassiopeia’s prominence extends beyond Greek mythology. In Aztec cosmology, for example, Cassiopeia symbolizes the journey of souls after death. It represents the path to the afterlife and is associated with the god Quetzalcoatl, who guides souls through the celestial realm. This link between Cassiopeia and the afterlife showcases the diverse interpretations and representations of constellations across different cultures and highlights the universal fascination with the stars above.
So, whether it’s through ancient Greek mythology, astrology debates, or cultural beliefs about the afterlife, the historical significance of the Cassiopeia Constellation is a testament to the enduring allure of the cosmos and its impact on human narratives and imagination.
1.2 Location and Visibility
Located in the northern hemisphere, the Cassiopeia Constellation graces the night sky with its distinctive “W” or “M” shape, depending on its orientation. It can be easily observed from latitudes above 30 degrees, making it visible to a large portion of the Earth’s population. The constellation’s right ascension falls between 1 and 4 hours, while its declination ranges from approximately 50 to 70 degrees. Its position in the sky places it near other notable constellations such as Perseus, Andromeda, and Camelopardalis. Depending on the time of year and location, Cassiopeia can be observed at various times during the night. In the northern hemisphere, its peak visibility usually occurs during the autumn and winter months, when it can be seen in the evenings above the horizon. Whether you’re an avid stargazer or just a casual observer, the radiant beauty of the Cassiopeia Constellation is sure to captivate you as you explore the wonders of the night sky.
The Non-Zodiac Stars
In the vast expanse of the Cassiopeia Constellation, a multitude of non-zodiac stars await exploration and admiration. Let’s embark on a journey to discover some of these hidden gems. First, we encounter Caph, the crown jewel of Cassiopeia, radiating a mesmerizing brilliance that captivates the eye. Schedar, the luminary princess, enchants with her ethereal glow, standing as a testament to the celestial wonders of this constellation. And then, there’s Ruchbah, the celestial arch, with its enigmatic allure that beckons us to unravel its secrets. These non-zodiac stars, each with their unique properties and stunning luminosity, add depth and character to the captivating tapestry of the Cassiopeia Constellation. Whether you are drawn to the missing zodiac sign of Ophiuchus, fascinated by mythological stories surrounding the zodiac signs, or curious about Aztec cosmology and the afterlife, the exploration of these non-zodiac stars offers a glimpse into the cosmic wonders that lie beyond. So, let us submerge ourselves in this celestial treasure trove and uncover the mysteries of the non-zodiac stars in Cassiopeia’s embrace.
2.1 Caph – The Crown Jewel
Caph, adorned with celestial brilliance, stands as the crown jewel of the Cassiopeia Constellation. This captivating star, also known as Beta Cassiopeiae, shines with a luminosity that rivals even the brightest of stars in the night sky. Caph holds a place of significance not only in the constellation but also in the realm of stellar classification. It is classified as a Delta Scuti variable star, meaning it undergoes subtle pulsations in brightness over a short period of time. These pulsations provide valuable insights into the internal structures and evolutionary stages of stars. Caph’s location in the constellation’s northernmost point makes it visible from a wide range of latitudes, facilitating its observation for both amateur and professional astronomers.
The iconic shape of the Cassiopeia Constellation finds its perfect anchor in Caph. As part of the constellation’s distinctive “W” or “M” pattern, depending on its orientation, Caph marks the topmost point, representing the queen’s head. Its radiance adds allure to the allure of Cassiopeia, drawing the eyes of countless stargazers. With a mass around four times that of our sun, this celestial gem emits a captivating glow that mesmerizes us, inspiring awe and wonder.
While Caph is indeed a star of astronomical significance, its name also holds an intriguing connection to the astrological world. In Astrology, the concept of Ophiuchus, the missing zodiac sign, has been a source of fascination for many. The inclusion of this hidden thirteenth sign has sparked debates and discussions about its impact on astrological predictions and personality traits. Whether you are delving into the mysteries of the zodiac signs or exploring the folklore of ancient civilizations, such as the Aztecs and their fascinating cosmology of the afterlife, the enigmatic Caph serves as a celestial guide to expand your horizons and deepen your understanding of the cosmos. So, set your sights towards the crown jewel of Cassiopeia, and let its luminosity light the path of your cosmic explorations.
