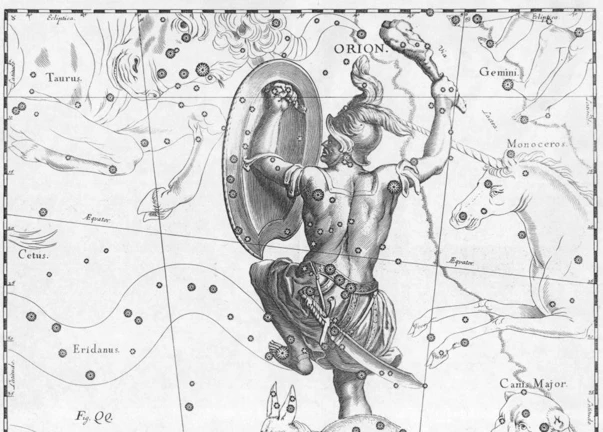
Ancient Constellations and their Influence on Modern Astronomy have captured the wonder and imagination of humans for centuries. These celestial patterns that adorn the night sky have fascinated ancient civilizations and continue to captivate astronomers today. The origins of constellations date back to ancient times when early cultures looked to the stars for navigation, timekeeping, and religious significance. This article explores the rich history of ancient constellations, their scientific importance, and their continued relevance in modern astronomy. Join us on a journey through time as we unravel the mysteries of these celestial wonders and their profound influence on our understanding of the universe.
Contents
- Ancient Constellations: A Brief History
- Scientific Significance of Ancient Constellations
- Ancient Constellations in Modern Astronomy
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are ancient constellations?
- How were ancient constellations created?
- What is the scientific significance of ancient constellations?
- How do astronomers identify and name ancient constellations?
- Do ancient constellations have cultural interpretations?
- What is the influence of ancient constellations on modern space exploration?
- Can ancient constellations be seen today?
- Are ancient constellations the same across all cultures?
- Are ancient constellations used in astrology?
- Do ancient constellations change over time?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How were ancient constellations named?
- 2. Were ancient constellations the same across different ancient cultures?
- 3. How were ancient constellations used for navigation and timekeeping?
- 4. Do modern astronomers still use ancient constellations?
- 5. How do ancient constellation names influence our modern understanding of the stars?
- 6. Can I see the ancient constellations in the night sky today?
- 7. How do ancient constellation stories differ from culture to culture?
- 8. Are the constellations we see today the same as ancient civilizations saw?
- 9. How do ancient constellations help us explore outer space?
- 10. Can I visit ancient sites where constellations were originally identified?
- References
- Read More
Ancient Constellations: A Brief History
The history of ancient constellations is as vast and diverse as the cosmos they represent. These constellations have their origins in various ancient cultures around the world. The Origins of Constellations can be traced back to ancient civilizations such as the Mesopotamians, Egyptians, and Greeks, who observed the stars and created intricate stories and myths around them. The Greeks, in particular, made significant contributions to the development of constellations, with the famous astronomer Ptolemy mapping out 48 constellations that are still recognized today. The Role of Ancient Cultures in shaping constellations cannot be understated, as different cultures imbued their own beliefs, legends, and religious significance into these celestial patterns. For example, the Chinese constellation system is heavily influenced by Chinese mythology, while the Aboriginal Australians have their Dreamtime stories woven into their depictions of the stars. Importance of Ancient Constellations lies not only in their cultural significance but also in their practical applications. These constellations served as navigation guides for early seafarers and travelers, helping them navigate the vast oceans and unknown territories. They also played a role in timekeeping and calendar systems, aiding agricultural practices and religious ceremonies. The rich history of ancient constellations has paved the way for our understanding of the cosmos, guiding astronomers in their exploration of the universe.
The Origins of Constellations
The origins of constellations can be traced back to ancient civilizations that gazed up at the night sky with awe and curiosity. Here are some key points about :
1. Mesopotamian Contributions: The Mesopotamians, one of the earliest civilizations, played a significant role in the development of constellations. They believed that the gods controlled the movement of celestial bodies and used them for divination and omens. They created star catalogs and identified patterns in the night sky, connecting stars to form constellations.
