Welcome to the captivating world of asteroids and comets, two celestial bodies that hold immense potential for space exploration. With their intriguing characteristics and enigmatic origins, these cosmic wanderers have fascinated scientists and astronomers for centuries. In this article, we will delve into the differences between asteroids and comets, explore their composition and structure, uncover their historical significance, and unravel the mysteries surrounding them. Join us on a journey through the cosmos as we examine missions and discoveries that have brought us closer to understanding these enigmatic objects and discuss the future of asteroid and comet exploration. Brace yourself for an adventure that will ignite your curiosity and expand your horizons!
Contents
- The Difference Between Asteroids and Comets
- Asteroids: The Building Blocks of the Solar System
- Comets: Cosmic Wanderers with Their Own Mysteries
- Exploring Asteroids and Comets: Missions and Discoveries
- The Future of Asteroid and Comet Exploration
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What are the main differences between asteroids and comets?
- 2. How do asteroids and comets differ in composition?
- 3. What causes the distinctive appearance of comets?
- 4. Where can asteroids be found in our solar system?
- 5. What are the origins of comets?
- 6. How do the orbits of asteroids and comets differ?
- 7. Do asteroids and comets pose any threats to Earth?
- 8. Can asteroids and comets provide valuable resources?
- 9. How do studying asteroids and comets help us understand the early solar system?
- 10. What are some of the notable missions that have explored asteroids and comets?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- FAQ 1: How are asteroids and comets different from each other?
- FAQ 2: Are all asteroids the same, or are there different types?
- FAQ 3: What is the historical significance of asteroids?
- FAQ 4: Can asteroids be mined for resources?
- FAQ 5: What are comets made of?
- FAQ 6: Where do comets originate from?
- FAQ 7: What can studying comets tell us about the early solar system?
- FAQ 8: Which missions have explored asteroids?
- FAQ 9: Can asteroids be redirected for future space missions?
- FAQ 10: Are there any strategies in place to protect Earth from near-Earth objects?
- References
- Read More
The Difference Between Asteroids and Comets

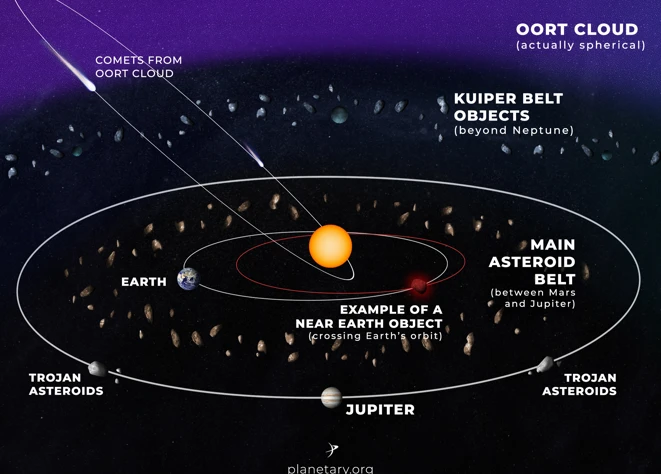
Asteroids and comets are both fascinating celestial objects, but they have distinct differences that set them apart. One of the main differences lies in their composition. Asteroids are rocky and metallic bodies that primarily consist of minerals and metals. They are often referred to as the building blocks of the solar system because they are remnants from the early stages of planetary formation.
On the other hand, comets are icy bodies comprised of frozen gases, dust, and organic compounds. These “dirty snowballs” originate from the outer regions of the solar system, such as the Oort Cloud and the Kuiper Belt. When a comet approaches the Sun, the heat causes the ice to vaporize, creating a glowing coma and often a spectacular tail.
Another distinction between asteroids and comets is their appearance. Asteroids typically have a solid and rocky surface, while comets are characterized by their coma – a surrounding cloud of gas and dust – and their tails. Comets’ tails can be quite magnificent, extending for millions of kilometers and pointing away from the Sun due to the solar wind.
The orbits of asteroids and comets differ. Asteroids mainly orbit the Sun in the asteroid belt, located between Mars and Jupiter. Their orbits are generally more circular and confined to this region. Comets, on the other hand, follow elongated, elliptical orbits that can take them much closer to the Sun and then back to the outer regions of the solar system.
Understanding the difference between asteroids and comets is crucial for studying the formation and evolution of our solar system. They provide valuable insights into the processes that shaped our celestial neighborhood and potentially even brought water and organic compounds to Earth, playing a role in the emergence of life as we know it. Now that we’ve explored the basic distinctions between asteroids and comets, let’s dive deeper into each of these fascinating celestial objects.
Asteroids: The Building Blocks of the Solar System
Asteroids play a crucial role in the formation and evolution of our solar system. These rocky and metallic bodies are the remnants of the early stages of planetary formation and are often referred to as the building blocks of the solar system. They can range in size from tiny boulders to large objects several hundred kilometers in diameter. Asteroids primarily reside in the asteroid belt, a region located between Mars and Jupiter, although they can also be found in other areas such as near-Earth orbits. The composition of asteroids varies, with some being rich in metals like iron and nickel, while others are composed of rocky materials and minerals. Scientists study asteroids to gain insights into the dynamics and processes that occurred during the early stages of our solar system’s development, shedding light on the origins of planets, moons, and other celestial bodies. Asteroids also hold potential for resource extraction and space exploration missions, with plans underway to mine their valuable metals and minerals in the future. Understanding the role of asteroids in the formation of our solar system is essential to unraveling the mysteries of our cosmic neighborhood.
Comets: Cosmic Wanderers with Their Own Mysteries