2.2 Schedar – The Luminary Princess
Schedar, also known as Alpha Cassiopeiae, takes its place as one of the most captivating stars within the Cassiopeia Constellation. This magnificent luminary princess shines with a stunning magnitude of 2.24, making it easily visible to the naked eye. Schedar is a supergiant star, approximately 50 times larger than our Sun and emitting an enchanting golden hue. Its name originates from the Arabic word for “breast,” as it represents the breast of the mythical Queen Cassiopeia.
Schedar’s radiance is not its only outstanding feature. This star is a rare spectral type K0 giant, showcasing its relatively cool surface temperature compared to other stars. Its grandeur and unique characteristics have made it a fascinating subject of study for astronomers. Scientists have been intrigued by Schedar’s stellar classification, which reveals its evolutionary stage and offers insights into its life cycle.
In the realm of astrology, Schedar holds an esteemed position within the Cassiopeia Constellation, offering astrological enthusiasts a glimpse into the cosmic influences attributed to this celestial princess. Whether you are exploring the missing zodiac sign of Ophiuchus, delving into mythological stories around zodiac signs, or intrigued by the intricate details of Aztec cosmology and the afterlife, Schedar’s presence adds an aura of mystique and wonder to the world of astrology.
As you gaze upon the starry tapestry of the Cassiopeia Constellation, allow Schedar’s brilliance to captivate your imagination as you ponder the vastness of our universe and the celestial wonders that lie beyond.
2.3 Ruchbah – The Celestial Arch
Ruchbah, also known as Delta Cassiopeiae, is one of the fascinating non-zodiac stars in the Cassiopeia constellation. Its name is derived from Arabic, meaning “the knee.” Positioned at the lower knee of Queen Cassiopeia, Ruchbah adds to the constellation’s charm and allure. Ruchbah is a binary star system composed of two stars orbiting each other. The primary star in this system is a giant with a spectral type of K3, giving it a distinct orange hue. It shines with an apparent magnitude of 2.68, making it one of the brighter stars in the constellation. The secondary star, on the other hand, is a blue-white dwarf, significantly smaller and hotter than its companion. This binary system provides a captivating contrast of colors when observed through a telescope. The two stars dance together, creating a mesmerizing celestial arch that adds depth to the beauty of Cassiopeia. Ruchbah has intrigued astronomers with its unique properties and behavior. Its study has contributed to scientific advancements in understanding stellar evolution and binary star systems. The celestial arch of Ruchbah is a sight to behold, reminding us of the vast wonders and intricacies of the universe. To learn more about other fascinating stars and constellations, delve into the mysteries of the missing zodiac sign of Ophiuchus or explore the captivating mythological stories behind the zodiac signs.
The Mythology Behind Cassiopeia
The Mythology Behind Cassiopeia enchants us with tales of gods, heroes, and cosmic punishment. According to Greek mythology, Cassiopeia was a beautiful but vain queen who boasted of her daughter’s beauty, claiming it surpassed that of the sea nymphs. This hubris caught the attention of Poseidon, god of the seas, leading to dire consequences. As a punishment, Cassiopeia was bound to her celestial throne in the night sky, condemned to forever circle the celestial pole. This mythological narrative not only adds a captivating layer of intrigue to the Cassiopeia Constellation but also serves as a cautionary tale against pride and vanity. To delve further into the fascinating world of mythological stories and zodiac signs, check out our article on Exploring Mythological Stories of Zodiac Signs.
3.1 The Queen’s Hubris
In the mythology surrounding the Cassiopeia Constellation, one of the most intriguing tales is that of “The Queen’s Hubris.” According to legend, Queen Cassiopeia was known for her unrivaled beauty and regal demeanor. However, her vanity and arrogance ultimately led to her downfall. The story goes that Queen Cassiopeia boasted about her beauty, claiming that she and her daughter, Andromeda, were more beautiful than the sea nymphs, known as the Nereids. This audacious claim angered the sea god Poseidon, who sought to teach Cassiopeia a lesson.