2. Egyptian Mythology: The ancient Egyptians also had their own system of constellations, which were closely tied to their mythological beliefs. They associated the stars with their gods and believed that constellations represented deities in the afterlife. The constellation of Orion, for example, was associated with Osiris, the god of the underworld.
3. Greek Contributions: The Greeks made great strides in the study of constellations, thanks to the work of astronomers like Hipparchus and Ptolemy. Ptolemy, in his influential work “Almagest,” presented a comprehensive catalog of 48 constellations that served as the foundation for Western astronomy. The constellations were named after various Greek mythological figures, offering a fantastical backdrop for the stars.
4. Cultural Influences: Different ancient cultures had their own unique constellations. In China, for instance, they developed a separate system of constellations based on their mythology and astrological beliefs. Native American tribes also had their own constellations, often tied to their legends and stories.
5. Practical Uses: While constellations held cultural and mythological significance, they also served practical purposes. Early civilizations used them for navigation, as the constellations provided markers to guide travelers, especially during long voyages across the seas. They also helped in determining the changing seasons for agricultural purposes and marking important celestial events.
Understanding The Origins of Constellations allows us to appreciate the rich tapestry of human history and our enduring fascination with the night sky. These ancient celestial patterns continue to inspire and guide us in our exploration of the universe.
The Role of Ancient Cultures
- Astronomy in Ancient Egypt: In ancient Egypt, the night sky held immense importance in their religious and spiritual beliefs. The Egyptians associated certain constellations with their gods and used them to align their temples and pyramids. For instance, the constellation Orion was linked to Osiris, the god of resurrection, while the star Sirius was significant in predicting the flooding of the Nile River.
- Greek Mythology and Constellations: Greek mythology heavily influenced the development of constellations. The Greeks assigned mythological characters and stories to various star patterns. The most famous example is the constellation Ursa Major, known as the Great Bear, which represents the nymph Callisto, who was transformed into a bear by the goddess Hera. Greek astronomers like Ptolemy further refined the constellations, creating a lasting impact on western astronomy.
- Chinese Constellations: In ancient China, constellations played a central role in both astrology and mythology. The Chinese celestial sphere consisted of four regions, symbolizing the cardinal directions. The constellations were associated with elements and animal signs from the Chinese zodiac. The Chinese believed that the movements of the celestial bodies directly influenced human affairs and used the positions of the stars for fortune-telling and divination.
- Indigenous Cultures and Their Skylore: Various indigenous cultures worldwide have fascinating celestial traditions. For example, the Aboriginal Australians have a rich system of Dreamtime stories that explain the creation of constellations. The Pleiades cluster, also known as the Seven Sisters, holds cultural significance for many indigenous groups, including the Navajo, Maori, and Native American tribes.
The role of ancient cultures in shaping constellations goes beyond mere observation of the night sky. They integrated their beliefs, stories, and cosmologies, creating a profound and interconnected relationship between the heavens and humans. Their celestial traditions have left a lasting legacy, managing link to their cultural heritage and ideologies. Through the understanding of these ancient cultures, we can gain insights into the diverse ways in which humanity has perceived and interacted with the heavens throughout history.
Importance of Ancient Constellations
The cannot be overstated when considering the impact they have had on human culture, navigation, and timekeeping. These celestial patterns, meticulously observed and studied by ancient civilizations, served as a roadmap for early explorers and travelers. Sailors, for instance, relied on constellations to navigate their way across the seas, using the positions of specific stars to determine their location and destination. Interestingly, the use of constellations as navigation aids continues to this day, with modern sailors and even astronauts relying on them during their journeys. Additionally, ancient constellations played a vital role in timekeeping, as they marked the passage of seasons and the cycles of the celestial bodies. By observing the changing positions of constellations throughout the year, ancient cultures were able to develop calendars and track important celestial events, such as solstices and equinoxes. Beyond practical applications, ancient constellations also held religious and mythological significance for many cultures. They were often associated with gods, heroes, and legendary creatures, giving rise to fascinating stories and belief systems. The enduring influence of ancient constellations is evident in the scientific field of astronomy, where their names and associations continue to be used to identify and locate objects in the night sky. The legacy of these ancient depictions continues to inspire and guide our exploration of the universe.