Comets are truly cosmic wanderers that hold their own mysteries waiting to be unraveled. These celestial objects have captivated human imagination for centuries with their dazzling displays and unpredictable behavior. Comets are composed of a combination of ice, dust, and organic compounds, giving them the nickname of “dirty snowballs.” They originate from the outer regions of the solar system, particularly the Oort Cloud and Kuiper Belt, and embark on long elliptical orbits that bring them closer to the Sun. As a comet approaches the Sun, the heat causes the ices within it to vaporize, creating a glowing coma and often a magnificent tail that points away from the Sun. This unique phenomenon is a result of the solar wind pushing the gas and dust particles away. Comets offer valuable insights into the early stages of our solar system and the potential ingredients for life. By studying comets, scientists hope to uncover the secrets of the universe and gain a deeper understanding of our place within it.
Exploring Asteroids and Comets: Missions and Discoveries

The exploration of asteroids and comets has been a remarkable journey of discovery, with various missions shedding light on these enigmatic objects. One notable mission is NASA’s OSIRIS-REx, which aims to collect samples from the asteroid Bennu and bring them back to Earth for analysis. This mission provides valuable insights into the composition and history of asteroids, potentially unlocking the secrets of our solar system’s formation. Another groundbreaking mission is the European Space Agency’s Rosetta mission, which involved a close encounter with comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko. Rosetta studied the comet in unprecedented detail, providing crucial information about the comet’s composition and structure, and even deploying a lander to its surface. Japan’s Hayabusa2 mission is yet another remarkable endeavor, as it provided unprecedented insights into the asteroid Ryugu through sample collection and the deployment of landers and impactors. These missions have revolutionized our understanding of asteroids and comets, and future missions hold even more promise for uncovering the mysteries of these celestial bodies.
The Future of Asteroid and Comet Exploration

The future of asteroid and comet exploration holds immense potential for scientific discovery, resource utilization, and planetary protection. One of the key initiatives in this field is the Asteroid Redirect Mission (ARM), which aims to leverage the resources of asteroids for future space missions. With ARM, astronauts will be able to practice key skills required for deep space exploration and potentially extract valuable resources, such as water and metals, from asteroids. This could revolutionize the way we approach space travel and establish long-term human presence beyond Earth. Protecting our planet from potential asteroid impacts is another crucial aspect of future exploration. Scientists are studying near-Earth objects (NEOs) and devising strategies to mitigate the threats they may pose. Developing technologies for deflecting or redirecting asteroids on a collision course with Earth could save lives and ensure the safety of our planet. Additionally, asteroid and comet mining is becoming an exciting prospect for resource utilization in space. These celestial bodies are rich in precious metals, rare elements, and even water, which could be utilized to sustain future space missions and support the establishment of colonies on other celestial bodies. The future of asteroid and comet exploration is indeed filled with possibilities, and with continued scientific advancements and technological breakthroughs, we are only beginning to scratch the surface of what these cosmic wanderers have to offer.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the study of asteroids and comets has propelled our understanding of the solar system and opened up new possibilities for space exploration. Through their unique compositions and structures, asteroids provide a glimpse into the early formation of our solar system, while comets offer insights into the origins of water and organic compounds. The missions and discoveries surrounding these celestial bodies have yielded invaluable data and knowledge about our cosmic neighborhood.
As we look towards the future, the potential for asteroid and comet exploration is immense. The Asteroid Redirect Mission aims to leverage the resources of these celestial bodies for future space missions, potentially paving the way for long-duration interplanetary travel. Additionally, the continued study of near-Earth objects is crucial for understanding and developing strategies to protect our planet from potential impacts.
One of the most fascinating prospects is the concept of mining asteroids and comets for valuable resources. With their abundance of metals, minerals, and even potentially precious metals like gold and platinum, these celestial bodies could become the source of valuable resources for future space endeavors, reducing the need for Earth-based mining and opening up new frontiers for human exploration.
As we continue to explore and unlock the secrets of asteroids and comets, our understanding of the early solar system and the potential for future space exploration will undoubtedly expand. The mysteries and wonders of these celestial objects continue to captivate our imagination and push the boundaries of human knowledge. So, let us embark on this cosmic journey and embrace the endless possibilities that asteroids and comets have to offer.
Frequently Asked Questions