In his wrath, Poseidon sent forth a sea monster to wreak havoc upon the kingdom. In desperation, Cassiopeia and her husband sought the counsel of an oracle, who revealed that in order to appease the gods and save their kingdom, they must sacrifice their daughter to the sea monster. Although torn by the decision, Cassiopeia agreed to sacrifice Andromeda.
However, the hero Perseus, who happened to be passing by, caught sight of the beautiful Andromeda and fell in love with her. He bravely fought and defeated the sea monster, rescuing Andromeda from her impending doom. As a reward, Perseus took Andromeda’s hand in marriage, forever linking their love in the stars as the neighboring Andromeda Constellation.
As a reminder of her arrogance, Queen Cassiopeia was immortalized in the night sky as a constellation, forever bound to her throne, rotating around the North Celestial Pole. Her prominent position in the heavens serves as a cautionary tale, reminding us of the consequences of hubris and vanity.
This mythological story not only adds an element of intrigue to the Cassiopeia Constellation but also highlights the interconnectedness of various constellations and their stories. So, while exploring the twinkling stars of Cassiopeia, take a moment to reflect on the timeless lessons embedded within its mythological tale and the significance of each celestial entity. If you are interested in delving deeper into the realm of zodiac signs or discovering more about the missing zodiac sign of Ophiuchus, be sure to check out our articles on astrology and the secrets of the stars.
3.2 The Starry Punishment
In the mythological tales surrounding the Cassiopeia Constellation, the story of the starry punishment stands out as a captivating tale of divine retribution. According to the myth, Queen Cassiopeia tragically boasted about her daughter Andromeda’s beauty, claiming her to be more beautiful than the Nereids, the sea nymphs. This prideful act drew the wrath of the gods, particularly Poseidon, who sought to teach Cassiopeia a lesson. As punishment for her hubris, Cassiopeia and her family were condemned to eternal torment in the night sky. Transformed into stars, they were forced to circle the celestial sphere, forever tied to their immortal fate. This cosmic punishment serves as a cautionary reminder of the consequences of arrogance and pride, a lesson that echoes across cultures and civilizations. To further explore the intriguing myths and legends associated with zodiac signs, including the missing sign of Ophiuchus, be sure to check out our article “Ophiuchus: The Missing Zodiac Sign in Astrology”. Alternatively, delve into the rich tapestry of Aztec cosmology and their beliefs about the afterlife by reading our article “Aztec Cosmology: Exploring the Afterlife”.
Scientific Significance

The scientific significance of the Cassiopeia Constellation extends far beyond its aesthetic beauty. Astronomers have classified the stars within Cassiopeia using the stellar classification system, unlocking valuable insights into their properties and behavior. From variable stars that exhibit fluctuations in brightness to binary star systems with two stars orbiting each other, Cassiopeia offers a diverse range of stellar phenomena to study. Scientists have conducted extensive astrophysical research in this constellation, leading to groundbreaking discoveries in areas such as stellar evolution, stellar atmospheres, and stellar remnants. By studying the Cassiopeia Constellation, astronomers have deepened our understanding of the universe’s structure and evolution. Exploring the scientific significance of Cassiopeia will undoubtedly ignite a sense of curiosity and wonder, revealing the hidden wonders of the cosmos that lie beyond our reach.
4.1 Stellar Classification and Properties
Stellar classification and properties are essential aspects of understanding the nature of stars within the Cassiopeia Constellation. Scientists employ specific classification systems to categorize stars based on their temperature, luminosity, size, and other characteristics. One such classification system is the Morgan-Keenan (MK) system, which categorizes stars into different spectral types, denoted by letters such as O, B, A, F, G, K, and M. Each spectral type represents a specific range of temperatures, with O being the hottest and M being the coolest. This classification enables astronomers to gauge a star’s intrinsic brightness and infer important information about its evolutionary stage.