Scientific Significance of Ancient Constellations
Ancient constellations hold great Scientific Significance in the field of astronomy. One of their key contributions is the Foundation of Celestial Coordinate Systems. By mapping the positions of stars and creating coordinate systems, ancient astronomers laid the groundwork for modern astronomical observations and calculations. These coordinate systems, such as the equatorial and ecliptic systems, allow astronomers to precisely locate and track celestial objects. Additionally, constellations played a crucial role in celestial navigation and timekeeping. Sailors and explorers used the positions of stars to determine their latitude and direction, aiding in long-distance travel and exploration. Ancient constellations have been instrumental in unlocking the mysteries of the universe. For example, the study of stellar evolution and the unraveling mystery of black hole mergers has benefited from our understanding of ancient constellations. These constellations provide a framework for astronomers to identify and study celestial objects and phenomena, enabling us to expand our knowledge and explore the depths of the cosmos.
Foundation of Celestial Coordinate Systems
The foundation of celestial coordinate systems can be attributed to the ancient constellations. These intricate patterns in the night sky provided a framework for astronomers to map and locate celestial objects with precision. Here are some key aspects of the :
1. Ecliptic Coordinate System: The ecliptic is the apparent path of the Sun in the sky as observed from Earth. The zodiac constellations align along this path. By dividing the ecliptic into twelve equal parts, each corresponding to a zodiac sign, the ecliptic coordinate system was born. This system plays a crucial role in astrology, as it helps determine an individual’s sun sign.
2. Equatorial Coordinate System: The equatorial coordinate system is based on the celestial equator, an imaginary line projected onto the sky that mirrors Earth’s equator. Ancient astronomers used the equatorial coordinate system to map celestial objects based on their declination and right ascension. This system allows for precise positioning of stars, planets, and other celestial bodies.
3. Epochs and Precession: The foundation of celestial coordinate systems also involves the concept of epochs and precession. Epochs are specific points in time used as a reference for celestial coordinates. Ancient astronomers established epoch points to track the movements of celestial bodies and create accurate star maps. Precession refers to the slow wobbling of Earth’s axis caused by gravitational forces, leading to a change in the positions of stars over long periods. Taking precession into account is crucial for maintaining the accuracy of celestial coordinate systems.
4. Modern Implementations: The ancient constellations and their role in defining celestial coordinate systems have laid the groundwork for modern implementations. Today, astronomers use advanced telescopes, star catalogs, and computer algorithms to precisely map and locate celestial objects. The coordinate systems established by ancient civilizations form the basis for these modern techniques, aiding in research, astrometry, and space exploration.
The ancient constellations provide the foundation for celestial coordinate systems, allowing astronomers to navigate the vast cosmos with remarkable accuracy. These systems, such as the ecliptic and equatorial coordinate systems, along with the concepts of epochs and precession, have been instrumental in advancing our understanding of the universe and continue to shape modern astronomy.
Ancient constellations played a vital role in navigation and timekeeping for early civilizations. Mariners relied on the position of specific constellations to navigate through the open seas. By observing the stars and their relative positions, sailors could determine their heading and estimate their latitude. For example, the North Star, also known as Polaris, became a valuable navigational tool for sailors in the Northern Hemisphere. It served as a fixed reference point, indicating the direction of the North Pole. Constellations like Orion, the Great Bear (Ursa Major), and the Southern Cross (Crux) were also used as navigation aids, assisting sailors in determining their location and navigating safely across vast distances.
In addition to navigation, ancient constellations played a crucial role in timekeeping. By observing the movement of specific constellations throughout the night sky, early cultures developed primitive calendars and marked the passage of time. The cycle of constellations rising and setting at different times of the year allowed for the tracking of seasons, which was vital for agricultural activities. The annual return of certain constellations, such as the Pleiades and the constellation Orion, coincided with significant agricultural events, signaling the time to sow or harvest crops. These celestial markers helped ancient civilizations plan their activities in harmony with natural cycles.