1. What are the main differences between asteroids and comets?
Asteroids are rocky and metallic bodies found in the asteroid belt, while comets are icy bodies that originate from the outer regions of the solar system.
2. How do asteroids and comets differ in composition?
Asteroids are primarily composed of minerals and metals, while comets are made up of frozen gases, dust, and organic compounds.
3. What causes the distinctive appearance of comets?
Comets have a glowing coma and a tail that forms when the heat from the Sun vaporizes the icy surface, releasing gas and dust particles.
4. Where can asteroids be found in our solar system?
Asteroids are found primarily in the asteroid belt, located between Mars and Jupiter, although they can also be found in other regions of the solar system.
5. What are the origins of comets?
Comets originate from the outer regions of the solar system, such as the Oort Cloud and the Kuiper Belt.
6. How do the orbits of asteroids and comets differ?
Asteroids have more circular orbits confined to the asteroid belt, while comets follow elongated, elliptical orbits that can take them much closer to the Sun.
7. Do asteroids and comets pose any threats to Earth?
While the majority of asteroids and comets pose no threat to Earth, there is a small possibility of a collision with a large asteroid or comet in the future. Scientists are actively studying and monitoring near-Earth objects to assess any potential risks.
8. Can asteroids and comets provide valuable resources?
Asteroids and comets are rich in resources such as metals, water, and organic compounds. The potential for asteroid mining and resource utilization is being explored for future space missions and sustainable resource extraction.
9. How do studying asteroids and comets help us understand the early solar system?
By studying asteroids and comets, scientists can gain insight into the formation and evolution of our solar system. These celestial objects carry ancient materials that can provide clues about the conditions and processes that occurred during the early stages of planetary formation.
10. What are some of the notable missions that have explored asteroids and comets?
Notable missions include NASA’s OSIRIS-REx, which collected a sample from asteroid Bennu, and the European Space Agency’s Rosetta mission, which closely observed and landed a probe on comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko.
References
Frequently Asked Questions

FAQ 1: How are asteroids and comets different from each other?
Asteroids and comets differ in their composition and origin. Asteroids are rocky and metallic objects found mainly in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter, while comets are made of ice, dust, and rocky material and come from the outer regions of the solar system.
FAQ 2: Are all asteroids the same, or are there different types?
Asteroids come in various types based on their composition. There are three main types: C-type asteroids, which are carbonaceous and the most common; S-type asteroids, which are silicate-rich; and M-type asteroids, which contain metals like nickel and iron.
FAQ 3: What is the historical significance of asteroids?
Asteroids hold great historical significance as they are remnants from the early stages of our solar system’s formation. By studying and analyzing asteroids, scientists can gain insights into the processes that shaped our celestial neighborhood billions of years ago.
FAQ 4: Can asteroids be mined for resources?
Yes, asteroids are rich in valuable resources such as metals, water, and organic compounds. Asteroid mining is a potential future industry that could provide essential resources for space exploration and even support activities in space, such as building colonies or refueling spacecraft.
FAQ 5: What are comets made of?
Comets are composed of a mixture of ice, dust, rocky material, and various organic compounds. The ice in comets is primarily frozen water, but it also contains other volatile substances, such as carbon dioxide, methane, and ammonia.
FAQ 6: Where do comets originate from?
Comets originate from two main regions in the outer regions of the solar system: the Oort Cloud and the Kuiper Belt. The Oort Cloud is a spherical shell of icy objects located far beyond the orbit of Pluto, while the Kuiper Belt is a region of icy bodies found beyond Neptune’s orbit.
FAQ 7: What can studying comets tell us about the early solar system?
Studying comets provides valuable insights into the early solar system because they are considered pristine objects that have preserved the materials from which the solar system formed. By analyzing the composition of comets, scientists can better understand the processes and conditions that led to the formation of planets.
FAQ 8: Which missions have explored asteroids?
Some notable missions that have explored asteroids include NASA’s OSIRIS-REx, which collected a sample from asteroid Bennu, the European Space Agency’s Rosetta mission, which closely studied comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko, and Japan’s Hayabusa2 mission, which provided unprecedented insights into asteroid Ryugu.
FAQ 9: Can asteroids be redirected for future space missions?
Yes, the Asteroid Redirect Mission is a proposed NASA mission that aims to redirect a small asteroid to a stable orbit around the Moon. This mission would leverage the resources found on asteroids and pave the way for future human exploration and space missions.
FAQ 10: Are there any strategies in place to protect Earth from near-Earth objects?
Yes, NASA and other space agencies actively monitor near-Earth objects and develop strategies to protect our planet. These strategies include early detection systems, asteroid deflection techniques, and international collaborations to ensure the safety of Earth from potential asteroid impacts.