Apart from spectral classification, stars also possess various properties that contribute to their distinctiveness. The luminosity of a star refers to its total amount of energy radiated per unit of time and is influenced by both temperature and size. The color of a star is closely linked to its temperature, with hotter stars appearing bluer and cooler stars exhibiting a reddish hue. Stellar sizes can vary greatly, from small dwarf stars to massive giants or even supergiants.
The Cassiopeia Constellation houses a diverse range of stars with intriguing properties. For example, Caph, the brightest star in the constellation, is classified as a g-type main-sequence star, similar to our Sun. It possesses a luminosity approximately 40 times greater than that of the Sun. Schedar, on the other hand, is a notable example of a K-type giant star, radiating a warm orange glow. Ruchbah belongs to the spectral type A5V, making it a bluish-white star with a luminosity nearly 28 times that of the Sun.
Understanding stellar classification and properties not only allows astronomers to unravel the nature of individual stars but also helps in studying the overall composition and evolution of the Cassiopeia Constellation. By examining multiple stars within the constellation, scientists can paint a comprehensive picture of its stellar population and gain insights into its formation and dynamics. This knowledge contributes to our broader understanding of the cosmos and enriches our exploration of the hidden gems scattered throughout the Cassiopeia Constellation.
4.2 Astrophysical Research and Discoveries
Astrophysical research has played a significant role in unraveling the mysteries of the Cassiopeia Constellation. Scientists and astronomers have diligently studied the stars within Cassiopeia, uncovering valuable insights into stellar classification, properties, and behavior. Through spectroscopic analysis, researchers have been able to determine the chemical composition of these celestial bodies. Stellar evolution studies have revealed the life cycles of stars within the constellation, shedding light on their birth, evolution, and eventual demise. Astronomers have also made remarkable discoveries within Cassiopeia, such as the identification of binary star systems, where two stars orbit around a common center of mass. These findings have expanded our understanding of the dynamics and interactions between celestial bodies. Observations of Cassiopeia have led to the exploration of various astrophysical phenomena, including stellar winds, supernovae remnants, and gamma-ray bursts. The constellation continues to be a focal point for ongoing research and discovery, providing valuable insights into the larger mysteries of our universe.
Notable Deep Sky Objects in Cassiopeia
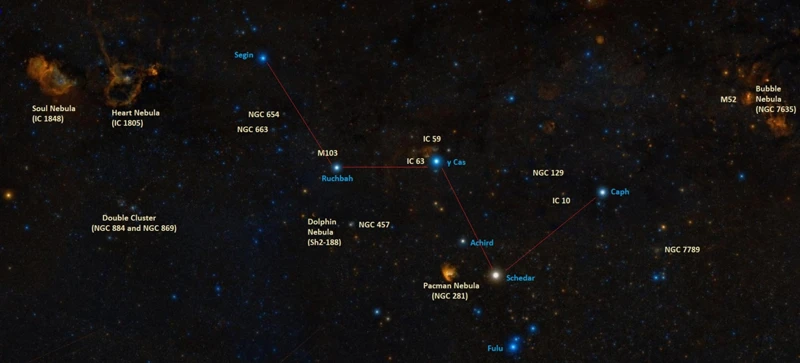
The Cassiopeia Constellation not only hosts a mesmerizing array of stars but also boasts several notable deep sky objects that will leave you in awe. One such celestial marvel is the Heart Nebula, also known as IC 1805. This emission nebula, located approximately 7,500 light-years away from Earth, derives its name from its resemblance to a human heart. Its intricate patterns and vibrant colors make it a favorite among astrophotographers and amateur astronomers. Another captivating deep sky object within Cassiopeia is the Pacman Nebula, or NGC 281. This emission nebula gets its name from its distinctive shape, resembling the iconic video game character. With its dense clouds of gas and dust, the Pacman Nebula is a stellar nursery, giving birth to new generations of stars. Last but certainly not least, the Wizard Nebula, also called NGC 7380, adds its own enchanting touch to the constellation. This emission nebula, located approximately 7,200 light-years away, showcases a mesmerizing combination of vibrant colors and intricate details that resemble a wizard’s face. Each of these deep sky objects provides a unique glimpse into the celestial wonders that Cassiopeia has to offer, making it a must-visit destination for astronomy enthusiasts and stargazers alike.