The alignment of constellations with the Sun and the Moon provided an early form of a calendar year. The zodiac, a band of constellations along the ecliptic path, marked the path of the Sun throughout the year and was divided into twelve equal parts, each representing a different zodiac sign. This celestial timekeeping system, developed by the Babylonians and later refined by the Greeks and Romans, forms the basis of modern astrology.
The influence of ancient constellations on navigation and timekeeping is still evident today. Advanced technology may have provided precise GPS systems and atomic clocks, but the knowledge passed down from ancient civilizations remains invaluable. Whether it’s a sailor charting a course across the ocean or an astronomer predicting the arrival of a celestial event, the legacy of ancient constellations lives on, connecting us to our seafaring and stargazing ancestors.
(Note: For more information on the compatibility of earth signs in astrology, you can refer to our article on intriguing compatibility of earth signs.)
Ancient Constellations in Modern Astronomy
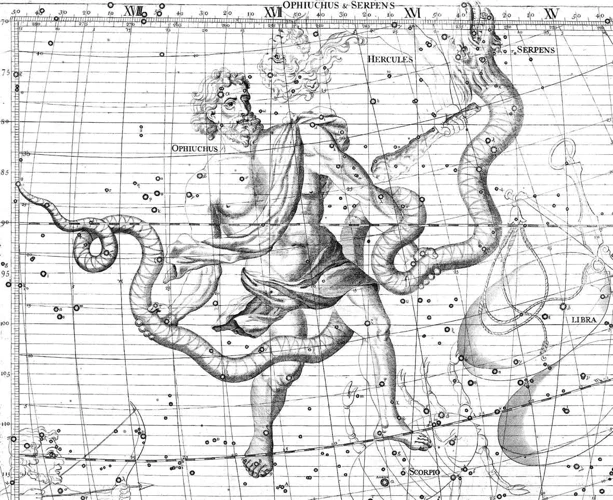
Ancient constellations continue to play a significant role in modern astronomy, bridging the gap between ancient wisdom and cutting-edge scientific exploration. One aspect of their influence is in the Identification and Naming of celestial objects. Many stars, galaxies, and other astronomical phenomena are still referred to by their traditional constellation names. For example, the North Star, Polaris, is part of the Ursa Minor constellation. Additionally, Cultural Interpretations of constellations have a lasting impact on our understanding of the universe. Ancient stories and myths associated with constellations provide a cultural context that enriches our exploration and interpretation of the cosmos. Ancient constellations have even influenced space exploration missions as certain missions are named after constellations, such as the Orion spacecraft, which takes its name from the prominent hunter constellation. It is fascinating to see how ancient knowledge continues to shape and inspire modern discoveries in the field of astronomy.
Identification and Naming
of ancient constellations has been a complex and ongoing process. In ancient times, different cultures had their own systems for identifying and naming constellations based on their mythology, folklore, and cultural beliefs. The Greeks, for example, named many constellations after figures from their myths, such as Orion and Hercules. Similarly, the Chinese named constellations based on animals, elements, and other celestial phenomena. Over time, astronomers from various cultures have sought to unify the identification and naming of constellations. One notable effort was made by the International Astronomical Union (IAU), which established a standardized set of 88 constellations in 1922. These constellations were based on Greek, Roman, and other cultural traditions, creating a globally recognized system. However, even though the IAU set the standard, there are still some cultural variations in identifying and naming constellations. For instance, the constellation known as Ursa Major in Western astronomy is referred to as the Big Dipper in North America. The identification and naming of constellations continue to evolve as new discoveries are made and cultural perspectives are considered. This dynamic process ensures that ancient constellations remain relevant and adaptable to our ever-expanding understanding of the universe.