5.1 The Heart Nebula
The Heart Nebula is a stunning emission nebula located in the Cassiopeia Constellation. Scientifically known as IC 1805, it earned its popular name due to its distinctive shape resembling a human heart. This celestial masterpiece is a stellar nursery where new stars are born. The nebula spans approximately 200 light-years and is located around 7,500 light-years away from Earth. Its vibrant reddish-pink hue is created by the ionized hydrogen gas that permeates the region. This region is also home to a massive star cluster called Melotte 15, which is responsible for illuminating the nebula. The intense radiation from these young, hot stars causes nearby gas clouds to glow with an otherworldly beauty. Photographing the Heart Nebula reveals intricate details of dust lanes, star-forming regions, and wispy tendrils. Its mesmerizing beauty serves as a reminder of the ongoing cycles of stellar birth and death in our universe. Exploring the Heart Nebula is a fascinating glimpse into the intricate tapestry of the cosmos.
5.2 The Pacman Nebula
The Pacman Nebula: Also known as NGC 281, the Pacman Nebula is a fascinating deep-sky object nestled within the borders of the Cassiopeia Constellation. This emission nebula gets its playful nickname from its striking resemblance to the iconic video game character when observed in certain images. Located approximately 9,500 light-years away from Earth, the Pacman Nebula spans about 80 light-years across and is a hub of stellar activity. At its center lies a young, massive star known as HD 5005, which illuminates the surrounding hydrogen gas, giving it its characteristic red glow. This glowing gas region is also surrounded by dark lanes of interstellar dust, creating an ethereal contrast against the vibrant background. With its intricately detailed structure and mesmerizing colors, the Pacman Nebula presents a captivating sight for astrophotography enthusiasts and seasoned astronomers alike.
5.3 The Wizard Nebula
The Wizard Nebula, also known as NGC 7380, is a breathtaking emission nebula located within the Cassiopeia Constellation. This celestial masterpiece gets its name from the intricate network of gas, dust, and young stars that form a shape resembling a wizard casting a spell. The nebula spans an impressive area of approximately 110 light-years, making it a prominent feature in the night sky. Its vibrant colors of red, green, and blue are caused by the presence of ionized hydrogen, oxygen, and sulfur gas. The Wizard Nebula is a haven for star formation, with numerous young, hot stars hidden within its nebulous clouds. These stars emit powerful stellar winds that shape and sculpt the surrounding gas and dust, creating striking structures and pillars. To truly appreciate the beauty of the Wizard Nebula, a telescope equipped with a narrowband filter is recommended. By isolating the specific wavelengths of light emitted by hydrogen, oxygen, and sulfur, the intricate details and delicate features of this celestial marvel become even more apparent. The Wizard Nebula is a favorite target for astrophotographers and amateur astronomers alike, who strive to capture its enchanting beauty and share it with the world. So, seek out the Wizard Nebula in the night sky, and let its magical presence inspire you to explore the wonders of the cosmos.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the Cassiopeia Constellation is a celestial masterpiece that offers a wealth of hidden gems waiting to be explored. From the fascinating non-zodiac stars like Caph, Schedar, and Ruchbah to the captivating mythology surrounding Queen Cassiopeia, this constellation never fails to captivate our imagination. Its scientific significance in stellar classification and astrophysical research further adds to its allure. Moreover, the presence of notable deep sky objects like the Heart Nebula, Pacman Nebula, and Wizard Nebula brings a mesmerizing touch to the Cassiopeia Constellation. Whether you are an avid astronomer or simply an admirer of the night sky, the wonders of Cassiopeia are bound to leave you in awe. So, next time you gaze up at the stars, remember to turn your eyes towards this celestial wonder and experience the hidden treasures it has to offer.
Frequently Asked Questions

FAQs about the Cassiopeia Constellation
Q: Can Cassiopeia be seen from both hemispheres?
A: No, Cassiopeia is a constellation primarily visible from the northern hemisphere.