Cultural Interpretations
Ancient constellations have not only been sources of scientific significance but also windows into the cultural beliefs and interpretations of various civilizations throughout history. Each culture has imparted its own unique meaning and stories to the celestial patterns they observed. The Greeks, for example, associated the constellation Orion with the mythological hunter of the same name, while the Egyptians believed it represented their god Osiris. In Chinese culture, the constellation known as the Big Dipper holds great importance and is associated with the Emperor of Heaven. The Aboriginal people of Australia have their own Dreamtime stories woven into their interpretation of the constellations. These cultural interpretations have served as a way for civilizations to connect with and explain the mysteries of the universe. They tell stories of heroes, gods, and mythical creatures, passing down cultural knowledge and traditions from generation to generation. Today, cultural interpretations of constellations continue to be explored and celebrated, providing insights into the diverse beliefs and rich heritage of different societies. By studying cultural interpretations, astronomers gain a deeper appreciation of the human connection to the stars and how our understanding of the universe has evolved over time.
Influence on Space Exploration
The ancient constellations have had a profound influence on space exploration, shaping our understanding of the cosmos and paving the way for our ventures beyond Earth. Here are some key ways in which ancient constellations continue to impact space exploration:
1. Navigational Reference: The ancient constellations remain crucial in providing navigational reference points for spacecraft and satellites. By using these familiar star patterns as celestial landmarks, scientists and engineers can accurately determine the position and orientation of spacecraft in space.
2. Mission Planning: When planning space missions, astronomers and mission designers often take into account the positioning of ancient constellations. These constellations help in determining optimal trajectories and routes for interplanetary missions, taking advantage of the gravitational interactions between celestial bodies.
3. Spacecraft Naming: Ancient constellations also inspire the naming of spacecraft and missions. For example, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, which is designed for deep space missions, draws its name from the prominent constellation Orion. Other missions, such as the Apollo missions to the Moon, have taken inspiration from ancient mythology and constellations in their naming.
4. Exploration Targets: Ancient constellations aid in identifying and selecting exploration targets. Astronomers study the positions and characteristics of stars within constellations to identify potential exoplanets or regions of interest for future exploration. The knowledge of ancient constellations provides a starting point for determining regions of the sky to focus on during space missions.
5. Cultural Heritage: Finally, the influence of ancient constellations goes beyond their scientific and navigational value. They enhance the sense of wonder and inspire a connection to the mysteries of the universe among astronauts, scientists, and the general public. The inclusion of ancient constellations in space missions and imagery serves as a reminder of our shared human history and the significance of these celestial wonders.
The influence of ancient constellations on space exploration is multi-faceted, ranging from practical navigational aids to cultural and inspirational significance. These ancient celestial patterns continue to shape our exploration of the cosmos, bridging the gap between the rich history of astronomy and the cutting-edge advancements in space exploration.
Conclusion

In , it becomes evident that ancient constellations hold great significance in the realms of history, culture, and science. These celestial patterns have been passed down through generations, representing the collective knowledge, beliefs, and stories of diverse civilizations. The origins of constellations can be traced back to ancient cultures like the Greeks, Mesopotamians, Egyptians, and many more, who observed the stars and created mythologies around them. Ancient constellations played a vital role in navigation, allowing early seafarers and travelers to explore the world with greater confidence. They also served as critical timekeeping tools, aiding in the development of calendars and agricultural practices. Today, these constellations continue to captivate astronomers, providing a foundation for celestial coordinate systems and serving as points of reference for object identification in the night sky. Moreover, ancient constellations have influenced cultural interpretations of the stars, enriching our understanding of different mythologies and astrological systems. From a scientific perspective, these constellations have influenced space exploration endeavors, with missions and celestial objects named after them. As we reflect on the profound influence of ancient constellations on modern astronomy, we are reminded of the enduring connection between humanity and the cosmos, and the everlasting fascination with the night sky.
Frequently Asked Questions

What are ancient constellations?
Ancient constellations are patterns formed by groups of stars that were identified and named by ancient civilizations. These patterns were often associated with mythological stories, religious beliefs, and served practical purposes such as navigation and timekeeping.
How were ancient constellations created?
Ancient constellations were created by connecting stars together to form recognizable patterns. Different cultures had their own unique constellations based on their mythology and cultural significance. Over time, these constellations were refined and standardized by astronomers.
What is the scientific significance of ancient constellations?
Ancient constellations have played a crucial role in the development of celestial coordinate systems, aiding in the precise mapping and identification of celestial objects. They have also provided a framework for astronomers to navigate the night sky, conduct astronomical observations, and study the movement and behavior of stars and other celestial bodies.