Q: What is the best time of year to observe Cassiopeia?
A: Cassiopeia is best observed during autumn and early winter in the northern hemisphere.
Q: Is Cassiopeia part of the zodiac?
A: No, Cassiopeia is not part of the traditional zodiac. It is considered a non-zodiac constellation.
Q: What are some notable stars in the Cassiopeia Constellation?
A: Caph, Schedar, and Ruchbah are among the notable stars in the Cassiopeia Constellation.
Q: What is the mythology behind the Cassiopeia Constellation?
A: According to Greek mythology, Cassiopeia was a queen who boasted about her beauty, leading to her punishment and placement in the stars.
Q: Are there any scientific research and discoveries associated with Cassiopeia?
A: Yes, Cassiopeia has been the subject of various astrophysical studies and research, leading to significant discoveries in stellar classification and properties.
Q: Are there any notable deep sky objects within the Cassiopeia Constellation?
A: Yes, the Heart Nebula, the Pacman Nebula, and the Wizard Nebula are some of the prominent deep sky objects found in Cassiopeia.
Q: Can I see the Cassiopeia Constellation with the naked eye?
A: Yes, Cassiopeia is easily visible with the naked eye, especially in areas with little light pollution.
Q: How far away is Cassiopeia?
A: Cassiopeia is approximately 54 light-years away from Earth.
Q: Can I use Cassiopeia to find other constellations?
A: Yes, Cassiopeia can be used as a reference point to locate other constellations, such as the Big Dipper and the North Star (Polaris).
References
- Cassiopeia Constellation Facts, Stars, Map and Myth …
- Cassiopeia Constellation – Features And Facts – The Planets
Frequently Asked Questions

1. What are some other prominent stars in the Cassiopeia Constellation besides the zodiac stars?
In addition to the zodiac stars, the Cassiopeia Constellation features several other prominent stars, including Caph, Schedar, and Ruchbah.
2. How is the Cassiopeia Constellation significant historically?
The Cassiopeia Constellation holds historical significance as it is named after Cassiopeia, a queen from Greek mythology. It has been studied and observed by astronomers for centuries.
3. Where is the Cassiopeia Constellation located? Can it be easily spotted?
The Cassiopeia Constellation is located in the northern sky, near the celestial north pole. It is easily visible in the evenings during the winter months in the northern hemisphere.
4. What makes Caph an exceptional star in the Cassiopeia Constellation?
Caph is often regarded as the crown jewel of the Cassiopeia Constellation. It is a bright star with a spectral classification of F2III, indicating its high luminosity and temperature.
5. What distinguishes Schedar as a remarkable star in the Cassiopeia Constellation?
Schedar, also known as Alpha Cassiopeiae, is one of the most luminous stars in the constellation. It is an orange giant star and showcases a rich amber color when observed.
6. What celestial arch does Ruchbah represent in the Cassiopeia Constellation?
Ruchbah, also known as Delta Cassiopeiae, is an important star in the constellation as it represents the celestial arch. Its name is derived from an Arabic word that translates to “the knee.”
7. What is the mythological story behind the Cassiopeia Constellation?
The mythological story behind the Cassiopeia Constellation revolves around Queen Cassiopeia’s hubris and subsequent punishment by the gods for her arrogance.
8. How are the non-zodiac stars in Cassiopeia classified and what are their properties?
The non-zodiac stars in Cassiopeia are classified based on their spectral types, which determine their temperature, luminosity, and other properties. Each star has unique characteristics and behaviors.
9. Has the Cassiopeia Constellation contributed to any significant astrophysical research or discoveries?
Yes, the Cassiopeia Constellation has been a subject of extensive astrophysical research. It has contributed to various discoveries, such as the study of star formation, stellar evolution, and gravitational waves.
10. Are there any notable deep sky objects within the Cassiopeia Constellation?
Absolutely! The Cassiopeia Constellation is home to several remarkable deep sky objects, including the Heart Nebula, the Pacman Nebula, and the Wizard Nebula, each displaying its own unique cosmic beauty.