How do astronomers identify and name ancient constellations?
Astronomers identify and name ancient constellations based on standardized celestial coordinate systems. These systems divide the celestial sphere into regions with specific coordinates, allowing astronomers to pinpoint the position of a constellation in the sky. The International Astronomical Union (IAU) is responsible for officially recognizing and naming constellations.
Do ancient constellations have cultural interpretations?
Yes, ancient constellations often have cultural interpretations associated with them. Different civilizations and cultures have ascribed their own beliefs, myths, and stories to the constellations, reflecting their unique perspectives and understanding of the universe.
What is the influence of ancient constellations on modern space exploration?
Ancient constellations have influenced modern space exploration in various ways. Astronomers and spacecraft engineers use these constellations as reference points for navigational purposes. Additionally, the exploration of constellations and their celestial objects has sparked curiosity and inspired future space missions and discoveries.
Can ancient constellations be seen today?
Yes, many ancient constellations are still visible in the night sky today. However, light pollution and environmental factors can make them difficult to observe in urban areas. To observe ancient constellations, it’s best to find a dark and clear location away from city lights.
Are ancient constellations the same across all cultures?
No, ancient constellations vary across different cultures. Each civilization or culture developed their own set of constellations based on their unique beliefs, stories, and celestial observations. While some constellations may overlap or share similar features, many have distinct differences and interpretations.
Are ancient constellations used in astrology?
Astrology, which is based on the belief that celestial bodies have an influence on human affairs and personality traits, does make use of ancient constellations. However, it’s important to note that astrology and astronomy are separate disciplines, and the interpretations of constellations in astrology differ from their scientific understanding.
Do ancient constellations change over time?
In terms of their positions in the sky, ancient constellations do not change significantly over time. However, the scientific understanding and interpretation of these constellations may evolve as astronomers make new discoveries and gain deeper insights into the cosmos.
References
Frequently Asked Questions

1. How were ancient constellations named?
Ancient constellations were typically named after mythological figures, animals, or objects that were of cultural or symbolic significance to the civilizations that identified them.
2. Were ancient constellations the same across different ancient cultures?
No, ancient constellations varied across different ancient cultures. While some constellations shared similar names or themes, each culture had its own unique interpretation and set of constellations.
Ancient civilizations used the positions of the stars in constellations to navigate and determine the time of year. By tracking the movement of specific constellations, they could identify direction and estimate the time of year based on the position of the stars.
4. Do modern astronomers still use ancient constellations?
Yes, modern astronomers still use ancient constellations as a basis for identifying and naming celestial objects. However, they have made some adjustments to account for scientific advancements and a better understanding of the universe.
5. How do ancient constellation names influence our modern understanding of the stars?
Ancient constellation names serve as a historical record of how early civilizations perceived and interacted with the night sky. By studying these names, modern astronomers can gain insight into cultural beliefs and important astronomical events throughout history.
6. Can I see the ancient constellations in the night sky today?
Yes, many of the ancient constellations are still visible in the night sky today. However, due to changes in celestial coordinates over time, the positions of some constellations may have shifted slightly.
7. How do ancient constellation stories differ from culture to culture?
Ancient constellation stories differ from culture to culture based on their unique mythologies, religious beliefs, and cultural practices. Each culture imparted its own narratives and interpretations onto the constellations.
8. Are the constellations we see today the same as ancient civilizations saw?
No, the constellations we see today are not exactly the same as those observed by ancient civilizations. The positions and visibility of stars and constellations have changed due to factors such as Earth’s precession and the movement of celestial bodies.
9. How do ancient constellations help us explore outer space?
Ancient constellations provide a framework for understanding and organizing the vastness of space. Modern space exploration missions often reference ancient constellations to aid in navigation and to identify specific regions of the sky.
10. Can I visit ancient sites where constellations were originally identified?
Yes, there are several ancient sites around the world where constellations were originally identified and studied. Places like Stonehenge in England or the ancient Greek ruins of Delphi provide insights into the ancient civilizations’ astronomical practices and beliefs.